Vocabulary Selection: Core Words Fringe Words
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
4 areas of communicative competence
linguistic
operational
social
strategic
LOSS
linguistic
expressive/receptive language
syntax, semantics
core words/fringe words
operational
how to physically operate the device
technical skills needed to operate the AAC system accurately and efficiently
turning it on/off
charging (battery)
navigation
social
how can I use it pragmatically
interactions such as taking turns, initiating
all communicative functions
strategic
How to best repair communication
compensatory strategies such as resolving communication breakdowns
interacting with unfamiliar people
the goal of AAC
autonomous communication
“being able to say what I want to say, to whoever I want to say it to, whenever I want to say it, ho
communication functions
Storytelling →real, imaginary
Recounting something/what happened
Requests
Safety/Care (abuse, medical needs)
Greetings
Small Talk
Jokes
Comment
Reject
Opinions
Reflection
Social Closeness
Social Etiquette
Establish/Maintain Relationships
candidacy
Outdated model
Based on prerequisites
People were viewed as “too”
Too young, old, delayed…
Gatekeepers of language/communication
If you don’t have language or a reliable means of communication, how can you be “tested”
participation
Endorsed by ASHA
Based on the functional participation requirements of peers without disabilities who are the same age
How do we remove barriers
Looks at communication needs for today and in the future
stakeholders
AAC user/client/patient/student
Parent/caregiver(s)
Family members
Peers
Teachers
SLPs
all people who are involved in the desicion making
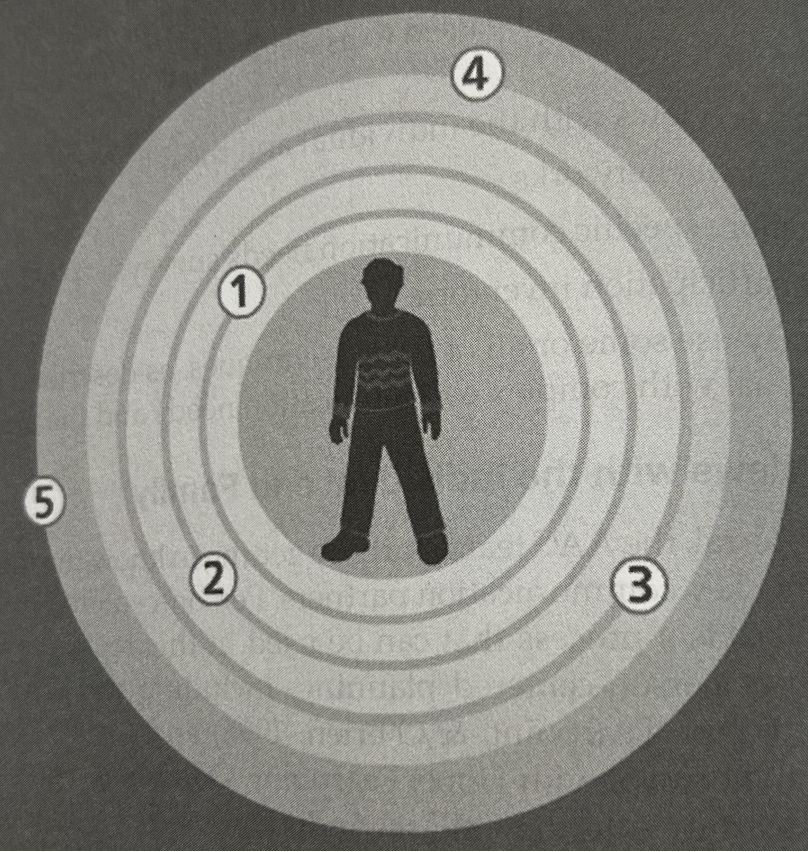
Life partners (mom, dad, spouse)
Close friends and relatives
Acquaintances
Paid Workers (us! we are pretty far out)
Unfamiliar Communication Partners
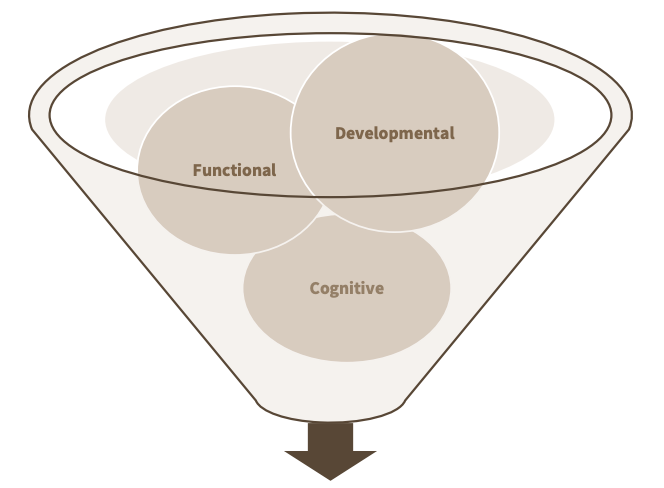
3 frameworks for selecting vocabulary
functional
developmental
cogntiive
functional framework
Health/Medical
Quick Phrases
High Frequency
Specific to the Environment
developmental framework
Language Learning
• Typical Development
cognitive framework
Reason
Complex ideas
Cognitive-conceptual
Recurrence=more
Non-existence=gone
AAC user’s language
core words
High Frequency, small set up words
Make up ~80% of what we communicate
Apply across settings (generalize)
Abstract
High Frequency, small set up words
core vs fringe
core
Make up ~80% of what we communicate
core vs fringe
core
Apply across settings (generalize)
core vs fringe
core
abstract
core vs fringe
core
when are core words powerful?
alone and when combined with fringe words
fringe words
Specific words
Make up ~20% of what we communicate daily
Mostly nouns
Easy to represent/understand out of context
Powerful when highly motivating
specific words
core vs fringe
fringe
Make up ~20% of what we communicate daily
core vs fringe
fringe
mostly nouns
core vs fringe
fringe
Easy to represent/understand out of context
core vs fringe
fringe
Powerful when highly motivating
core vs fringe
fringe
Can be combined with core words to grow language
fringe words
5 things to think about when selecting vocabulary
Context/environment in which the vocabulary might be used
Length of time the word will be relevant
Whether it can elicit and maintain interaction with people
Whether the word will facilitate the development of grammatical structures
Whether the word supports the acquisition/expression of new structures
balance of core and fringe words
you have to have a balance of both!
we are focusing on core because everyone else focuses on fringe because they are tangible and not abstract
Aided Language Input/Modeling/Stimulation
Aided=external aid/device
light/mid/high tech
modeling on the system of the AAC user is using