BIO 214 UWEC Lecture C5
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
50 trillion
How many cells are in the human body?
histology
Microscopic anatomy-study of tissues and how they are arranged
Tissue
a group of similar cells working together to perform a specific role in an organ
Matrix
Extracellular material
Fibrous proteins, ground substance
The matrix is composed of
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
3 primary germ layers
Ectoderm
(Outer) gives rise to epidermis and nervous system
Endoderm
(Inner) give rise to mucus membrane lining digestive and respiratory tracts.
Mesoderm
(Middle) becomes gelatinous tissue called mesenchyme, bone, blood, muscle
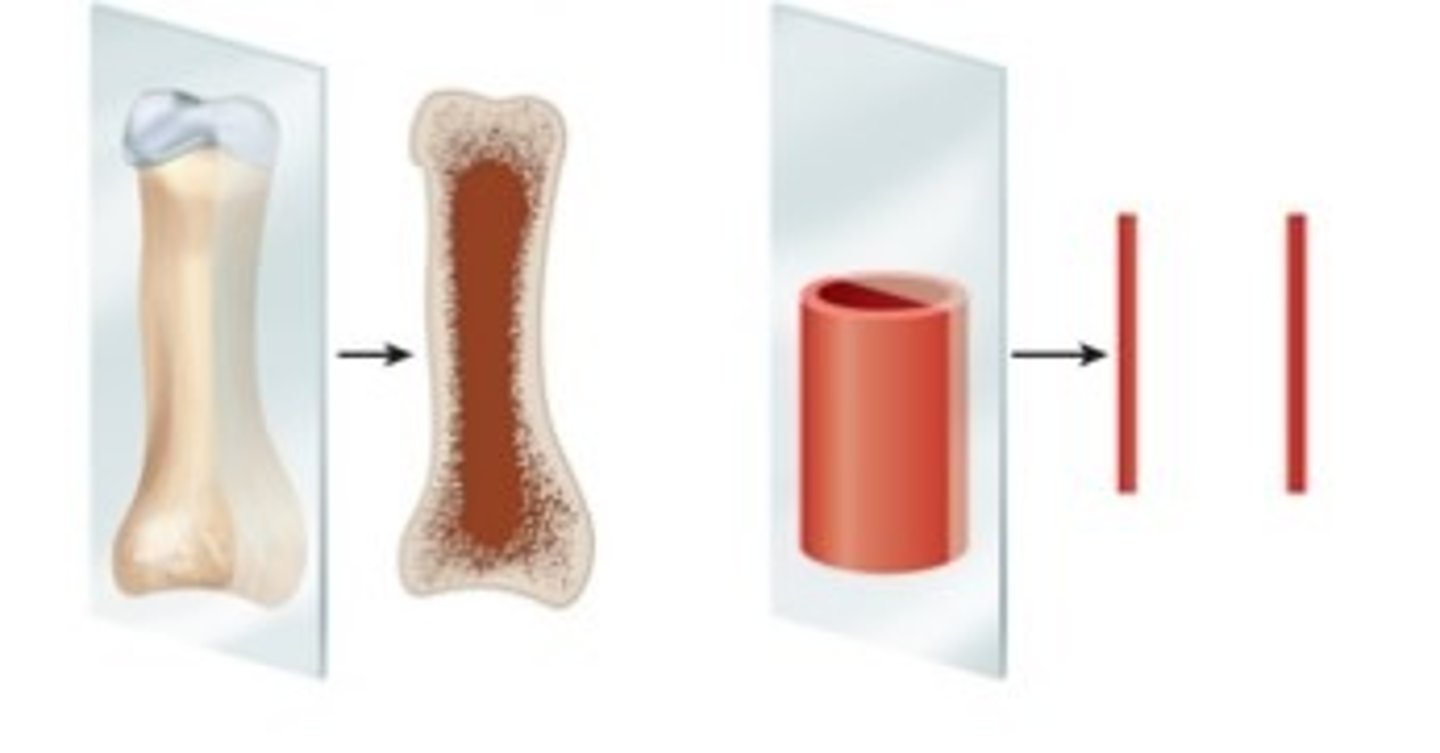
longitudinal section
Tissue cut on its long axis
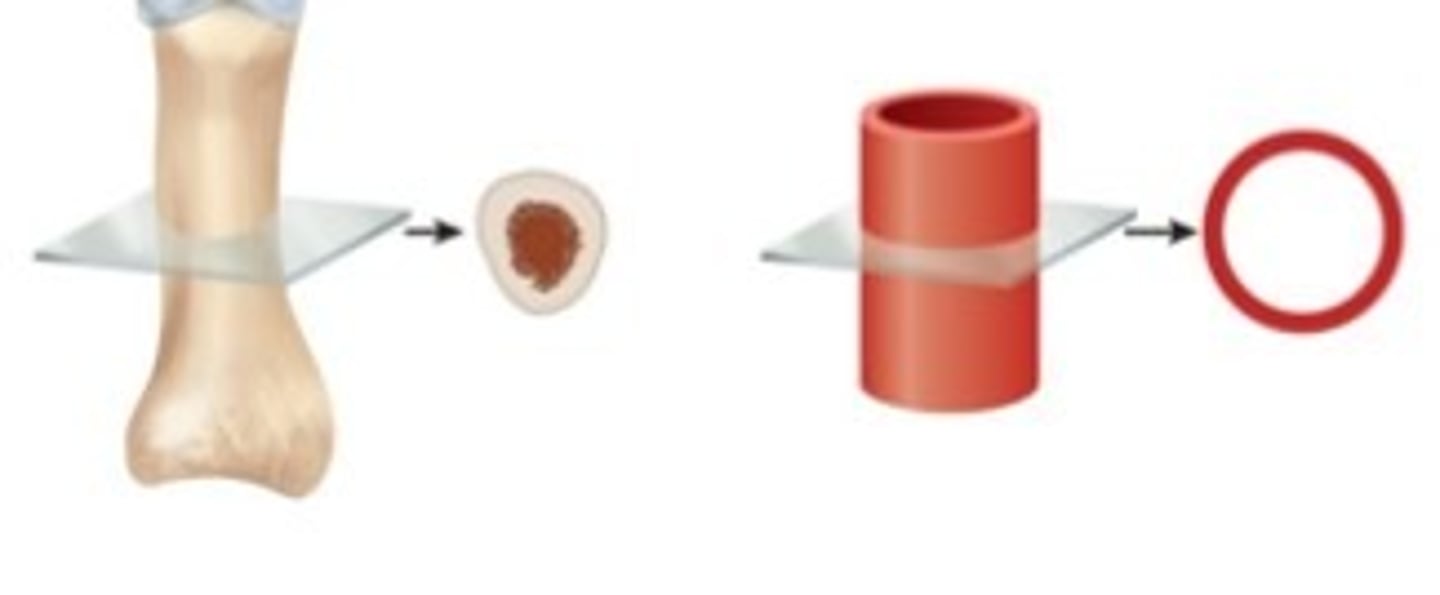
cross section
tissue cut perpendicular to long axis of organ
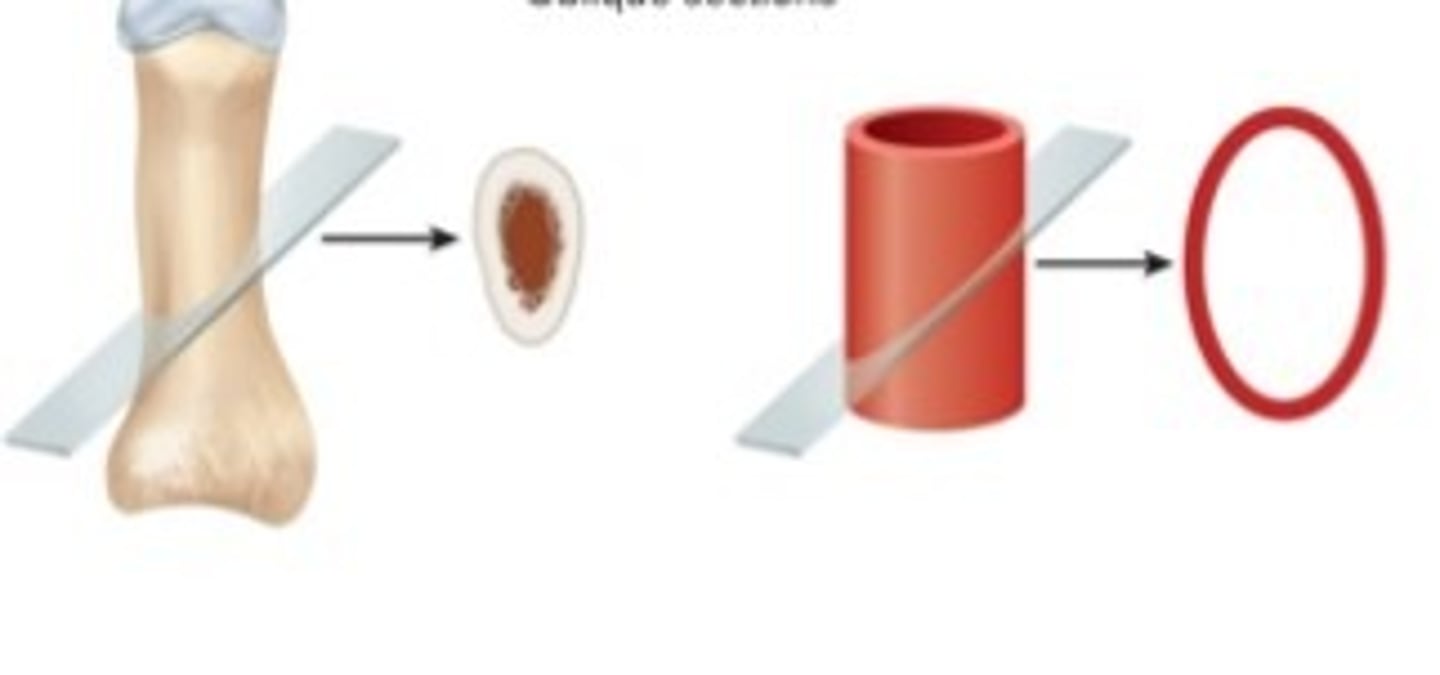
Oblique section
Tissue cut at angle between cross and longitudinal sections
epithelia
sheets of closely adhering cells, one or more cells thick
avascular
no blood vessels
protection, absorption, filtration, secretion, sense stimuli
functions of epithelial tissue
basement membrane
layer between an epithelium and underlying connective tissue
basal surface
surface of epithelial cell facing the basement membrane
apical surface
surface of epithelial cell that faces away from the basement membrane
simple epithelium
single layer of cells
stratified epithelium
several layers of cells
alveoli, glomeruli, endothelium, and serosa
location of simple squamous epithelium
goblet cells
wineglass-shaped mucus-secreting cells in simple columnar and pseudostratified epithelia
lining of GI tract, uterus, kidney, uterine tubes
location of simple columnar epithelium
liver, thyroid, mammary and salivary glands, bronchioles, and kidney tubules
location of simple cuboidal epithelium
respiratory tract and portions of male urethra
location of pseudostratified epithelium
stratified squamous
most widespread epithelium in the body
desquamation/exfoliation
when cells flake off and die
keratinized
found on skin surface, abrasion resistant
locations: epidermis, palms, soles
nonkeratinized
lacks surface layer of dead cells
locations: tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, vagina
cell junctions
connections between two cells
tight junctions
linkage between two adjacent cells by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins
Gap (communicating) junctions
formed by ring-like connexons
glands
cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or releases them for elimination from the body
secretion
product useful to the body
endocrine glands
have no ducts; secrete hormones directly into blood
exocrine glands
maintain their contact with surface of epithelium by way of a duct
capsule
connective tissue covering of exocrine gland
stroma
connective tissue framework of the gland
parenchyma
cells that preform the task of synthesis and secretion
serous glands
- Produce thin, watery secretions
- Perspiration, milk, tears, digestive juices
mucous glands
Produce glycoprotein, mucin, which absorbs water to form mucus
mixed glands
Contain both serous and mucous cell types and produce a mixture of the two types of secretions
Apocrine
lipid droplet covered by membrane and cytoplasm buds from cell surface
merocrine
(used by eccrine glands) uses vesicles that release their secretion by exocytosis
holocrine secretion
cells accumulate a product until they disintegrate
The cutaneous membrane (skin)
largest membrane in the body
Mucous membrane (mucosa)
lines passages that open to the external environment (example: digestive tract)
serous membrane (serosa)
Simple squamous epithelium resting on a layer of areolar tissue
Produces serous fluid that arises from blood
Covers organs and lines walls of body cavities
Endothelium lines blood vessels and heart
Mesothelium lines body cavities (pericardium, peritoneum, and pleura)
Hyperplasia
cell multiplication
hypertrophy
enlargement of preexisting cells
Neoplasia
development of a tumor
blood
the only tissue type that is a liquid at room temperature
Differentiation
development of more specialized form and function by unspecialized tissue
Example: embryonic mesenchyme becoming cartilage and bone
Metaplasia
Changing from one type of mature tissue to another
Simple cuboidal tissue of vagina before puberty changes to stratified squamous after puberty
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium of bronchi of smokers to stratified squamous epithelium
stem cells
undifferentiated cells that are not yet performing any specialized function
Have potential to differentiate into one or more types of mature functional cells
developmental plasticity
ability of a stem cell to give rise to a diversity of mature cell types
totipotent
have potential to develop into any type of fully differentiated human cell including accessory organs of pregnancy
Pluripotent
can develop into any type of cell in the embryo (but not accessory organs of pregnancy)
Source—cells of inner cell mass of embryo (blastocyst)
Multipotent
Adult stem cells—undifferentiated cells found in mature organs
Some are ________________________ —able to develop into two or more cell lines (example: bone marrow stem cells)
Some are unipotent—produce only one cell type (example: cells giving rise to sperm)
induced pluripotent stem cells
Start as a multipotent stem cell, reprogrammed to mimic a pluripotent stem cell.
Regeneration
replacement of dead or damaged cells by the same type of cell as before Examples: repair of minor skin or liver injuries
Fibrosis
replacement of damaged cells with scar tissue
Scar holds organs together, but does not restore function
Examples: repair of severe cuts and burns, scarring of lungs in tuberculosis
Histamine
first stage of skin healing: Mast cells and damaged cells release__________
blood vessels
second stage of skin healing: Histamine dilates_________ and makes capillaries more permeable
antibodies, clotting protiens
third stage of skin healing: Blood plasma seeps into the wound carrying______
blood clot forms
4th stage Knits edges of cut together
Inhibits spread of pathogens
phagocytize
5th stage Macrophages _______ and digest tissue debris
capillaries
6th stage: New ______ sprout from nearby vessels
granulation tissue
7th stage: Deeper portions of clot become infiltrated by capillaries and fibroblasts
Transform into soft mass called__________ ________
Macrophages remove the blood clot
Fibroblasts deposit new collagen
Begins 3-4 days after injury and lasts up to 2 weeks
atrophy
shrinkage of a tissue through loss in cell size or number
neorosis
pathological tissue death due to trauma, toxins, or infections
infraction
sudden death of tissue when blood supply is cut off
gangrene
tissue necrosis due to insufficient blood supply (usually involves infection)
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
less space
Connective tissue—a diverse, abundant type of tissue in which cells occupy _______________than matrix
functions of connective tissue
connecting organs, support, physical protection, immune protection, movement, storage, heat production, transport
tendons and ligaments
Connecting organs: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
bones and cartilage
support: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
cranium, ribs, sternum
physical protection: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
white blood cells attack foreign invaders
immune protection: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
bones provide lever system
Movement: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
fat, calcium, phosphorus
storage: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
metabolism of brown fat in infants
heat production: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
blood
transport: this function of connective tissue occurs where?
Fibroblasts
fibrous connective tissue cell: produce fibers and ground substance of matrix
Macrophages
fibrous connective tissue cell: phagocytize foreign material and activate immune system when they sense foreign matter (antigens)
Leukocytes
fibrous connective tissue cell: white blood cells
Neutrophils attack bacteria
Lymphocytes react against bacteria, toxins, and other foreign agents
plasma cells
fibrous connective tissue cell: synthesize antibodies (proteins)
Arise from lymphocytes
mast cells
fibrous connective tissue cell: often found alongside blood vessels
Secrete heparin to inhibit clotting
Secrete histamine to dilate blood vessels
Adipocytes
fibrous connective tissue cell: store triglycerides (fat molecules)
collagenous fibers
Fibers of fibrous connective tissue: Collagen is most abundant of the body's proteins—25%
Tough, flexible, and stretch-resisant
Tendons, ligaments, and deep layer of the skin are mostly collagen
Less visible in matrix of cartilage and bone
reticular fibers
Fibers of fibrous connective tissue: Thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein
Form framework of spleen and lymph nodes
elastic fibers
Fibers of fibrous connective tissue::
Thinner than collagenous fibers
Branch and rejoin each other
Made of protein called elastin
Allows stretch and recoil
Glycosaminoglycans
Ground substance of fibrous connective tissue
Usually has a gelatinous to rubbery consistency
random
Fibers run in ______________ directions
Mostly collagenous, but elastic and reticular also present
areolar tissue
Nearly every epithelium rests on a layer of ____________
reticular tissue
Mesh of reticular fibers and fibroblasts
Forms supportive stroma (framework) for lymphatic organs
Found in lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and bone marrow
parallel, muscles
Dense regular connective tissue
Densely packed, ______________ collagen fibers
Compressed fibroblast nuclei
Elastic tissue forms wavy sheets in some locations
Tendons attach ______________ to bones and ligaments hold bones together
unpredictable
Dense irregular connective tissue
Densely packed, randomly arranged, collagen fibers and few visible cells
Withstands ______________ ______________ stresses
Locations: deeper layer of skin; capsules around organs
adipose
______________ tissue (fat)—tissue in which adipocytes are the dominant cell type