Lecture 13: Shigella and Salmonella
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
T/F: E. coli, Shigella, and Salmonella are all closely related
True
T/F: Shigella is zoonotic
True
Shigellosis in humans is also known as….
Bacillary Dysentary
_______ are the most natural reservoir of Shigella
Humans
Shigella and E. coli are very similar bacterium, what two key features separate the two?
Shigella can’t ferment lactose (E. coli can )
Shigella is Non-motile (E. coli is motile)
What are the 2 Virulence factors of Shigella?
Invasion plasmid
Shiga Toxin (Stx)
Shigella possesses a Shiga Toxin (Stx) as a virulence factor. Another bacterium possesses a similar type of virulence factor, name that bacterium
STEC (Shiga-Toxin producing E.coli)
Stx1/Stx2
Shigella is spread ____-____, and has a very _____ infectivity
Fecal-Oral
High Infectivity (<10 bacteria can cause disease)
Where does Shigella replicate (Intracellular, Extracellular, Both)?
Intracellular
Shigella bacteria are limited to one part of the G.I tract, what part is it?
Colon
T/F: Salmonella shares the shame general features of Enterobacteriaceae
True
Does Salmonella replicate inside/outside/both the cell?
Both, it’s a facultative intracellular bacterium
You isolate a bacterium that could either be Shigella, E. coli, or Salmonella. After further testing you discover this bacterium produces Hydrogen Sulfide Gas (H2S), which type of bacteria is this most likely to be?
Salmonella it’s the only one that normally produces Hydrogen sulfide gas
In regards to Salmonella, what is the Vi antigen? Which strains of Salmonella is it found in?
Vi Antigen
Virulence antigen, it is a virulence-associated capsular polysaccharide
Typhi, Paratyphic C, and Dublin
All Salmonella are motile except for which 2 strands?
S. Pillorum
S. Gallinarum
What are the two species of Salmonella? How many subspecies of each?
S. enterica
6 Subspecies
S. bongori
Which type of Salmonella has the most serovars?
S. enterica subspecies enterica
The serovars of Salmonella denote the _______ and _______ that is associated with that particular type of Salmonella
Syndrome (Typhi for typhoid fever) and host specificity (S. Abortusovis or S. Abortusequi)
What are all the subcategories of Salmonella?
Genus → ______ → ________ → ________
Genus → species → subspecies → Serotype
T/F: When writing the Serotype of Salmonella, the first letter is Capitalized and the whole word is not italicized
True
Which 2 of these Salmonella serovars are Host Adapted (not host-restricted)?
Typhi
Dublin
Paratyphyi
Gallinarum
Enteritidis
Cholerasuis
Abortusovis
Dublin
Cholerasuis
Host-adapted is when they are associated with one specific host species and cause severe disease in that species but are capable of infecting humans and other species accidentally
Most Salmonella serovars are _________ (Host-adapted/Non-host-adapted)
Nonhost-adapted (Generalists)
The Salmonella Dublin serotype infects _______
Cattle
What are the clinical signs of Salmonella Dublin?
Acute/chronic diarrhea
Septicemia
Abortion
What are the 2 main Salmonella-specific virulence factors? What do they do?
SPI-1
Invasion
SPI-2
Intracellular surivial
SPI= Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands
What are the 5 steps of Salmonella Pathogeneicity?
Transmission
Attachment
Distal ileum and Colon
Invasion (SPI-1)
Inflammatory Signals (This step causes cell death and sloughing)
Phagocytosed by macrophages
Activation of SPI-2 allows for survival and multiplication within macrophages within the SCV (Salmonella containing vacuole)
Macrophages disseminate Salmonella systemically
When an animal is a carrier for Salmonella, where does this bacterium reside?
Salmonella can remain dormant in the Liver or gall bladder
It can reactivate and shed into the gut
Without ________ Salmonella cannot spread systemically through the body
Macrophages
Which virulence factor of Salmonella allows it to evade phagocytosis by Macrophages?
SPI-2
Other than avoiding phagocytosis by macrophages, how else does Salmonella evade the immune system?
Alteration in LPS chain lengths
Antigenic switching of flagella
Changing between two flagellar antigens, making it harder for the immune system to detect it
Flagella antigens H1 and H2
S. Gallinarum is host adapted to _______
Poultry
T/F: Salmonella Gallinarum is a reportable disease
True
Salmonella Enteritidis is a very important disease in chicken eggs as it can infect the outside and inside of the eggs (penetration of the bacteria through the egg shell) and spread diseases to humans. However, there is another way that it can infect the inside of the egg without penetrating the shell, what is it?
Ser. Enteriditis phage type (PT) 4
Infection of the ovary and oviduct
Ser. Enteritidis PT 4 are already internally infected when laid
T/F: The gut microbiome of the animal plays no role in Salmonella infections
False, having a good microbiome can help prevent Salmonella infection by competitive exclusion
What is the name of the broth that is selective for Salmonella?
Rappaport Vassiliadis (RV) Broth
T/F: Salmonella infected macrophages are harder to treat with antibiotics and allow for the Salmonella to surivive in a “dormant“ state
True
T/F: Shigella is transmitted by fecal contamination of food and water
True
T/F: Dublin is a host adapted serovar of Salmonella
True
T/F: Salmonella Typhimurium is an example of a host-adapted Salmonella serovar
False
T/F: Salmonella carriers look healthy but can shed large numbers of Salmonella bacteria in their feces
True
T/F: Reptiles are not a risk for Salmonella infections in humans
False
T/F: Poultry eggs can be contaminated internally and externally with Salmonella Bacteria
True
T/F: Salmonella replicates inside macrophages
True
List the surface antigens that determine a serotype
LPS (O antigens)
Flagella (H-antigens)
Capsular Antigens (Vi Antigens)
Summarize the pathogenesis of Salmonella in a few lines
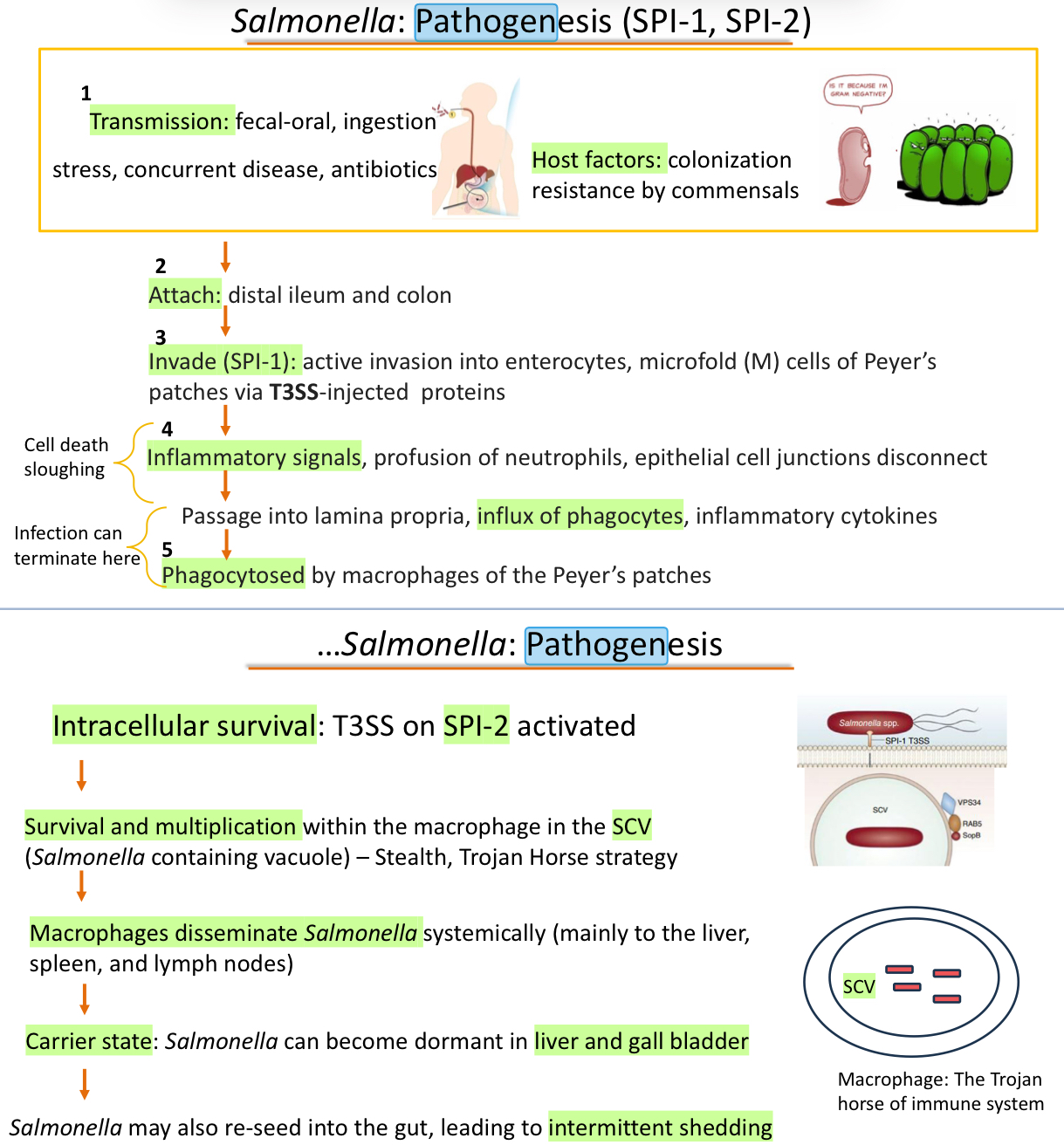
Salmonella becomes latent in which organs?
Gall bladder and Liver
T/F: Salmonella is a facultative intracellular pathogen
True