Organic Chemistry Exam #1
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pKa values, functional groups, branched alkanes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Csp3-H pKa
55-60
Csp2-H pKa
45
R2N-H pKa
35
Csp-H pKa
25
HO-H pKa
15.7
RO-H pKa
16
R3N+-H pKa
10
RCOOH pKa
5
HCl pKa
-4
H2SO4 pKa
-5
alcohol
ROH
ether
ROR’
carboxylic acid
RCOOH
ester
RCOOR’
ketone
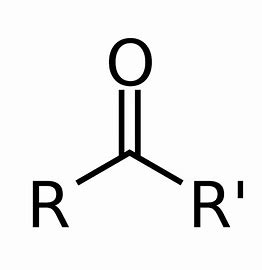
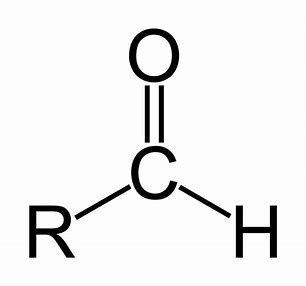
aldehyde
alkylhalide/haloalkane
RX (X=halogen)
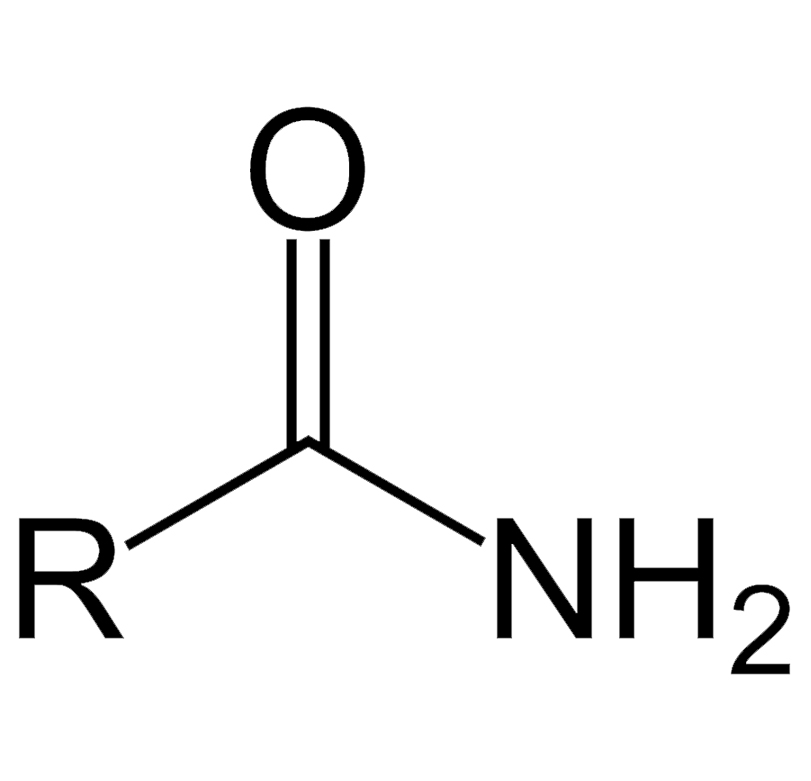
amide
amine
RNR’R’’
alkene
C=C
alkyne
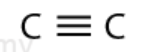
the more stable the base, the _______reactive
less
lower pKa indicates __________ acid
stronger
constitutional isomers
same formula and different connectivity of atoms
F (halogen branch name)
fluoro
Cl (halogen branch name)
chloro
Br (halogen branch name)
bromo
I (halogen branch name)
iodo
Hydrocarbons have _____(IMF)
london dispersion forces
Alcohols have ______(IMF)
hydrogen bonds, london dispersion forces, dipole-dipole
Alkylhalides have _____(IMF)
dipole dipole and london dispersion forces
larger halogen has __________ boiling point
higher
meth-
1
eth-
2
prop-
3
but-
4
pent-
5
hex-
6
hept-
7
oct-
8
non-
9
dec-
10
formal charge=
VE-bonds-lone e-
With resonance, the negative charge is most stabilized when it is on the ____ electronegative atom
most
Do NOT exceed the octet on period ___ elements
2
2 effective electron pairs: EG? hybridization?
linear, sp
3 effective electron pairs: EG? hybridization?
trigonal planar, sp2
4 effective electron pairs: EG? hybridization?
tetrahedral, sp3
Bronsted-Lowry acid
any species that can donate a proton
Bronsted-Lowry base
any species that can accept a proton
conjugate acid
acid that results from protonation of a base
conjugate base
base that results from loss of a proton from an acid
Conjugate base of a strong acid must be a ____ base
weak
A more stable conjugate base=_______acid
stronger
a more electronegative element (inc from left→right on periodic table) gives a _______ acid
stronger
As you go down a column in the periodic table, the size increases which corresponds to a __________ acid
stronger
energy of gauche 60deg methyl-methyl interaction
3.8kJ/mol
energy of methyl eclipsing a methyl
11 kj/mol
energy of a methyl eclipsing a H
6 kj/mol
The most important resonance contributers have the greatest number of ___________
filled octets
The resonance structure with ________ formal charge is more important
fewer
When the pH of the environment is ____ than the pKa of the compound, the environment is considered acidic and the compound will exist predominately in its protonated form
less
Resonance structures with equally good Lewis structures are _______ and contribute ______ to hybrid
equivalent, equally
decalin
two fused rings
Where are arrows drawn with an acid base reaction?
One is drawn from the base and attacking the proton, the second arrow is drawn from the bond and going to the atom connected to the bond
cis 1,2 pattern
axial, equatorial
trans 1,2 pattern
axial, axial or equatorial, equatorial
cis 1,3 pattern
axial axial or equatorial equatorial
1,3 trans pattern
axial equatorial
1,4 cis pattern
axial equatorial
1,4 trans pattern
axial axial or equatorial equatorial