Pulmonary Exam 2: Pulmonary Disease and Dentistry (Dr. McBrine)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
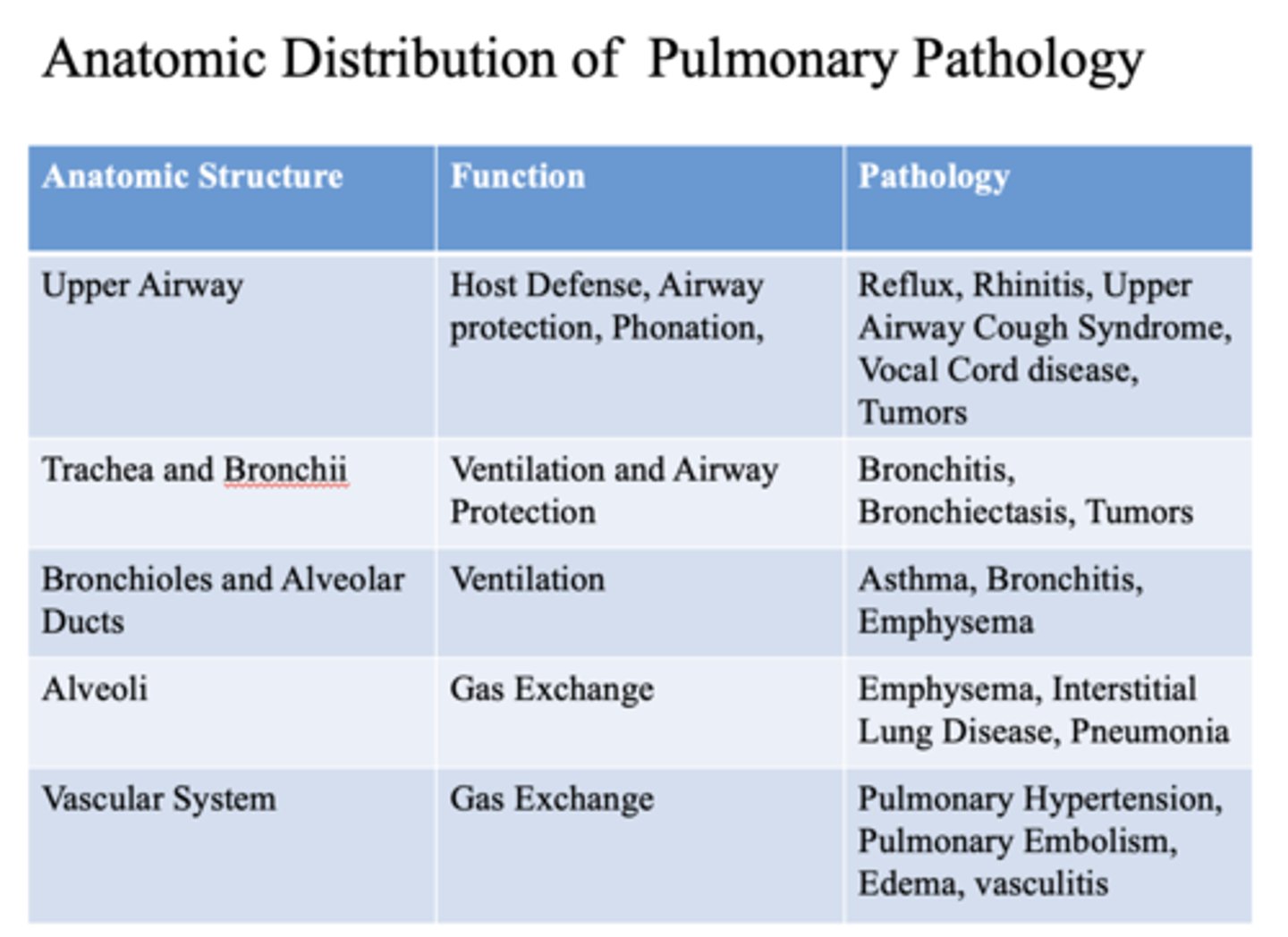
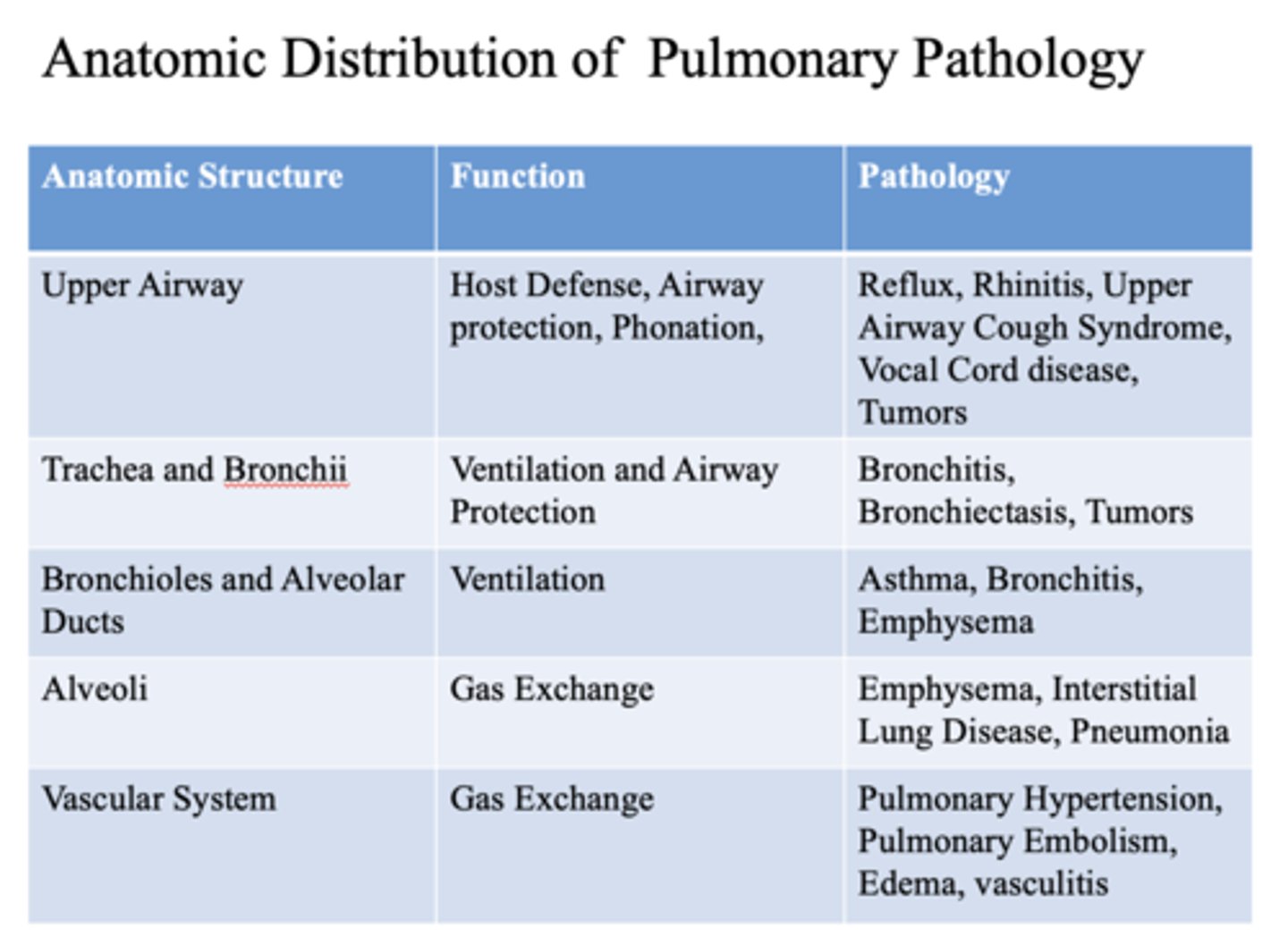
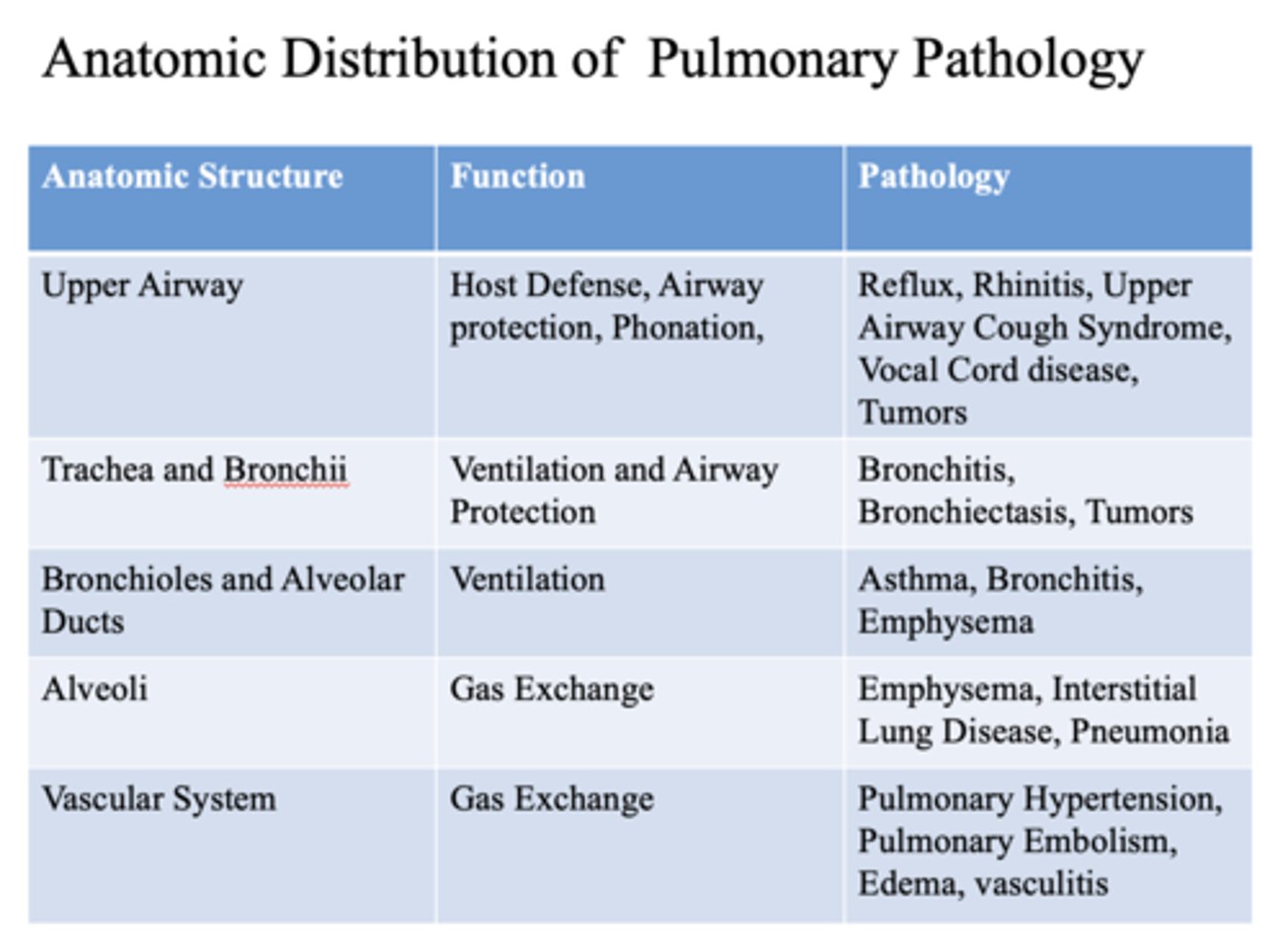
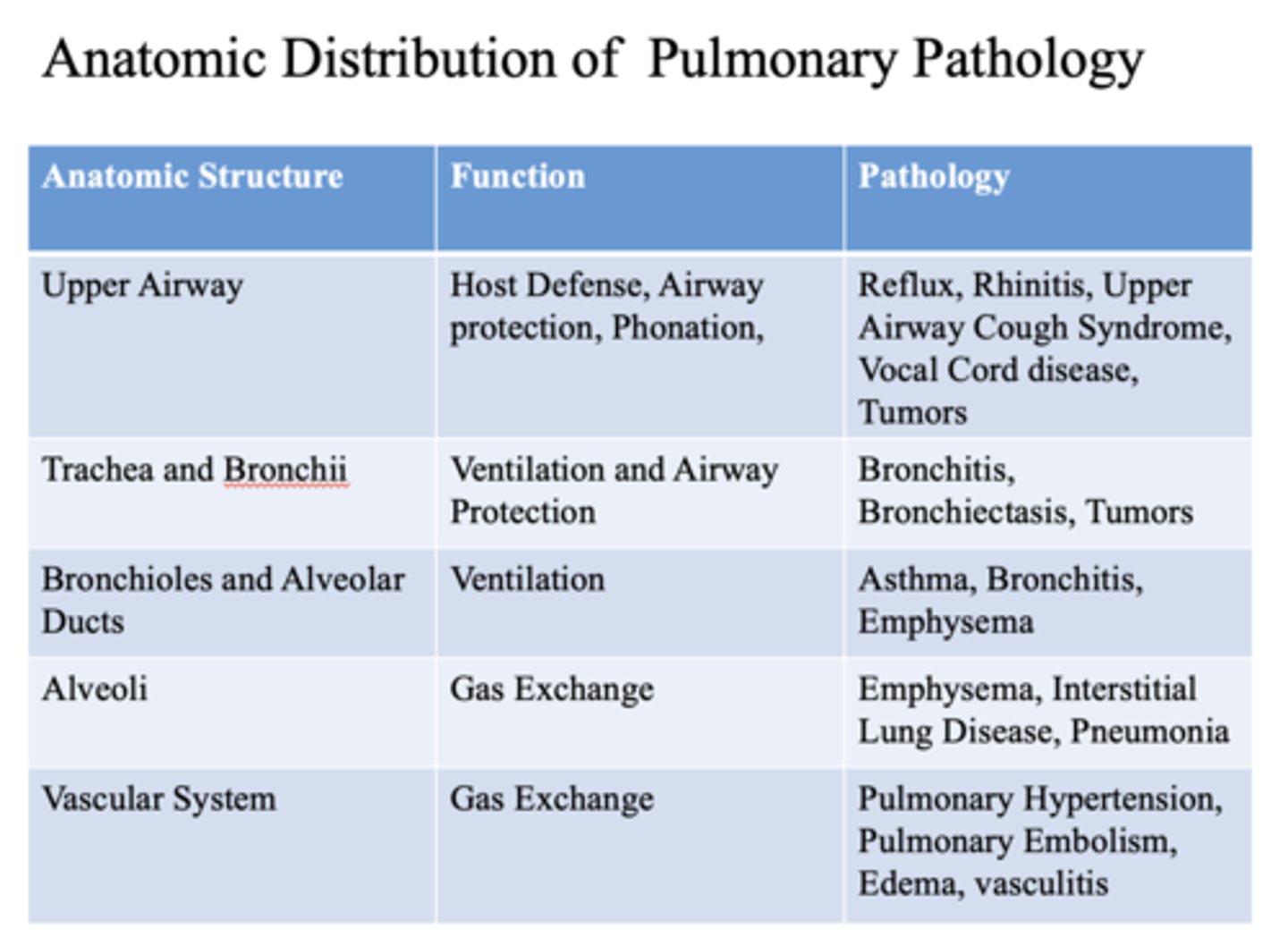
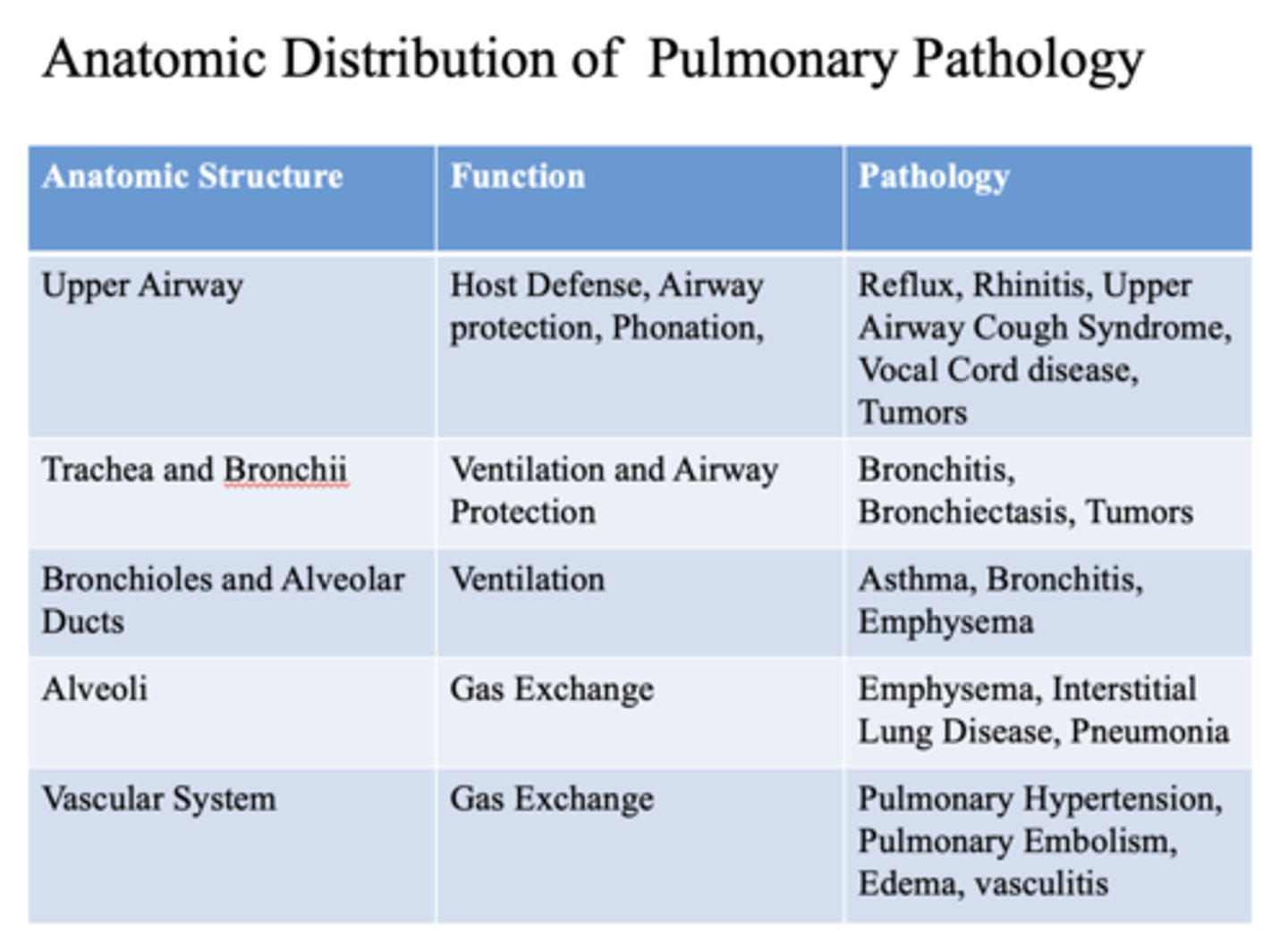
These are pathology of what anatomic structure?
- Reflux
- Rhinitis
- Upper Airway Cough Syndrome
- Vocal Cord disease
- Tumors
Upper airway
These are pathology of what anatomic structure?
- Bronchitis
- Bronchiectasis
- Tumors
- Trachea
- Bronchii
These are pathology of what anatomic structure?
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
These are pathology of what anatomic structure?
- Emphysema
- Interstitial Lung Disease
- Pneumonia
alveoli
These are pathology of what anatomic structure?
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Edema
- Vasculitis
vascular system
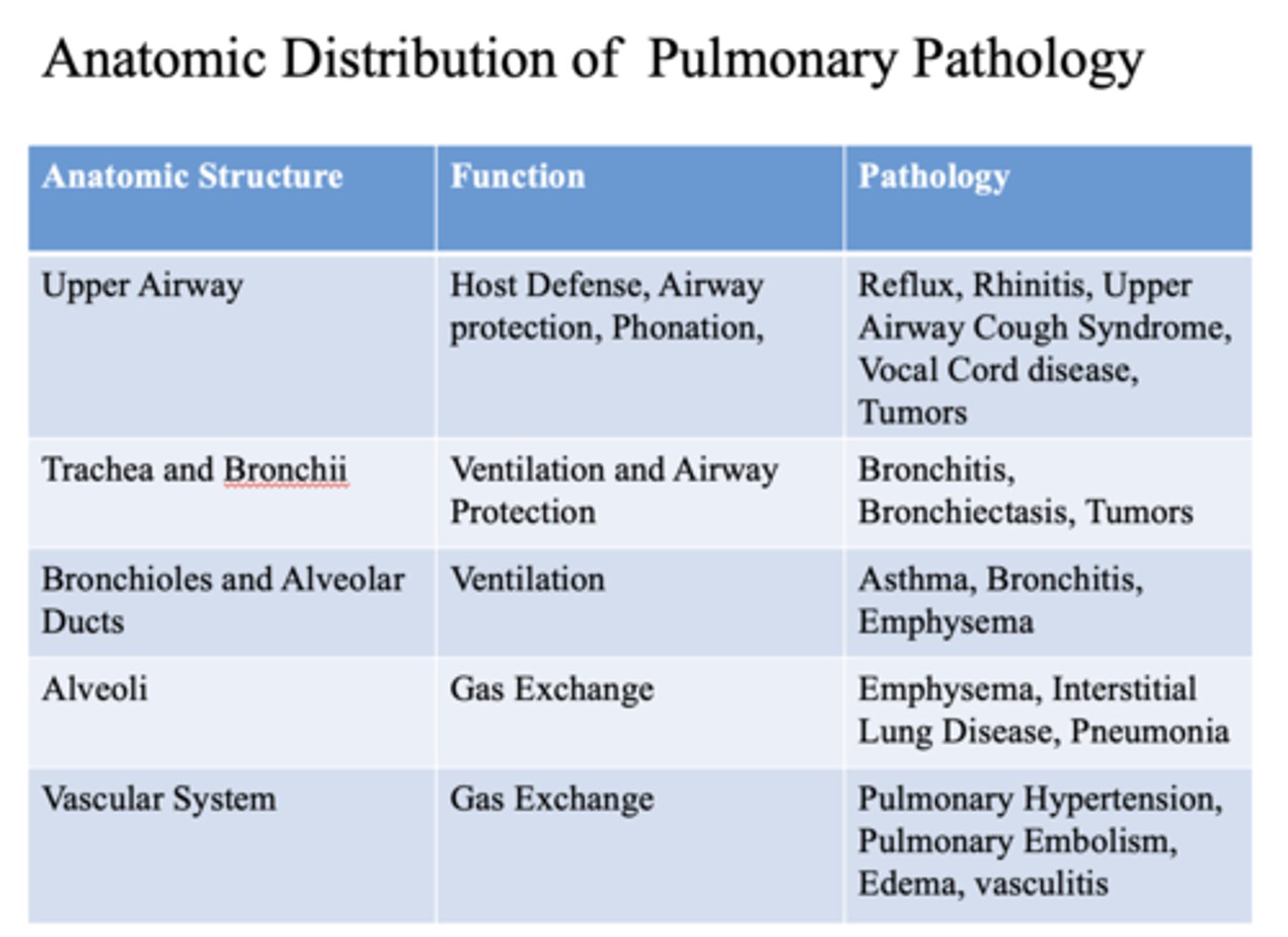
This is a function of what anatomic structure?
- Host Defense
- Airway protection
- Phonation
upper airway
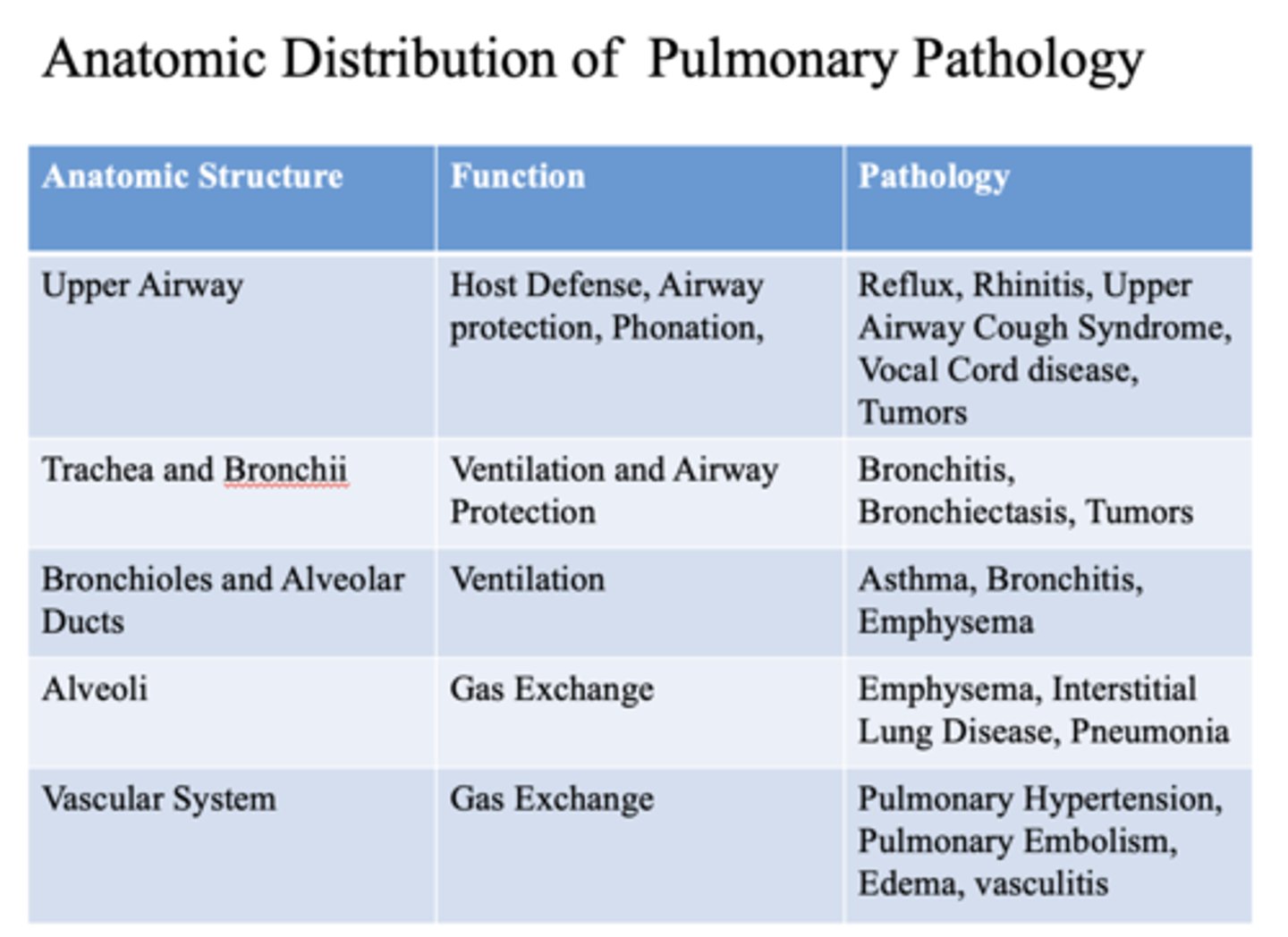
This is a function of what anatomic structure?
- Ventilation
- Airway Protection
- Trachea
- Bronchii
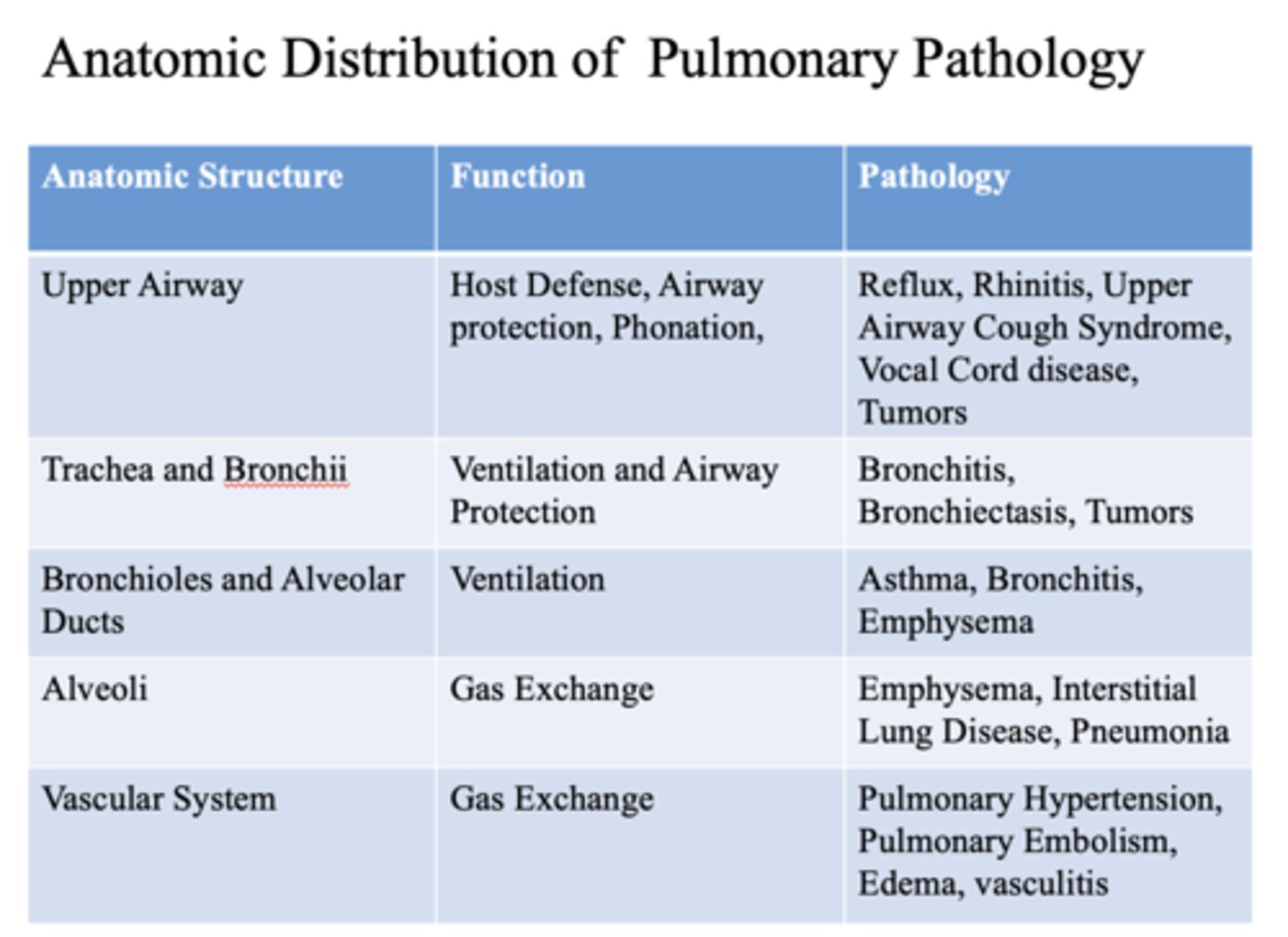
This is a function of what anatomic structure?
Ventilation
- Bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
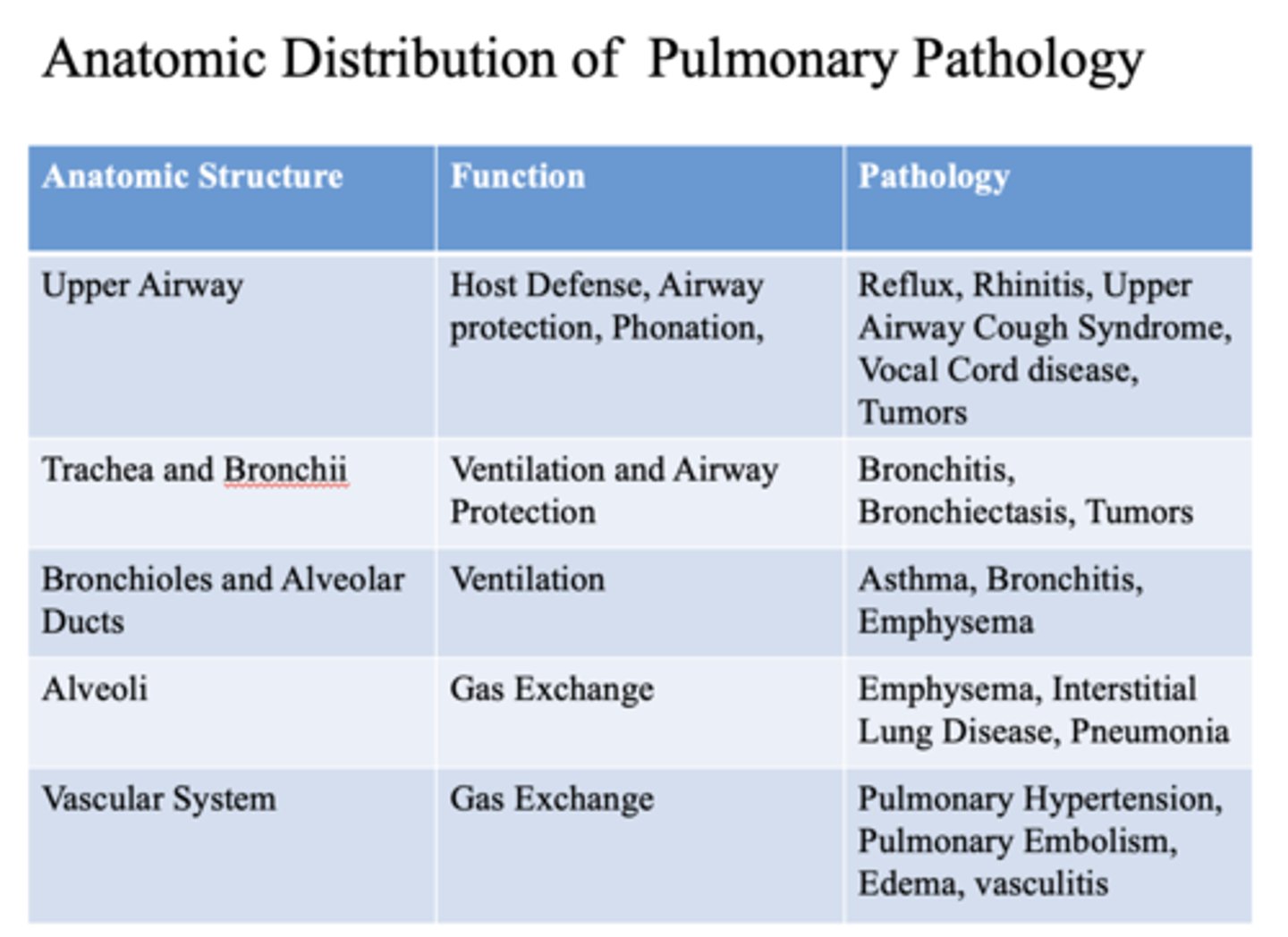
This is a function of what anatomic structures?
Gas exchange
- Alveoli
- Vascular system
What are diagnostic modalities used to diagnose lung disease?
- History and Exam
- Laboratory tests (ABG)
- Pulmonary Function Studies
- Radiology
- Bronchoscopy
- Pathology

When taking pulmonary history, these are all what?
- Dyspnea
- Cough
- Wheezing
- Hemoptysis
- Sleepiness
- Snoring
- AM headache
- Allergy symptoms
- Sinus congestion
- Throat clearing
symptoms

When taking pulmonary history, these are all what?
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Joint pains
- Orthopnea
- LE edema
- Dysphagia
- Dry eyes/dry mouth
- Rash
systemic symptoms

When taking pulmonary history, these are all what?
- Smoking
- Occupation
- Hobbies
- Pets
- Travel
social history

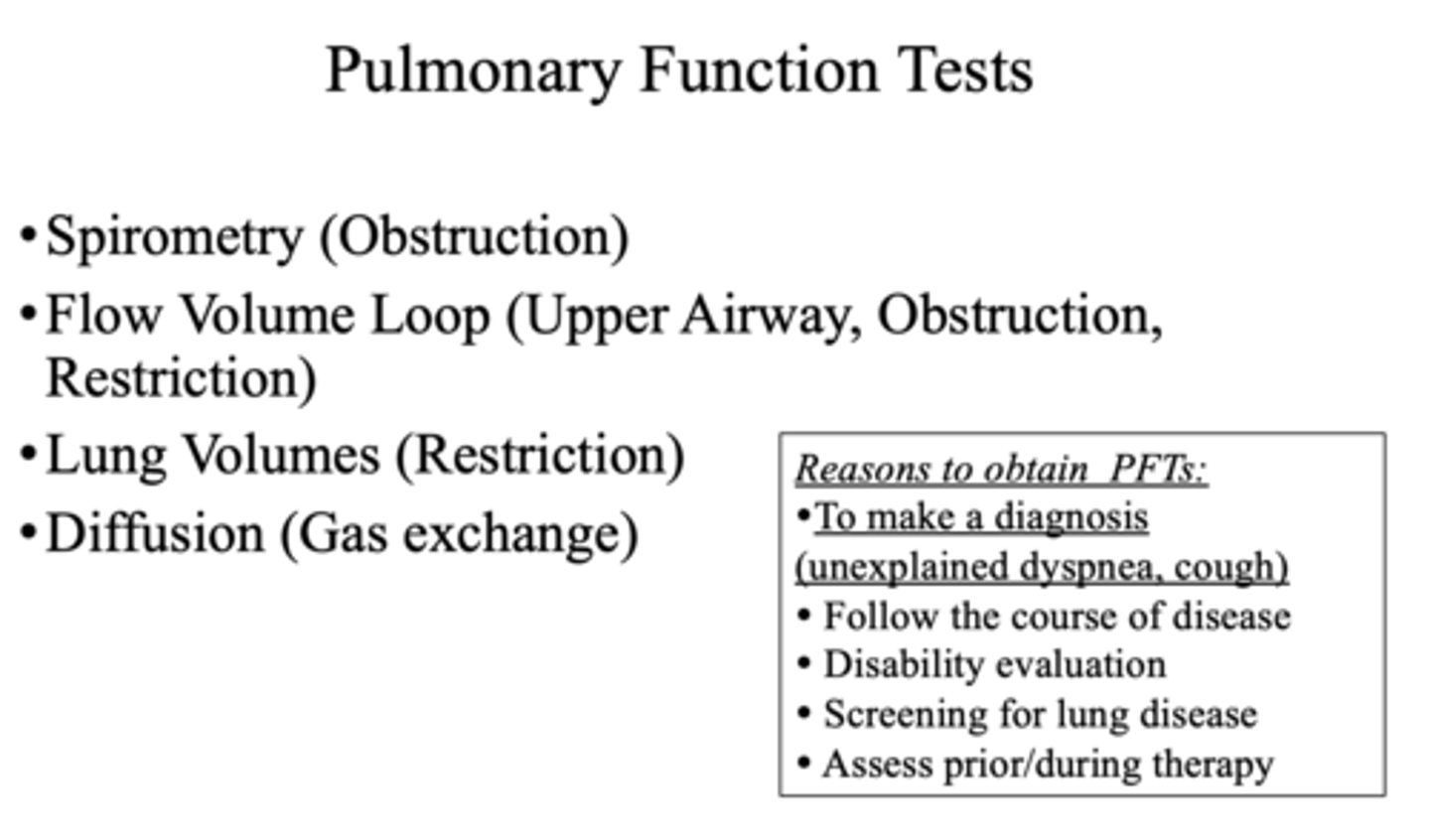
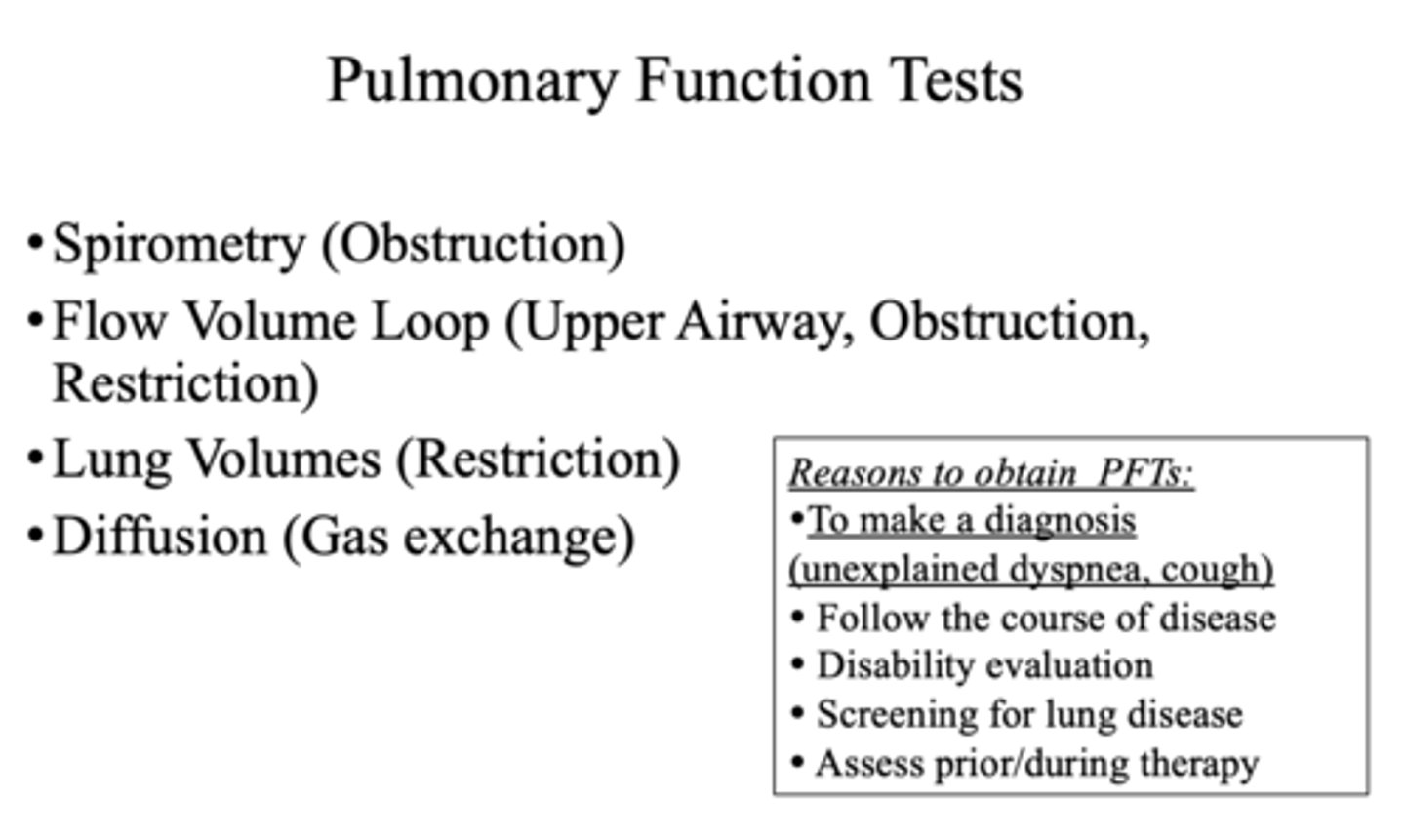
Spirometry is used to test ___________ and lung volumes are used to test ___________
Obstruction, Restriction
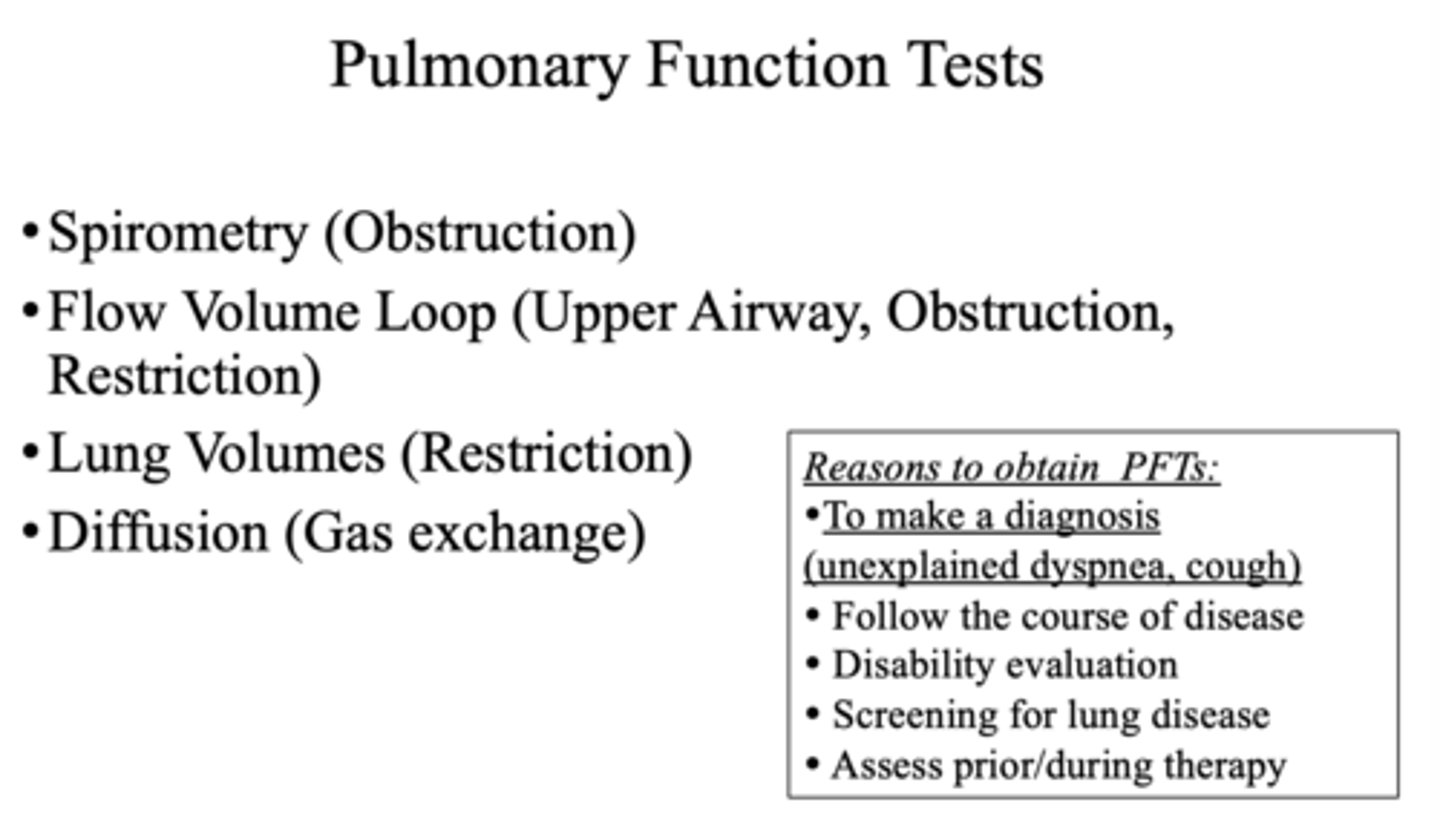
What pulmonary function test can test the upper airway, obstruction, and restriction?
Flow volume loop
The respiratory system includes structures starting from _____ down to _______
nares, alveoli

How is pathology diagnosed and categorized?
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs)
If FEV1/FVC <0.7, is it obstruction or restriction?
Obstruction
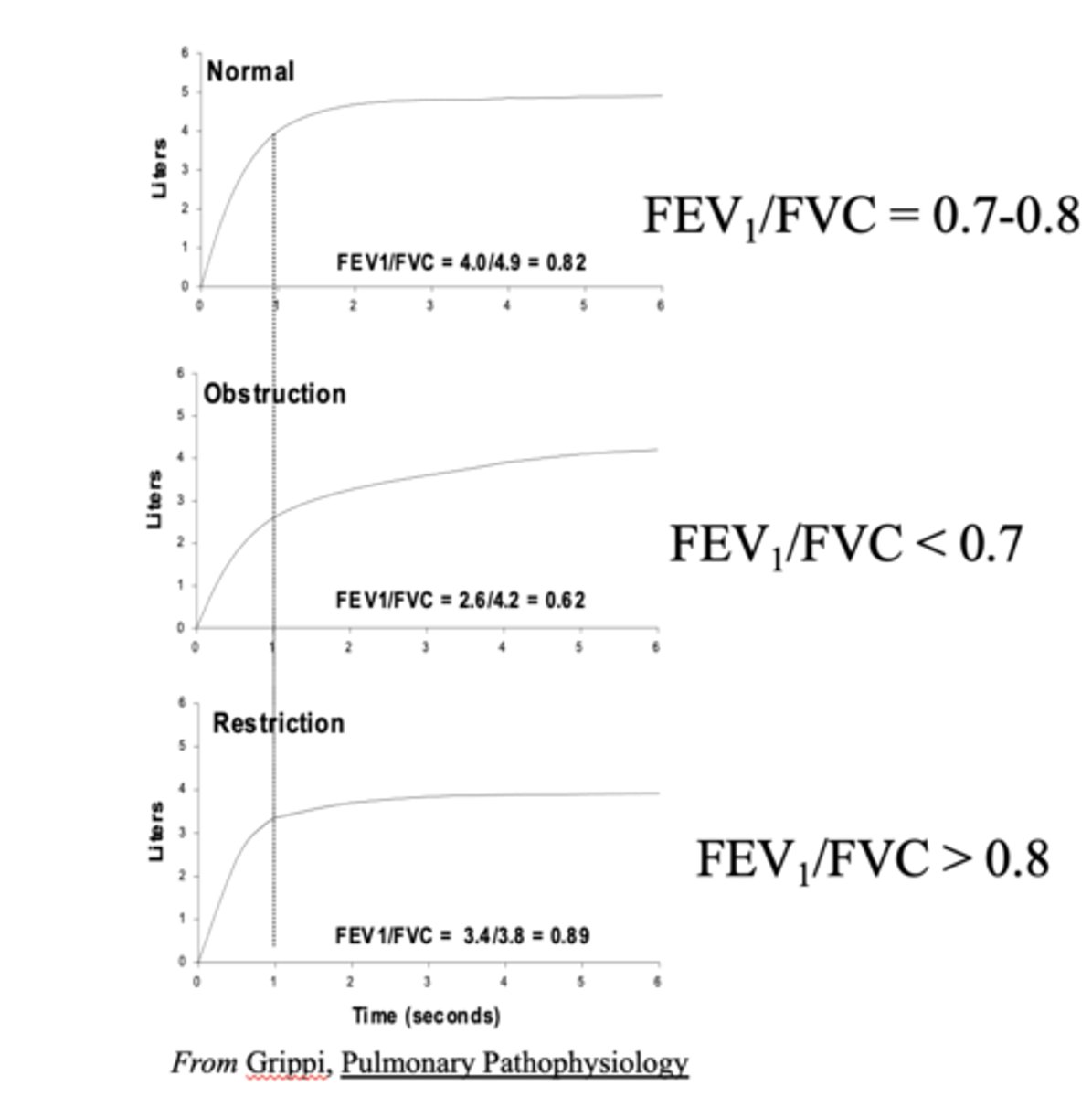
If FEV1/FVC >0.8 is it obstruction or restriction?
Restriction
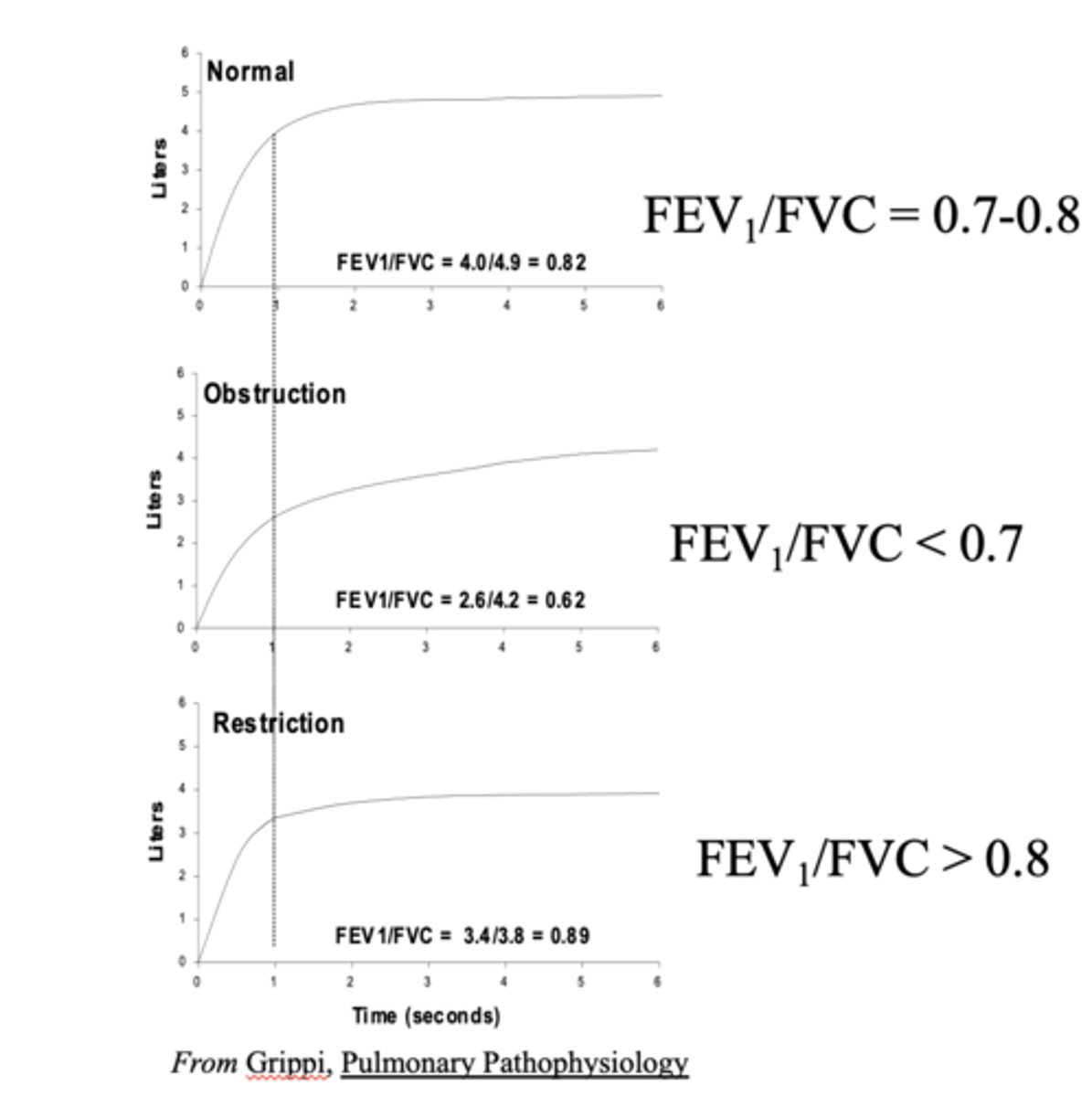
Obstructive disease (asthma, emphysema) leads to trouble exhaling and hyperinflation which manifest as _______ Total Lung Capacity (TLC) on PFTs
increased
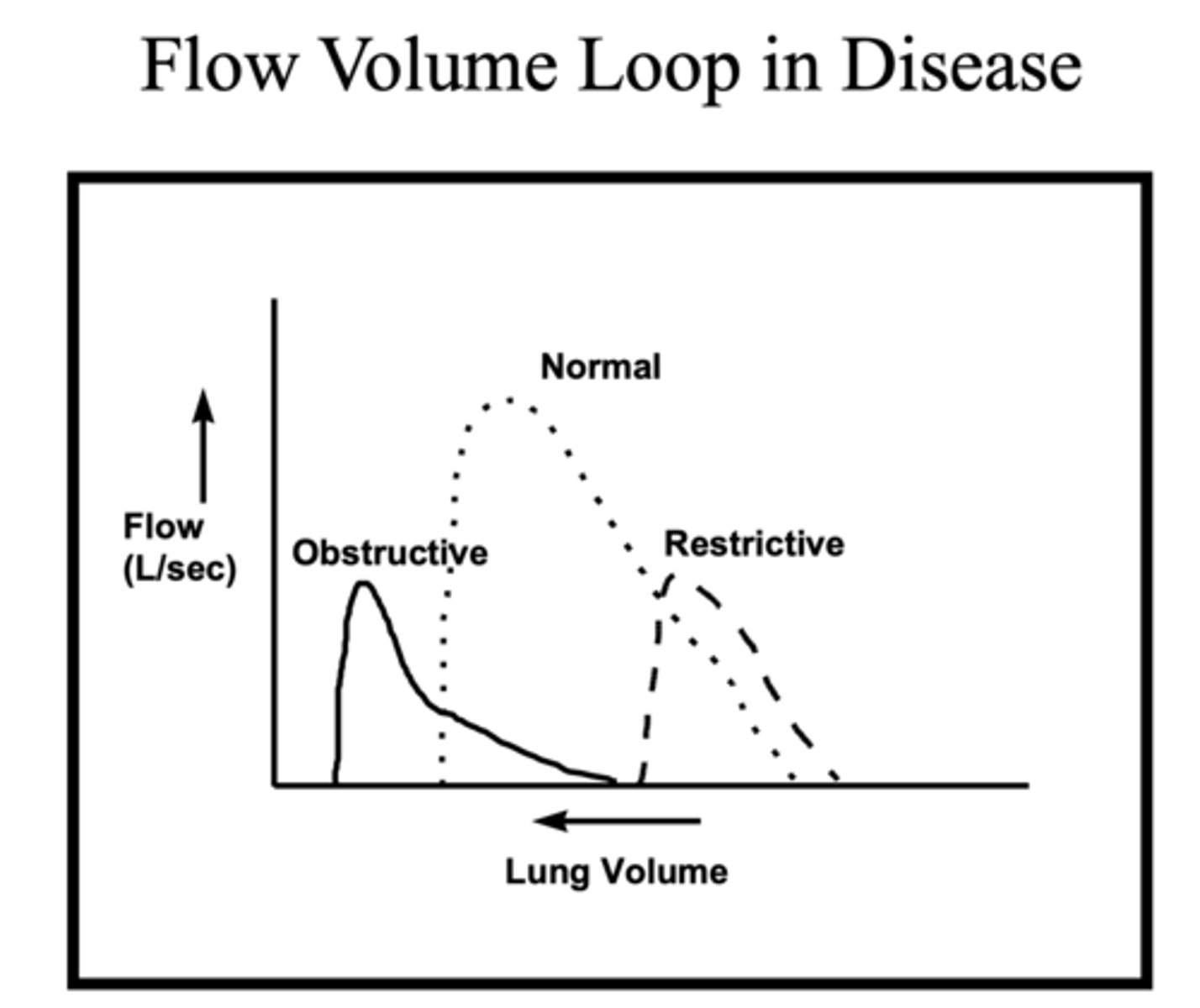
When a lung disease principally manifests as disease of the airways, with increased airways resistance, it is called ________
obstructive

Any process that abnormally narrows airway radius will result in ______ airway resistance
increased

The following are abnormal factors that influence _________:
- Smooth Muscle hypertrophy
- Mucus Glands (Goblet Cells)
- Epithelium
- Airway wall
Airway radius

Categories of obstructive lung diseases uses the acronym FACES which stands for what?
- Foreign body
- Asthma
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Small airways disease

Case study:
A 50 year old woman presents with one year of increasing dyspnea & productive cough. She smoked 2ppd for 35 years On exam she uses accessory respiratory muscles to breathe. Respiratory rate is 24. Chest exam notable for poor air entry, expiratory wheezing, prolonged expiratory phase (I/E 1/5), positive Hoovers sign, and thoraco-abdominal paradox.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Pulmonary fibrosis
B. Emphysema
C. Pleural Effusion
B. Emphysema

What is a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, expectoration, exacerbations) due to abnormalities of the airway (bronchitis, bronchiolitis) and/or alveoli (emphysema) that cause persistent, often progressive, airflow obstruction.
COPD

What is a chronic productive cough for 3 months of two consecutive years in a patient in whom other causes of chronic cough has been excluded?
chronic bronchitis

What is an abnormal and permanent enlargement of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, accompanied by destruction of their walls and occurs without obvious fibrosis?
emphysema

The following are all things to consider for what diagnosis?
In patient > 40 years old with:
- Chronic cough
- Chronic sputum production
- Progressive dyspnea
- History of exposures (> 1 pack of cigarettes x 20 years)
- Obtain spirometry
COPD

What happens to the airway with a loss of radial traction?
Airway collapse in expiration
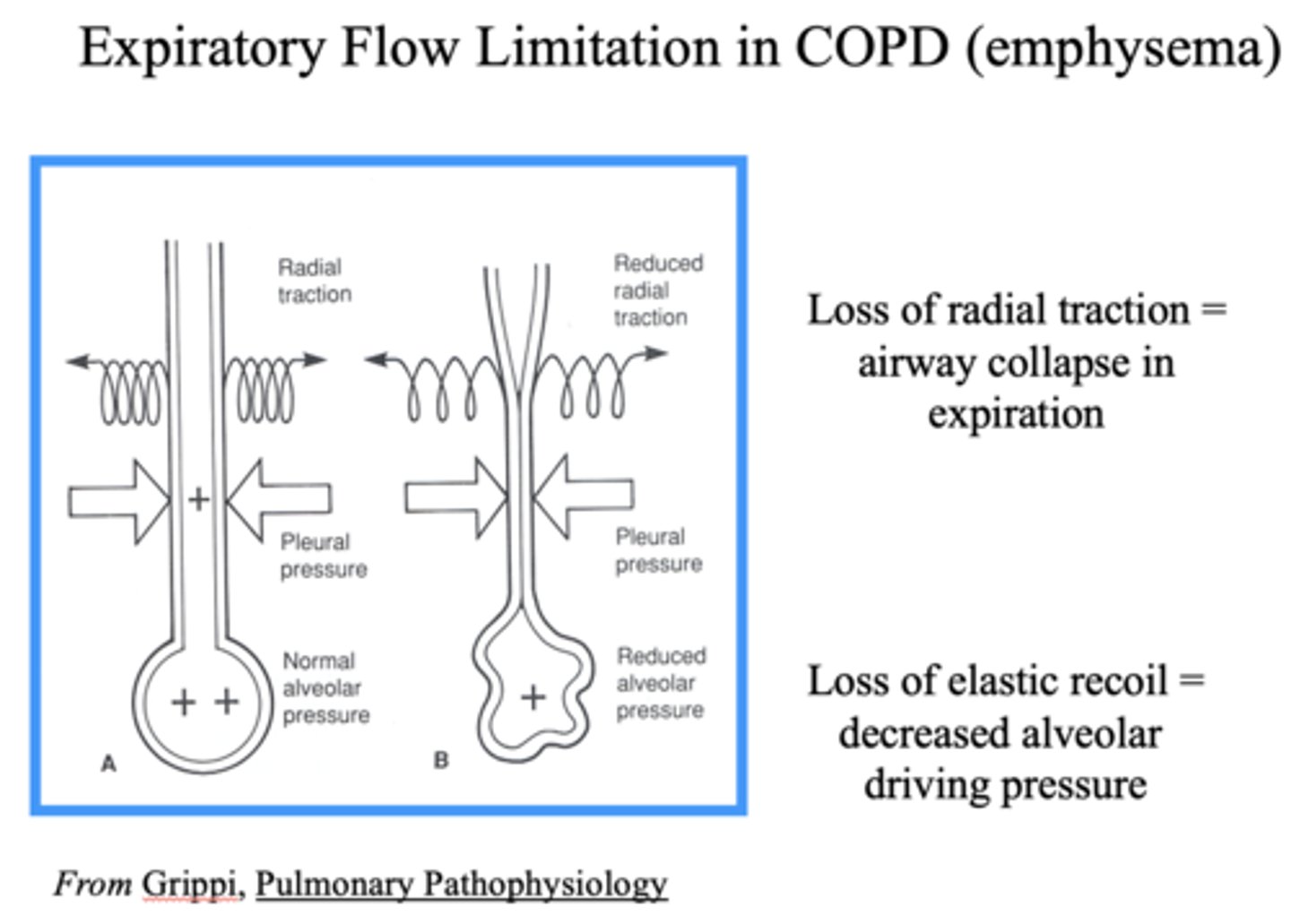
What happens to the alveoli with a loss of elastic recoil?
Decreased alveolar driving pressure
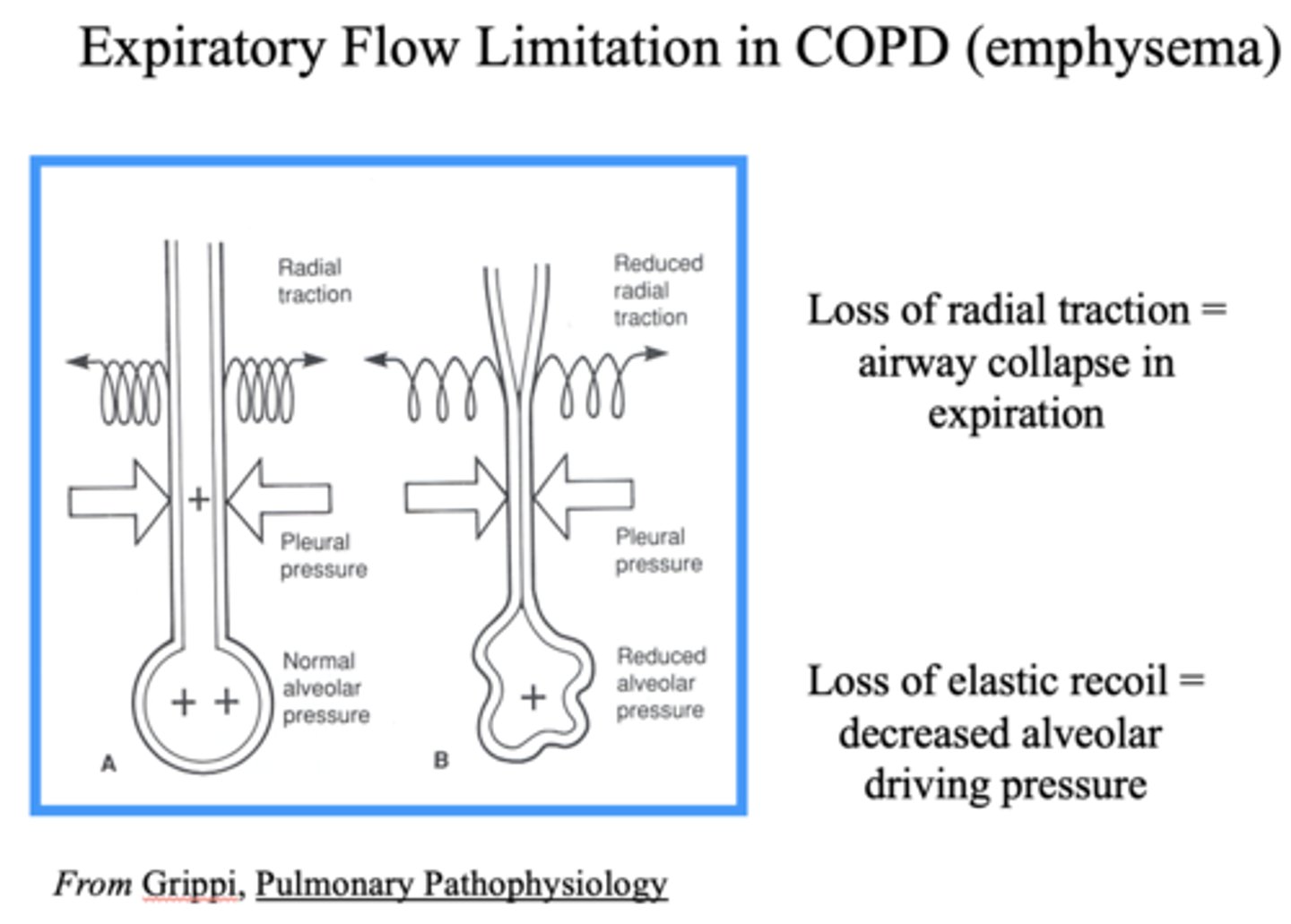
Define the following:
Decrease symptoms, decrease exacerbations, improve quality of life
Inhalers

What is a common side affect of anticholinergics for inhaled bronchodilators?
Dry mouth

What do you use to treat inflammation in asthma patients?
inhaled corticosteroids

What is the goal of pulmonary rehabilitation?
- Increase exercise capacity
- Increase quality of life
- Reduce dyspnea

Since smoking cessation is difficult, what has a greater efficacy?
Combination of behavioral counseling and pharmacotherapy
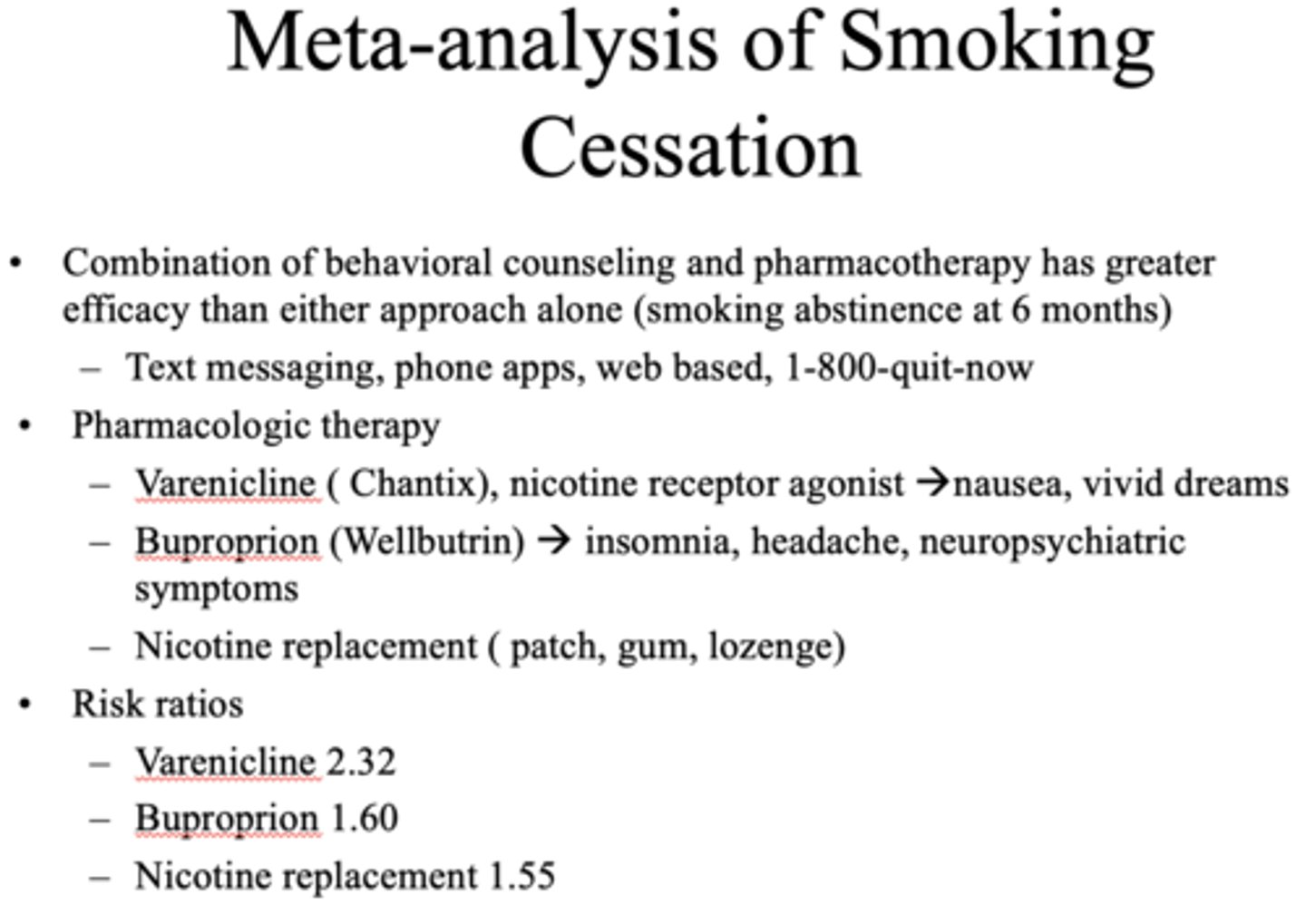
What are the five steps in the US Preventive Services Task Force Guidelines?
1. ASK about tobacco
2. ADVISE quitting
3. ASSESS readiness
4. ASSIST
5. ARRANGE follow-up

Case Study:
A 35 year old woman presents with 2 months of coughing that was triggered by an upper respiratory infection. She denies smoking, but her parents smoked when she was a child. On exam she is not using accessory respiratory muscles to breathe. Respiratory rate is 20. Chest exam notable for good air entry and scattered expiratory wheezes. Cardiac exam is normal. Spirometry at her visit was normal.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Pulmonary fibrosis
B. COPD
C.Asthma
C.Asthma

Define the following:
Chronic inflammatory disease of airways:
- Intermittent airflow obstruction
- Bronchoconstriction & airway edema
- Airway hyperresponsiveness & remodeling
Asthma

Asthma is an inflammatory disease usually affecting what patient population?
younger patients

What should you avoid if you have asthma?
triggers (allergies, cold air, perfume)

What causes airway inflammation in individuals with asthma?
- Overproduction of Th2 cytokines
- Activated allergy-associated cells
- Airway physiological abnormalities
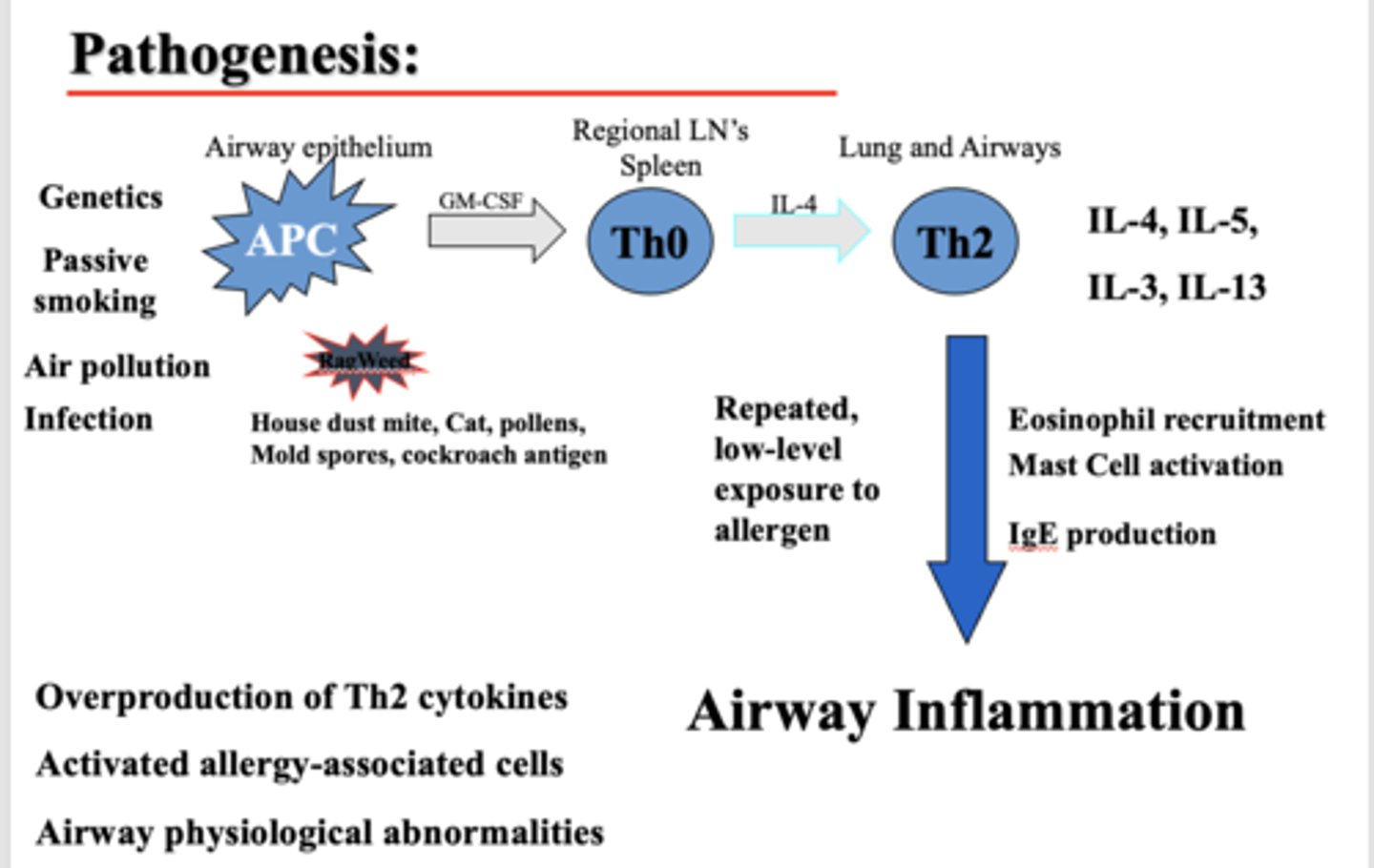
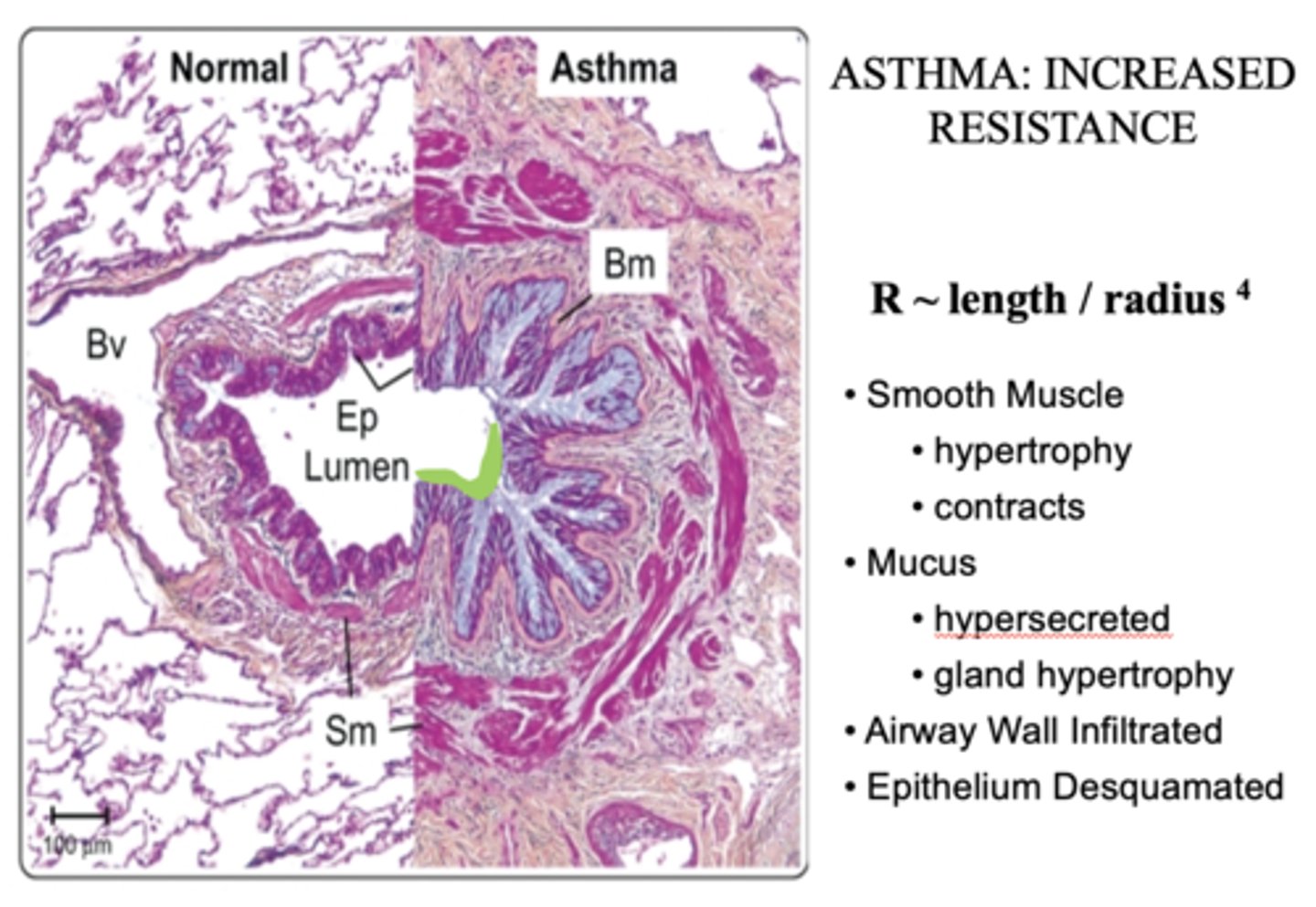
Does resistance increase or decrease in asthma?
Increase (decreased radius from inflammation)
Inhaled corticosteroids can cause _________
Thrush

What has the following functions?
- Maintains Patency & Stability Of the Upper Airway
- Swallowing/close airway
- Manage secretions/cough
Upper Airway ("Bulbar") Muscles
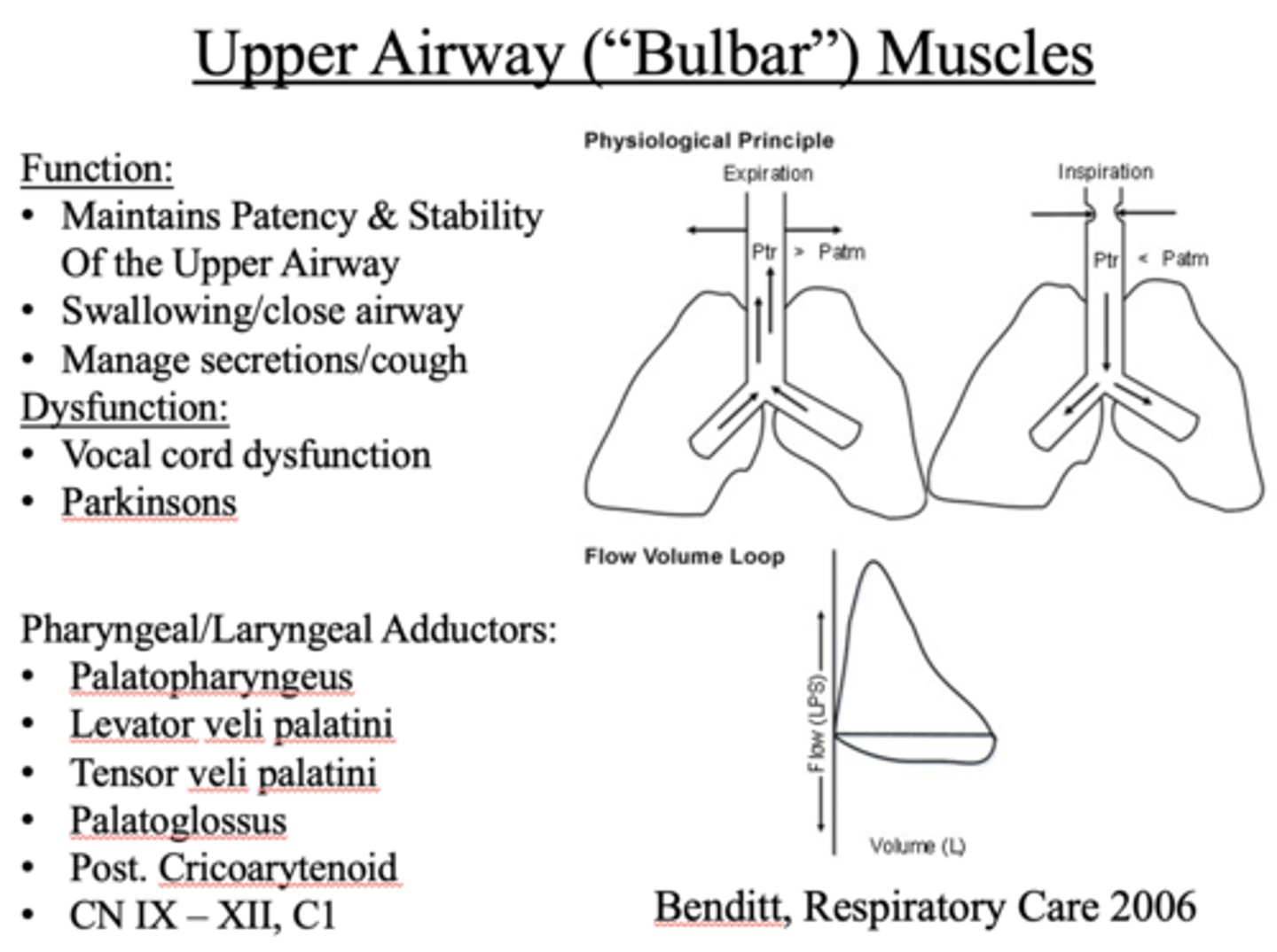
What is a major concern with conscious sedation?
Decreases function of upper airway muscles

Case Study:
A 65 year old woman presents with one year of increasing dyspnea, fatigue & cough. She has a prior smoking history but quit 20 years ago. On exam her respiratory rate is 30. Chest exam is notable for velcro crackles posteriorly. Extremity exam reveals clubbing. Her O2 saturation by pulse oxymeter is 94% at rest, but drops to 88% with exertion.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Pulmonary fibrosis
B. Emphysema
C. Asthma
A. Pulmonary fibrosis

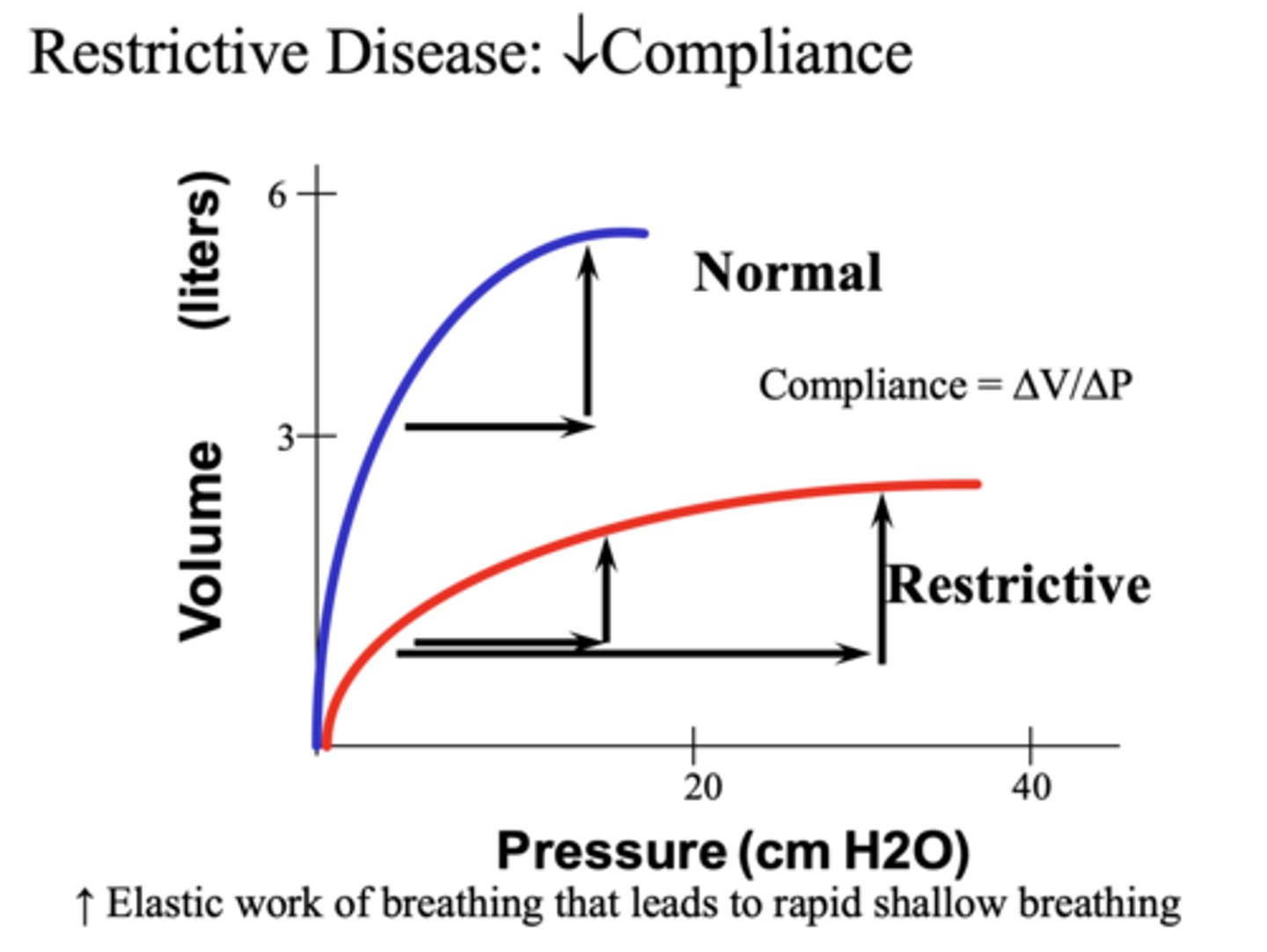
___________ disease (e.g. pulmonary fibrosis) is characterized by decreased compliance (more work to generate a change in volume)
Restrictive

The pathophysiologic correlate of Restrictive Lung Disease is a ___________ compliance
Reduced (increased pressure is required to distend the lung a given volume).

In restrictive diseases, we see a _______ total lung capacity on PFTs
decreased
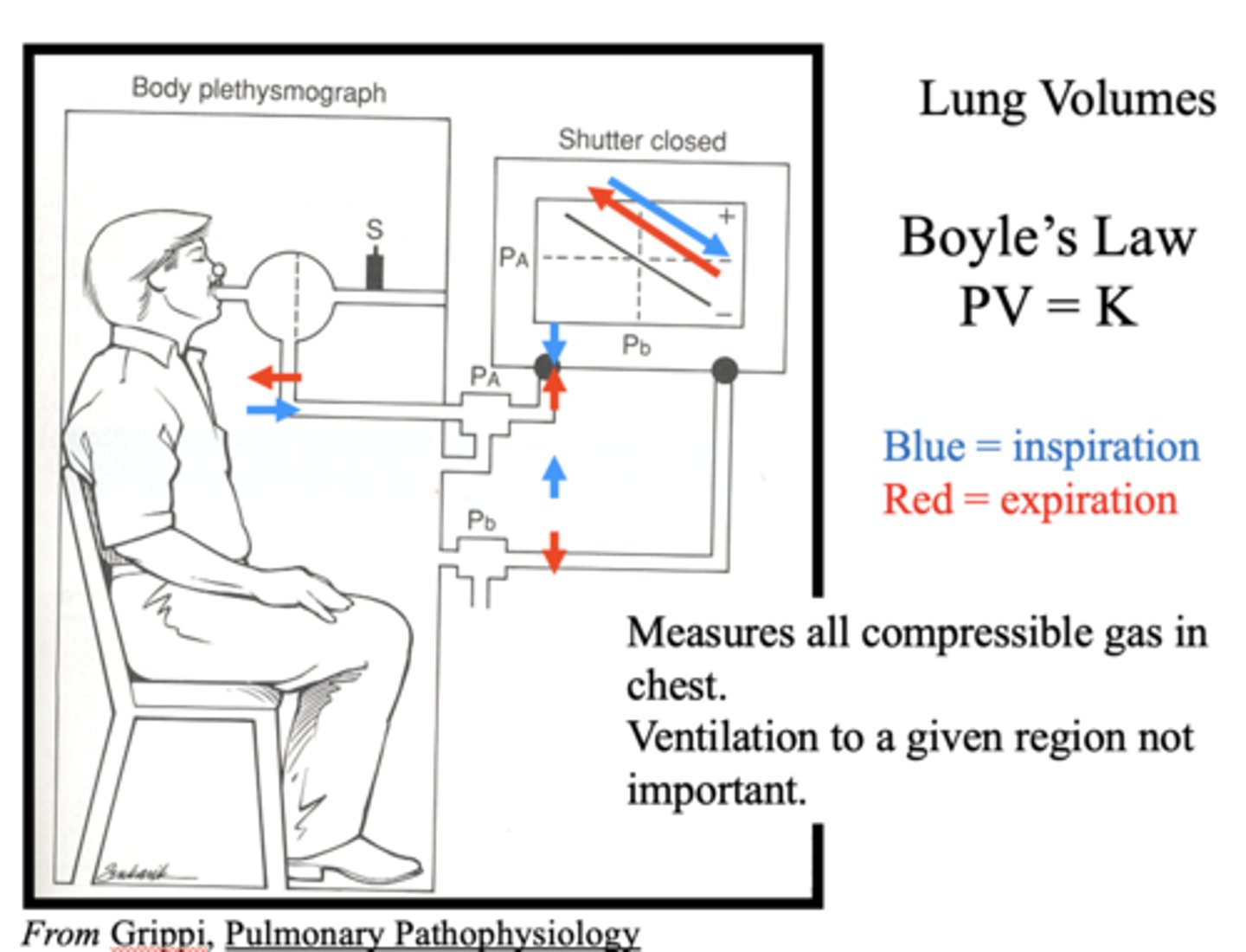
Which law is the following:
PV = K
Boyle's Law
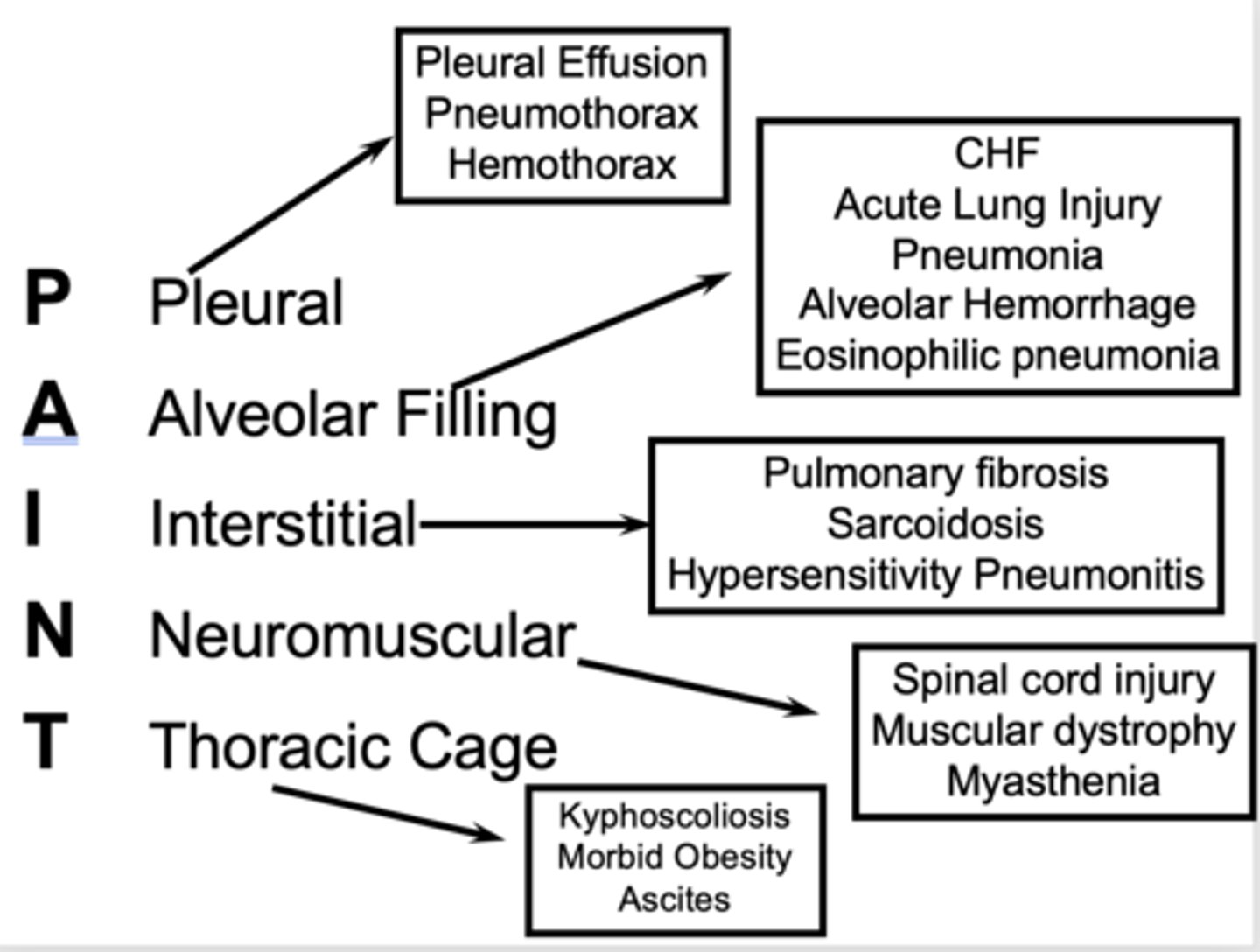
For categories of restrictive lung diseases, PAINT is the acronym used. What does it stand for?
- Pleural
- Alveolar filling
- Interstitial (pulmonary fibrosis)
- Neuromuscular
- Thoracic cage
Pre-procedural screeing is about what two things for pulmonary complications?
- Identifying risks
- History taking

What can cause respiratory complications for all, especially those with OSA?
conscious sedation (BZDs, opioids)

_______ is characterized by repetitive upper airway obstruction with subsequent catecholamine surges that leads to cardiovascular morbidity (hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction etc.)
OSA

______ symptoms include excessive sleepiness and sometimes, is difficult to distinguish from generic sleep deprivation
OSA

What disease has risks that include large neck size, snoring, redundant upper airway tissue?
OSA

These are treatments for what?
- Weight loss
- Avoiding alcohol at night
- MAD
- CPAP
OSA

Where is the major site of infection of TB?
Lungs

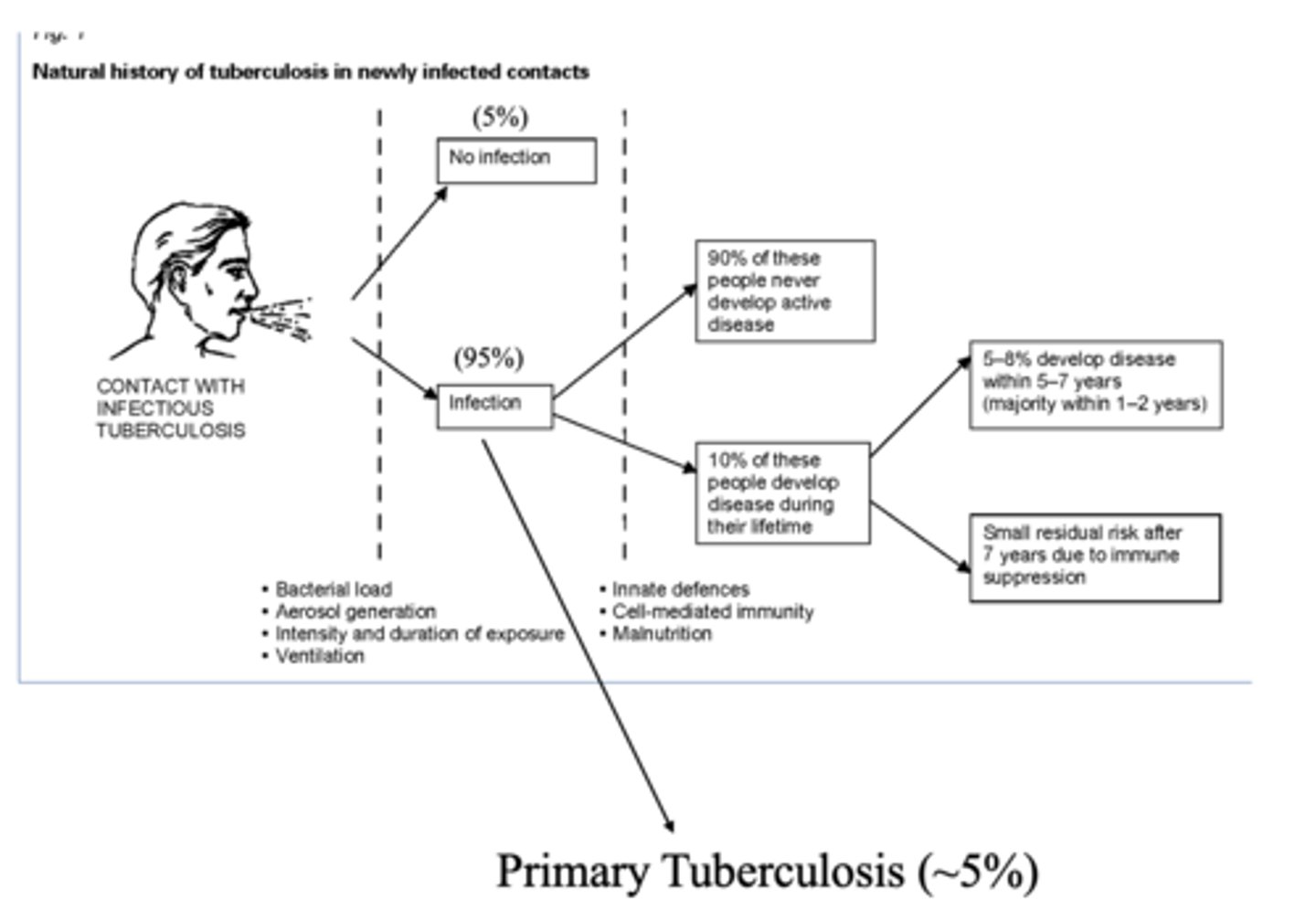
T/F: 90% of people with TB infection will never develop the active disease
true
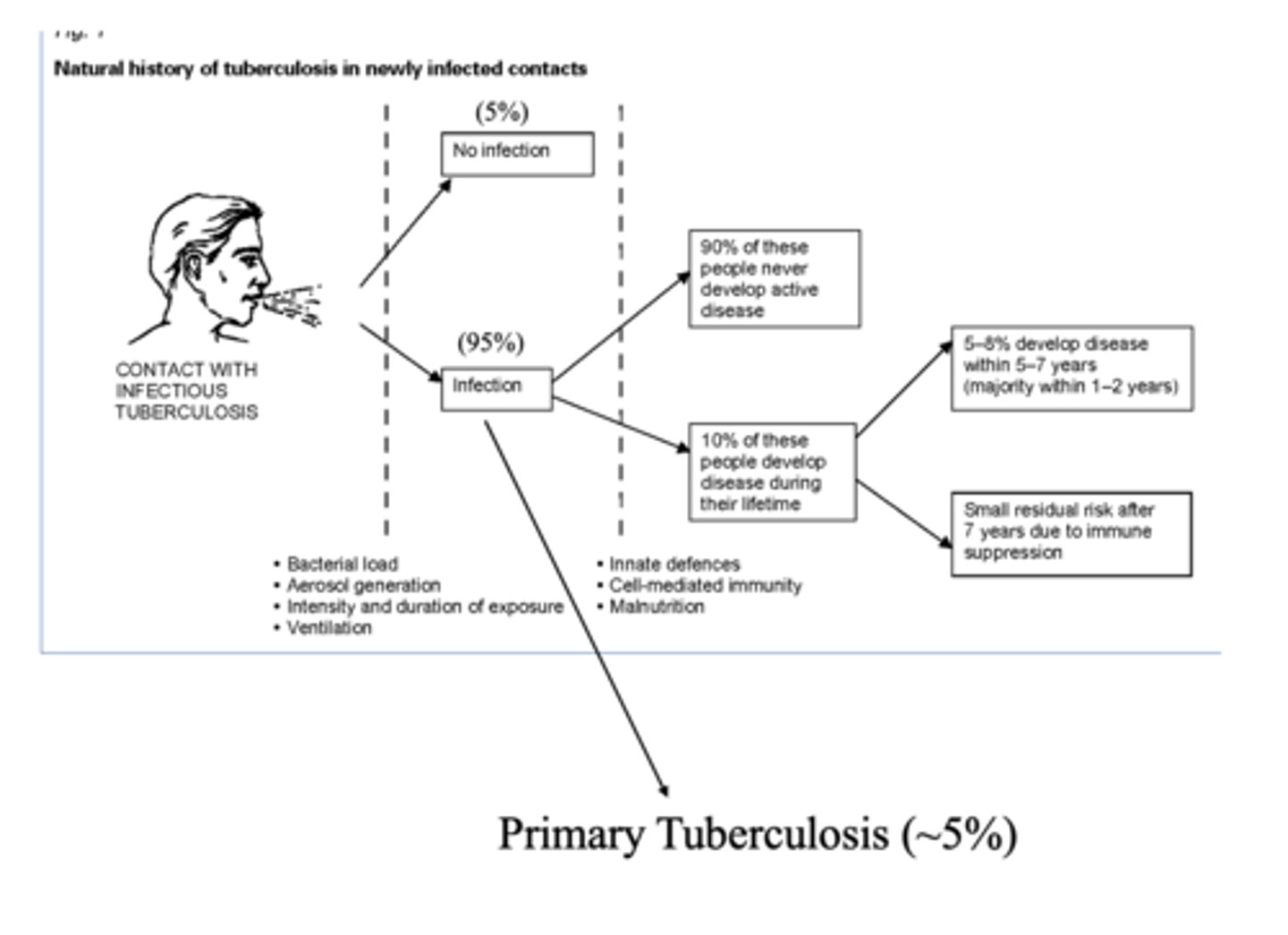
What percent of people with TB infection develop primary TB?
~5%
Tuberculosis is ________
endemic

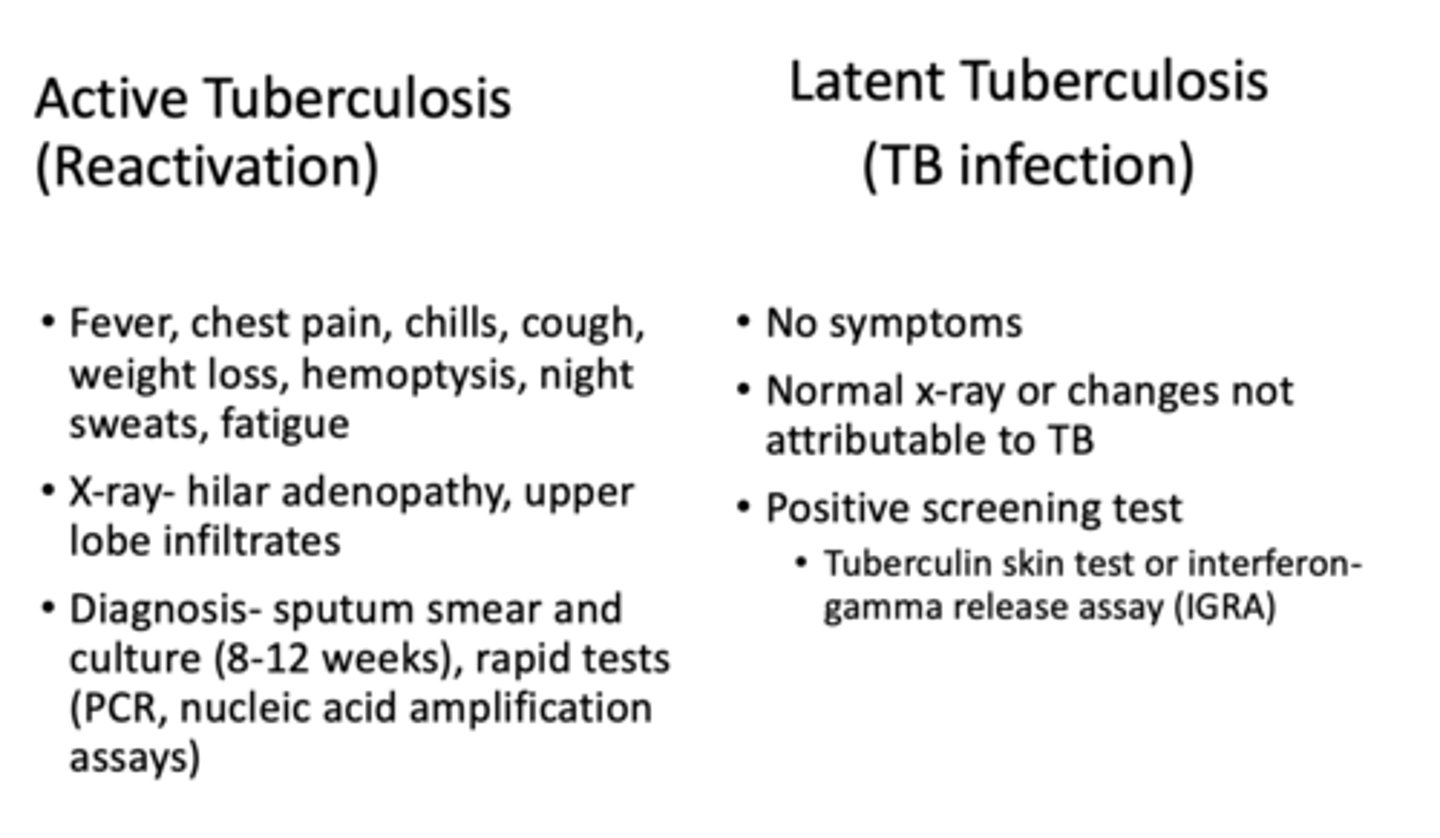
What type of TB would have a positive skin test, no symptoms, normal x-ray?
latent
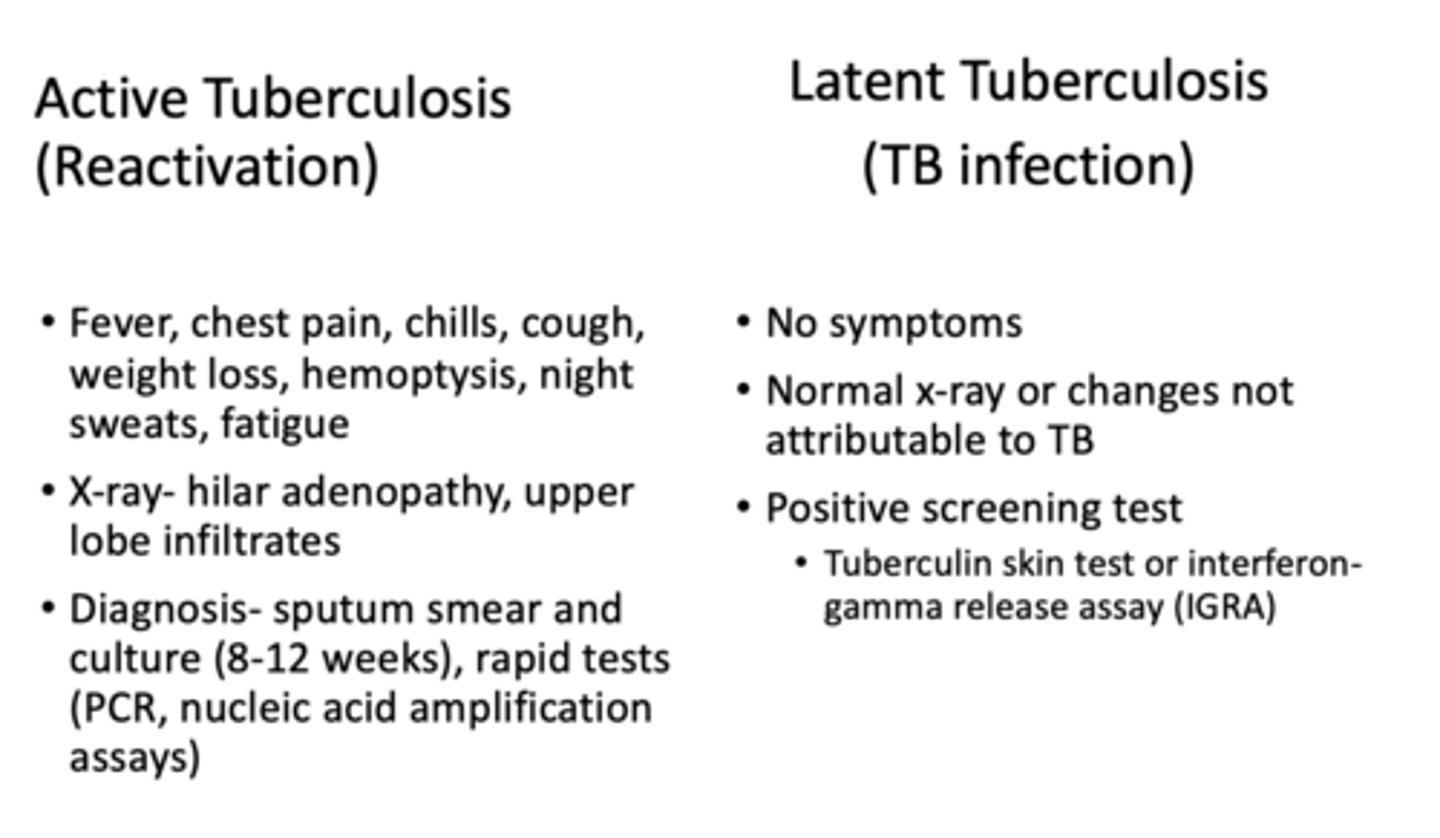
What type of TB would have +/- skin test, positive symptoms and an abnormal x-ray?
active
What has the following characteristics?
Delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in persons with MTB infection
- Measure reaction 48-72 hr (induration)
Tuberculin Skin Testing

What two tests for TB are the most common?
- TB skin test
- Blood assay (Quantiferon)

These are risks for developing what ?
- HIV
- Diabetes
- Alcohol use disorder
- Close tuberculosis contact
- Health care worker
- Incarceration
active TB

What is the drug for treating latent TB?
Rifampin

T/F Treatment for latent tuberculosis (to prevent active tuberculosis) is much different than treatment for active tuberculosis (1 drug versus 4 drugs)
true
