citric acid cycle
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
citrate synthase; acetyl-coA; oxaloacetate
the first reaction of the citric acid cycle is the _________ reaction. the inputs are _______ and ______.
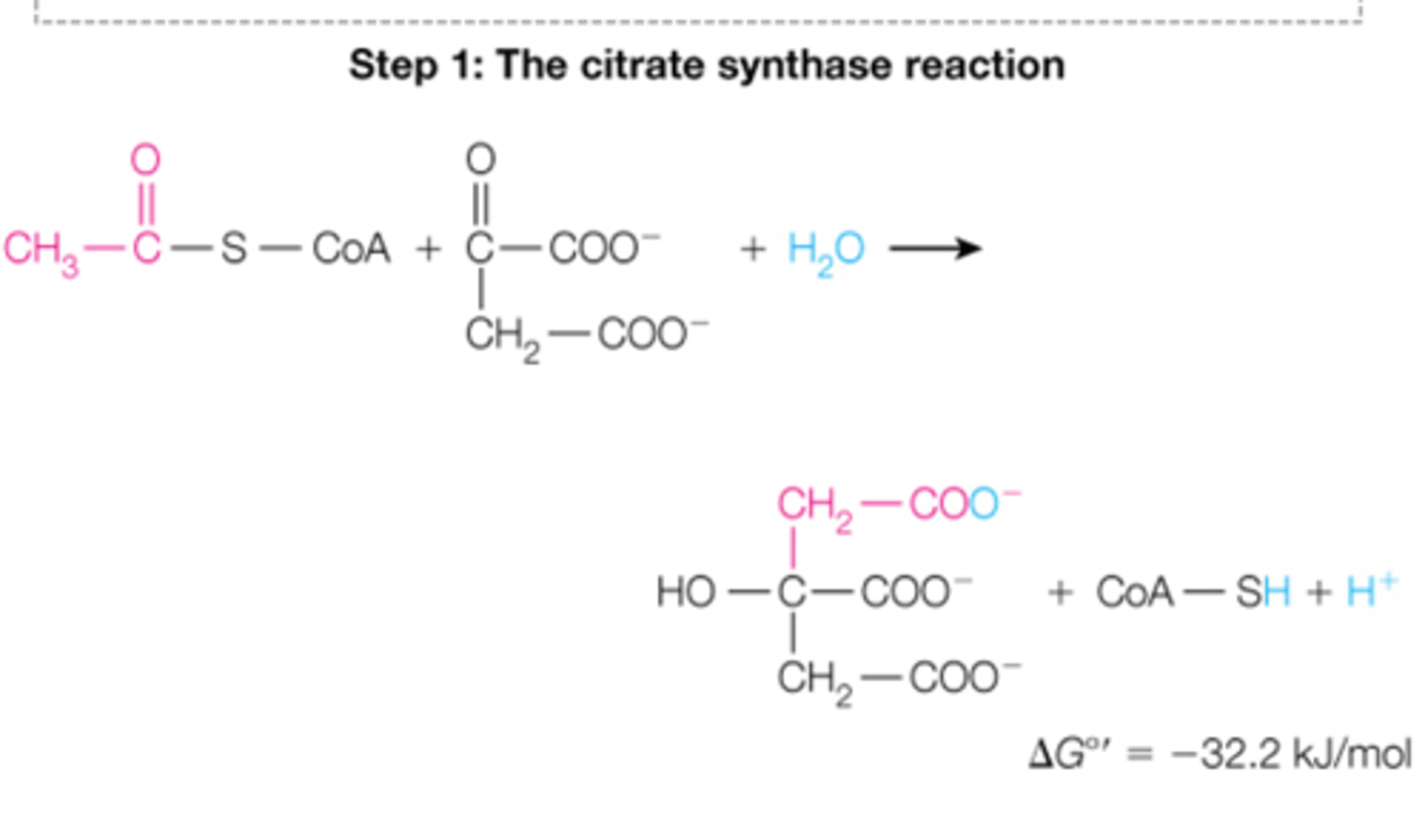
aconitase; citrate; isocitrate; can't have a secondary alcohol for decarboxylation
step 2 is the CAC is called the _______ reaction. which converts _______ to ______. why does this occur?
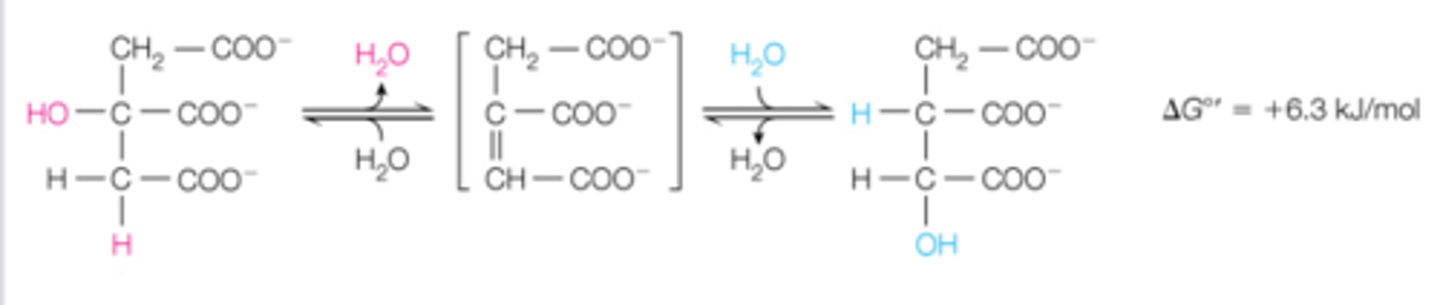
dehydrogenase; decarboxylation; ketoglutarate
the third reaction is when isocitrate undergoes a _______ reaction. Carbon is removed via __________. the end product is ________
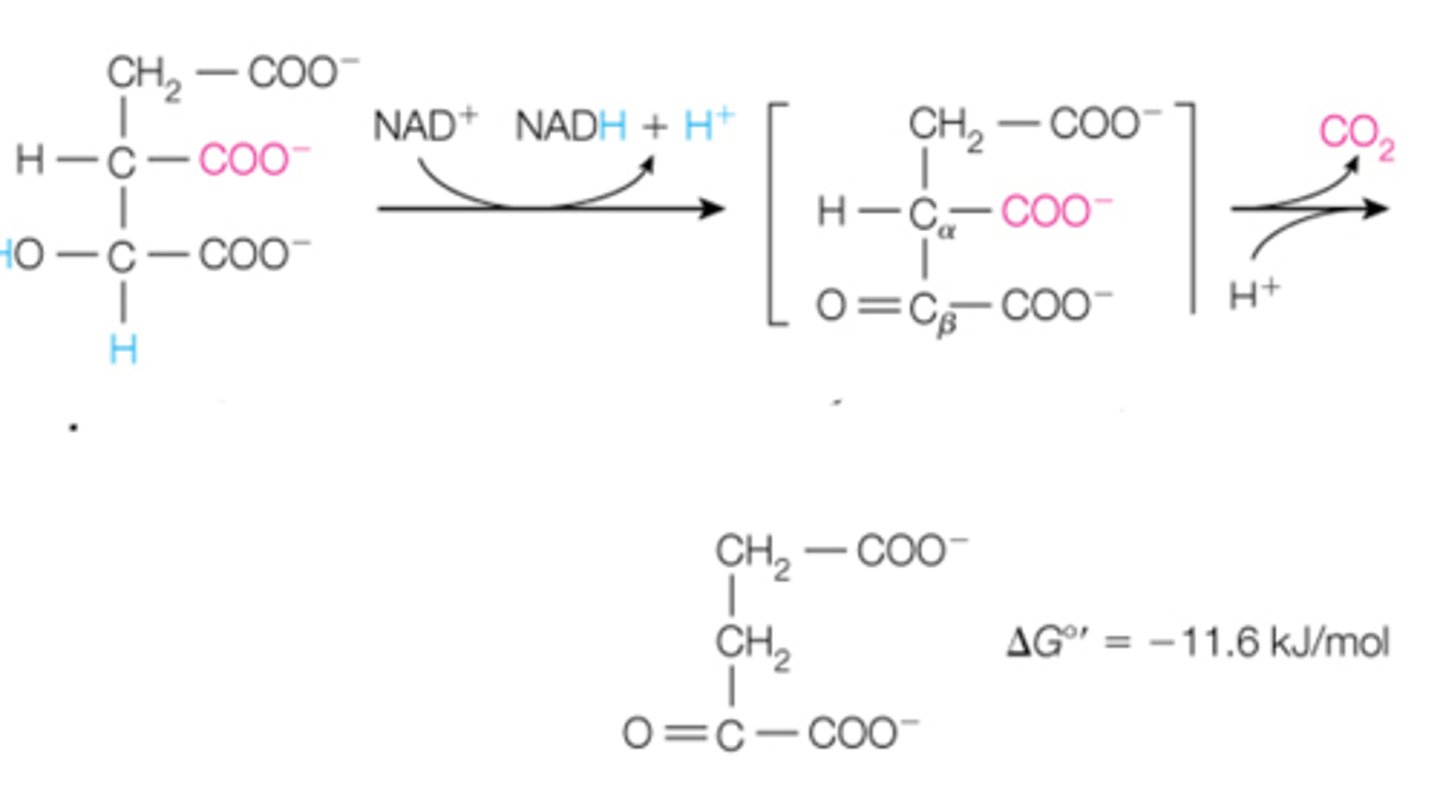
alpha-ketoglutarate; carbon dioxide; CoASH; succinyl-CoA; decarboxylation
step 4 of the CAC is the _______ dehydrogenase reaction. this is when ______ get removed and replaced by _______ to create. what kind of reaction is this?
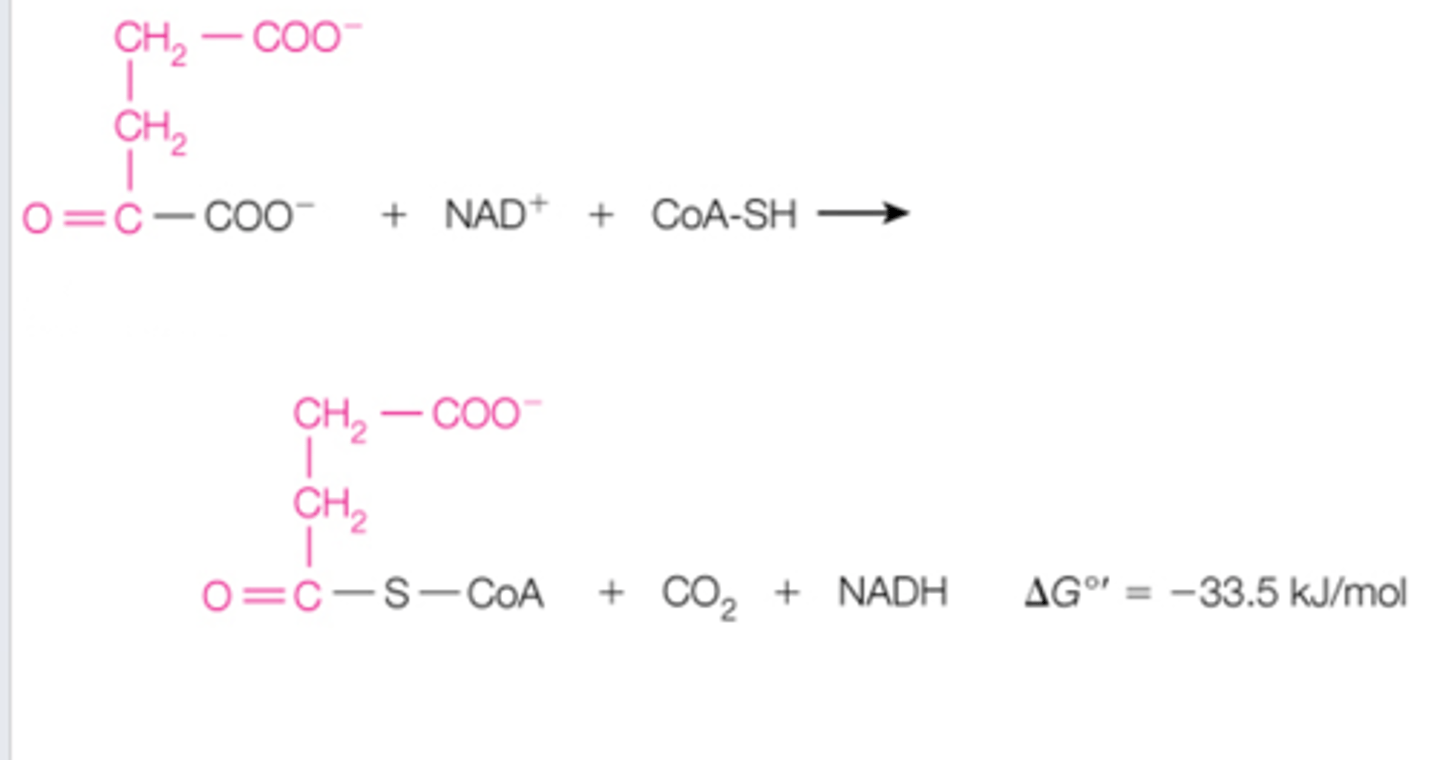
succinyl-CoA synthetase; succinyl-coA; succinate; thioester, substrate-level phosphorylation
step 5 is the ________ reaction, where _____ is converted to _____. the ______ bond drives ATP synthesis via ________.
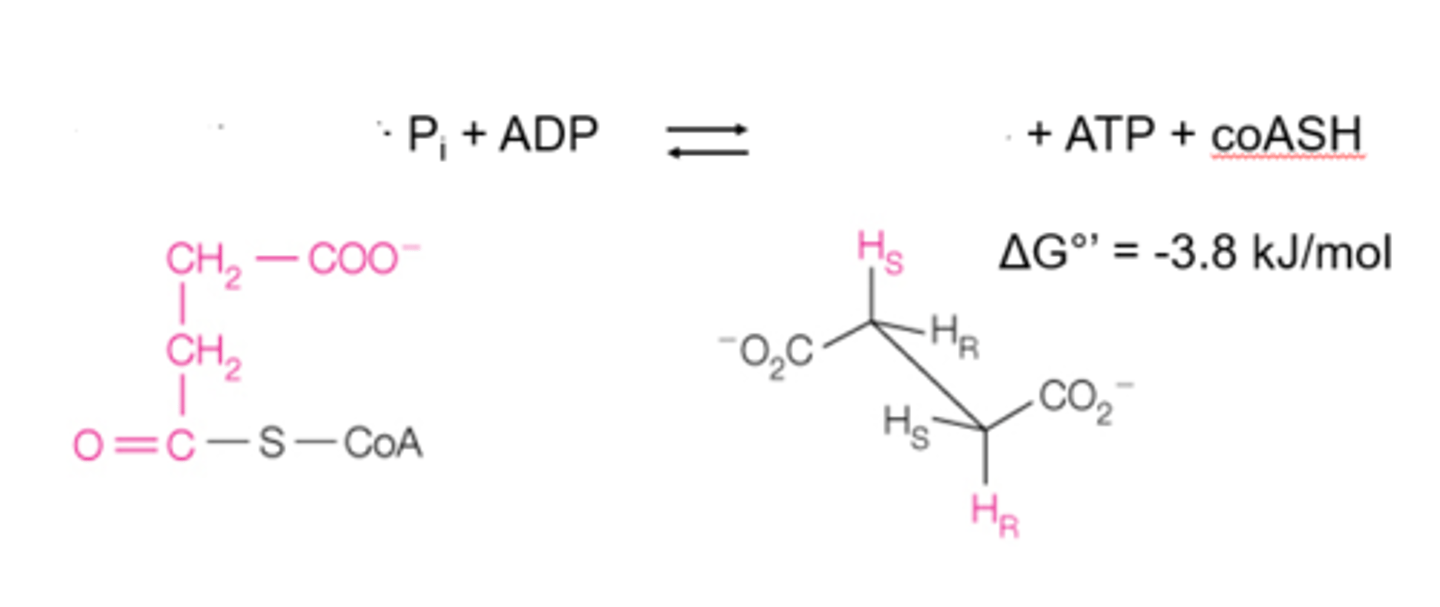
succinate dehydrogenase; succinate; fumarate; FADH2
step 6 is the _______ reaction, where ______ is converted to _______ by using _______ as an electron acceptor.
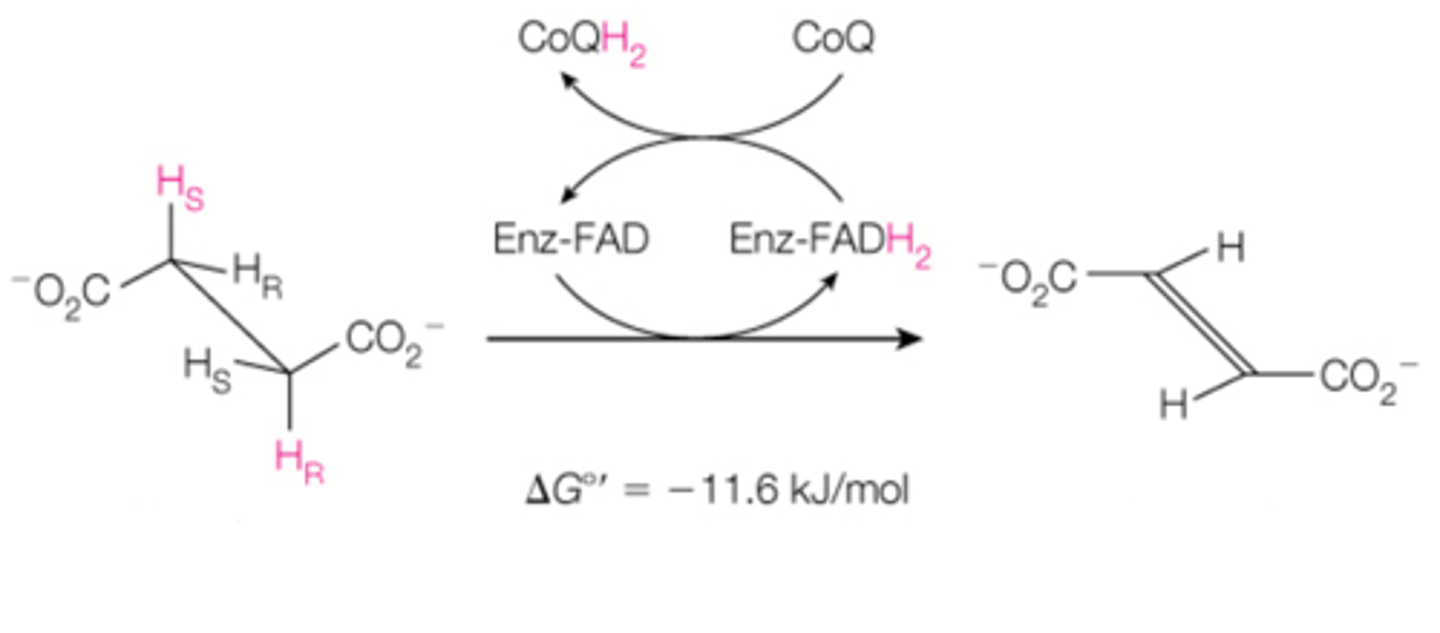
fumarase; fumarate; malate; hydration
step 7 is the _______ reaction. it converts ______ to ______ via a _______ reaction.
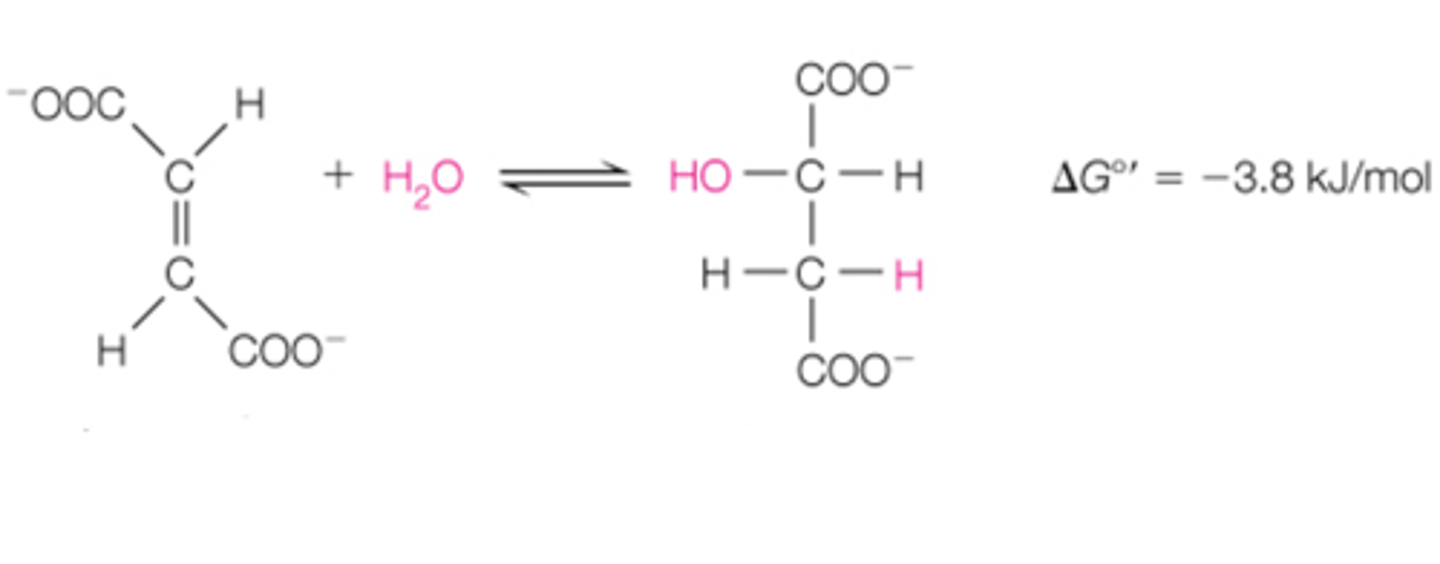
malate dehydrogenase; malate; oxaloacetate; oxaloacetate
the last step in the CAC, step 8 is the _______ reaction. it converts ________ to _______. ______ is put back into the CAC and the cycle will start again.
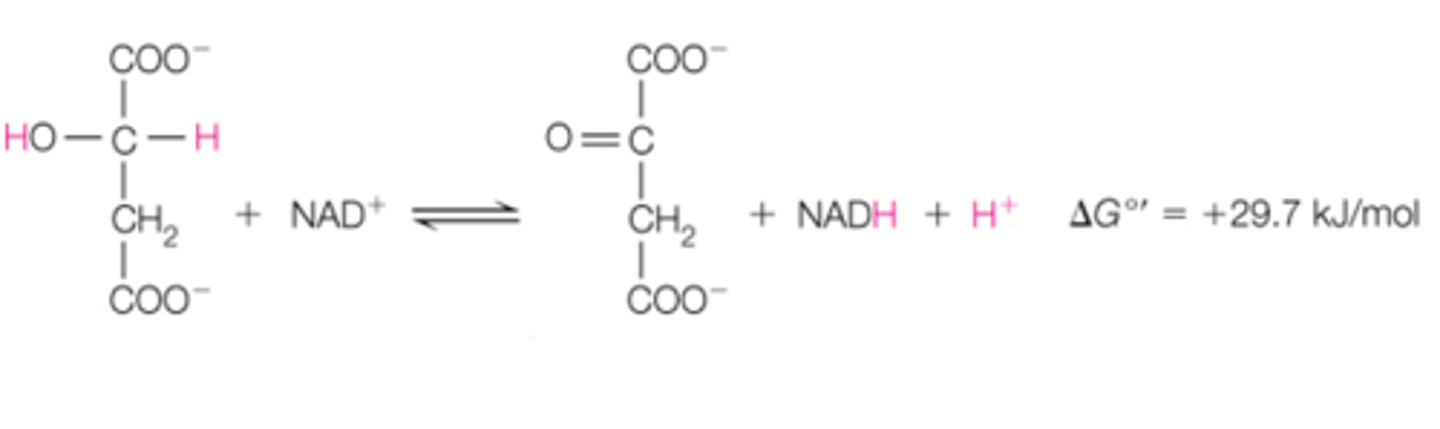
to create oxaloacetate to put back into the cycle
what is the main goal of steps 4-8 of the citric acid cycle?