Lecture 5 - Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What process do myoglobin and hemoglobin play a part in?
Oxygen transport and storage
Why do we need myo and hemoglobin?
O2 has limited solubility in water
O2 oxidizes and creates free radicals = toxic to us
Though Fe2+ binds O2, it is not soluble either
Heme allows Fe2+ to bind O2 without the negatives
Myoglobin primary function
Store oxygen in muscles, and when O2 level is high
Hemoglobin primary function
Transport oxygen from lungs to tissues
Can bind in lung when oxygen is high
Can release in tissues when oxygen is low
Where is myoglobin found?
Muscles/tissues
Where is hemoglobin found?
Lungs or tissues; erythrocytes (RBCs)
Myoglobin structure
Globular protein with 8 a-helices connected by loops
A Helix, B Helix connected at AB corner
Amphipathic helices
Helices with both non-polar and polar faces (facing inside and outside respectively)
Prosthetic Group
Non-protein group that binds to protein and is required for function
What type of group is Heme?
Prosthetic group; it is required in myoglobin and hemoglobin for function
What role does Heme play?
Solubilize Fe
Prevent Fe2+ oxidation by O2
Heme structure
4 nitrogens in a porphyrin ring, coordinated to an iron atom
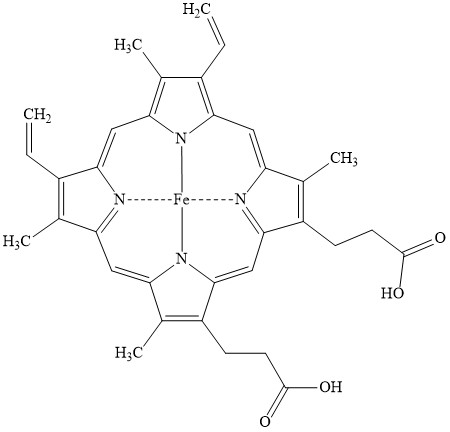
How many bonds can Fe form?
Six bonds (4 with nitrogen, 1 with proximal Histidine, 1 with O)
Proximal Histidine
Histidine that binds directly to Fe in Heme
Distal Histidine
Hydrogen bonds with oxygen
What happens to Heme upon oxygenation?
It flattens; conformation change
Deoxy-Mb
5 Fe ligands (bonds); 4 from Heme and 1 from protein (proximal Histidine)
Oxy-Mb
Oxygen is the 6th ligand to iron
What is Q?
Fractional saturation with oxygen (.75 = 75%)
P(O2)
Concentration of oxygen measured by pressure
P50
O2 needed to saturate myoglobin/hemoglobin 50%
Why does myoglobin bind O2 effectively?
It has a high affinity; doesn’t let go easily though
Unique property of histidine
It can bind metals like Fe
Mb and Hb are…
Homologous proteins (share properties due to shared sequences)
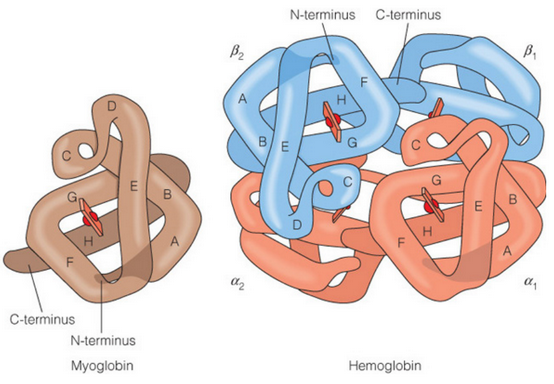
How many hemes does hemoglobin have?
4 (compared to 1 in myoglobin)
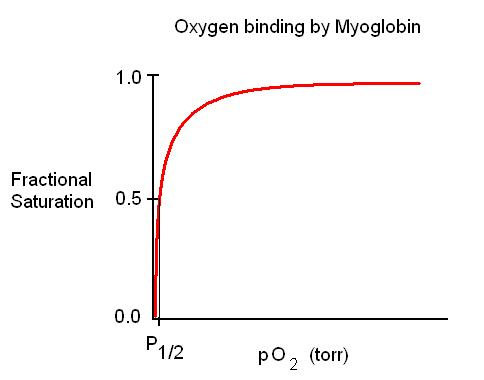
Expected curve for myoglobin
Hyperbolic (efficient at binding, inefficient at release)
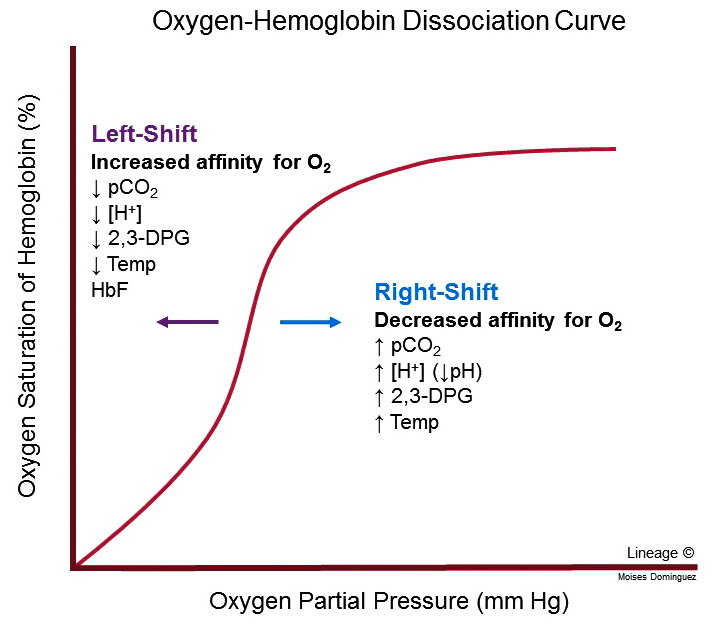
Expect curve for hemoglobin
Sigmoidal (cooperative binding; good at binding and release)
Cooperative Binding
Change in protein’s affinity for ligan as a function of ligand concentration
What makes hemoglobin good at transport?
It can transition from high to low affinity (cooperative binding)
Cooperativity is also known as…
Allostery
Requirements for cooperativity
Multiple, connected binding sites
Communication between sites
Quaternary structure (usually)
Hill plot
Graph that allows us to analyze cooperativity (index - nH - of cooperativity)
Slope of 1 on Hill Plot means…
No cooperativity
Increasing number of binding sites…
Increases index of cooperativity
If nH > 1…
Positive cooperativity
If nH < 1…
Negative cooperativity
Positive cooperativity
Binding of one ligand increases the likelihood of binding to another (Hemoglobin)
Negative cooperativity
Binding of one ligand decreases likelihood of another binding
Important of Hemoglobin’s Allostery
Allows to bind weakly to O2 when oxygen is low
Allows to bind strongly to O2 when oxygen is high
Unique Structure of Hemoglobin
Dimer of 2 Dimers
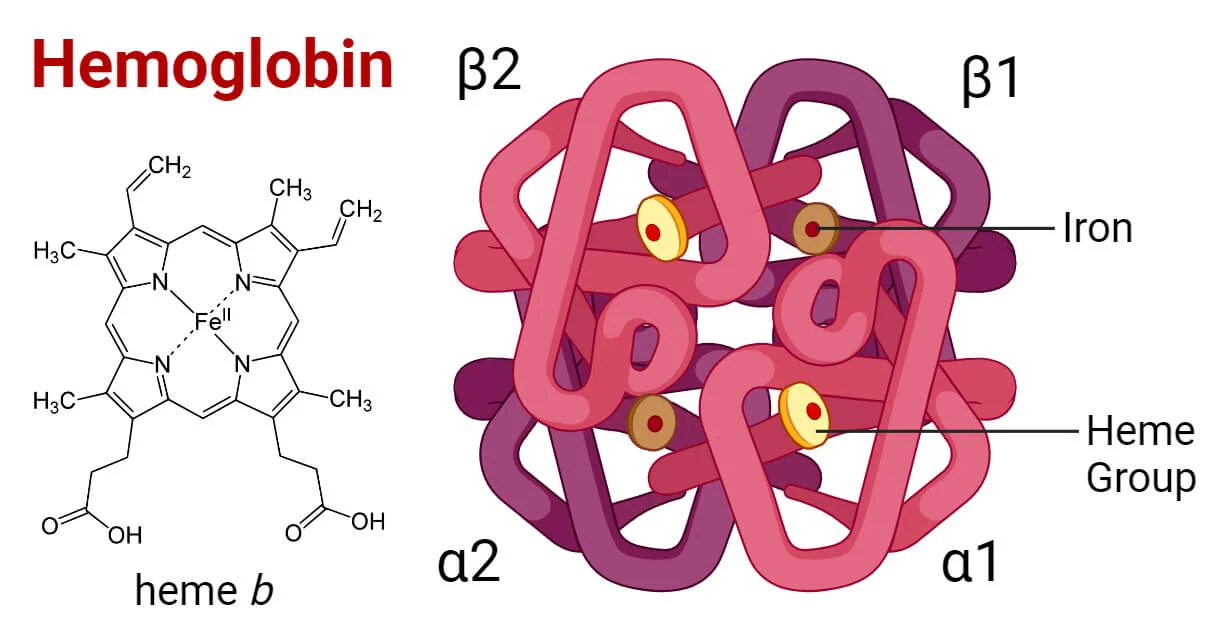
a1 to a2 and b1 to b2
Few contacts of polar salt bridges (weakest)
a1 to b1 and a2 to b2 (vertical)
VERY strong due to many contacts = not easily altered
a1 to b2 and a2 to b1
Fairly strong but can be altered