Fibers
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Trace Evidence class w/ Dr. Elizabeth Chesna
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Fundamental unit of textiles
Fibers
Natural fiber
Involves a process by cleaning vegetables and animal fibers, followed by carding to align and prepare them for spinning.
Man-made fiber
Produced by extruding polymer solutions through spinnerets, followed by drawing to strengthen the fiber.
Cordage
_____ is the twisted threads or yarns, measured by counting plies, measuring diameter, and assessing twist direction (Z or S). Braided ____ is examined similarly, with attention to number of plies and presence of distinctly colored strands.
Non-woven fibers
Created by bonding, needle punching, or felting.
Woven fabric
Involves a loom, with warp yarns (lengthwise) and weft yarns (interlaced crosswise). Less elastic in warp direction.
Knitted fabric
Created using needles to form interlocking loops from yarn, with greater elasticity. Two main techniques are warp _____ and weft ______.
Plain weave
What is this?
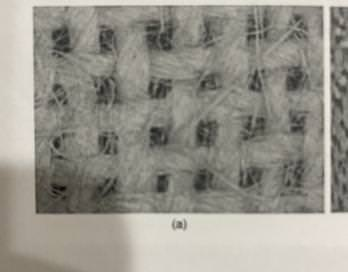
Pattern weave
What is this?

Twill weave
What is this?
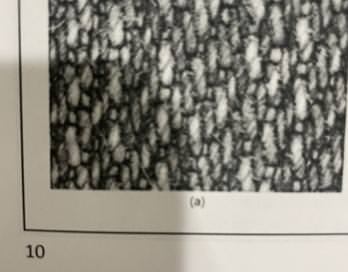
Satin weave
What is this?

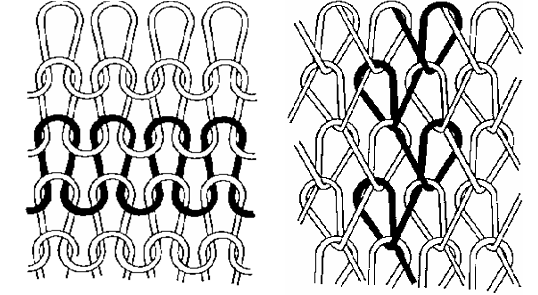
Weft, warp
Fill in the blanks:
The picture on the left demonstrates ____ knitting and the picture on the right demonstrates ____ knitting
Turfting
Carpet production occurs through ______ looped yearns through a backing material. with ____ either cut to create a smooth pile or left as loops.
Wool, hair, fur, silk
What four materials does animal fiber come from?
Seed, stem, leaf, fruit
What four materials does plant fiber come from?
What material does mineral fiber come from?
Asbestos
Seed fibers
Derived from materials surrounding or attached to plant seeds for protection or distribution
Cotton, kapok, and akund
What are examples of seed fibers?
Bast fibers
extracted from the stems of dicotyledonous plants. They undergo processing steps including retting, strutching, and heckling to separate and prepare them for use.
What are examples of bast fibers
Flax, jute, hemp, and ramie
Leaf fibers
These fibers come from leaves or stalks of monocotyledonous plants and are processed into bundles or technical fibers for use in rough textiles or cordage.
Agave and abaca
What are examples of leaf fibers?
Fruit fibers
These fibers come from soaking husks in water, and are typically used for ropes, mats, and stuffing.
Coconut husks
What is an example of a fruit fiber?
Wool
This type of fiber is obtained primarily from sheep and goats, but also other mammals like camels and rabbits. This fiber is known for its elasticity, water retention, and heat retention.
Silk
This type of fiber comes from silk worms, and is known for its luster, strength, and soft texture.
Melt spinning
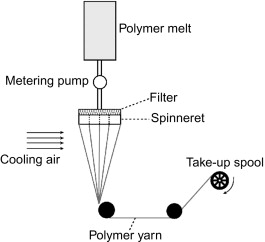
Melt spinning
This type of spinning process involves melting polymer chips and forcing them through spinneret holes, solidifying into fibers as they cool.
Dry spinning
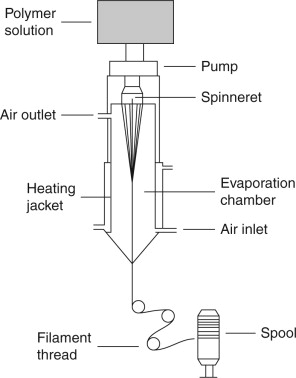
Dry spinning
This type of spinning process involves dissolving the polymer into a solvent, extruding it through a spinneret, and then evaporating the solvent in a hot gas chamber.
Wet spinning
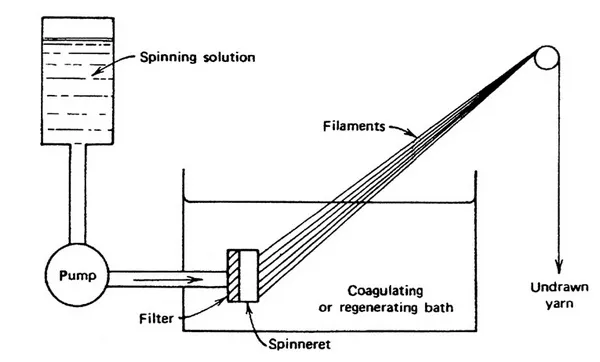
Wet spinning
This type of spinning process dissolves the polymer in a solvent, extruding it into a liquid bath to coagulate the filament and remove the solvent.
Gel spinning
This type of spinning process combines wet and dry spinning, initially forming rubber solids that cool in air and liquid baths, primarily used for high-strength polyethylene fibers.
Drawing fibers
Aligns polymer chains with the fiber, enhancing its strength.
Cellulosic fibers
These types of fibers are produced by dry spinning (acetate) or wet spinning (rayon). They tend to have low refractive indexes with a striated surface. Show bluish, bright blue, brown, white, or yellow/orange interference colors under crossed polars.
Acetate
This is a manufactured fiber composed of cellulose acetate, with a minimum of 92% hydroxyl group acetylation qualifying it as triacetate.
Rayon
This is composed of regenerated cellulose, with a lyocell used as a generic term for fibers composed of cellulose precipitated from an organic solution without substitution of hydroxyl groups or formation of chemical intermediates.
Acrylic fibers
These fibers are produced by wet and dry spinning. They consist of at least 85% acrolonitrile units.
Mod______ fibers were patented in the 1940’s, and are flame-resistant, abrasion-resistant, and produced by wet spinning. They would have a low birefringence and appear gray under cross-polarized light.
Nylon fibers
These fibers are produced by melt spinning, and are thermoplastic (can melt under high heat). Typically lustrous, strong, water-proof, and resistant to sunlight/weathering.
Nylon will dissolve in acids
Why are acid dyes not used for nylon?
FTIR
How can nylon be identified?
Polyester fibers
These fibers are produced by melt spinning, have a high refractive index, and are dyed with acidic dyes.
PET, PTT, and PBT
What are condensation polymer fibers?
Elastomeric fibers
These fibers are known for high elasticity, elongation, and recovery properties. They are resistant to heat/sunlight, weathering, and chemicals. Spandex is an example.
Aramid fibers
These fibers are produced by wet spinning, and have a high refractive index. They are extremely strong, highly flame-resistant, and resistant to stretching. Examples are kevlar and nomex.
Mordants
May be used to enhance dye affinity, color intensity, and long-term stability.
Pigments
Insoluble in water and are attached to fiber surfaces or added to spinning solutions.
Hand-picked, scraped, taped, or vacuumed
What ways can fiber be collected from a crime scene?
Alkaline, acidic
Plant fibers fare better in _____ conditions, while animal fibers like wool preserve better in slightly _____ environments.
Cotton fibers
Elongated single spindle-shapes cells with varying thicknesses of cell walls and a hollow lumen. Exhibit twists and convolutions in length and diameter.
Kapok fibers
Smooth, hollow, cylindrical fibers with thin cell walls that often bend sharply. Known for buoyancy, they were traditionally used as stuffing material in life jackets.
Bast fibers
Derived from the stems of plants like flax, hemp, jute and ramie. Differentiated by the shape of their ultimates, transverse joints, cross-sectional shape, and variable lumen form.
Leaf fibers
Often processed in bundles for use in sack clock and cordage, ie… sisal and abaca
Fruit fibers
Coarse with silica stigmata spaced along their length, used for ropes, maths, and stuffing material, ie… coir
The Herzog test
Conducted with polarized light microscopy (PLM) to help differentiate the direction of twist or growth in fibers.
S twist
With the Herzog test, this twist will appear yellow-orange under polarized light when oriented at the extinction position, and blue when oriented 90 degrees off.
Z twist
With the Herzog test, this twist will appear blue under polarized light when oriented at the extinction position, and yellow-orange when oriented 90 degrees off.
Man-made
Which fiber would appear more uniform in morphology? (Natural or Man-made)
Microspectrophometry (MSP)
Which fiber technique helps in color discrimination?
FTIR
Which fiber technique helps confirm fiber type?
Raman spectroscopy
Which fiber technique helps identify dye components?
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
Which fiber technique helps separate dye mixtures?
PLM, FM, Comparison microscopy, and SEM
Which techniques are good for microscopic analysis of fibers?
Refractive index
Ratio of apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium.
Solubility testing
Fill in the blank: _____ ______ provides insights into fiber composition
Tears
Torn and frayed yarn edges with overstretch marks and torn stitching holes.
Cut
Relatively straight yarn edges with no overstretch marks.
Natural, man-made, and mineral
What are the three types of fibers?