Glycolysis, Glycolysis
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
1. Glucose
2. Aldehyde
2. Aldehyde
What molecule is this? Is it a ketone or an aldehyde?
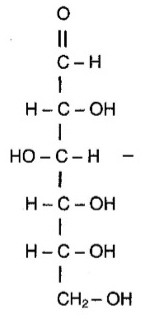
2
New cards
Create Glucose 6 Phosphate out of Glucose
What is the purpose of hexokinase?
3
New cards
Hexokinase
What enzyme creates Glucose 6 Phosphate from Glucose?
4
New cards
Change Glucose 6 Phosphate to Fructose 6 Phosphate
What is the function of Phosphoglucose Isomerase?
5
New cards
Phosphoglucose Isomerase
What enzyme changes Glucose 6 Phosphate to Fructose 6 Phosphate?
6
New cards
Change Fructose 6 Phosphate to Fructose 1,6 BisPhosphate.
What is the function of Phosphofructokinase (PFK)?
7
New cards
Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
What enzyme changes Fructose 6 Phosphate to Fructose 1,6 BisPhosphate?
8
New cards
To change Fructose 1,6 BisPhosphate to Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
What is the function of Aldolase?
9
New cards
Aldolase
What enzyme changes Fructose 1,6 BisPhophate to Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate?
10
New cards
Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
What molecule is this?
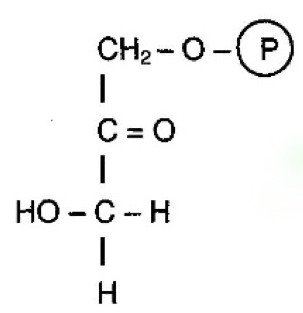
11
New cards
Triose Phosphate Isomerase
What enzyme changes Dihydroxyacetone to Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate?
12
New cards
To change Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate to Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate.
What is the function of Triose Phosphate Isomerase?
13
New cards
Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate
What molecule is this?
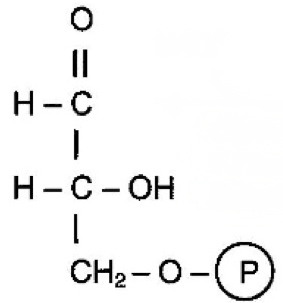
14
New cards
To change Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate to 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate
What is the function of Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate Dehydrogenase?
15
New cards
Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate Dehydrogenase
What enzyme changes Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate to 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate?
16
New cards
1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate
What molecule is this?
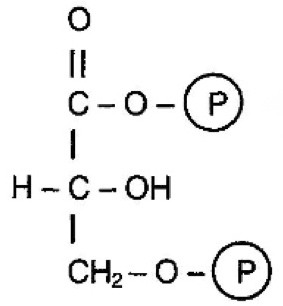
17
New cards
To change 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate to 3 Phosphoglycerate
What is the function of Phosphoglycerate Kinase
18
New cards
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
What enzyme changes 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate to 3 Phophoglycerate?
19
New cards
3 Phosphoglycerate
What molecule is this?
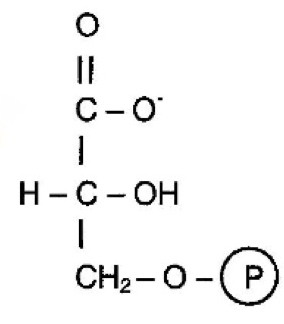
20
New cards
To change 3 Phosphoglycerate to 2 Phosphoglycerate.
What is the function of Phosphoglycerate Mutase?
21
New cards
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
What enzyme changes 3 Phosphoglycerate to 2 Phosphoglycerate?
22
New cards
2 Phosphoglycerate
What molecule is this?
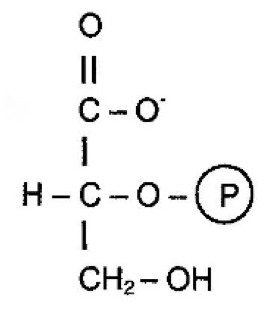
23
New cards
To change 2 Phosphoglycerate to Phosphoenolpyruvate
What s the function of Enolase?
24
New cards
Enolase
What enzyme changes 2 Phosphoglycerate to Phosphoenolpyruvate?
25
New cards
Pyruvate
What molecule is this?
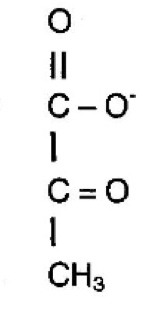
26
New cards
To change Phosphoenolpyruvate to Pyruvate.
What is the function of Pyruvate Kinase?
27
New cards
Pyruvate Kinase
What enzyme changes Phophoenolpyruvate to Pyruvate?
28
New cards
To change Pyruvate to Lactate
What is the function of Lactate Dehydrogenase?
29
New cards
Lactate Dehydrogenase
What enzyme changes Pyruvate to Lactate?
30
New cards
1. Glycolysis is the oxidation of glucose. Pyruvate is the end product.
2. Provides ATP. NADH is also produced.
3. In aerobic organisms, glycolysis yields precursors to the Krebs Cycle & Electron Transport System
2. Provides ATP. NADH is also produced.
3. In aerobic organisms, glycolysis yields precursors to the Krebs Cycle & Electron Transport System
What are the 3 purposes of Glycoysis?
31
New cards
In the cytosol
Where does glycolysis take place?
32
New cards
1. Bring glucose into the cell
2. Change glucose into an "energy rich sugar"
2. Change glucose into an "energy rich sugar"
What are the 2 functions of the first half of glycolysis?
33
New cards
1. Adds a phosphate group
How does the first half of glycolysis "trap" glucose in the cell?
34
New cards
Glycolysis is what kind of pathway
catabolism
35
New cards
1 Glucose leads to how many pyruvate
2
36
New cards
What are the products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 atp , 2 NADH
37
New cards
How many intermediates are bisphosphorylated
2
38
New cards
What is the first high energy forming reaction catalyzed by?
glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (inorganic P added to NAD+-->NADH)
39
New cards
how is a mutase different from an isomerase
the mutase moves the phosphate group to different carbon position
40
New cards
What are pyruvates 2 fates
lactate dehydrogenation and alcohol dehydrogenation
41
New cards
Where is NAD+ regenerated?
lactate fermentation of the skeletal muscle ( through contraction) and Electron Transport Chain
42
New cards
Where is another location for NAD+ regeneration that is less beneficial for human cells?
yeast through alcohol dehydrogenation (through metabolism) and Electron Transport Chain