UNIT 1 GENERAL BIOLOGY Q3
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Central Dogma
describes the flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA) to protein
Replication, Transcription, Translation
3 processes in Central Dogma
polynucleotides
Nucleic acids are polymers called __________.
nucleotides
Each polynucleotide is made of monomers called ____________________.
nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group
Each nucleotide consists of a __________.
nucleoside
The portion of a nucleotide without the phosphate group is called a __________.
2nd carbon
DNA does not contain oxygen in the _________.
Phospate
found at the end, the same in both DNA and RNA
Sugar
found at the end of the DNA.
Nitrogenous Base
rods of the DNA
Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
Adenine Uracil
Pyrimidine
single six-membered ring
Purine
six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring
Nucleotide polymers
______________ are linked together to build a polynucleotide.
anti-parallel
DNA strands are __________ - runs alongside each other bit on different directions.
DNA
found only in the nucleus
RNA
can be found in both nucleus and cytoplasm
Conservative Replication
original parent double strands remain intact and two completely new double helix strands are synthesized ; the new strand is 100% new.
Semi-conservative Replication
the two strands come apart – each acts as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand ; the new strand is 50% old, 50% new.
Dispersive Replication
both original parent strands are broken up into small pieces and incorporated into newly synthesized strands ; mix of original and new
Origin of Replication
special sites where the replication of a DNA molecule begins wherein the two strands are separated.
Prokaryotes
has circular DNA ; one origin of replication ; 1 bubble 2 forks
Eukaryotes
has linear DNA ; multiple origins of replication ;
Helicase
protein in eukaryotes that unwinds and separates parent strands
Topoisomerase
protein in eukaryote that smoothens strain
Single strand binding proteins
protein in eukaryote that is used to stabilize ; “hair clip”
Primase
protein in eukaryotes that jump start the process of replication
DNA Polymerase
catalyzes the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork
DNA Polymerase 1
replaces the RNA primer with DNA
DNA Polymerase 3
main enzyme for DNA elongation
anabolic
DNA replication is _________.
Triphosphate
The incoming nucleotide has three phosphate groups attached to it. _______ stores energy that is needed for the binding reactions to happen.
Deoxythimidine triphosphate (dTTP)
Deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP)
Deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP)
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP)
Types of Triphosphates
Anti-parallel Elongation
one strand is synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction while the other is synthesized in the 3′ to 5′ direction
Leading Strand
follows helicase ; can synthesize continuously
Lagging Strand
away from replication fork ; synthesized as Okazaki fragments
Okazaki Fragments
series of segments ; replaced with DNA polymerase 1
DNA Ligase
connects the Okazaki fragments ; finishes the synthesis
mRNA
instructions on DNA are transcribed onto ________.
Ribosome
reads mRNA ; uses info to string amino acids together into proteins
wrong until END
if DNA is wrong = ________
break down RNA
if RNA is wrong = ________ to form a correct one
simultaneously in the cytoplasm
In prokaryotes , transcription and translation happens _________.
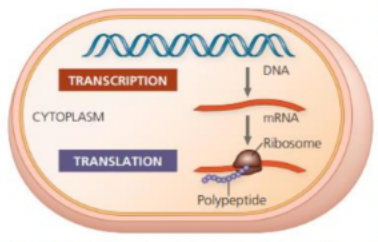
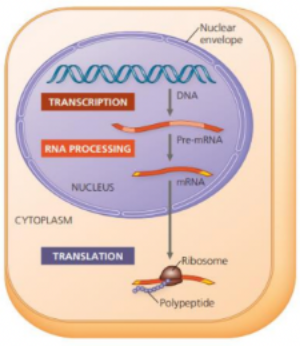
nucleus ; cytoplasm
In eukaryotes , the transcription happens inside the ______ and the translation happens in the ______.
Codons
nucleotides in an mRNA sequence code for amino acids
64
How many possible codons are there?
UAA, UAG, UGA
What are the stop codons?
Reading frame
refers to which nucleotide starts the first codon
6
For each segment of DNA, how many possible reading frames are there?
DNA Transcription
gene’s DNA sequence is copied to make an RNA molecule
DNA Transcription: Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter ; has helicase activity
DNA Transcription: Elongation
polymerase moves downstream unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript 5’ - 3’ ; DNA strand re-forms a double helix
DNA Transcription: Termination
RNA transcript is released and polymerase detaches from DNA ; amino acid chain is processed
Promoters
sequence in the DNA that signals the initiation of RNA synthesis.
TATAAT and TTGACG
Most genes have ______ and ______ as promoters.
conserve energy
Not all parts of DNA are transcribed to __________.
Transcription Factors
proteins that help eukaryotic RNA polymerase recognize promoter sequences ; present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
40 nucleotides per second
Elongation of DNA transcription occurs at a rate of __________.
Polyribosomes
Ribosomes attach to RNA resulting in more protein products. Ribosomes move along the mRNA translating it into a polypeptide chain.
Modified Nucleotide Cap
In the processing of mRNA in eukaryotes, this is received by the 5’end (guanine).
Poly-A Tail
In the processing of mRNA in eukaryotes, this is received by the 3’ end(adenine).
RNA Splicing
removes introns and joint exons
Introns
intervening sequences that need to be removed ; evolutionary remnants that regulate how mRNA is spliced
Exons
coding sequences ; intron splicing is not the only way to splice
Alternate Splicing
introns can stay behind or leave, exons should always stay behind
Protein Synthesis
decodes mRNA to produce polypeptide
Polypeptide Formation
formed when the amino group of one amino acid forms and amide bond with the carboxyl group of another amino acid ; reaction is catalyzed by ribosomes
Translation Machinery: tRNA / Transfer RNA
consists of a single RNA strand that is only about 80 nucleotides long ; roughly L shaped ; has base pairs for stability
Translation Machinery: Ribosomes
facilitate the specific coupling of tRNA anticodons with mRNA codons during protein synthesis
Ribosomal Units
constructed of proteins and RNA molecules(rRNA)
E site
exit site of RNA
P site / peptidyl-tRNA binding
formation of peptide bonds
A site / aminoacyl-tRNA binding
holds tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added
DNA Translation: Initiation
mRNA attaches to the smaller subunit of the ribosome. A tRNA with the appropriate anticodon attaches, then the larger subunit of the ribosome then comes in.
DNA Translation: Elongation
tRNA moves in with appropriate amino acid, then amino acid chain grows using peptidyl transferase
DNA Translation: Termination
Stop codon is reached, then amino acid chain is processed.
Genetic Engineering
a process of manipulating the genetic material of an organism to alter its characteristics or traits.
Transgenic Organism
other term for Genetically Modified Organism(GMOs)
Artificial Selection
Cloning
Recombinant DNA Technology
Modes of Genetic Engineering
Artificial Selection
Breeders choose which organism to mate to produce offspring with desired traits. They cannot control what genes are passed. When they get offspring with the desired traits, they maintain them.
Selective Breeding
organisms with desired characteristics are mated to produce offspring with those desired traits ; important genes are passed to next generation
Dachshunds
once bred to hunt badgers and other burrowing animals, must be small to fit into animal’s hole in the ground
Hybridization
unlike characteristics are crossed to produce the best in both organisms
Luther Burbank
________ created a disease-resistant potato called the Burbank potato.
Burbank potato
disease-resistant plant was crossed with another that had a large food-producing capactiy
Inbreeding
breeding of organisms that are genetically similar to maintain desired traits
recessive genetic disorder
In inbreeding, the chance that the offspring will get a __________ is high.
Organismal Cloning
produces one or more organisms genetically identical to parent that donated the single cell
Totipotent Cell
cell that can generate a complete new organism
Meristematic Cells
transverse sections of an organism that divide after culturing.
Nuclear Transplantation
nucleus of unfertilized egg cell or zygote is replaces with nucleus of differentiated cell
older ; lower percentage
The _____ the donor nucleus, the ______ of normally developing tadpoles.
Dolly the Sheep
a cloned lamb from an adult sheep by nuclear transplantation
Stem Cell
relatively unspecialized cell that can reproduce itself indefinitely and differentiate into specialized cells of one or more types
Embryonic Stem Cells
stem cells isolated from early embryos at the blastocyst stage ; able to differentiate into all cell types
Adult Stem Cells
replace non-reproducing specialized cells ; generates a limited number of cell types
Animal Stem Cells
can be isolated from early embryos or adult tissues grown in culture
Recombinant DNA Technology
used to create new combinations of DNA molecules by combining genetic material from different sources
Human Insulin
hormone that lowers blood sugar ; absent in diabetic people