TEST FOR UNIT VI
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
Muhammad: (570 to 632 CE)
1. Founder of Islam who was also a military and political leader
2. Muslims believe he was greatest prophet of Allah (God)
3. Led Muslim armies who conquered much of the surrounding territory
2
New cards
**Hijrah**
**-**The hostilities aroused in Mecca led Muhammad to encourage his followers to emigrate to the city of Medina.
\-He left Mecca and reached Medina on Sept. 24, 622.
\-This flight is called hijrah in Arabic and has come into English as Hegira. It provides the starting date for the history of Islam.
\-He left Mecca and reached Medina on Sept. 24, 622.
\-This flight is called hijrah in Arabic and has come into English as Hegira. It provides the starting date for the history of Islam.
3
New cards
**Five Pillars of Islam:**
1. A profession of faith “Allah is the only God, and his prophet was Muhammad”
2. To give to charity and the poor
3. Making a Haji (pilgrimage or holy journey) to Mecca ONCE in their lifetime
4. Prayer 5 times a day
5. Fasting during the month of Ramadan
4
New cards
**“People of the Book”**
Jews and Christians (tolerated and treated with some respect)
5
New cards
Umayyad Caliphate: (661 to 750)
1. Took over after last “rightly guided” caliph murdered in struggle for power
2. Moved capital to Damascus in Syria
3. Many Muslims felt they were too concerned with wealth and power and not true to Muhammad’s/Qu’ran’s teachings
6
New cards
Abisaid Caliphate:
Abbasid Caliphate (750 to 1258)
1. Overthrew the Umayyads in 750
2. Moved the capital to Baghdad
3. Controlled trade routes in central Asia
4. Ended in 1258 when the Mongols destroyed Baghdad and killed the caliph D. Other Caliphates
1. One Umayyad prince fled from Abbasids and established a Umayyad caliphate in Spain that lasted until 1031
2. The Shia Fatimid caliphate ruled north Africa and parts of Middle East (909 to 1171)
1. Overthrew the Umayyads in 750
2. Moved the capital to Baghdad
3. Controlled trade routes in central Asia
4. Ended in 1258 when the Mongols destroyed Baghdad and killed the caliph D. Other Caliphates
1. One Umayyad prince fled from Abbasids and established a Umayyad caliphate in Spain that lasted until 1031
2. The Shia Fatimid caliphate ruled north Africa and parts of Middle East (909 to 1171)
7
New cards
**Golden Age of Islam:**
* ibn al-Haythm invented the first camera and was able to form an explanation of how the eye sees
* Doctor and philosopher Avicenna wrote the Canon of Medicine, which helped physicians diagnose dangerous diseases such as cancer
* Al-Khwarizmi, a Persian mathematician, invented algebra, a word which itself has Arabic roots
* established a House of Wisdom in Baghdad—a dedicated space for scholarship.
* made a special effort to recruit famous scholars to come to the House of Wisdom. Muslims, Christians, and Jews all collaborated and worked peacefully there
* coincided with Europe dark age
* -Arabian Peninsula, Mediterranean, north Africa
* -Qu’ran and hadith influence
* -science art and commerce
* -first astronomical observatory and closest to modern day math
* -smallpox vs measles and pharmacies became a constant and there were 24-hour hospital
* -ended with the Mongols and Genghis Khan
* -threw books into Tigris River and river turned black (other conquerors would save architecture and art because it was beautiful)
* Doctor and philosopher Avicenna wrote the Canon of Medicine, which helped physicians diagnose dangerous diseases such as cancer
* Al-Khwarizmi, a Persian mathematician, invented algebra, a word which itself has Arabic roots
* established a House of Wisdom in Baghdad—a dedicated space for scholarship.
* made a special effort to recruit famous scholars to come to the House of Wisdom. Muslims, Christians, and Jews all collaborated and worked peacefully there
* coincided with Europe dark age
* -Arabian Peninsula, Mediterranean, north Africa
* -Qu’ran and hadith influence
* -science art and commerce
* -first astronomical observatory and closest to modern day math
* -smallpox vs measles and pharmacies became a constant and there were 24-hour hospital
* -ended with the Mongols and Genghis Khan
* -threw books into Tigris River and river turned black (other conquerors would save architecture and art because it was beautiful)
8
New cards
**Fatimid Caliphate:**
The Shia Fatimid caliphate ruled north Africa and parts of Middle East (909 to 1171)
9
New cards
sub-Saharan Africa:
Geography of Sub-Saharan Africa
1. most areas cut off from Mediterranean by Sahara Desert
2. diseases spread by tsetse flies in rainforest made it (pronounced “see-see”) hard to domesticate cattle or horses
1. most areas cut off from Mediterranean by Sahara Desert
2. diseases spread by tsetse flies in rainforest made it (pronounced “see-see”) hard to domesticate cattle or horses
10
New cards
Nok:
Nok of West Africa (500 BCE-200 CE)
1. lived in modern day Nigeria
2. made iron tools and weapons and detailed art from terra cotta
3. Few other details available
1. lived in modern day Nigeria
2. made iron tools and weapons and detailed art from terra cotta
3. Few other details available
11
New cards
Djenné-Djenno: (250 BCE-1400 CE)
1. oldest known African city south of Sahara located in modern day Mali
2. prior to its discovery in 1977, most historians assumed little culture existed in this region that early
12
New cards
Ghana Empire:
Empire of Ghana (c. 800 to 1100 CE)(middle ages in europe)
1. Use of camels made trans-Saharan trade easier by 200 CE
2. Ghana become major power by controlling/taxing gold-salt trade (gold from West Africa, salt from the Sahara)
3. Rulers and upper class convert to Islam but most continue to follow animism\*
4. Invasions by Muslims from the north and shifting trade routes weaken Ghana
1. Use of camels made trans-Saharan trade easier by 200 CE
2. Ghana become major power by controlling/taxing gold-salt trade (gold from West Africa, salt from the Sahara)
3. Rulers and upper class convert to Islam but most continue to follow animism\*
4. Invasions by Muslims from the north and shifting trade routes weaken Ghana
13
New cards
**trans-Saharan trade:**
Use of camels made trans-Saharan trade easier by 200 CE
14
New cards
**gold-salt trade:**
Ghana become major power by controlling/taxing gold-salt trade (gold from West Africa, salt from the Sahara)
As Ghana weakened, Mali emerged as new power and also controlled gold-salt trade along with trade of enslaved people
As Ghana weakened, Mali emerged as new power and also controlled gold-salt trade along with trade of enslaved people
15
New cards
**Mali Empire:**
Empire of Mali (1235 to 1400s)
1\. As Ghana weakened, Mali emerged as new power and also controlled gold-salt trade along with trade of enslaved people
2\. Sundiata Keita (1235-1255) AKA “The Lion King”
1\. As Ghana weakened, Mali emerged as new power and also controlled gold-salt trade along with trade of enslaved people
2\. Sundiata Keita (1235-1255) AKA “The Lion King”
16
New cards
**Sundiata Keita:**
Sundiata Keita (1235-1255) AKA “The Lion King”
a. considered the first emperor of Mali
b. came to power by overthrowing an unpopular leader
c. according to legend, his use of cavalry (soldiers on horses) provided advantage over infantry (foot soldiers)
d. appointed skilled administrators to help him rule
a. considered the first emperor of Mali
b. came to power by overthrowing an unpopular leader
c. according to legend, his use of cavalry (soldiers on horses) provided advantage over infantry (foot soldiers)
d. appointed skilled administrators to help him rule
17
New cards
**Mansa Musa:**
Mansa Musa (1312-1332)
a. Sundiata’s grandnephew “?”
b. was strong leader who expanded empire
c. divided empire into provinces to help rule more efficiently
d. was Muslim so took hajj to Mecca c. 1325
e. made city of Timbuktu a center of Muslim learning
\-brought riches and wealth/gold
a. Sundiata’s grandnephew “?”
b. was strong leader who expanded empire
c. divided empire into provinces to help rule more efficiently
d. was Muslim so took hajj to Mecca c. 1325
e. made city of Timbuktu a center of Muslim learning
\-brought riches and wealth/gold
18
New cards
**Timbuktu:**
a center of Muslim learning in sub-saharan Africa
19
New cards
**Sunni Ali:** (1464 to 1492)
created Songhai empire with army of war canoes and riders on horseback
20
New cards
Askia Muhammad
Askia Muhammad (1493 to 1538) overthrew Sunni Ali’s son because he was not a devout enough Muslim
21
New cards
Songhai Empire
Songhai replaced Mali; also controlled gold-salt (and enslaved person) trade, Empire falls to Moroccans from North Africa armed with gunpowder and cannons (1591)
22
New cards
**Ibn Battuta:**
Ibn Battuta wanted to go to Mecca to complete his hajj, he wanted to learn from scholars about Islam
\-great Muslim Explorer
\-Moroccan
\-30 year journey
\-originally traveled to Alexandria, Cairo, Damascus, Mecca
\-he became a traveling judge
\-he is the only known medieval traveler to have visited the lands of every Muslim ruler of his time
\-great Muslim Explorer
\-Moroccan
\-30 year journey
\-originally traveled to Alexandria, Cairo, Damascus, Mecca
\-he became a traveling judge
\-he is the only known medieval traveler to have visited the lands of every Muslim ruler of his time
23
New cards
Kingdom of Benin:
1. founded c. 1200
2. c.1500, controlled much of West Africa
3. 1480s, begin trading with Portuguese traders (ML)
24
New cards
**Benin Bronzes:**
Important artifacts called Benin Bronzes were stolen by British and other Western colonizers
25
New cards
**Great Zimbabwe:**
Great Zimbabwe controlled gold trade in Southern Africa (c. 1000 to 1400)
a. Abandoned by 1450 for unknown
reasons
b. Ruins “discovered” by Europeans in
1871 are only source of info
GREAT ENCLOSURE:
The greatest accomplishment in sub-saharan africa
Curved walls up to 4 story tall buildings
1m stone blocks
Stones were stacked NOT CONNECTED with anything just straight up stacked
a. Abandoned by 1450 for unknown
reasons
b. Ruins “discovered” by Europeans in
1871 are only source of info
GREAT ENCLOSURE:
The greatest accomplishment in sub-saharan africa
Curved walls up to 4 story tall buildings
1m stone blocks
Stones were stacked NOT CONNECTED with anything just straight up stacked
26
New cards
**Mutapa Empire:**
Mutapa Empire grew wealthy through
gold trade c. 1450
a. Portuguese unable to fully conquer them
b. so Portuguese overthrow their leader and replace with one they can control
gold trade c. 1450
a. Portuguese unable to fully conquer them
b. so Portuguese overthrow their leader and replace with one they can control
27
New cards
Differences Between Sunni and Shia Muslims (Sunni)
* Sunnis accept Umayyads
* one of the two major branches of Islam
* Majority of followers are Sunni
* regard their denomination as the mainstream and traditionalist branch
* recognize the first four caliphs as the Prophet Muhammad’s **rightful successors**
* regarded the leadership of Islam as being determined **not by divine order or inspiration** but by the prevailing political realities of the Muslim world
* acceptance of unexceptional and even foreign caliphs
* the caliph must be a member of Muhammad’s tribe, the Quraysh, but devised a theory of election that was **flexible enough to permit others**
* institution of consensus **(ijmāʿ) evolved by the Sunnis** allowed them to **incorporate various customs and usages** that arose through ordinary historical development but that nevertheless **had no roots in the Qurʾān**
* recognize the six “sound” books of Hadith, which **contain the spoken tradition attributed to Muhammad**
* numbered about 900 million in the early 21st century and constituted a majority of all the adherents of Islam
* one of the two major branches of Islam
* Majority of followers are Sunni
* regard their denomination as the mainstream and traditionalist branch
* recognize the first four caliphs as the Prophet Muhammad’s **rightful successors**
* regarded the leadership of Islam as being determined **not by divine order or inspiration** but by the prevailing political realities of the Muslim world
* acceptance of unexceptional and even foreign caliphs
* the caliph must be a member of Muhammad’s tribe, the Quraysh, but devised a theory of election that was **flexible enough to permit others**
* institution of consensus **(ijmāʿ) evolved by the Sunnis** allowed them to **incorporate various customs and usages** that arose through ordinary historical development but that nevertheless **had no roots in the Qurʾān**
* recognize the six “sound” books of Hadith, which **contain the spoken tradition attributed to Muhammad**
* numbered about 900 million in the early 21st century and constituted a majority of all the adherents of Islam
28
New cards
Differences Between Sunni and Shia Muslims (Shia)
\-Shi’ite (Shia) reject Umayyad’s authority and think caliph should be a descendant/relative of Muhammad
\
\-a. Currently, only about 15% of Muslims are Shiite but they have a majority in Iran and Iraq
\
\-generally regarded as the most conservative
\
\-members supported Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law as the prophet’s heir after the murder of the 3rd caliph.
\
\-Members of the smaller Shiʿite branch are called Shiʿites. They believe that the truths of the Koran are revealed only through a community leader called the imam. Interpretations by other people are not accepted. For this reason Shiʿites are not as open to other views as Sunnis are
\
\-a. Currently, only about 15% of Muslims are Shiite but they have a majority in Iran and Iraq
\
\-generally regarded as the most conservative
\
\-members supported Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law as the prophet’s heir after the murder of the 3rd caliph.
\
\-Members of the smaller Shiʿite branch are called Shiʿites. They believe that the truths of the Koran are revealed only through a community leader called the imam. Interpretations by other people are not accepted. For this reason Shiʿites are not as open to other views as Sunnis are
29
New cards
Islam’s Connection to Judaism and Christianity
1. Monotheistic and worship the same God as Judaism and Christianity
2. Believe in the Jewish prophets and that Jesus was a prophet but not divine in Islam and contains the divine messages Muhammad received from the angel Gabriel
3. According to Muslims, in 610 an angel told Muhammad that Allah had chosen him as a prophet. Throughout his life, Muhammad continued to receive messages that he believed came from God. Roots back to Abraham Islamic, Jewish, and
4. Christian scholars all came together in the House of Wisdom (in Baghdad) to share knowledge/cultural diffusion Showed much respect and peace in coexistence
30
New cards
Impact of Islam on Africa
1. Arab traders spread Islam and enslave some Africans
2. Bantu and Arabic blend to form Swahili language
3. About 35 major cities emerge as centers of trade along coast of Indian Ocean (c. 1300)
\-Islam was spread to african societies because Muslim men often served as peacemakers and working in politics, socially, and religiously in addition to pleading for those who broke the king’s laws
\-Askia Muhammed: Remodeled Sudan/Songhai empire a;omg Islamic lines, introducing legal and social reforms appointing islamic judges and justice was served according to islamic principles
\-Rulers and upper class convert to Islam but most continue to follow animism\* Invasions by Muslims from the north and shifting trade routes weaken Ghana
31
New cards
Cultural Achievements of Sub-Saharan Africa (beyond gold-salt empires)
Zimbabwe
\-Important artifacts called Benin Bronzes
\-Great Zimbabwe controlled gold trade in Southern Africa
\
Nigeria
\-made iron tools and weapons and detailed art from terra cotta
in Ghana
\-Use of camels made trans-Saharan trade easier by 200 CE
in Empire of Songhai
\-Songhai replaced Mali; also controlled gold-salt (and enslaved person) trade
\-created Songhai empire with army of war canoes and riders on horseback
\-Empire falls to Moroccans from North Africa armed with gunpowder and cannons (1591)
\-Important artifacts called Benin Bronzes
\-Great Zimbabwe controlled gold trade in Southern Africa
\
Nigeria
\-made iron tools and weapons and detailed art from terra cotta
in Ghana
\-Use of camels made trans-Saharan trade easier by 200 CE
in Empire of Songhai
\-Songhai replaced Mali; also controlled gold-salt (and enslaved person) trade
\-created Songhai empire with army of war canoes and riders on horseback
\-Empire falls to Moroccans from North Africa armed with gunpowder and cannons (1591)
32
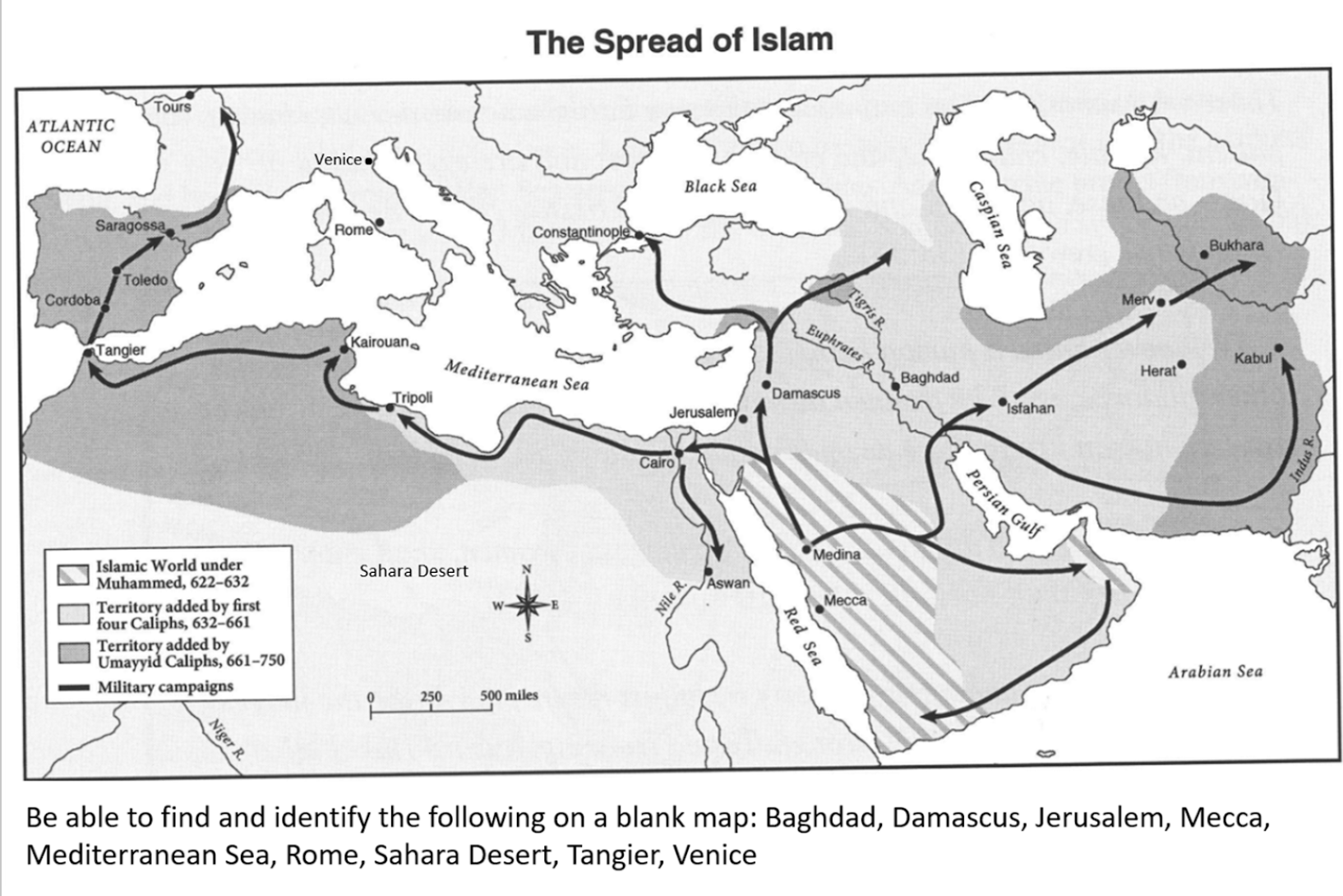
New cards
Map of Sub-saharan africa
33
New cards
Why did Muhammad and his followers flee from Mecca to Medina in an event known as the Hijrah? (Hint: see the Britannica article on Muhammad for help).
This idea that there is only one God was unusual for Arabs at the time. Many people in Muhammad’s hometown of Mecca disliked the new religion because of that belief. To avoid their hostility, Muhammad encouraged his followers to move to the nearby city of Medina. Muhammad’s journey to Medina ended on September 24, 622, which is considered the starting point of Islamic history.
The hostilities aroused in Mecca led Muhammad to encourage his followers to emigrate to the city of Medina. He left Mecca and reached Medina on Sept. 24, 622. This flight is called hijrah in Arabic and has come into English as Hegira. It provides the starting date for the history of Islam.
The hostilities aroused in Mecca led Muhammad to encourage his followers to emigrate to the city of Medina. He left Mecca and reached Medina on Sept. 24, 622. This flight is called hijrah in Arabic and has come into English as Hegira. It provides the starting date for the history of Islam.
34
New cards
Why were many Western historians surprised by some of the relatively recent archeological discoveries in sub-Saharan Africa?
**Western historians in the past may have been surprised because of the stigma and misinformation that many people in the West used to believe about African civilizations, as they believed that they were not advanced at all. Also the ruins of Great Zimbabwe had shown signs of total abandonment, which is shocking for that highly advanced of a civilization.**