Chapter 13 - Molecular Spectroscopy 1: Rotational and Vibrational Spectra (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Emission spectroscopy
A molecule undergoes a transition from a state of high energy E1 to a state of lower energy E2 and emits the excess energy as a photon
2
New cards
Absorption spectroscopy
The net absorption of nearly monochromatic (single frequency) incident radiation is monitored as the radiation is swept over a range of frequencies
3
New cards
Stokes radiation
When incident photons collide with the molecules, give up some of their energy, and emerge with a lower energy
4
New cards
Anti-Stokes radiation
When incident photons collect energy from the molecules (if they are already excited), and emerge with a higher frequency
5
New cards
Spectrometer
An instrument that detects the characteristics of light scattered, emitted, or absorbed by atoms and molecules
6
New cards
Dispersing element
It separates radiation into different frequencies
7
New cards
Transmittance
The ratio of the transmitted intensity to the incident intensity at a given frequency
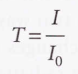
8
New cards
Beer-Lambert law
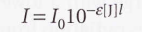
9
New cards
Absorbance

10
New cards
Beer-Lambert law with absorbance
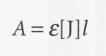
11
New cards
Integrated absorption coefficient
The sum of the absorption coefficients over the entire band
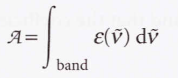
12
New cards
Stimulated absorption
The transition from a low energy state to one of higher energy that is driven by the electromagnetic field oscillating at the transition frequency
13
New cards
Transition rate
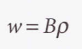
14
New cards
Total rate of absorption (W)
The transition rate of a single molecule multiplied by the number of molecules N in the lower state
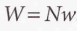
15
New cards
Gross selection rule
It specifies the general features a molecule must have if it is to have a spectrum of a given kind
16
New cards
Specific selection rules
They express the allowed transitions in terms of the changes in quantum numbers
17
New cards
Doppler effect
In which radiation is shifted in frequency when the source is moving towards or away from the observer
18
New cards
Collisional deactivation
Arises from collisions between molecules or with the walls of the container
19
New cards
Collisional lifetime
The mean time between collisions
20
New cards
Moment of inertia
The mass of each atom multiplied by the square of its distance from the rotational axis through the center of mass of the molecule
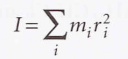
21
New cards
Rigid rotors
Bodies that do not distort under the stress of rotation
22
New cards
Spherical rotors
They have three equal moments of inertia
23
New cards
Symmetric rotors
Two equal moments of inertia
24
New cards
Linear rotors
One moment of inertia
25
New cards
Asymmetric rotors
Three different moments of inertia
26
New cards
Stark effect
The splitting of states by an electric field
27
New cards
For a molecule to give a pure rotational spectrum
it must be polar.
28
New cards
Gross selection rule for rotational Raman transitions
The molecule must be anisotropically polarizable
29
New cards
Nuclear statistics
The selective occupation of rotational states that stems from the Pauli principle
30
New cards
Ortho-hydrogen
The form with parallel nuclear spins
31
New cards
Para-hydrogen
The form with paired nuclear spins
32
New cards
Vibrational terms
The energies of its vibrational states expressed in wavenumbers
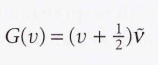
33
New cards
Infrared active vibrations
Where the electric dipole moment of the molecule must change when the atoms are displaced relative to one another
34
New cards
Anharmonic motion
When the restoring force is no longer proportional to the displacement
35
New cards
Morse potential energy
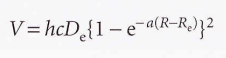
36
New cards
Birge-Sponer plot
Graphical technique used to determine the dissociation energy of the bond when several vibrational transitions are detectable
37
New cards
Branches
Groups in which absorptions are divided
38
New cards
P branch
All transitions with J = -1
39
New cards
Q branch
All lines with J = 0
40
New cards
R branch
Lines with J = +1
41
New cards
Combination differences
A procedure used widely in spectroscopy to extract information about a particular state
42
New cards
Gross selection rule for vibrational Raman transitions
The polarizability should change as the molecule vibrates
43
New cards
Normal mode
An independent, synchronous motion of atoms or groups of atoms that may be excited without leading to the excitation of any other normal mode and without involving translation or rotation of the molecule as a whole
44
New cards
Gross selection rule for infrared activity
The motion corresponding to a normal mode should be accompanied by a change of dipole moment
45
New cards
Parallel bands
The transitions arising when the dipole moment change is parallel to the principal axis
46
New cards
Perpendicular bands
Transitions involving the perpendicular change of a dipole to the principal axis
47
New cards
Force field
The set of force constants corresponding to all the displacements of the atoms
48
New cards
Tumbling
The random change of orientation in molecules
49
New cards
Exclusion rule
If the molecule has a center of symmetry, then no modes can be both infrared and Raman active
50
New cards
Depolarization ratio
The ratio of the intensities of the scattered light with polarizations perpendicular and parallel to the plane of polarization of the incident radiation
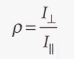
51
New cards
Depolarized line
If the depolarization ratio is close to or greater than 0.75
52
New cards
Polarized line
If the depolarization ratio is less than 0.75
53
New cards
Resonance Raman spectroscopy
A modification of the basic Raman effect involves using incident radiation that nearly coincides with the frequency of an electronic transition of the sample
54
New cards
Infrared active mode
If the symmetry species of a normal mode is the same as any of the symmetry species of x, y, or z
55
New cards
Raman active mode
If the symmetry species of a normal mode is the same as the symmetry species of a quadratic form