geology test 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
1
New cards
law of superposition
in an undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, each bed is older than the one above it.
2
New cards
principle of original horizontality
layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position.
3
New cards
principle of cross-cutting relationships
in order for the fault to cut those layers they had to be there already
4
New cards
inclusions
pieces of one rock unit that are contained with another
5
New cards
unconformities
breaks that interrupt the deposition of sediment
6
New cards
angular unconformity
tilted rocks overlain by horizontal rocks
7
New cards
disconformity
missing time between two sedimentary layers
8
New cards
nonconformity
when you have an igneous or metamorphic rock overlain by a sedimentary rock
9
New cards
half-life
the required time for half of the nuclei of a sample to decay is called the half life of an isotope
10
New cards
replacement
type of fossilization when hard parts are replaced with a harder material as water flows through
11
New cards
petrified
type of fossilization when the original material is organic and replaced by silica or pyrite then it is called petrification
12
New cards
mold
if the body is buried then decays, a hole may be left where the body was mimicking the shape of the remains
13
New cards
cast
the shape made when a mold is filled in
14
New cards
carbon-rich plant preservation
carbon plants may leave a thin film that is preserved in materials like silt
15
New cards
impressions
pattern left on a fine-grained material
16
New cards
index fossils
allow us to date the layers they are in
17
New cards
precambrian
earliest life on earth, comprises nearly 90% of geologic time but only simple forms of life existed during this time. nothing with hard parts.
18
New cards
paleozoic
this time was dominated by several major groups of marine animals including corals, creatures likes clams and various types of fish. The end of this time is called the Great Dying
19
New cards
mesozoic
This is the age of dinosaurs. the end of this time is marked by the extinction of dinosaurs.
20
New cards
cenozoic
the age of mammals, most recent
21
New cards
hypocenter
the point at depth within the earth where the earthquake occurred
22
New cards
epicenter
the point at the surface above the hypocenter where the earthquake occured
23
New cards
normal dip slip fault
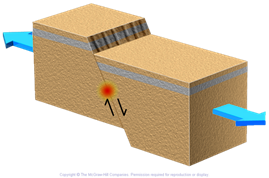
24
New cards
reverse dip slip fault
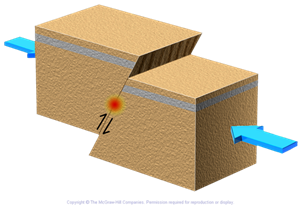
25
New cards
strike slip fault
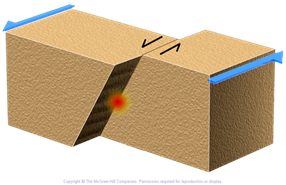
26
New cards
fault scarp
a cliff where a fault meets the earth’s surface
27
New cards
surface waves
travel on or near the earth’s surface
28
New cards
body waves
travel through the earth
29
New cards
P waves
the primary set of waves, can move through solid and liquid materials
30
New cards
S waves
the secondary set of waves, move through solids but not liquid
31
New cards
richter scale
takes into account the distance from the epicenter and the amplitude of the wave
32
New cards
modified mercali scale
considers the effects of shaking on people, structures, and surroundings
33
New cards
spring tide
When the sun and moon are on opposite sides of the Earth both exerting pull there will be the largest difference between high and low tide.
34
New cards
neap tide
when the sun and moon are at right angles to each other.
35
New cards
delta
Where a river enters the ocean a __________ forms
36
New cards
sea cliff
Hard rock eroded into cliffs along shore.
37
New cards
sea arches
As cliffs are undercut caves or arches are formed.
38
New cards
wave cut platforms
Waves cut notches cut into cliffs which eventually form a platform.
39
New cards
sea stacks
Continued erosion of arches or caves leaves rocks in the ocean.
40
New cards
spit
a sand bar that extends part of the way across the bay
41
New cards
groins
built perpendicular to the beach into the water to influence the lateral transport of sand.
42
New cards
jetties
These are built in pairs typically on each side of a bay to keep sediment from closing off the bay
43
New cards
sea level rising
Estuaries are a sign of
44
New cards
alpine glaciers
Glaciers that flow out of the mountains into broader open areas
45
New cards
calving
As a glacier meets a lake or ocean, Parts of the glacier may break off into the water
46
New cards
medial moraine
Sediment that is deposited in the center where two glaciers join
47
New cards
arete
Large jagged ridges that occur where two cirques meet are an erosional feature
48
New cards
frost wedging
There is a crack and water fills in the crack. At night it drops below freezing and the water turns to ice and expands making the crack slightly larger.
49
New cards
salt crystal growth
This occurs in rocks along rocky shorelines where salt water moves into the cracks and salt precipitates out. The salt crystals enlarge the cracks in the rocks.
50
New cards
sheeting
When large masses of igneous rock, particularly granite, are exposed by erosion, concentric slabs begin to break loose.
51
New cards
oxidation
oxygen dissolving in water on iron-rich minerals
52
New cards
O horizon
top layer made mostly of organic material
53
New cards
A horizon
under O horizon, mostly mineral matter but lots of biological activity and humus
54
New cards
E horizon
under A horizon, light in color and contains little organic material
55
New cards
over steepened slopes
trigger of mass wasting events when erosion or human activity makes land at more of an angle
56
New cards
earthquakes
shaking can trigger mass wasting events by disturbing loose material
57
New cards
vegetation removal
triggers mass wasting events because there is nothing for the soil to hold onto
58
New cards
noise
vibrations can cause avalanches
59
New cards
blasting
using nearby explosives can weaken slopes
60
New cards
freefall
falling without disruption
61
New cards
slides
when the material slides along zones of weakness down a slope
62
New cards
flow
has the most water, and occurs when material moves downslope as viscous fluid
63
New cards
slump
downward sliding of a mass of rock or unconsolidated material as a unit along a curved surface
64
New cards
rockslides
occur when blocks of bedrock break loose and slide down a slope
65
New cards
lahars
Debris flows composed mostly of volcanic material on the flanks of a volcano
66
New cards
earthflows
When water saturates the soil and regolith on a hillside, the material may break away, leaving a scar on the slope and forming a tongue- teardrop- shaped mass that flows downslope
67
New cards
creep
Involves gradual downslope movement of soil and regolith
68
New cards
laminar flow
stream flow parallel to the shoreline
69
New cards
turbulent flow
more the norm, swirling, erratic flow
70
New cards
dissolved load
will depend on the rock type and whether it is easily dissolved in water
71
New cards
suspended load
material that can be carried along in a stream. Typically only fine grained materials are carried
72
New cards
bed load
movement along the bottom of the stream
73
New cards
capacity
is the maximum load of solid particles that a stream can transport
74
New cards
competence
the largest particle a stream can carry
75
New cards
settling capacity
the amount of energy required to allow sediment to settle out of the water
76
New cards
sorting
occurs as velocity slows down slowly the first thing to drop out will be the larger particles as it continues to slow down the smallest particles will drop out
77
New cards
alluvium
a general term for all stream deposited sediment
78
New cards
bars
channel deposits usually composed of sand and gravel
79
New cards
braided stream
stream with many bars
80
New cards
narrow valleys
associated with high slopes, rapids, and waterfalls
81
New cards
wide valleys
associated with lots of curves, floodplains, and sediment
82
New cards
point bar
the depositional feature found on the inside of a meander where the energy is lower and sediment is deposited in a crescent shape
83
New cards
cut bank
erosional feature found on the outside of a meander where the energy of the stream flows into the bank causing erosion
84
New cards
oxbow lake
a curve in a stream becomes so severe that the stream cuts through the banks and finds an easier way to flow
85
New cards
dendritic
common drainage pattern, looks like branching
86
New cards
radial
associated with volcanoes or domal uplifts
87
New cards
rectangular patterns
follows the joints between bedrock
88
New cards
stream piracy
occurs when a stream erodes headward and then capturing a stream from a different basin
89
New cards
water table
point below which all pore spaces are filled with water
90
New cards
zone of saturation
areas where all pore spaces are filled with water
91
New cards
zone of aeration
zone where pore spaces contain air and water
92
New cards
capillary fringe
area where water tension pulls water up slightly at the edge between the water table and the aeration zone
93
New cards
porosity
the amount of void spaces in a rock or sediment
94
New cards
permeability
the ability of a material to transmit fluid
95
New cards
specific yield
the portion of water which will drain or move through a material under the influence of gravity
96
New cards
specific retention
how much water is retained by the sediment
97
New cards
aquifer
is a rock layer or sediment which has a high porosity and high permeability
98
New cards
aquitard
have little permeability
99
New cards
hot springs
This water has typically flowed near a magma to get heated
100
New cards
geysers
pressurized fountains of water