PT7130: Comprehensive Review of Liver and Gallbladder Anatomy and Functions
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Cholesterol; clotting factors; toxins; glucose; ammonia; bile; immune
Functions of Liver:
- Synthesis of fats, proteins (albumin), ________________________
- Produces _________________________
- Metabolizes nutrients from food, _______________________, medications
- Stores ______________________, vitamins, and minerals
- Converts ________________________ to urea
- Makes ______________________ for fat digestion
- ________________________ function
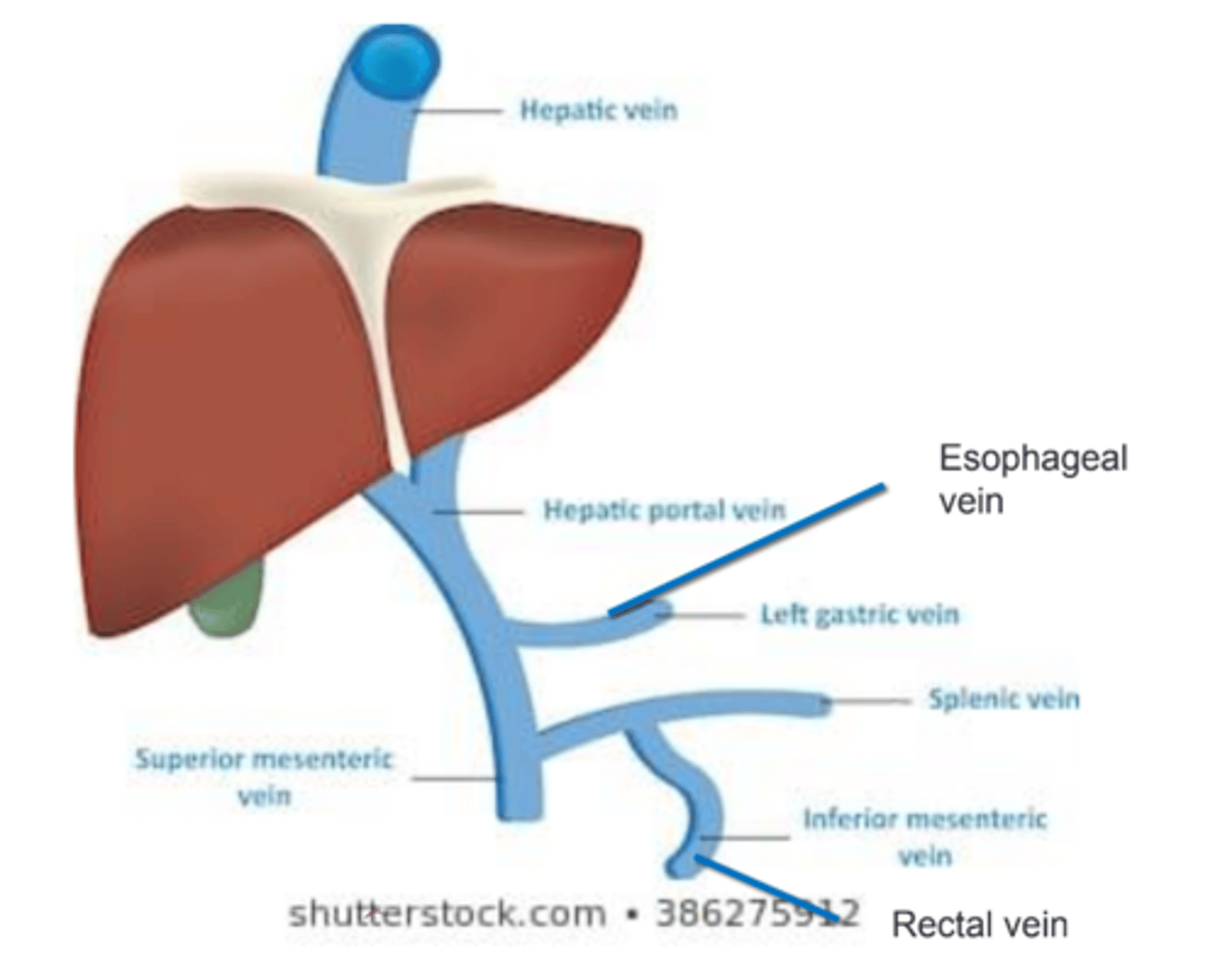
Portal vein
Drains venous blood from the intestine, pancreas, and spleen and transports it to the liver for filtration. → Blood flow could go either way depending on pressure gradient.
Valveless
Portal vein is ________________________.
Portal HTN
Defined as pressure in the portal vein >10 mmHg.
Liver damage
What is major cause of portal HTN?
Varicosing and hemorrhaging
Uncontrolled portal HTN can lead to ___________________________.
- Rectal vein → rectal bleeding
- Esophageal varices → esophageal bleeding
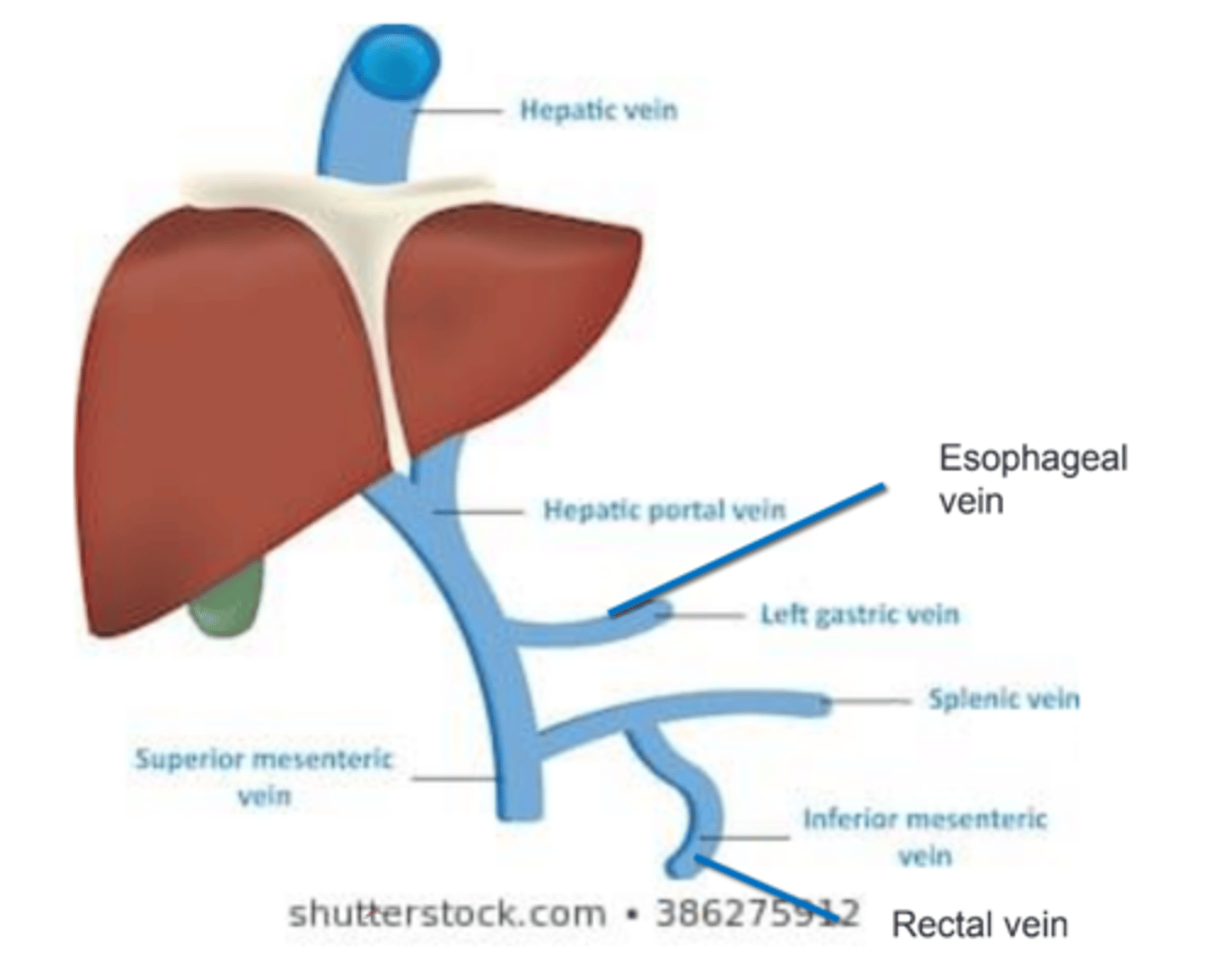
Valsalva maneuver; stool; cough secretions
_________________________ and anything that leads to ↑ intra-abdominal pressure can lead to backflow of blood into esophageal and rectal vv. in presence of portal HTN. → Blood in _______________________ and _______________________.
Fulminant liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma
What are non-cirrhotic types of liver dysfunction?
Fulminant liver failure
Hepatic insufficiency in the absence of chronic liver disease.
CMV; mononucleosis; acetaminophen; poisonous plant; thrombosis
Causes of Fulminant Liver Failure:
- Acute viral infection: Hepatitis A, B, _______________________, Epstein-Barr virus, ________________________
- Drug overdose: _________________________
- ___________________________
- ___________________________
Pain; appetite; dark; ammonia; liver enzymes
Signs and Symptoms of Fulminant Liver Failure:
- GI symptoms: Abdominal ____________________, N+V, poor _____________________, _____________________ urine
- SIRS
- ↑ _______________________ and ______________________ via lab values
Hepatic encephalopathy
Progression of fulminant liver failure can be rapid and lead to _________________________.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Non-cirrhotic liver cancer.
Cirrhosis
Chronic and progressive disease where liver cells are damaged, fibrosis development → increases resistance to blood flow.
Alcohol; viral; autoimmune
Causes of Cirrhosis:
- _____________________ (#1 in US)
- ______________________ (Hep B, C)
- _______________________
Asymptomatic
Early in cirrhosis, patient may be _______________________. Chronic alcohol use requires ~10 years.
Jaundice; loss; weakness; ascites; AMS
Signs and Symptoms of Late/Advanced Cirrhosis:
- _____________________
- Weight ____________________
- Malaise
- _____________________
- _____________________
- _____________________ (encephalopathy)
Protein; capillary
Ascites:
Liver failure leads to ↑ _____________________ in interstitium d/t imbalance, ↑ water pulled into interstitium from ______________________.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
When cirrhosis is caused by chronic alcoholism, there is risk of development of ___________________________ (delirium tremens "DTs").
GABA; glutamate; hallucinations
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (Delirium Tremens):
- Alcohol is depressant → long-term ________________________ production
- Body compensated by creating ______________________.
- If the individual stops drinking alcohol glutamate > GABA.
- Can lead to ________________________ and AMS.
CIWA scale
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome is commonly mild, but if severe, the individual is hospitalized and ______________________ scale is used to monitor and determine level of treatment.
Prolonged; ↑; thrombocytopenia; ↓
Labs /c Cirrhosis:
- ________________________ PT time
- _________________________ INR
- _________________________ d/t splenomegarly secondary to portal HTN
- _________________________ albumin
Sedative effects
Patients /c cirrhosis have ↑ sensitivity to medications, especially those /c ________________________ (i.e., narcotics and benzodiazepines). → Do not metabolize as quickly!
Clotting factors and platelets
Patients /c cirrhosis have a high bleeding risk d/t ↓ ________________________.
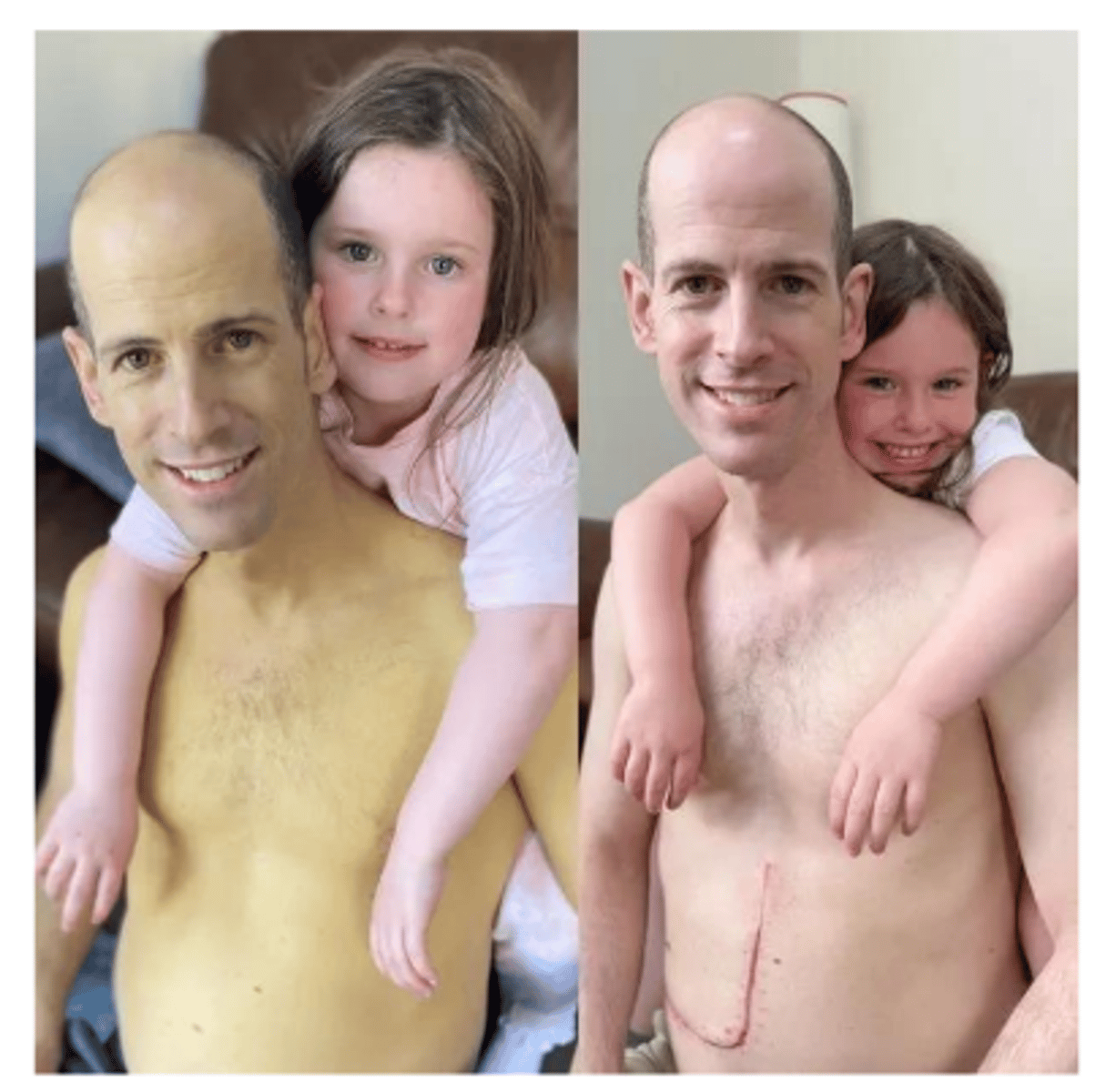
Jaundice
What symptom of liver failure does patient in image demonstrate?
Hepatic encephalopathy
Reversible, but common complication of cirrhosis.
Ammonia
Hepatic Encephalopathy:
Liver cannot clear ________________________, excess build up and toxic to brain. Monitor levels.
15-45 u/dL
What is normal value for ammonia?
AMS; sleep cycles; amnesia; ataxia; hyperreflexia
Signs and Symptoms of Hepatic Encephalopathy:
- Confusion
- _________________________
- Altered _______________________
- Poor memory and concentration
- Lethargy
- Fall risk
- ________________________
- ________________________
- Reflexes: _________________________
- ↑ in muscle activity
Coma, seizure, death
Severe cases of hepatic encephalopathy can lead to _______________________.
Esophageal varices
___________________________ is a threatening complication of cirrhosis d/t low platelets.
Asterixis
Wrist flexion/extension tremor /c passive wrist extension while elbow is in extension; also called flapping tremor or liver flap; indicative of hepatic encephalopathy.
Liver enzymes
Used to assess liver function.
Elevated
________________________ levels of liver enzymes are early indicators of liver injury.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
What are enzymes present in liver cells?
Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score
Score assess risk of death while on liver transplant list.
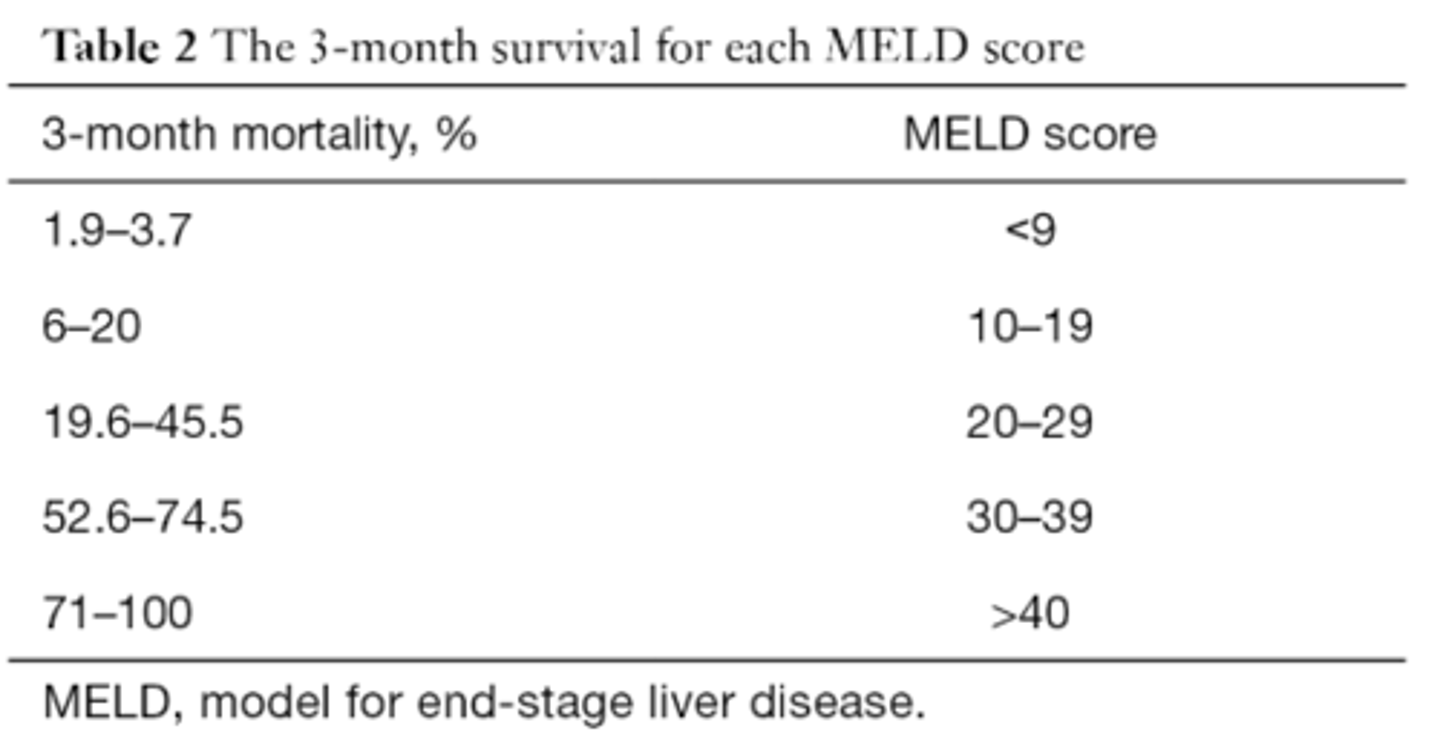
Shorter; higher
Higher MELD = ______________________ life expectancy = _______________________ on transplant list
Kidney; clotting factor; bilirubin
MELD Score is based on ______________________ function, ______________________ levels, and _________________________ levels.
Once a week
If MELD Score is >25, how often is it re-checked?
Once a year
If MELD Score is <9, how often is it re-checked?
Orthotopic
Diseased liver removed, donor liver replaced.
Living donor
Single lobe of living donor donated, regrowth.
Split liver
1/2 liver to adult, 1/2 liver to child.
Domino liver
Diseased liver (familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy) goes to new recipient, donot liver goes to FAP recipient.
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP)
Metabolic liver defect with fibroids deposited in intestine, heart, nerves, kidney.
40-60 years
FAP liver will still cause fibroids to deposit but will take _______________________ to manifest. → May live a full, health life /c no liver issues till mid-60s when fibroids start to develop.
Glycogen; osteoporosis; ascites; weakness; fatigue
Liver Transplant - Premorbid Condition:
- Deconditioned, malnourished /c loss of muscle d/t breakdown of muscle protein and fat
- ↓ ability to store glucose as _________________________
- Failure to absorb vitamin D → ________________________ → susceptible to fx
- Anasarca and/or ________________________ lead to weight gain → Balance issues d/t new COM location.
- Extreme _______________________ and _______________________
Check prior to PT session; log roll
Liver Transplant - Post-Op Considerations:
- Lots of JP drains! → ___________________________
- Very painful
- Abdominal precautions → ________________________ for bed mobility
Reverse isolation; postural hypotension; ascites; biliary T tube; PNA and atelectasis; abdominal
Liver Transplant - Post-Op Considerations:
- Isolation precautions to reduce risk of infection → _______________________
- Common to need many units of PRBC's, platelets, and plasma during surgery → Hypotensive events, ________________________
- May still have _________________________ and lots of pain d/t abdominal drains and sutures: Increased abdominal girth and LE edema → Balance and COM
- Caution JP drain and ________________________
- Deep breathing exercise → Large risk of ________________________, limited chest expansion d/t pain, ineffective cough
- _______________________ precautions
Log rolling for bed mobility, <20 lbs lifting restriction for 6 weeks
What are abdominal precautions?
Positive; surgical healing; monitoring
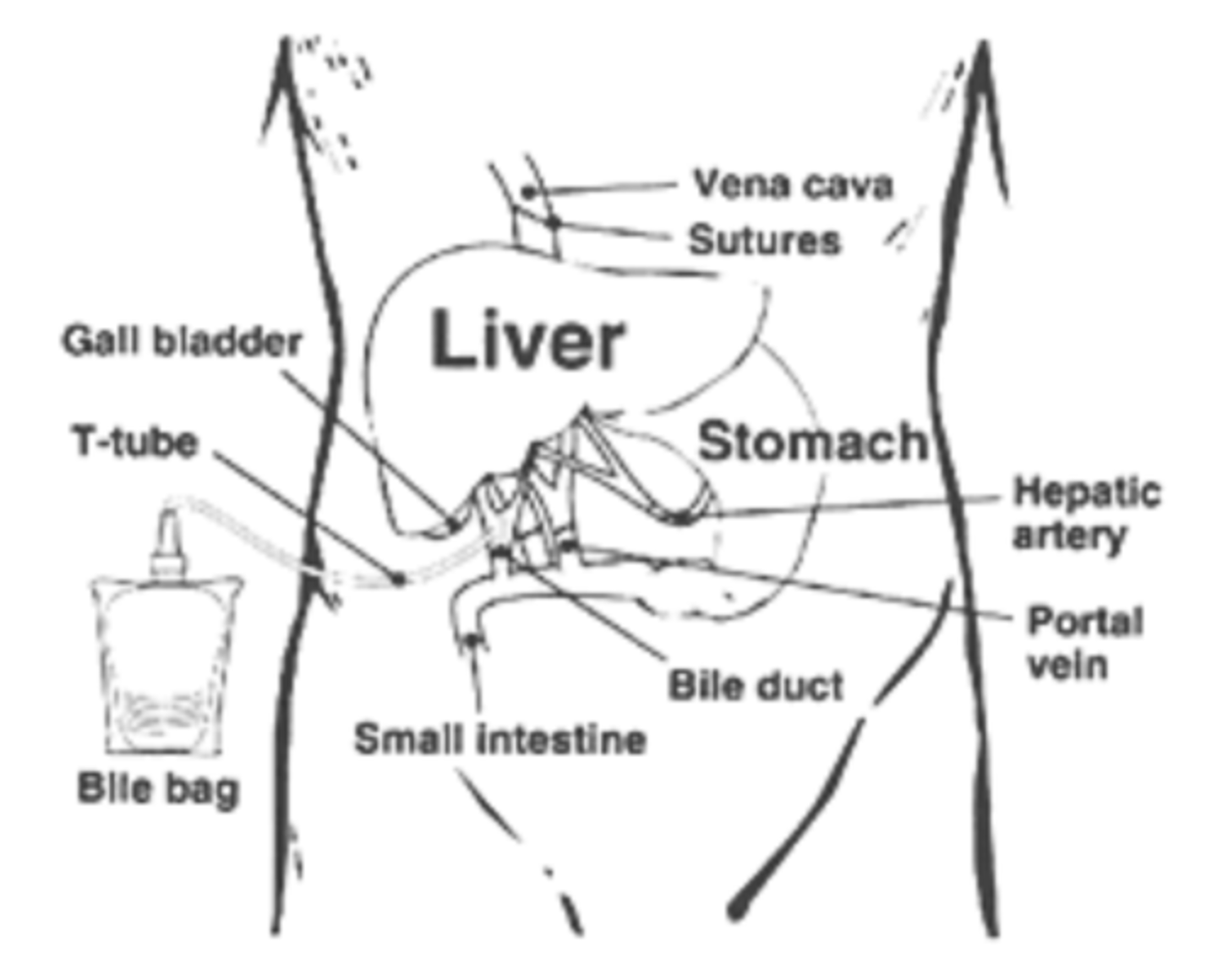
Bile production is ______________________ prognostic indicator because it means that new liver is working! → We have to offload it into bile bag for ~3 months post-op d/t _______________________ and _______________________.
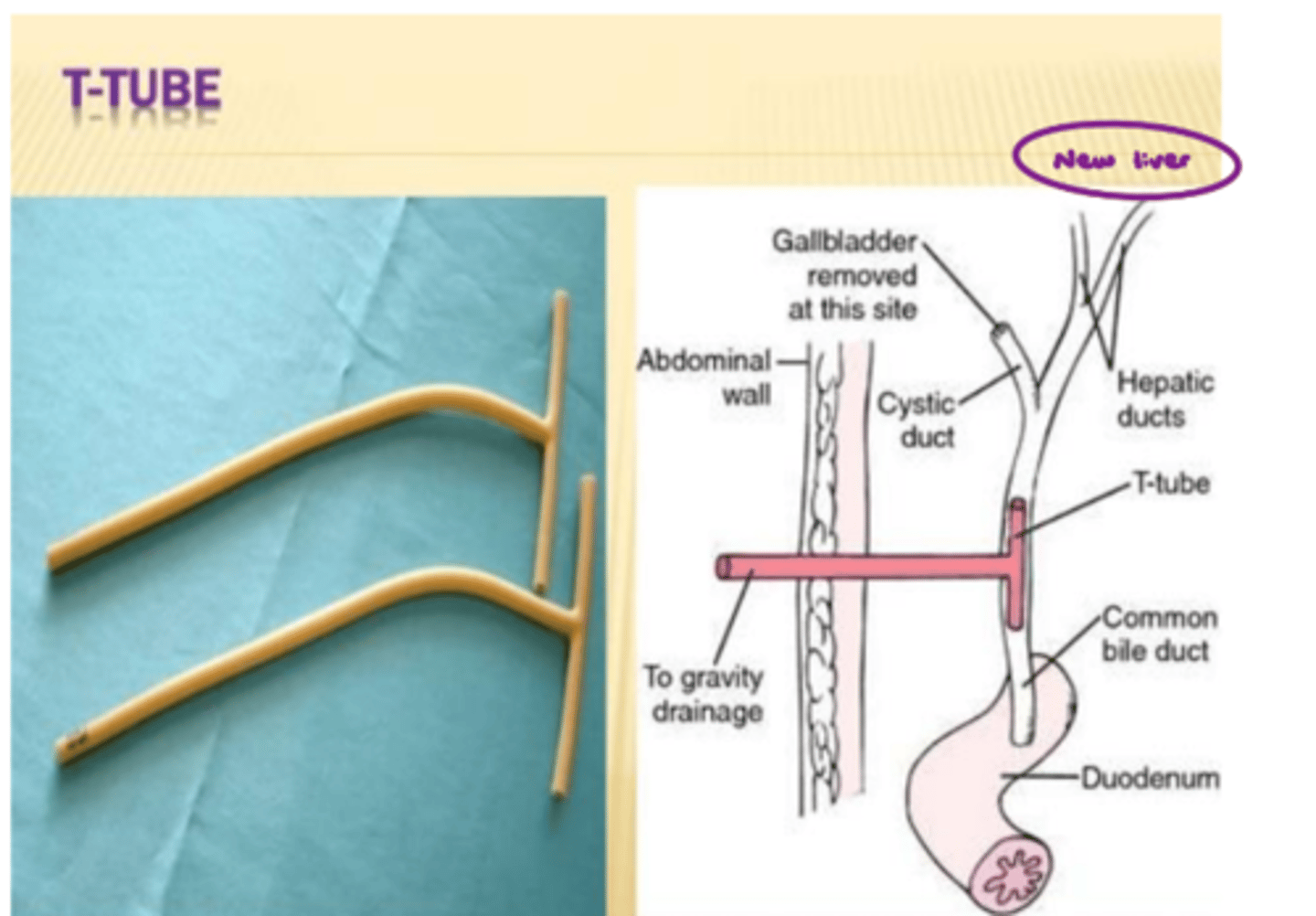
Biliary T-tube
What does image show?
Coagulation factors; hyperglycemia; potassium
Liver Transplant - Post-Op Considerations:
- Check _______________________ d/t ↑ risk of bleeding /c prolonged clotting times, should trend back to normal /c return of liver function
- LFT's should trend toward normal
- _______________________ can be a good indicator of return. → Elevations in blood sugar when new liver can convert stored glycogen into glucose.
- Caution and monitor ________________________ trends.
Hypokalemia
Toward __________________ when hepatocytes can extract K+ from the blood.
Hyperkalemia
Toward __________________ is a sign of cell death and nonfunctional hepatocytes.
Tacrolimus (Prograf)
Immunosuppressant, most common anti-rejection medication used after liver transplant.
Tremor; fatigue
Side effects of Tacrolimus (Prograf) include ______________________, paresthesias, and headache, dizziness, and ______________________ (appears similar to stroke).
Prednisone
Corticosteroid used after liver transplant.
Osteoporosis
Long-term use of Prednisone increases risk of ________________________ and fracture.
Fluid retention/edema
Side effect of Prednisone is __________________________.
Changing schedule
If patient is immunocompromised and has low WBC count, talk to team leader about _________________________.
Gallbladder
Stores and concentrates bile.
Bile
Composed of bile salts, cholesterole, bilirubin, lecithin, fatty acids, water, and electrolytes.
Emulsifies fats
What is function of bile?
Cholelithiasis
Gallstones.
Stasis; cholesterol; bilirubin
Causes of Cholelithiasis:
- _____________________ of bile
- ↑ saturation of ______________________ in bile
- ↑ concentration of insoluble ______________________ in bile
US, CT scan, nuclear medicine
Diagnosis of Cholelithiasis:
- Imaging: __________________________
- Can detect stones as small as 1-2 cm
Cholcystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder - acute or chronic.
Gallstone ductal obstruction
90% of cholecystitis cases are related to _________________________.
Right upper quadrant; gallbladder attacks; rigidity; jaundice; fever
Signs and Symptoms of Cholecystitis:
- Abdominal pain in ______________________, severe /c abrupt onset and steadily increasing over 2-8 hours → soreness
- ________________________ usually subside s/p 7-10 days
- Rebound tenderness, abdominal _________________________
- _________________________
- N+V
- _________________________
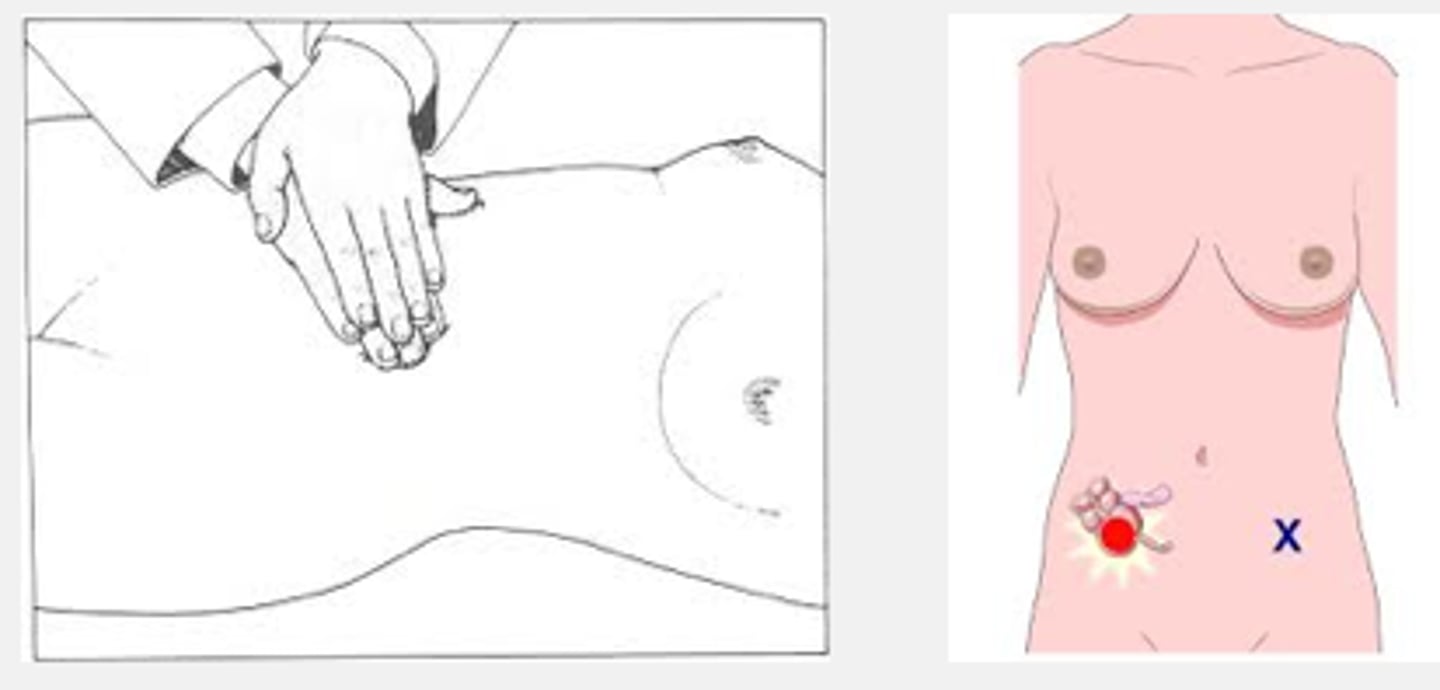
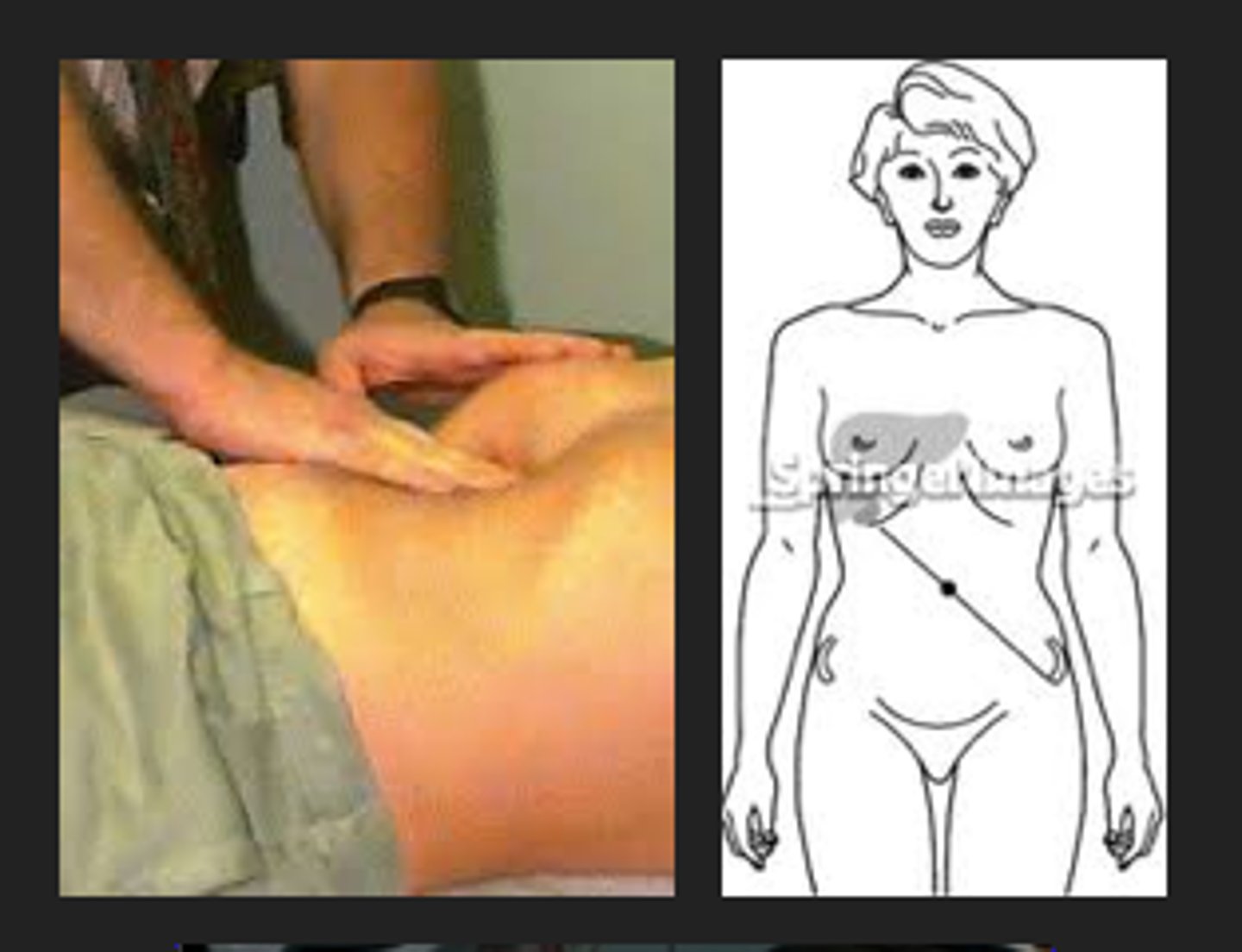
Murphy's sign
Pain /c inhalation when fingers hooked under R ribs; indicative of cholecystitis.
NG; pain; IV
Treatment of Cholecystitis:
- Bowel rest → _______________________ suctioning
- ERCP
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Cholecystostomy
- ________________________ management
- ______________________ fluids
- Antibiotics
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Remove stones blocking bile ducts or cystic duct.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Remove gallbladder.
Cholecystostomy
Gallbladder drainage catheter placement.
McBurney's point
Pain upon palpation of R LQ point (1/2 of the way from the ASIS to the umbilicus); indicative of appendicitis.
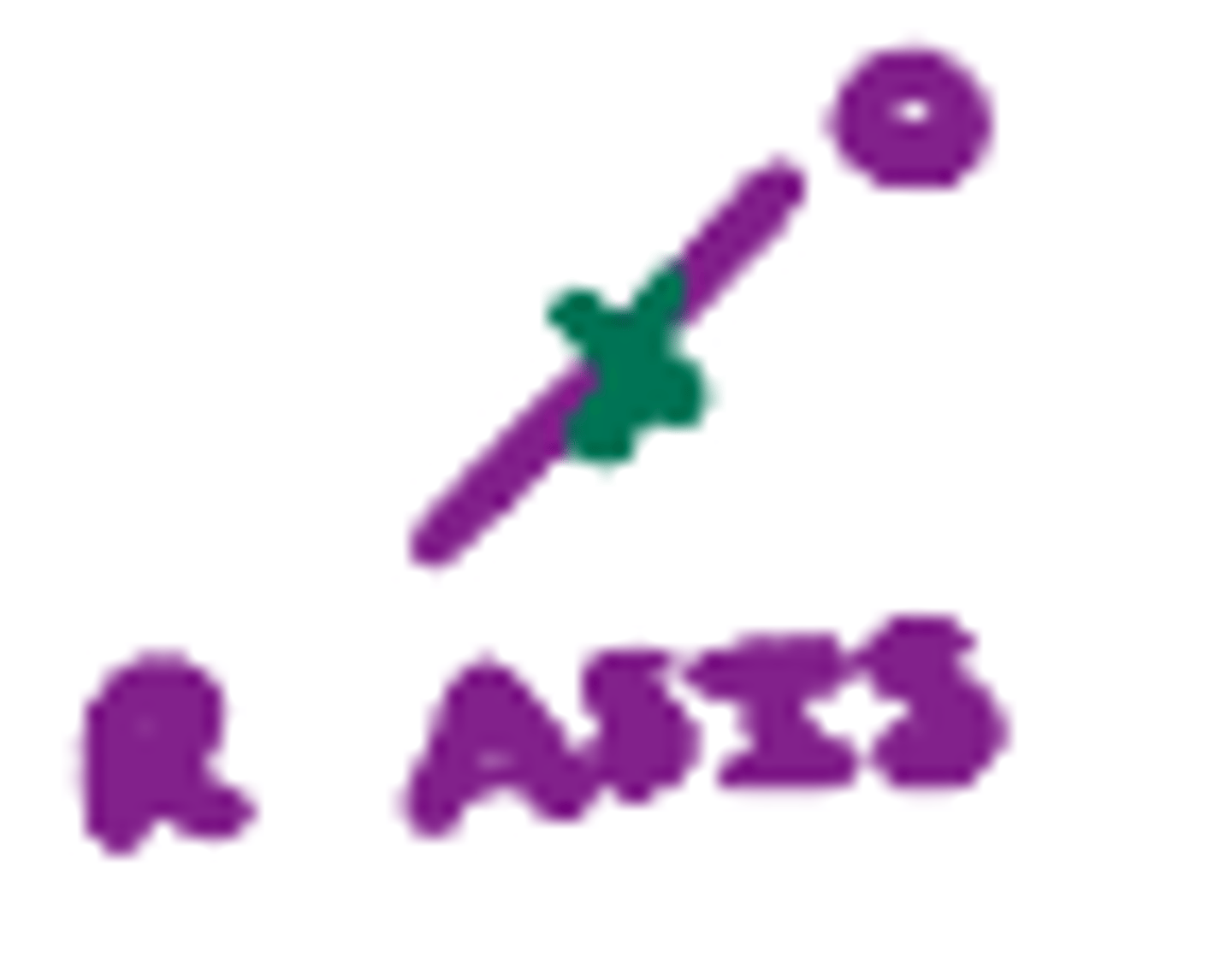

Rovsing's sign
Pain in R LQ /c application of pressure to L LQ; indicative of appendicitis.