ALEVEL BIOLOGY - biological molecules
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Polymers
large, complex, monomers joined together
what is the reaction to making polymers
condensation
what is the reaction to breaking polymer
hydrolysis
what is a hydrolysis reaction
reaction breaking the chemical bond between two monosaccharides using a water molecule
what is condensation
chemical bond between two molecules joining together with the elimination of a water molecule
Most carbohydrates are polymers including
proteins and nucleic acids
Examples of monomers
monosaccharides, amino acids and nuceotides and fatty acids and glycerol
Monomers
small, basic molecuar units. which builds to make larger molecules such as polymer
Monomers that make carbohydrates
monosaccharides
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
All carbohydrates contain the elements
carbon, oxygen and hydrogen
Glucose is a
hexose sugar
what is a monsaccharide
a monomers that contains one sugar unit.
They are the monomers which larger carbohydrates are made
Hexose sugar
a monosaccharide that contains 6 carbon atoms in every molecule
2 types of glucose
alpha glucose and beta glucose
Alpha and Beta glucose are both
isomers
Alpha glucose
hydrogen at top, OH at bottom
Beta glucose
OH at top, hydrogen at bottom
Reaction that joins monosaccharides together
condensation reaction
Condensation reaction
when 2 monosaccharide are joined together with the formation of a new chemical bond and a water molecule is released
Bond formed in condensation reaction
glycosidic bond
Glycosidic bond formed when
water molecule is released
Disaccharide
when 2 monosaccharides join together
Glucose + glucose
maltose
Glucose + fructose
sucrose
Glucose + galactose
lactose
Amino acids make
proteins
Monosaccharies make
carbohydrates
Nucleotides make
nucleic acids
Fatty acids and glycerol make
lipids
Lots of amino acids make
polypeptides
Lots of monosaccharides make
polysaccharides
Lots of nucleotides make
polynucleotides
Lots of fatty acids and glycerol make
triglycerides
Lots of monomers make
polymers
Hydrolysis
addition of a water molecule to break glycosidic bond
Sugars
monosaccharides, glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose and lactose
Example of a hydrolysis reaction
carbohydrates can be broken down into constituent monosaccharides
Test for reducing and non reducing sugars
benedict's test
Reducing sugars
donate electrons to other chemicals
Benedicts test for reducing sugars includes
all monosaccharides, glucose and some disaccharides, maltose and lactose
Process of Benedicts test for reducing sugars
benedicts reagent is added to sample, heated in water bath which has been brought to the boil
Positive result for Benedicts test
coloured precipitate, brick red
Coloured precipitate in Benedicts solution
solid particles suspended in solution
Colours will change from for Benedicts test
blue, green, yellow, orange, brick red
Higher concentration of reducing sugar
the further the colour will change
Colour change can be used for
comparing amount of reducing sugars in different solutions
Benedicts test for non-reducing sugars
broken down into monosaccharides first by using a hydrolysis reaction, sample is taken, dilute hydrochloric acid is added, heated in boiling water bath, soultion is neutralised with sodium hydrogencarbonate, benedicts reagent is added
what is a colorimeter
to mesure the abundance of remaining benedict reagent
Mor accurate way for Benedicts result
filter solution and weigh precipitate
or
Removing the precipitate and using a COLORIMITER to mesure the abundance of remaining benedict reagent
Negative result for benedicts test for non-reducing sugar
solution will stay blue, no sugars present, neither reducing or non-reducing
Disaccharide involved in non-reducing Benedicts test
sucrose
Lots of alpha glucoses form
amylose
2 alpha glucoses form
maltose
what are polysaccharides
when two or more monosaccharides join together by condensation reaction. they form long chains of monomers
examples of polysaccharides
starch , cellulose, glycogen
Cells get energy from
glucose
what is Starch used for
main energy storage material in plants, it is insoluable . it is a mixture of amylose and amylopectin
way in which starch molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells.
1. Insoluble;
2. Don't affect water potential;
OR
3. Helical;
Accept form spirals
4. Compact;
OR
5. starch is a Large molecule;
6. so it Cannot leave cell.
Explain how cellulose molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells.
Long and straight chains;
2. Become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils;
3. Provide strength (to cell wall).
what happened when starch is broken down
they break down and release glucose which provides energy to the plant
plants store excess glucose as
starch
When a plant needs more glucose for energy
they break down the starch to release the glucose
2 polysaccharides that make up starch
amylose and amylopectin
Coiled structure of amylose
makes it compact so good for storage as more can fit into a smaller area
bond between amylose
1-4 gylcosidic bond
Amylopectin
long, branched chain of alpha glucose and has 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Amylose
long, unbranched chain of alpha glucose, angles of glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure making it compact and good for storage. it has has 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Side branches of amylopectin allow
enzymes that break down the molecule to get at the glycosidic bonds easier so glucose can be released quickly
bonds in amylopectin
1-4 and 1-6 gylcosidic
Starch is
insoluble and has a helical shape
Insoluble
does not affect water potential which does not cause water to enter cells through osmosis which would make them swell
Test for starch
iodine test
Process of iodine test
iodine is dissolved in potassium iodide solution and is added to test sample
Positive result for iodine test
solution will turn from a browny/orangey colour to a dark blue/black
Glycogen
main energy storage material in animals
Glyogen is a
compact molecule
Structure of glycogen
is similar to amylopectin except that it has more branches, very compact
Animals store excess glucose as
glycogen
Glycogen is good for
storage animals
Glycogen is a polysaccharide of
alpha glucose
Cellulose
is major component of cell walls in plants
Cellulose is made of
long, unbranched chains of beta glucose and alternate beta glucose molecules are inverted
Lots of branches on glycogen is good because
glucose can be released quickly
When Beta glucose molecules bond they form
straight cellulose chains
Cellulose chains are linked together by
hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres
Microfibrils
strong fibres mean that cellulose provides structural support for cells in plant cell walls
test for lipids
emulsion test
how do you test for lipids
sake the test substance with wthanol for a minite and pour solutioninto water
any lipid produces will show a milky emulsion
- the more lipids the more notisable milky colour
what are lipids
lipids are made from a mixture of componats which are all hydrocarbons
what are the two types of lipids
Trigylcerides
Phospholipids
what is the structure of trigylceride
one molecule of glycerol and 3 molecule of fatty acids
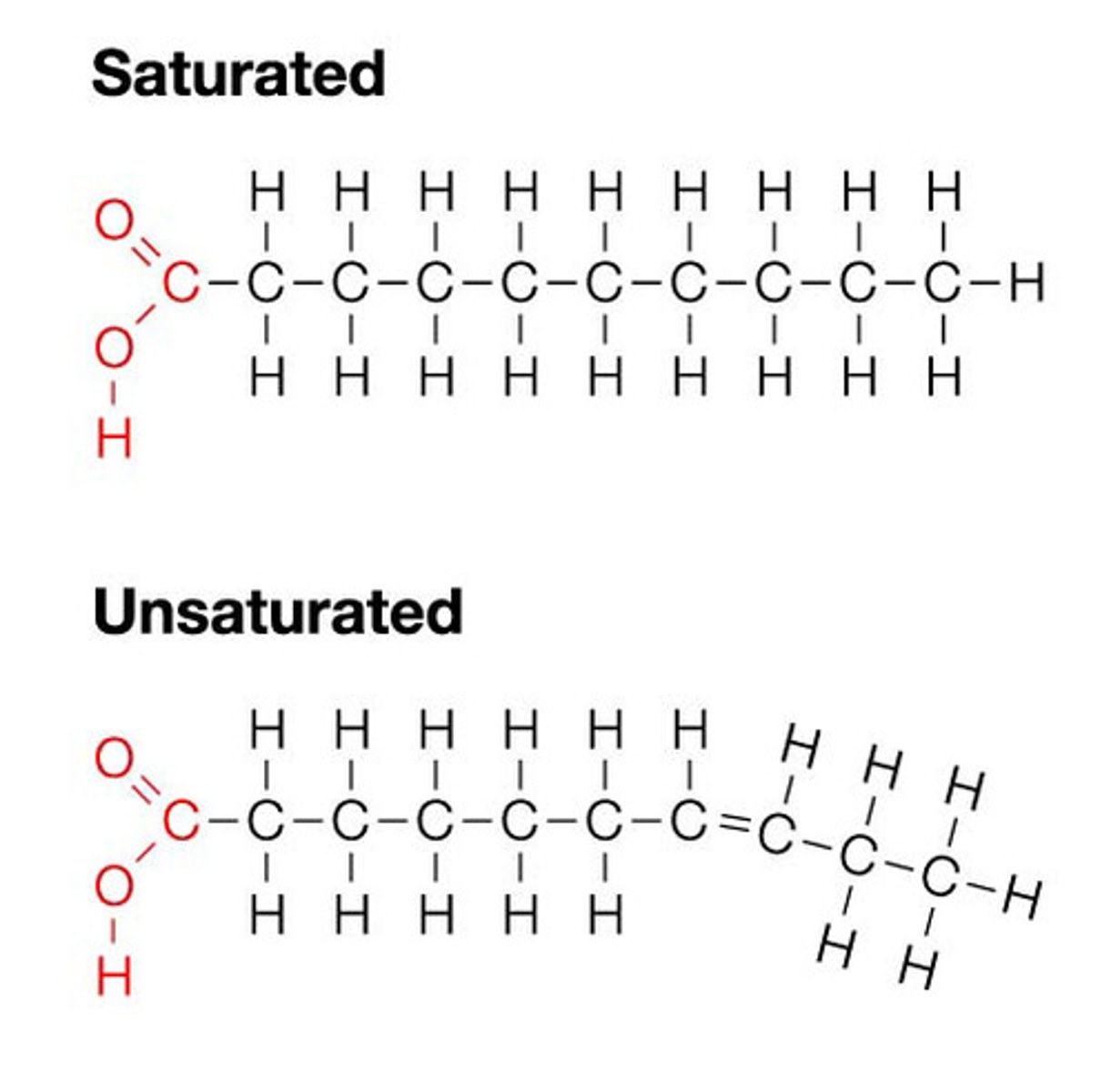
what is the structure of fatty acid
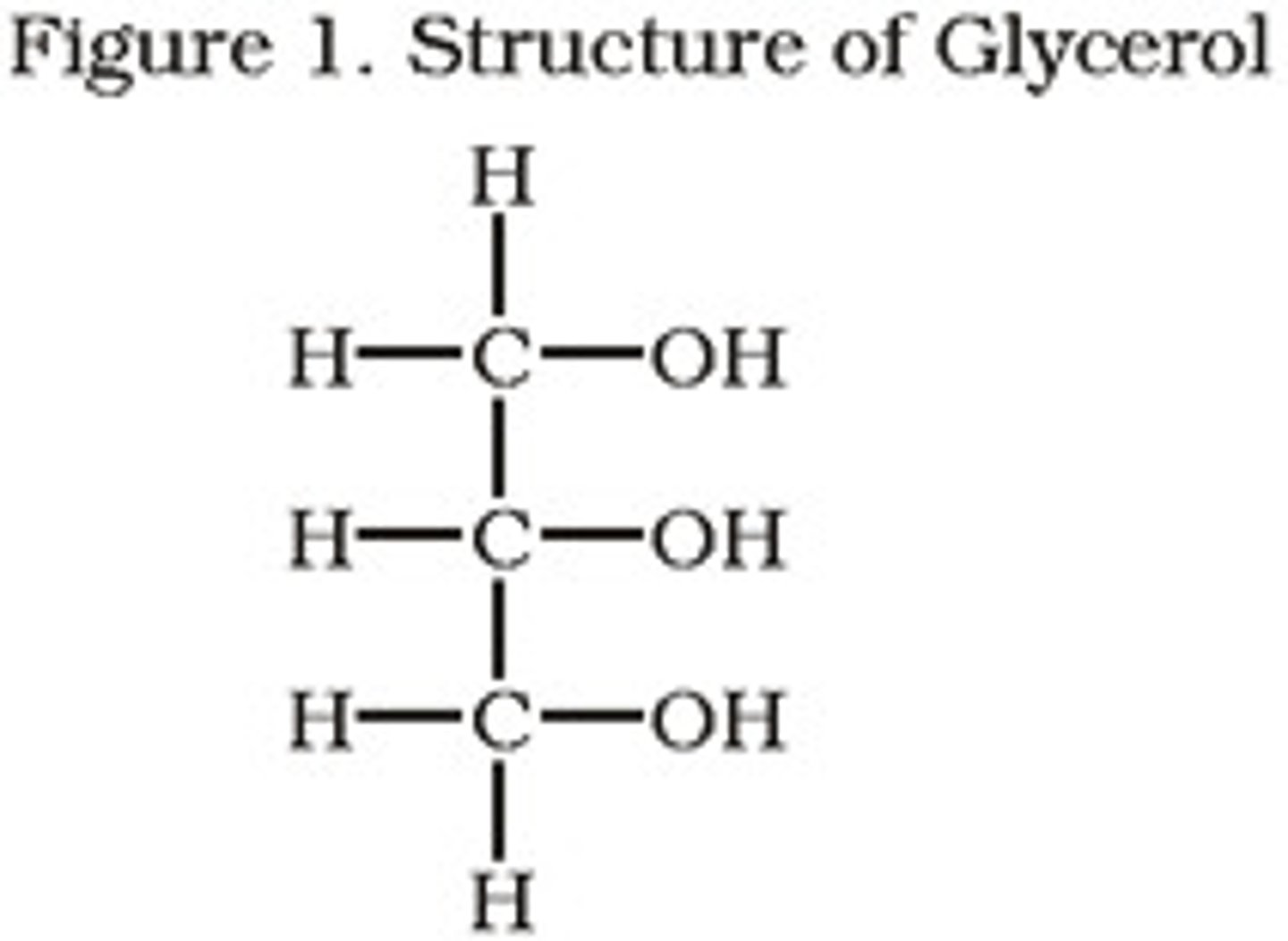
what is the structure of glycreol
what are fatty acids made from
hydrocarbons
fatty acids in lipids are hy...
hydrophopic- they repel water . the tail is insoluable so it doent affect the water potential so osmosis can't occur
what are the two types of fatty acids
saturated and unstaurated hydrocarbons
what is a saturated fatty acid
it doesnt contain any double bond
what is saturated fatty acids
it has double bonds
how to test for saturated and unsaturated fats
bromein test if unsaturated it would go colourledd
if saturated it would remain orange