Coordination and Response (Bio IGCSE)
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Central nervous system
Coordinates the messages travelling along the nervous system
Neurons (as electrical impulses)
Information carried by the Nervous system travel through
Dendrites
Short fibers that pick up electrical signals from the other neurons lying nearby
Axon
Long fiber carrying information away from body cells
Cell body
Controls the metabolism of nerve cell
Myelin sheath
Layers of fats covering axon
Why does the Mylin sheath cover the axon?
Speeds up nerve impulse
Protects nerve fiber
Prevent leakage of electrical signals
Motor end plate
Passes the electrical signals to another nerve cell
Synapse
The junction between two nerve cells with a minute gap between the nerve cells across which impulses pass by diffusion of neurotransmitters
How does synapse act like a one-way valve?
As there are neurotransmitters and receptors on only one side of the synapse, so the impulse can only pass from that side. This prevents the backward flow of impulses
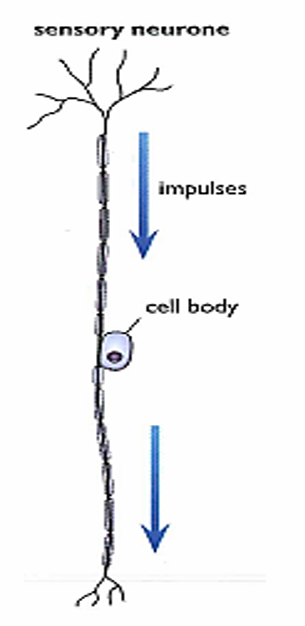
Sensory Neuron
Carries electrical impulses from receptors to the Central Nervous system
One direction
Myelin sheath
Cell body in the middle of the cell
Short Axons
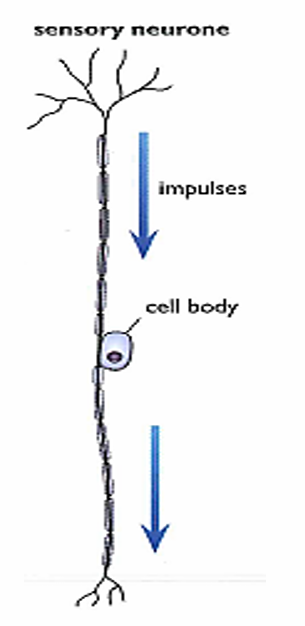
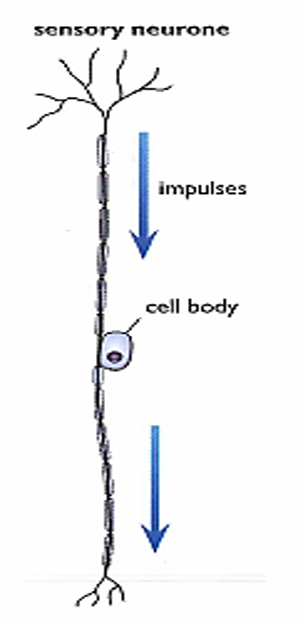
Sensory neuron location
Present in Ganglion (group of neuron cell bodies in P.N.S)
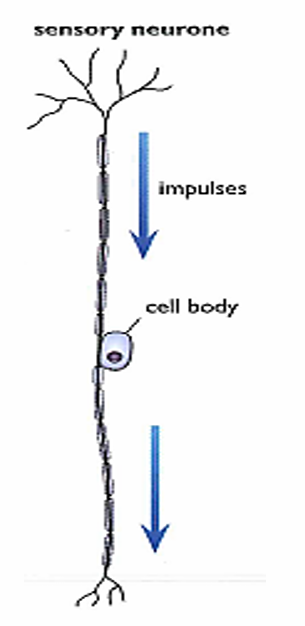
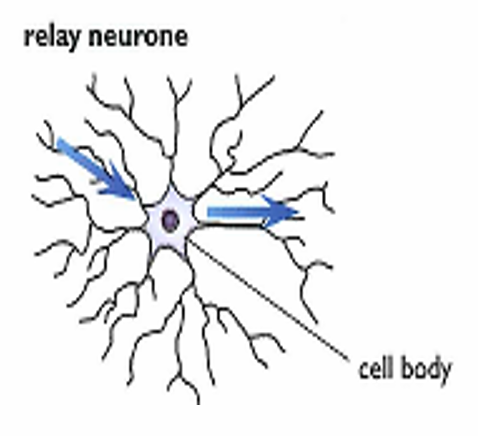
Relay neuron
Carries electrical impulses from sensory neuron to motor neuron in C.N.S
No Myelin Sheath
Relay neuron location
C.N.S present in grey matter in spinal cord
Why doesn’t the Relay neuron have Myelin sheath?
So the impulses can be carried slowly across spinal cord

Motor Neuron
Carries electrical signal from the C.N.S to the effector organ showing response
Myelin sheath
Cell body present at one end of the cell


Motor neuron location
grey matter of the spinal cord
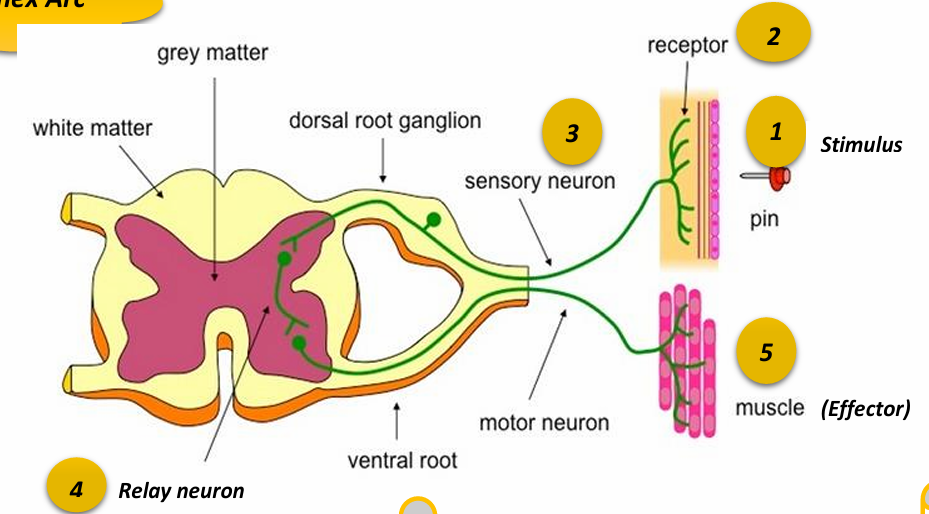
Stimulus
change in the internal or external environment of the body
Receptors
Parts of the body that can detect the Stimulus and convert it to an electrical impulse
Effector organ
Muscle to contract
OR
Gland to secrete
Reflex Action
It’s involuntary, protective and rapid response to a stimulus. The Reflex Action message gets from the receptors to the effector very quickly. The function of the reflex action is protection of the body from mechanical damage or injury. The center is located in the spinal cord.
Examples of Reflex Actions
Stimulus —→ Hot Pan
Response —→ Muscles in arm contract so the hand pulls away
Stimulus —→ Bright light falling on Retina
Response —→ Contraction of circular muscles of Iris
Voluntary Action
Non-automatic action that requires a conscious decision by the Brain
Involuntary Action
Automatic action that doesn’t involve a conscious decision by the brain
Sense organs
Organs containing group of receptor cells responding to a specific stimulus
Sense organs examples
Eyes
Receptor —→ Photo receptors
stimulus —→ Light
Ear
Receptor —→ Sound receptors
stimulus —→ Sound
Nose/Tongue
Receptor —→ Chemoreceptors
stimulus —→ Chemicals
Skin
Receptor —→ Skin receptors
stimulus —→ Temperature, Touch, Pressure and Pain
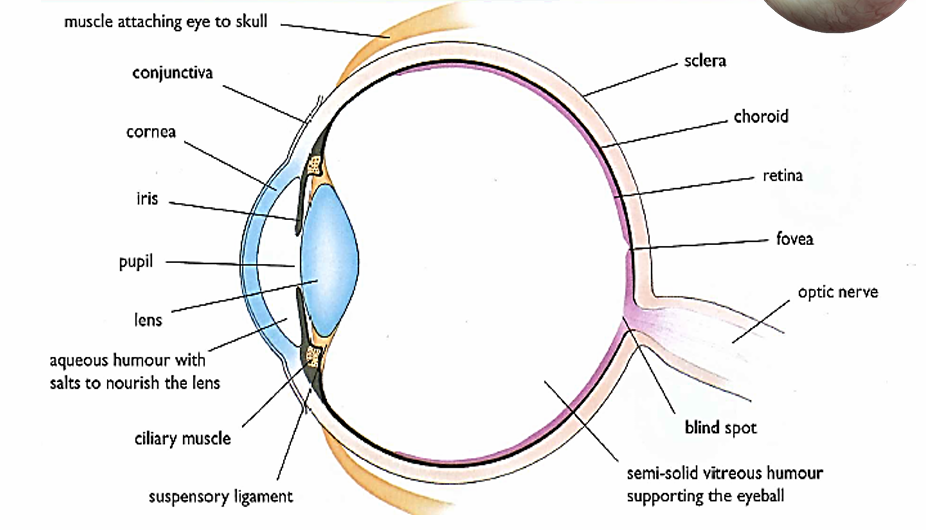
Conjunctiva
Thin, transparent membrane that protects the cornea
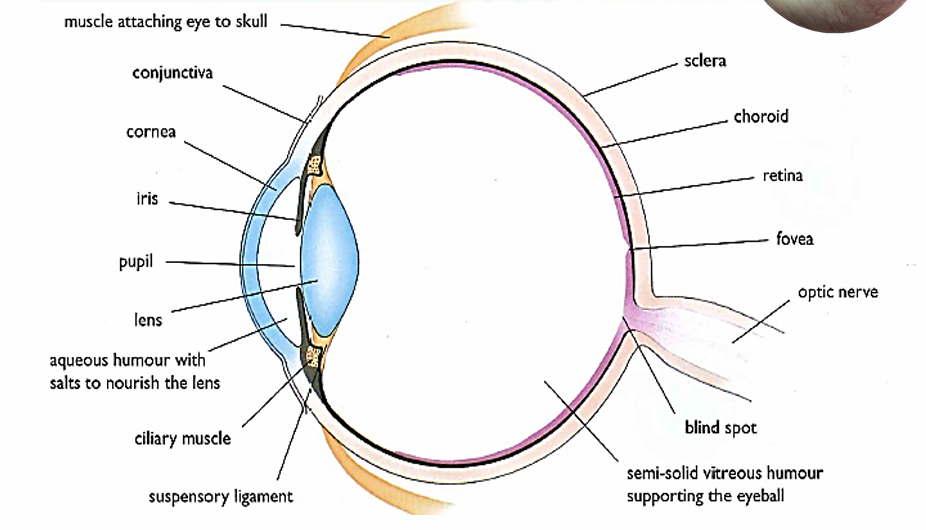
Cornea
Transparent layer which allows light to penetrate eye and bends the light rays that enter
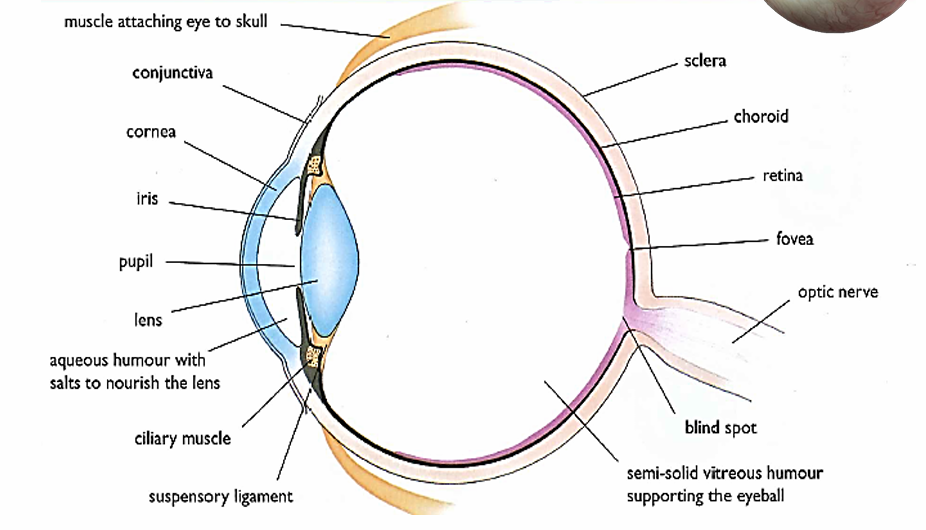
Aqueous humor
Water fluid that supports the Cornea and Front chamber of eye
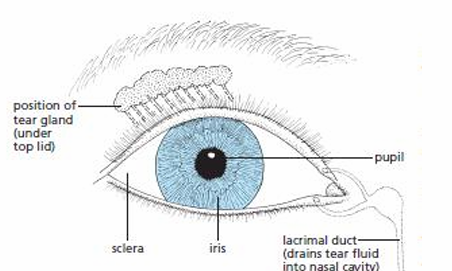
Iris
Colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters by controlling the pupil’s diameter to protect the retina from excess light
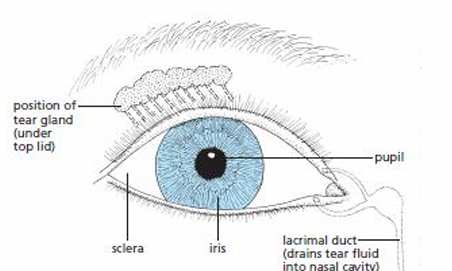
Pupil
Circular opening that allows light to enter, appears black because the choroid is visible
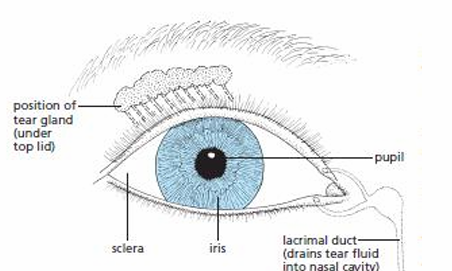
Sclera
Tough outer layer that protects eye from damage
Lens
Changes shape to focus light into the retina
Accommodation
A reflex that changes the refractive power of the lens