cell and molec exam 1 What is the cell theory of life?
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What is the cell theory of life?
All cells come from preexisting cells, all living things are made of cells, cell is the basic unit of life
Is a virus a living organism?
no
Who coined the term “cell” and what else did he do?
robert hooke, elasticity
What type of microscope was necessary to determine the ultrastructure
inside of cells?
tem
What type of microscopy uses specific wavelengths of light to resolve
specific structures inside of cells?
flourescent
What is the size of a normal animal cell? Bacteria?
20 microns, 5 microns
A change the organism’s genome is called a mutation. Are all mutations
bad?
no
True or false: Since humans are the most complex of all the organisms, we
have the most genes and the largest genome.
false
What model organism was used to determine the proteins that regulate the
cell cycle in human cancer?
baker’s yeast
Name two membrane bound organelles that have their own genome?
chlorolasts, mitochondria
These organelles support what theory of eukaryotic evolution?
endosymbiotic theory
What cell structures maintain cell shape in animal cells?
cytoskeleton
What four atoms make up 99% of the atoms of the human body?
C, H, N, O
What is an isotope?
same protons, different neutron
What kind of bond shares electron pairs?
covalent
Why does oxygen pull electrons closer to itself during a covalent bond than a carbon atom?
oxygen has a higher eletronegativity than carbon
What is usually required to make or break a covalent bond in a cell?
enzymes
What happens when salt is added to water? What have the Na and Cl atoms become in the
water?
dissociates, they become ions
What allows for water to be liquid at room temperature?
the hydrogen bonding
What kinds of bonds are hydrophilic/hydrophobic?
What happens when an acid/base is added to water?
hydrophilic - ionic/polarcovalent
hydrophobic - nonpolarcovalent
What is pH?
the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration
What is a condensation reaction and what happens during one?
condensation reactions join two monomers and produce water as a byproduct (requires energy)
What is a hydrolytic reaction and what happens during one?
breaks apart a bond between two monomers and consumes water (releases energy)
What part of the nucleotide is different between DNA and RNA?
the sugar, deoxyribose vs ribose (deoxyribose has one less oxygen on the bottom right of the ring)
What is an amphipathic molecule and what is an example of a one that is an important
biomolecule?
amphipathic molecules have one side that’s hydrophobic and one that is hydrophilic; common example is a phospholipid
Since cells create and maintain highly-ordered systems how do they not violate the 2nd law of
thermodynamics?
they’re open systems and release energy into the universe
What is the ultimate source of energy for most all cells?
the sun
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration complimentary processes?
the products and reactants kind of match
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction? Which one is used during catabolism?
OIL RIG, oxidation
How do enzymes increase the rates of reactions?
lower the initial activation energy
How can thermodynamically unfavorable reactions such as anabolic reactions take place in a
cell?
energy coupling, where one is positive delta g and one is negative so in principle they cancle each other out
What is the standard free energy of a reaction and how is it denoted?
measure of the maximum useful energy available from a chemical reaction under specified standard conditions, denoted by ΔG°
What is the most common energy carrier in all cells on earth?
atp
What are NAD+ and NADPH used for?
carrying electrons
During a synthesis reaction, a phosphate is added to a molecule to create a high energy
intermediate. Where did the phosphate group most likely come from?
atp
What kinds of reactions are hydrolytic and condensation reactions? Which are used to create
cellular polymers?
hydrolytic - catabolic
condensation - anabolic
condensation is used to make polymers
What is a little different about DNA and RNA polymerization?
A reaction is shown to be substrate independent. What kind of reaction is it?
dna needs a primer
What is the equation that defines enzyme characteristics?
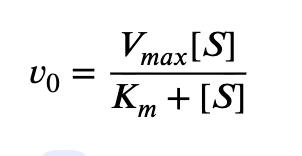
What is KM’s definition and what is it a measure of?
Michaelis constant (Km) is a measure of the concentration at which a substrate/ligand causes 50% of its maximum activation potential (Vmax) of its binding partner at saturation
What kind of inhibitor only affects Vmax?
non-competitive
What kinds of proteins are there and what do they do?
enzymes, structural, hormonal, receptor, contractile, transport, storage, defense
How are proteins built and in what direction do they build?
synthesis (transcription + translation), n-terminus to c-terminus
What is a peptide bond?
a covalent bond that links two amino acids together, forming the fundamental unit of a polypeptide chain
How do the Amino Acid sidechains impact protein structure and function?
determine how the protein will fold
What kinds of side chains do Amino Acids have?
polar, nonpolar, acidic, basic
What forces influence protein folding?
mainly hydrophobic
What are disulfide bonds and how do they affect protein stability?
covalent bonds that form between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids, creating a stable cross-link within a protein's structure
What are proteins called that change their shape when they bind other substances?
allosteric
What is the primary structure of a protein?
amino acid sequence
What two kinds of elements make up the secondary structure of a protein?
alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet
What are enzymes and how do they work?
catalyzing proteins that can speed up reactions without being consumed
A ligand binds a protein by using many ______ _______ bonds.
non covalent
What do B-cells produce in an immune response?
antibodies
How can proteins be modified?
phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, glycolysation, methylation, proteolation
What is co-factor vs an activated carrier?
cofactors are required to bind to an enzyme for it to function, activated carriers carry the energy for an enzyme to complete a reaction
How does feedback regulation work? Give an example.
system output affects the rate at which something is occuring to stabilize/drive a reaction. thermoregulation (sweating - negative feedback)
How can the activity of proteins be controlled?
changes in their conformation, concentration, etc.
How did Griffith’s ability to transform bacteria from a non-lethal to a lethal stain support that DNA was the genetic material of life?
The genetic ability was transferred between bacteria, which was later identified as DNA
How did Avery, McCarthy and McLeod reinforce these findings?
the removal of DNA and RNA prevented hereditary change
What made the Hersey/Chase blender studies definitive?
showed that DNA, NOT PROTEINS, carried genetic information
How did Chargaff’s rules support the Watson and Crick model of DNA?
AT GC
Who should have gotten the Nobel prize for her image of the X-Ray diffraction pattern of crystalized DNA?
Rosalind Franklin
What is the difference in RNA and DNA?
the sugar is different, Uracil instead of Thymine
Chromosomes are a ___________ molecule that has ______ strands that run _____-Parallel in a ’ to ’
direction.
DNA 2 anti 5’ to 3’
Chromosomes have ______ telomeres, _______ centromere, and _______ numbers of Origins of Replication
two, one, multiple
What is Chromatin composed of?
DNA, RNA, primary histones, proteins
What is the fundamental unit of chromatin?
nucleosome
What proteins make up a nucleosome? And how many?
octamer, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
How can nucleosomes be modified and what is the result of modifying them?
post-translational modifications, remodeling
What is the difference between Heterochromatin and Euchromatin?
hetero - dense, eu - loose
What protein complexes condense chromosomes further by making different-sized loops in Interphase
chromosomes?
cohesion (SMC)
What protein complexes condense chromosomes even further (10,000 X) during mitosis?
condensin
In human chromosomes, genes are ______ly spread in chromosomes.
nonrandom
What are the three regions of a chromosome that remain densely condensed (heterochromatic) throughout the cell cycle (interphase & mitosis) and what are their functions?
telomeres, centromeres, NORs
What is X-inactivation and why is it important?
one of the two X chromosomes in female mammals is randomly and permanently shut down in each cell
When using the following equation to generate an
estimate, Xest = √(XL * XU), XU represents the:
upper estimate
The estimate for the number of viral
particles an earth is
10 ^ 31
Viruses which attack bacteria
are referred to as
bacteriophages
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a type of _____
yeast
The best estimate for the diameter of a
protein is
3-6 nanometers
The best estimate for the size of influenza A
is
80-120 nanometers
Glutamate, acetylcholine and GABA
are all examples of
neurotransmitters
The estimated time for a molecule to
diffuse across the synaptic divide is
1 millisecond
___ are famed as the energy
factories of eukaryotic cells”
mitochondria
Which of the following cell types is the
largest contributor to a person’s total
mass?
adipocytes
What kind of biological particle is SARS Co-V-2?
virus
How does Sars Co-v-2 enter cells and what is it made of?
bind to ang-2 receptor and inject rna
What role did the invention of microscopy play in the development of the Cell Theory
of life?
hooke saw the dead cork cell
What are some common protozoans and what kinds of locomotion to they have?
paramecium, celia
What role does selection play in evolution?
selection is the “engine” of evolution
How long does evolution take?
depends on the generation time
What are the different kinds of bonds used in biological systems and their relative
strengths in water?
covalent - ionic - hydrogen - ldf
Compare and contrast anabolism and catabolism.
catabolism - releases energy
anabolism - takes energy
What is “ Gibbs free energy”? What is it’s value in a thermodynamically favorable
reaction?
entropy, negative delta g
Would viruses follow Chargaff’s rules?
no, they don’t have double-stranded dna
How does DNA reposition itself around a nucleosome and what does this require?
nucleosome sliding, cromatin remodeling complexes
How can Histone 3 be modified to increase or decrease gene activity (be specific)?
acetylation increases, methylation decreases
How is X-inactivation inherited from one cell to another?
cell division via an epigenetic mechanism