IGCSE Breathing and Gas Exchange
5.0(1)Studied by 18 people
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:52 AM on 8/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
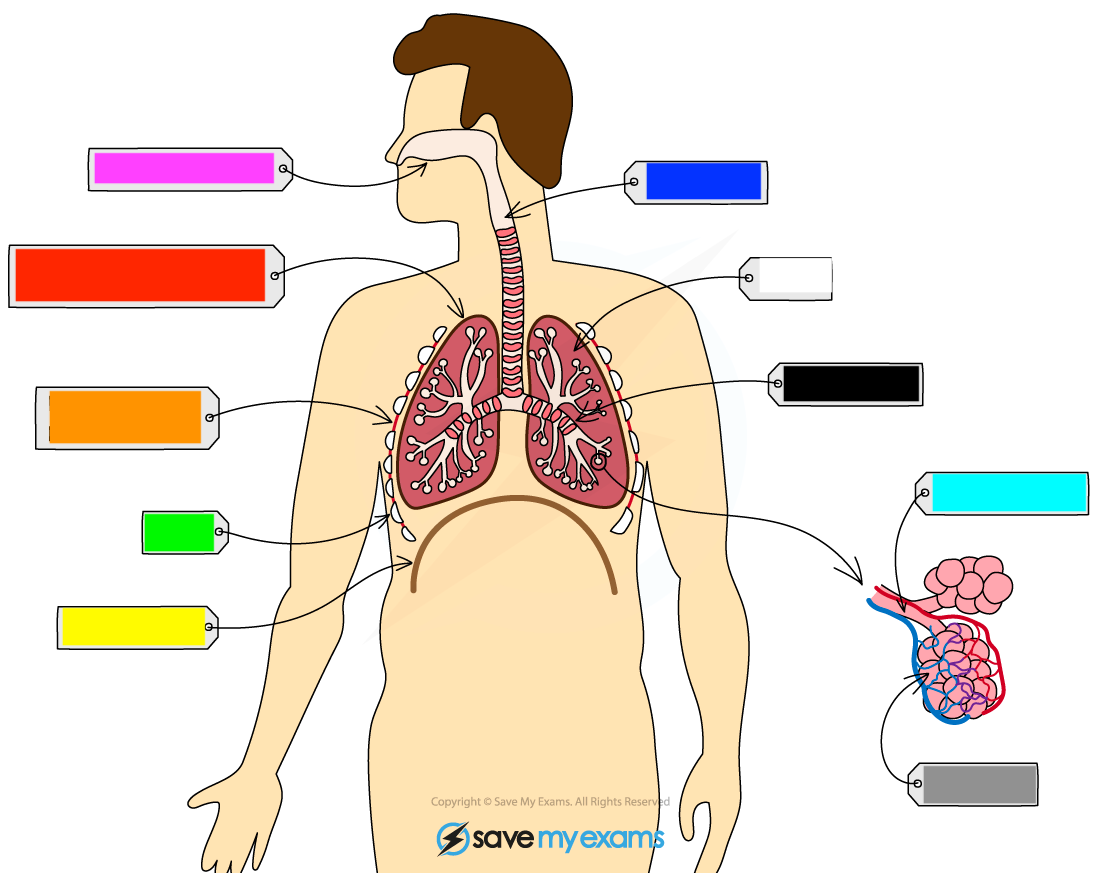
What is the pink?
nasal cavity
2
New cards
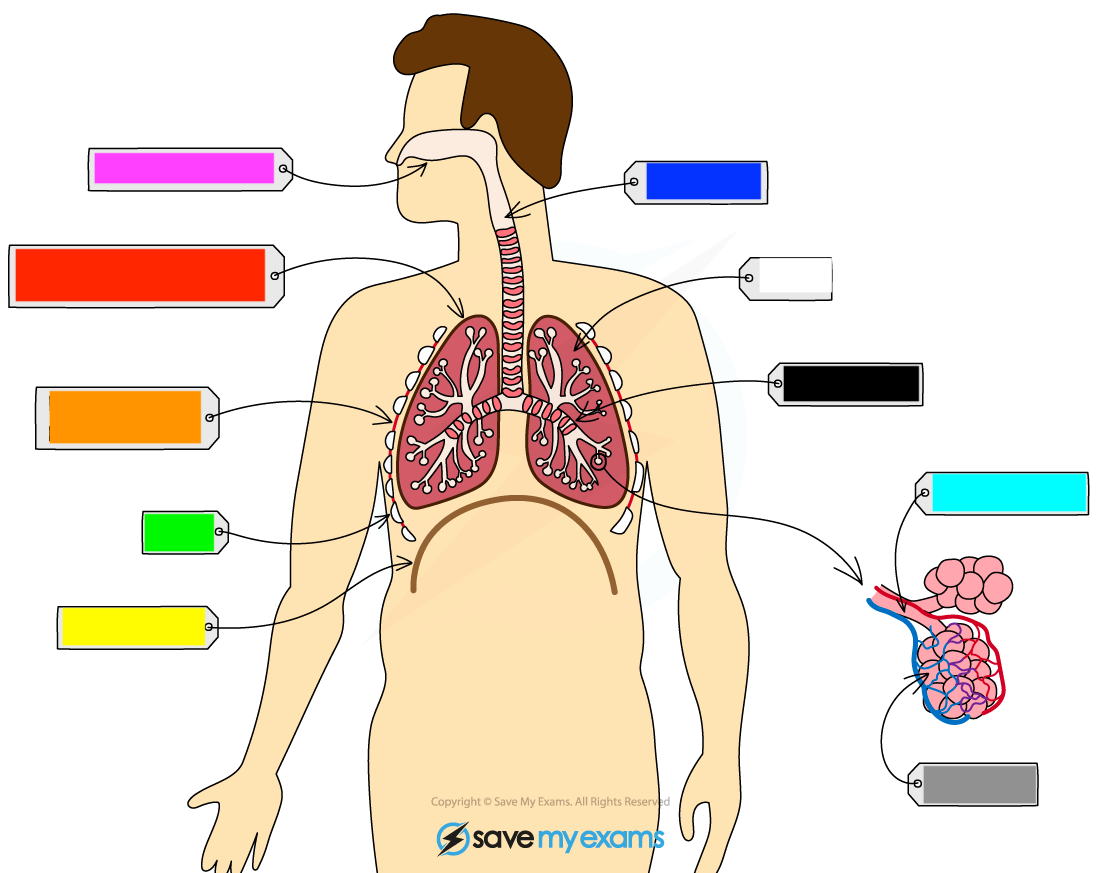
What is the red?
pleural cavity
3
New cards
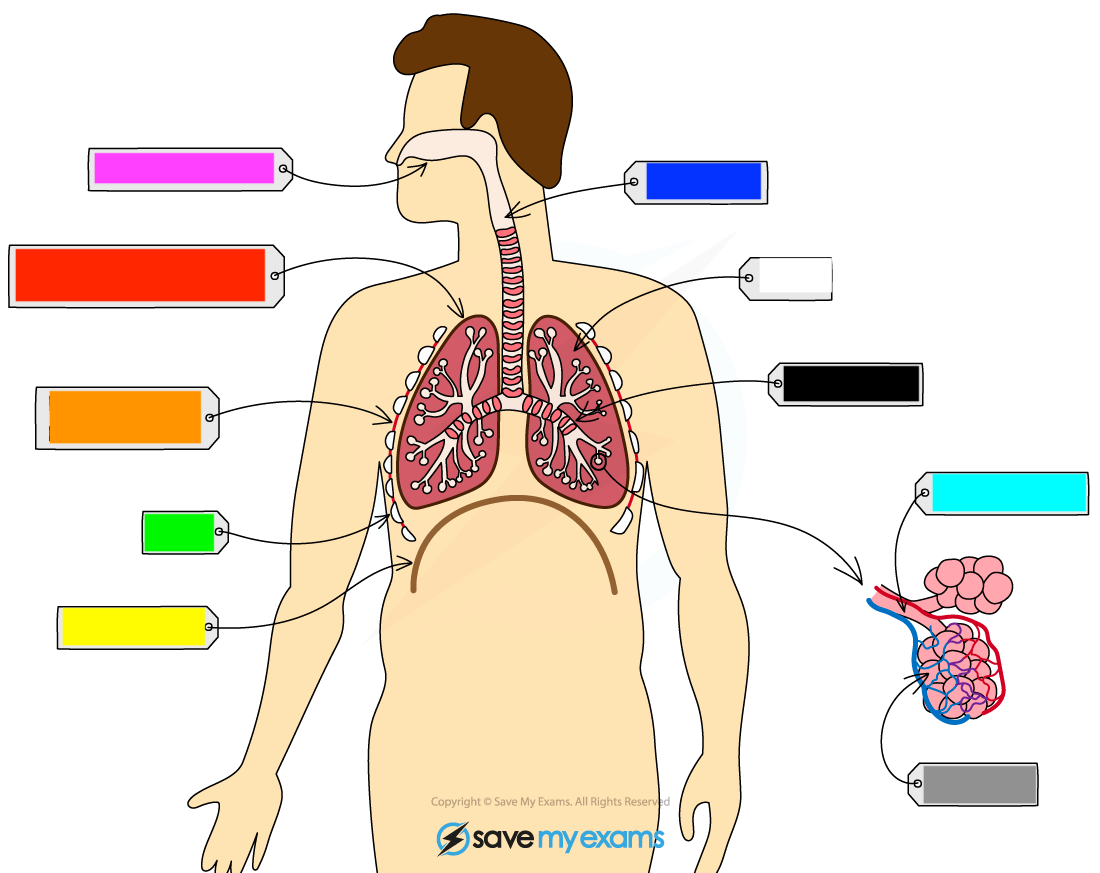
What is the orange?
intercostal muscle
4
New cards
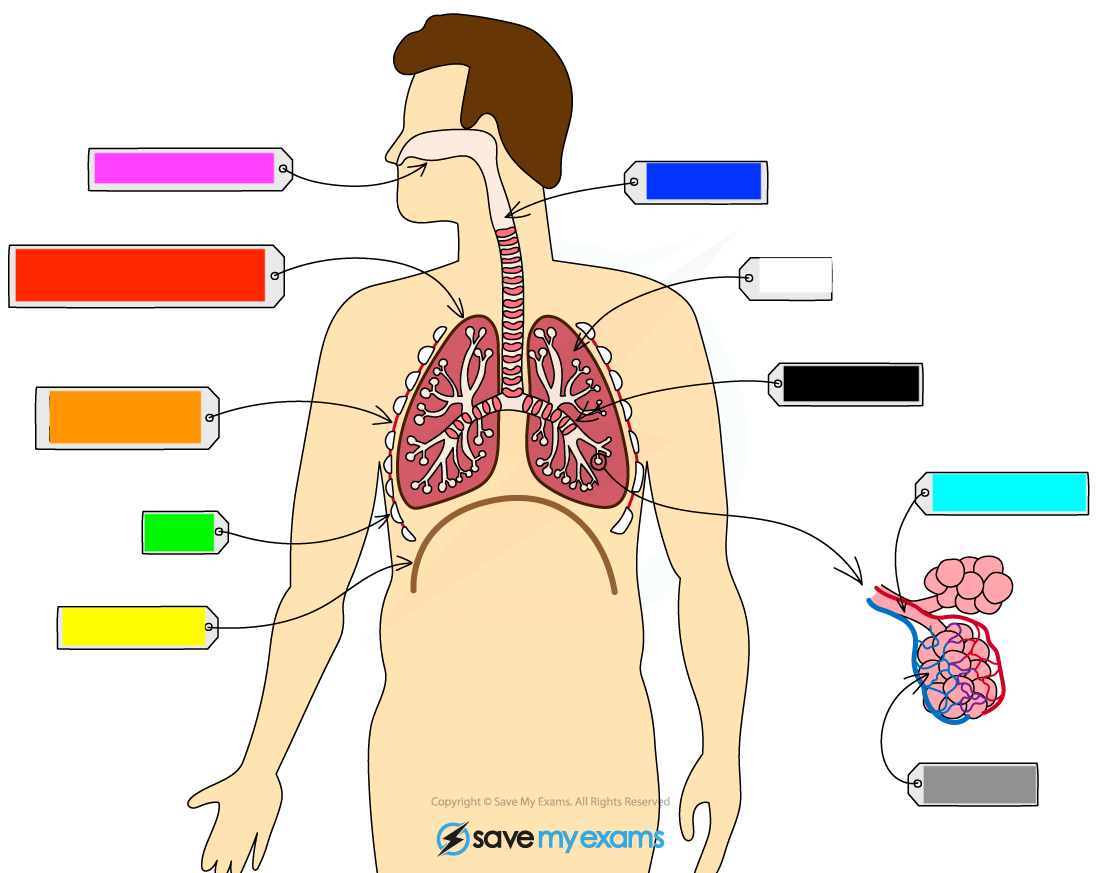
What is the green?
ribs
5
New cards
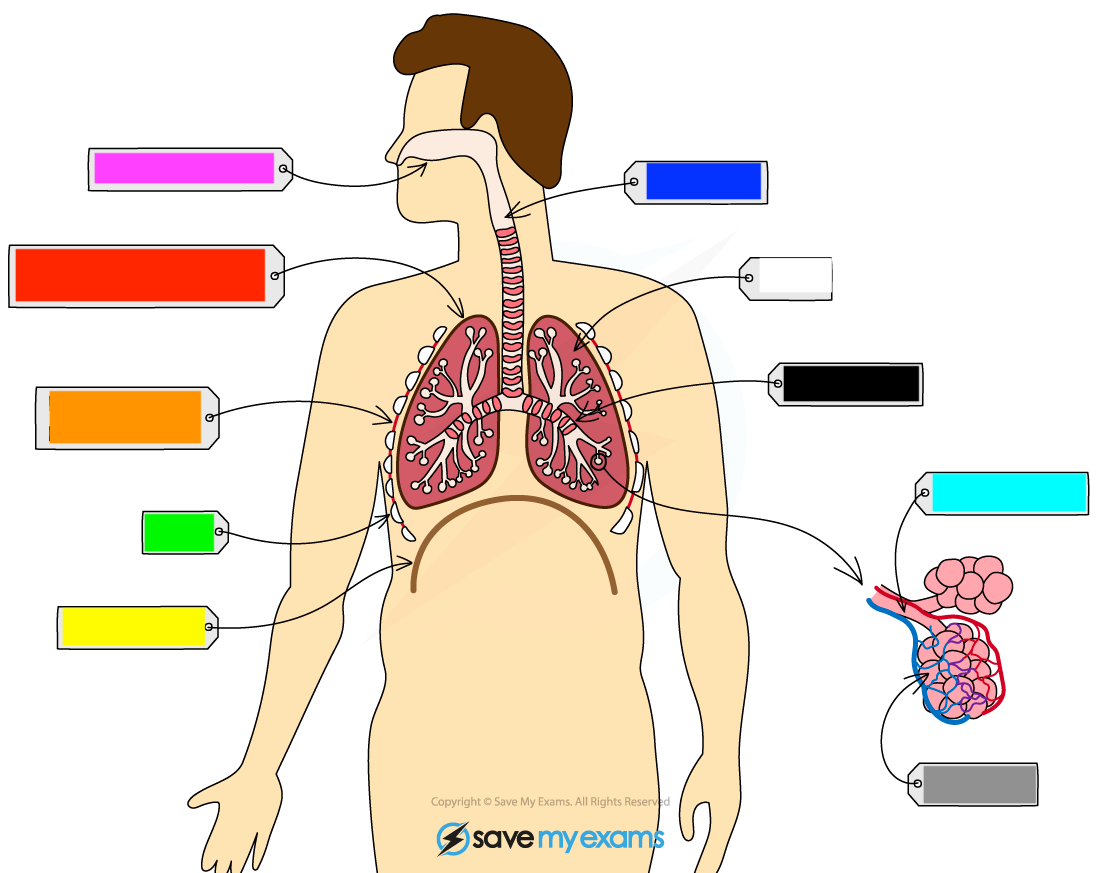
What is the yellow?
diaphragm
6
New cards
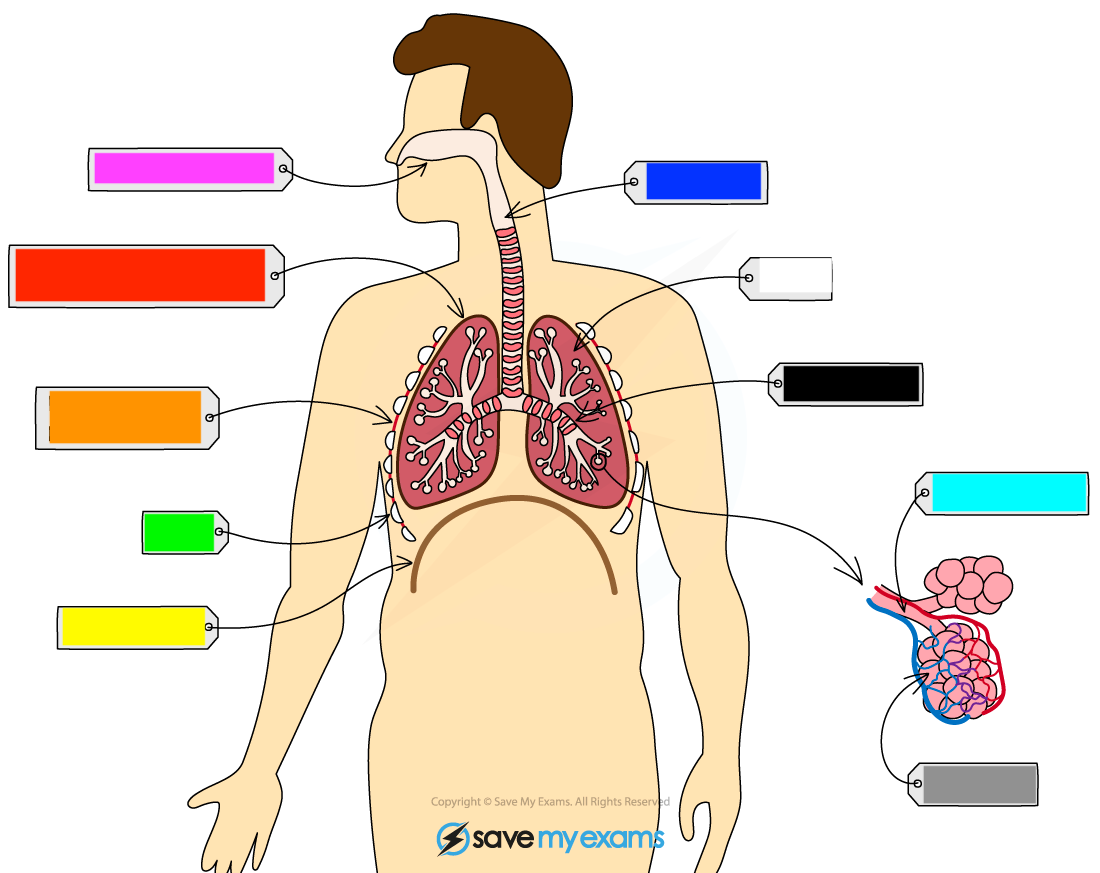
What is the dark blue?
trachea
7
New cards
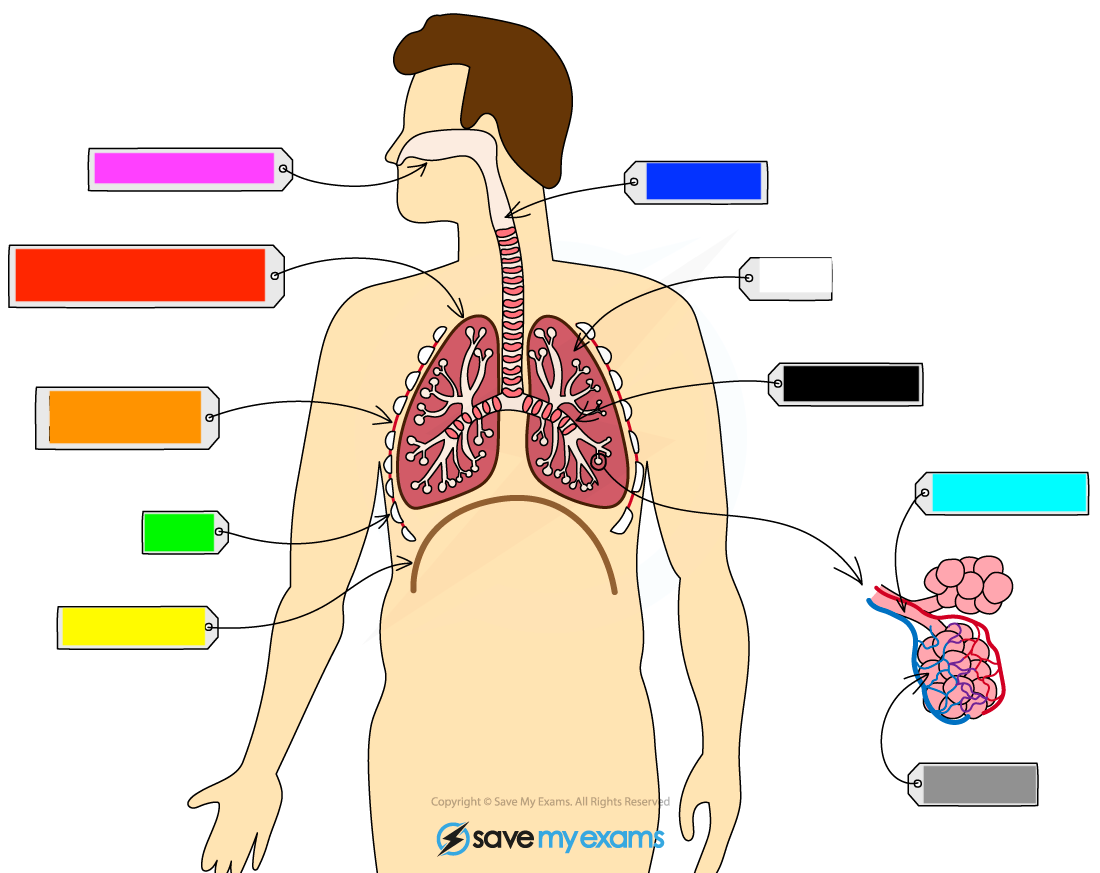
What is the white?
lung
8
New cards
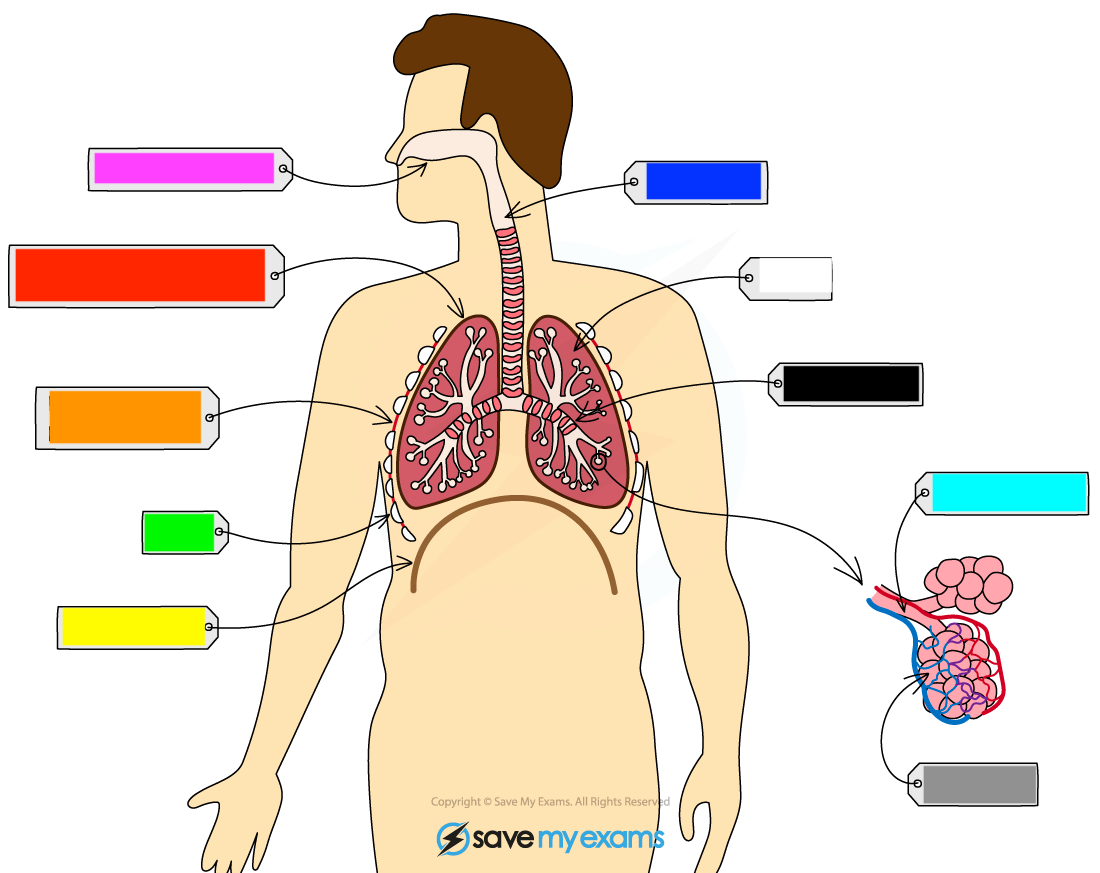
What is the black?
bronchus
9
New cards
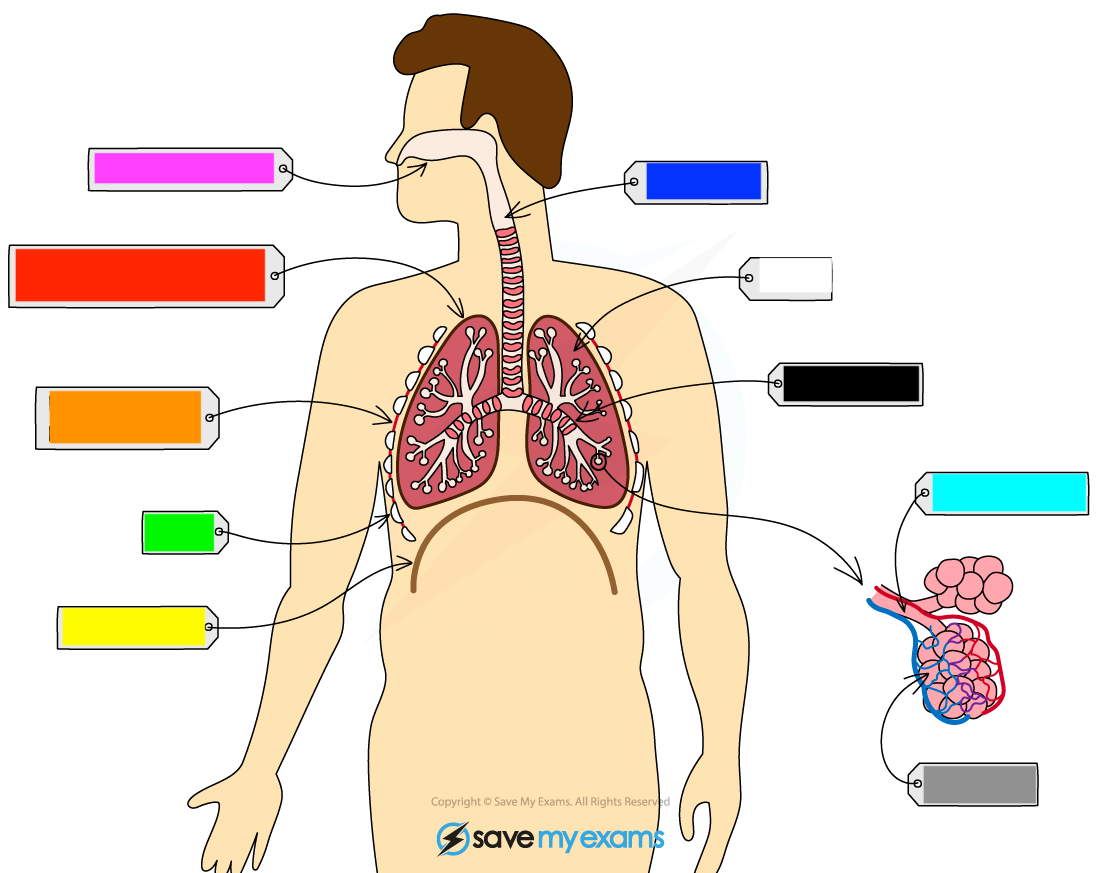
What is the light blue?
bronchiole
10
New cards
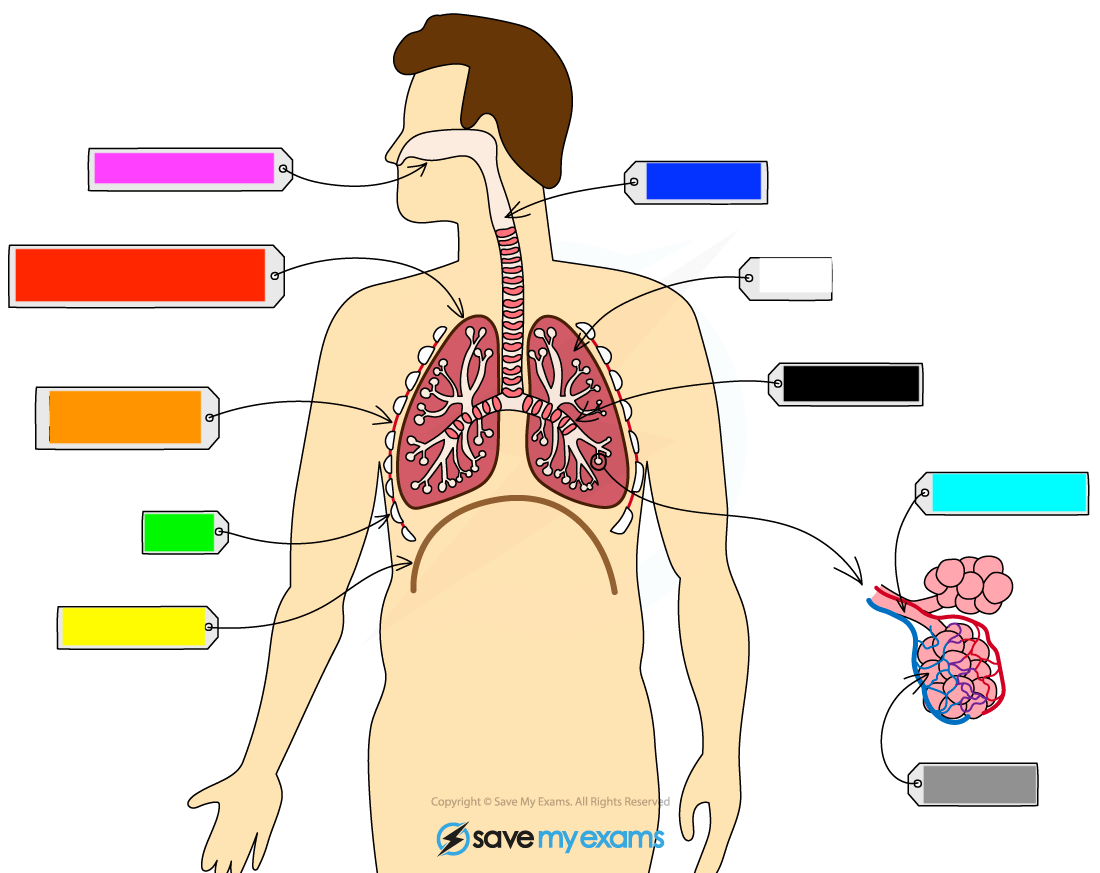
What is the grey?
alveoli
11
New cards
What is the pleural cavity filled with?
fluid
12
New cards
What is the function of cartilage in trachea?
incomplete rings of cartilage for expansion when breathing
13
New cards
What is another name for inhalation?
inspiration
14
New cards
What happens to the intercostal muscles in inspiration?
external intercostals contract to elevate ribs
15
New cards
Which intercostal muscles move in inspiration?
external
16
New cards
What happens to the diaphragm in inspiration?
contracts to expand the thoracic cavity
17
New cards
What happens to the air pressure in the lungs in inspiration?
decreases
18
New cards
What happens to lung volume in inspiration?
increases
19
New cards
What is another name for exhalation?
expiration
20
New cards
what happens to the intercostal muscles in expiration?
internal intercostals contract to pull ribs down
21
New cards
Which intercostal muscles are involved in expiration?
internal
22
New cards
What happens to the diaphragm in expiration?
relaxes to reduce thoracic activity
23
New cards
What happens to the air pressure in the lungs in expiration?
increases
24
New cards
What happens to lung volume in expiration?
decreases
25
New cards
Does inhaled or exhaled air have more oxygen content?
inhaled (20-16)
26
New cards
Does inhaled or exhaled air have more carbon dioxide content?
exhaled (0.04-4)
27
New cards
Does inhaled or exhaled air have more nitrogen content?
same
28
New cards
What are the adaptions of an alveolus?
large surface area, moist lining, thin walls, good blood supply
29
New cards
How thin is a wall of an alveolus?
one cell thick
30
New cards
What is the test for carbon dioxide?
limewater
31
New cards
How does physical activity affect breathing?
increases rate and depth
32
New cards
What are three uses of energy in humans?
muscle contraction, growth, cell division
33
New cards
What is respiration?
chemical reactions that break down nutrients molecules in living cells to produce energy
34
New cards
Is respiration endothermic or exothermic?
exothermic
35
New cards
What does respiration involve?
the action of enzymes in cells
36
New cards
How much energy does aerobic respiration produce?
38 ATP
37
New cards
What is aerobic respiration?
using oxygen to break down nutrients for energy
38
New cards
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
mitochondria
39
New cards
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide and water
40
New cards
What is the chemical formula for aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
41
New cards
How much energy does anaerobic respiration produce?
2 ATP
42
New cards
What is anaerobic respiration?
a reaction in cells that breaks down nutrients without using oxygen
43
New cards
What is the word formula for anaerobic respiration in humans?
glucose = lactic acid + energy
44
New cards
What is the word formula for anaerobic respiration in plants?
glucose = ethanol + CO2
45
New cards
What is the chemical formula for anaerobic respiration in plants?
C6H12O6 = 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
46
New cards
What is another name for anaerobic respiration in plants?
fermentation
47
New cards
Where are two situations that fermentation occurs?
yeast and for wine
48
New cards
Why does anaerobic respiration occur?
if not enough oxygen is reaching muscle, it is an incomplete breakdown of glucose
49
New cards
Why does breathing rate and death increase while exercising?
to supply more oxygen to muscles
50
New cards
Why does heart rate increase when exercising?
it allows oxygen and glucose to reach muscles faster
51
New cards
Why does your body temperature increase when exercising?
respiration is happening faster which causes heat because energy is being created
52
New cards
Why do glycogen stores decrease when exercising?
stored glucose is used for respiration
53
New cards
Why do blood vessels widen during exercise?
more blood to flow to respiring tissues and skin to cool you down
54
New cards
What causes oxygen debt?
lactic acid building up in the muscles and blood during exercise
55
New cards
What is the recovery period?
when oxygen becomes available again after anaerobic exercise you respire aerobically to remove lactic acid
56
New cards
How does aerobic exercise remove lactic acid?
reacting lactic acid with oxygen to provide CO2 and H2O
57
New cards
What is the oxygen debt?
the amount of oxygen needed to completely break down lactic acid