P3: particle model of matter
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
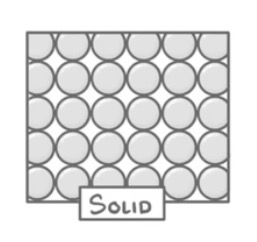
How are the particles arranged in a solid?
Very close together
Regular pattern
Particles vibrate but don’t move around
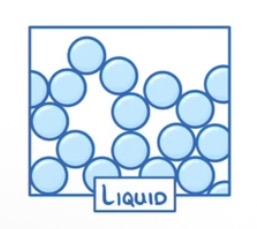
How are the particles arranged in a liquid?
Close together
Not arranged in a regular pattern
Can move around each other
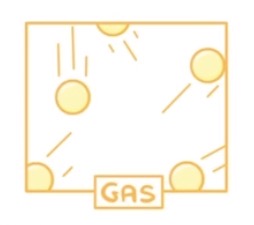
How are the particles arranged in a gas?
Very far apart
Not arranged in any pattern
Moving very rapidly constantly
Explain the density of solids, liquids and gases.
SOLIDS
Very high density
Can’t be compressed - particles already tightly packed so cannot move closer to eachother
LIQUIDS
High density
Can’t be compressed - particles already tightly packed so cannot move closer to eachother
GASES
Low density
Can be compressed
Required Practical: calculating density
REGULAR OBJECTS
Find the object’s mass using a balance.
Use a ruler to measure the length, width and height of the object, then multiply them together to find the volume.
Use the equation density = mass / volume to find the density.
IRREGULAR OBJECTS
Find the object’s mass using a balance.
Put a beaker under a Eureka can spout and fill the can with water. Water should be dripping; wait for it to stop.
Now place a measuring cylinder under the spout.
Put the object into the Eureka can.
Measure the volume of the water displaced in the measuring cylinder.
Use the equation density = mass / volume to find the density.
What is internal energy?
The total kinetic energy and potential energy of all the particles (atoms and molecules) that make up a system.
How does heating affect internal energy?
Heating increases the energy of the particles in a system, which either raises the temperature of the system or produces a change of state.
Explain changes of state key points and name them.
Mass is always conserved during changes of state
They are physical changes not chemical changes - easily reversible to original properties
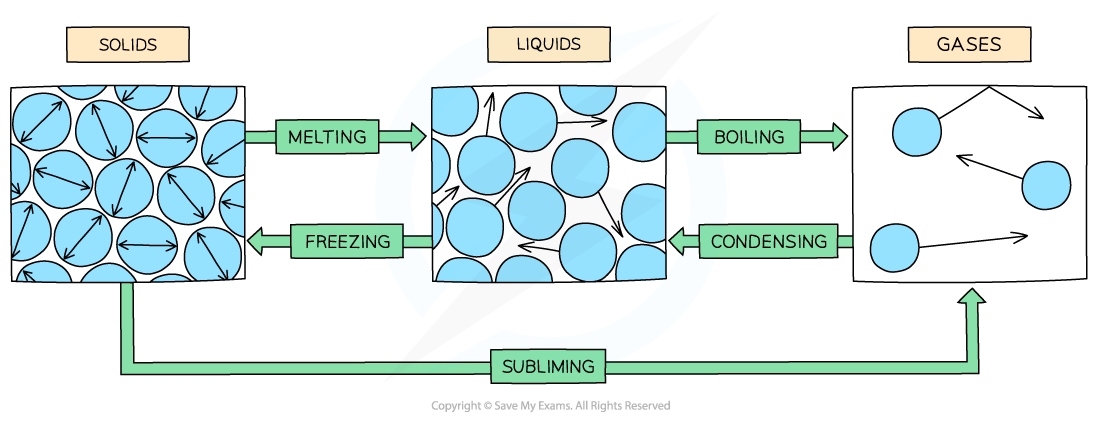
What is the specific heat capacity of a substance?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1°C.
Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant when it changes state?
The energy supplied is used to weaken / break the forces between the particles rather than heat the substance. It changes the internal energy but not the temperature.
What is the specific latent heat of a substance?
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1kg of the substance with no change in temperature.
What is the specific latent heat of fusion?
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a solid to a liquid with no change in temperature.
What is the specific latent heat of vaporisation?
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a liquid to a vapour with no change in temperature.
What in a heating / cooling graph indicates a change of state?
When the temperature stops rising / the line is straight, a change of state is happening (see picture example).
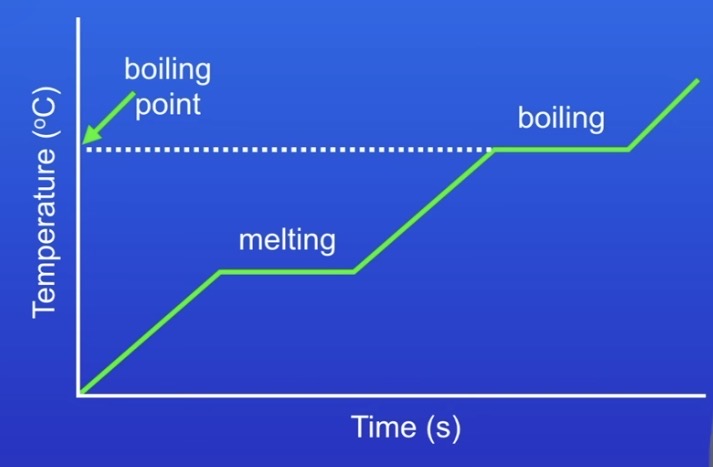
What causes pressure in a gas?
The particles colliding with the walls of the container that the gas is held in.
How can we increase gas pressure?
Increase the number of collisions per second
Increase the energy of each collision
How does temperature affect gas pressure?
Lower temperature + pressure: less kinetic energy so fewer collisions per second with less energy
High temperature + pressure: more kinetic energy so more collisions per second with more energy