SocSci LT 1 [Contains all Readings]
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Who wrote the Sociological Imagination and when?
C Wright Mills, in 1959
What was the relationship shared between Rizal’s writings and C Wright Mills’s sociological imagination?
Rizal connected personal troubles to a deeper issue in society, more specifically the Spanish colonialization of the Philippines.
Rizal’s storytelling and C Wright Mills both agreed that sociology is a tool for what, and what did they both emphasize the need for?
They both agreed that Sociology was a tool for connecting individual people’s lives with larger social issues
Both emphasized the need for intellectual engagement with the public and a commitment societal transformation.
What did the social scientist Burawoy in 2008, advocate for?
Burawoy advocated for organic public sociology which challenges social scientists to engage in dialogue and “the political imagination”.
Under what conditions should sociology be studied to result to the most impact for society?
It should be studied with respect to the society as the understanding of society via sociology helps improve society at large.
From C. Wright Mills what is the sociological imagination?
“The capacity to shift from one perspective to another – from the political to the psychological”
Under the sociological imagination, what is a trouble?
It is something experienced by an individual
Individuals are tempted to hold themselves accountable for these troubles
Under the sociological imagination, what is a issue?
A public matter that many people experience
There are existing debates on the matter and what threatens it →(Aki Explanation not A PROFESSIONAL) i.e. somethings are troubles that we dont necessarily know of (random example : invasion of privacy on the basis of the internet is a possible issue)
What does the sociological imagination observe?
How unique circumstances of reality affect people and in turn history. It is a quality of mind.
What benefit may occur if us as normal people are able to utilize the sociological imagination?
This allows us to better situate ourselves in this inequality as individuals may not always be held accountable for their troubles. These troubles may be linked to OVER-ARCHING SOCIAL ISSUES OF THE WORLD
What is the paradox of the self?
It is authentic yet performative, autonomous yet interdependent, a product of bioecological and sociocultural interactions over time.
Who wrote Positionality Statements?
Kendal A. King
Under positionality statements what is a promise?
A promise
enhances transparency
Improve theory building for cross context to study outcomes
Under positionality statements what is a peril?
A peril
• overemphasis on the “Self” / personal narratives
Performative
superficial and can overshadow empirical findings
What do positionality statements aim to address?
They aim to address researcher reflexivity by revealing how personal identities influence research processes.
To be able to fulfill the full potential of positionality statements what should it focus on?
They should focus on explaining how researchers’ identities shape research decisions and outcomes, integrated meaningfully into research discussions rather than standing alone. This shift could foster stronger, more inclusive research practices in applied linguistics and beyond.
What is positionality?
“These statements, which vary from a few sentences to a few pages, typically outline the demographic, professional, or personal characteristics of the author(s) and, to a greater or lesser extent, their position relative to the research topic or research participants.”
What is Reflexivity?
“The practice of sustained analysis of a researcher’s impact on their own scholarship” It makes research more rigorous.
Who wrote The Presentation of Self in
Everyday Life
Ervin Goffman
Under the presentation of self, what is a mask?
Masks are arrested expressions and admirable echoes of feeling, at once faithful, discreet, and superlative.
Under the presentation of self what is impression management?
We enact roles to come across as “digestible” for social circumstances.
Note : The roles are the character as each of us have more or less a fixed identity that we merely derive from and show depending on the situation.
What may social life be described as?
a stage allowing us to better grasp the intricacies of human behavior being presented to the real world.
What is Modus Vivendi?
is the working consensus in social interactions of the appropriate conduct & etiquette that is to be displayed or acted out.
In a dramaturgical sense what is a routine?
is the pre-established pattern of action
In a dramaturgical sense what is an Interaction?
is the reciprocal influence of the other’s performance
In a dramaturgical sense what is a Performance?
is ALL activities of a particular situation seeking to infuence.
In a dramaturgical sense what is a Role?
is the particular image that a person wants to convey to others
In a dramaturgical sense what is a Team?
is a group of people who are in confluence in order to foster a certain perception of a situation.”
What do first impressions do?
1st Impressions aim to control the conduct + responsive treatment of individuals.
Every projected “face” has what of the actor’s character? In addition to this what are the different tactics?
a sliver of the actor’s moral character.
Tactics
Defensive
protects one’s own projection
(saving face)
Protective
to save the definition of the situation projected by another
What is situation propriety?
An interaction depends on the context i is situated in
What is the front stage and back stage, differentiate.
Front Stage : where you put up a front (u act differently maybe more professionally)
Back Stage : where you let loose
What does the Dramaturgy focus on?
focuses on how the real self is built on every interaction we have.
What is sociology a discipline of?
is a discipline studying who you are based on how other people perceive you.
In self presentation life can also be compared to what?
A theatre, and thus is a framework of interaction (self presentation) that also uses costumes, props, setting and a script.
Who wrote the Sociocultural Theory of Cognitive Development?
Lev Vygotsky
What is the zone of proximal development
an area of learning that occurs when a person is assisted by a teacher or peer with a higher skill set
Divided into
Interpersonal Plane
Intrapersonal Plane
What is Vygotsky’s theory about
its about the dialectic interaction between the external (social) and internal (mental) planes, one transforming the other. This dialectic relation rejects separation of the human mind and body, mental and social processes, the individual and society, and language and context.”
What is Phylogenesis
Evolution
What is Socio-cultural history
community/society
What is Ontogenesis
Development of person
What is Microgenesis
“very short period[s] of time”
According to Lev Vygotsky what is the effort of individuals in relation to the kind of activities they engage in?
the effort of individuals are not separate from the kinds of activites in which they engage in & the institutions they’re part of.
How are Cultural tools formed?
they are both inherited & transformed by successive generations ; it is not static & formed by the collective effort of people working together.
What do we focus on to analyze human development?
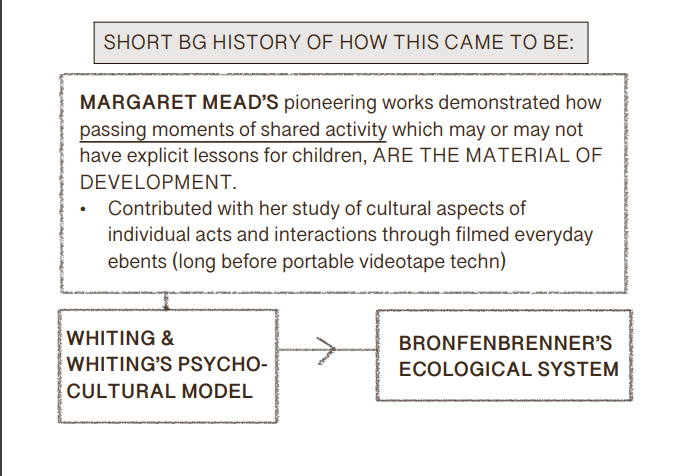
the interpersonal, personal & cultural, institutional aspects of an event, all of which constitute human activity.
See Diagram
Who wrote Thinking Fast and Slow
Daniel Kahneman
What is system 1
It is the Experiential System of Epstein.
unconscious & instinctual
based on vibes & memory
Prone to bias & error
What is system 2
It is the Rational System of Epstein
sense of self
Logic & reasoning
Self-control
What is Cognitive Ease
a state of “intuitive thinking” in a relaxed mental state.
What is Metacognition
is the acknowledgement of when you’re lost and need to reorient yourself.
What is the Exposure Effect
the constant presence of someone/something will make them seem more believable (= tolerance)
What is Rationalization?
the process where one attempts to understand one’s unconscious processing system by their conscience. process. system.
What is Heuristics
one cognitive shortcut method for decision making wherein it simplifies a complex question, allowing for quick judgements without accounting for bias
What is the Peak End Rule?
when we judge experiences based on how they felt at the end rather by the sum of its god & bad parts.
How does remembering work in terms of judging experiences?
“did it hurt”
Has the decision-making power but is something wrong due to a difference of perception
“ What we learn from the past is to maximize the qualities of our future memories —hence the tyranny of the remembering self. It is the one that keeps score and governs what we learn form the living. “
How does experiencing work in terms of judging experiences?
• “does it hurt now?
• does not have a voice
What is Duration Neglect
It is where we forget the middle part of an experience as it is the end that counts and not the means to it.
“ A memory that neglects duration will not serve our preference for long pleasure and short pains ”
What are the traps of system 1?
Availability Trap
Sunken Cost Fallacy
What is the availability trap of system 1?
a cognitive bias where people tend to overestimate the likelihood of events based on how easily they can recall examples of those events
What is the sunken cost fallacy of system 1?
the cognitive bias where someone continues to invest time, money, or effort into something even when it's no longer beneficial, simply because they've already invested significantly in it
What are the interpersonal functions of emotions?
Emotional Expressions Facilitate Specific Behaviors in Perceivers
Emotional Expressions Signal the Nature of Interpersonal Relationships
Emotional Expressions Provide Incentives for Desired Social
Behavior
Sociocultural Functions of Emotions
What are the intrapersonal functions of emotions?
Emotions Help us Act Quickly with Minimal Conscious Awareness
eating spoiled food
Emotions Prepare the Body for Immediate Action
fight vs flight response
Emotions Influence Thoughts
memories & moral / ethical values
Emotions Motivate Future Behaviors
What is social referencing
seeking out information from others to clarify a situation, thereby using that situation to act — facial expressions as regulators of social interaction.
What are cultural display rules
define the management of expressions according to social circumstances to maintain social order.
Who wrote the science of subjective well being?
Michael Eid & Randy J. Larsen
In Promoting Positive Affect, what are some ways to increase positivity
Practicing Gratitude
Engaging in Physical Activity
Building Strong Social Connections
Cultivating Mindfulness and Savoring
Pursuing Meaningful Goals
How do we practice gratitude
Keeping a gratitude journal or expressing appreciation strengthens positive emotions and social bonds.
Science of Sustainable Happiness

What is Mindfulness
helps us catch our stressful, negative thoughts before they become too strong to manage or regulate.”
What is Decentering
“to be able to look at your mental space and notice with interest and curiosity what thoughts are present”
What is Focus?
“strengthens your ability to bring your mind back to the point of focus so you can respond more appropriately”
What is the broken and built theory?
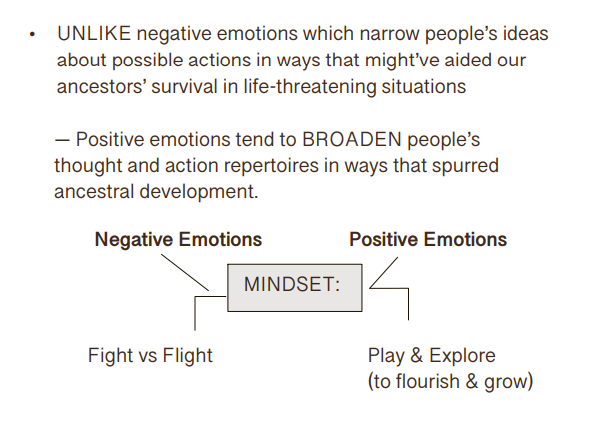
What is Rumination
a mental habit prolonging feelings of sadness &
increasing ones odds of falling prey to depression
Will good intentions alone, make someone happier, if not what may make someone happier?
GOOD INTENTIONS ALONE will not make anyone happier. One must act on it to rouse a feeling of positivity.
Find Positive Meaning
Be Open ( Focus on the “Now” )
Do Good
Be Social