Unit 3.2 Body Guards
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Prions
Any of various infectious proteins that are abnormal forms of normal cellular proteins
Viruses
Any of a large group of nonliving, submicroscopic infective agents that typically comprise of an RNA or DNA core
Bacteria
Single-celled prokaryotic microorganism
Protist
Living, multicellular eukaryotic organisms
Helminths
Living, multicellular, eukaryotic worms
Pathogen
Disease causing organism
Parasites
Organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its food at the expense of the host
Epidermis
top layer of skin that provides a barrier, make new skin, and provides skin color
Dermis
middle layer that contains collagen and elastin, grows hair, makes oil, and sweat, contains blood vessels and nerve endings
Subcutaneous Fatty Tissue
Bottom layer of the skin consisting of fat that cushions muscles and bones and helps regulate body temp
Importance of skin
primary border that protects us from pathogens, maintain homeostasis, and induces immune responses
How does the way skin cells reproduce help skin protect your body from invaders.
Induces immune response
Sepsis
The body's immune system overreacts to an infection causing inflammation
Sever sepsis
Organs in the body begin to malfunction, blood pressure is low, and inflammation continues
Septic Shock
Extremely low blood pressure that does not respond to IV fluids
T (Temperature)
Higher or lower than normal temperature
I (Infection)
Signs and symptoms of an infection (swollen lymph nodes)
M (Mental Decline)
Confused, sleepy, difficult to rouse
E (Extremely Ill)
Severe pain or discomfort
Lymph nodes
Glands in the immune system that usually enlarge in response to bacteria or viral infection or cancer
Lymph
Watery fluid that maintains fluid levels in the body, absorbs fats, protects the body from pathogens, and transports and removes waste from lymph fluid
Lymph nodes function
Enlarge in response to bacteria or viral infection or cancer
Lymph vessels function
Carries lymph through the body to lymph nodes and back to veins
Liver function
contributes to immune defense by collecting and eliminating foreign compounds from blood
Thymus function
Helps in the development of T-cells that help fight off infections
Tonsils function
Helps to stop germs from entering the body through the mouth or nose
Spleen function
Filters blood of foreign cells and old red blood cells
Bone marrow function
Produces new blood cells
Lymphatic filtration
Process of filtering lymph through lymph nodes.
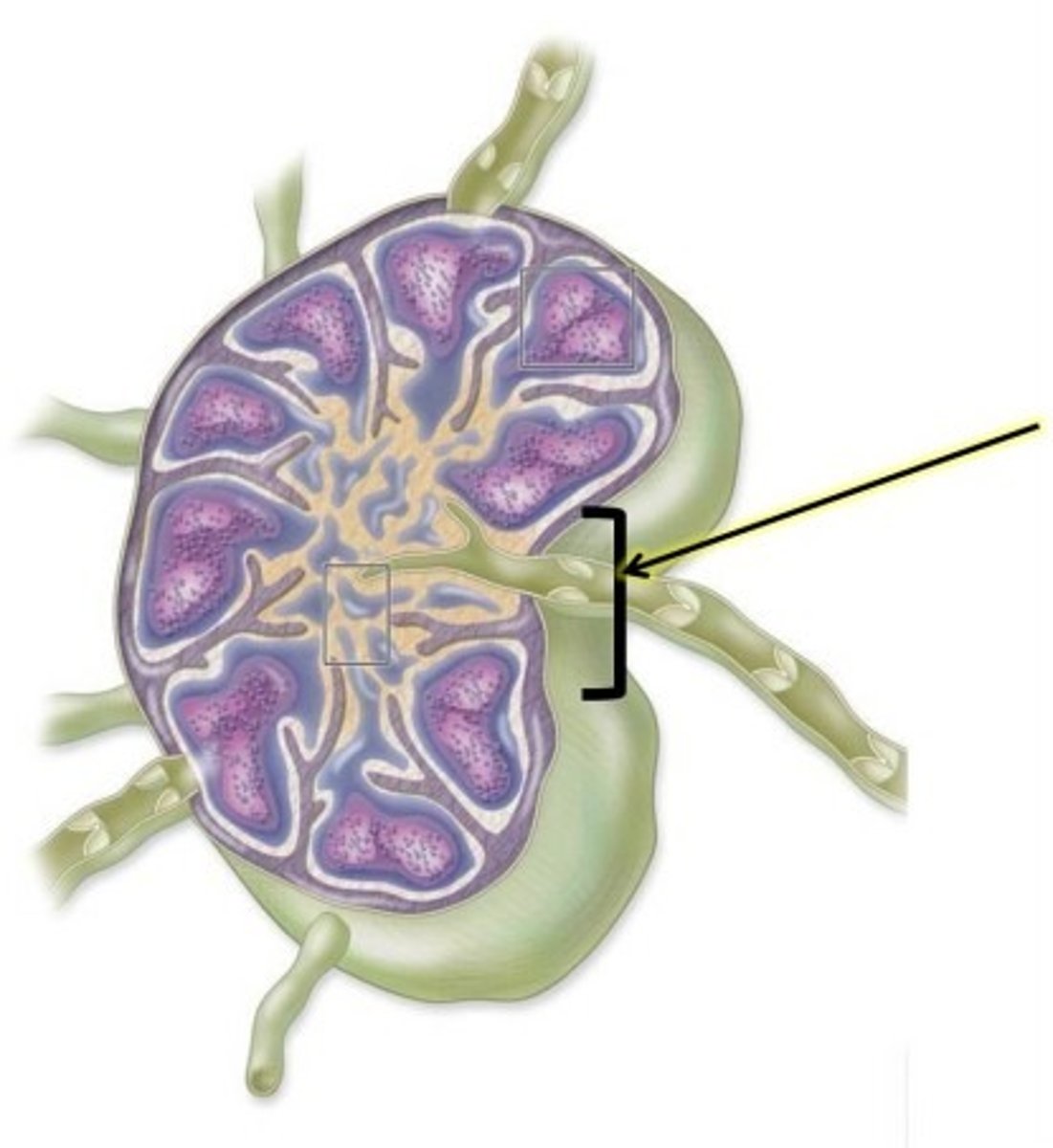
What would the lymphatic, cardiovascular, and immune systems do when a person cuts their hand?
Platelets
fragments that assist in protecting the body by helping blood clot
Red blood cells
helps transport oxygen throughout the body
White blood cells
destroys invaders that make it through your body's nonspecific defenses
Innate immunity
Non-specific immune defense mechanisms that people are born with, keeps anything outside from coming in.
Acquired immunity
Specific immune defenses, acquired over a lifetime
Active immunity
acquired after an infection and recovery from a vaccine
Passive immunity
acquired as a child from its mother through the placenta or breast feeding
antigen
foreign invader such as a pathogen
B-cells
stimulates specific white blood cells
Antibodies
proteins that work to neutralize pathogens
T-cells
type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in immune response by recognizing/attacking cells infected with foreign pathogens or cancer cells
Immune response concept map
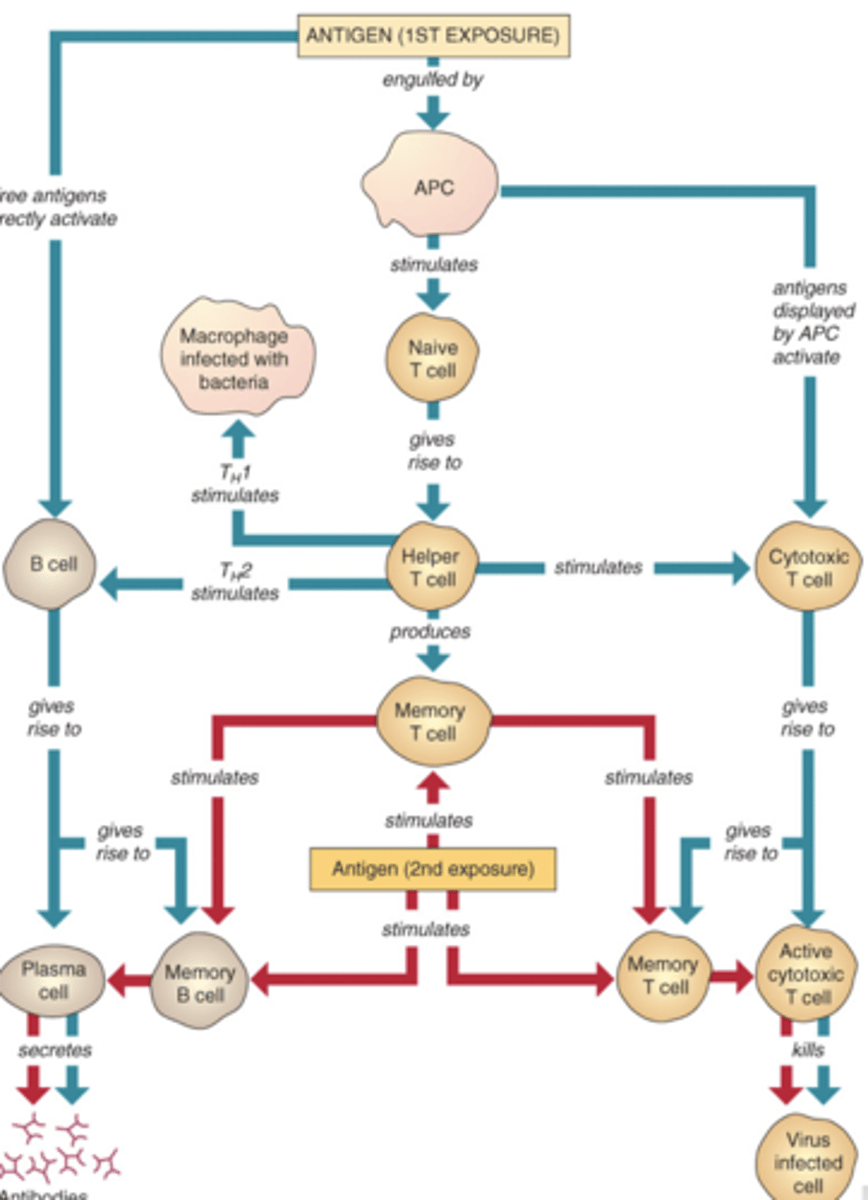
Helper T-cell
stimulates cytotoxic T cell, antigen, and exposure stimulating memory B cell and T cell
Cytotoxic T-cell
Gives rise to activate cytotoxic T-cell and memory T-cell
Viral Reproduction
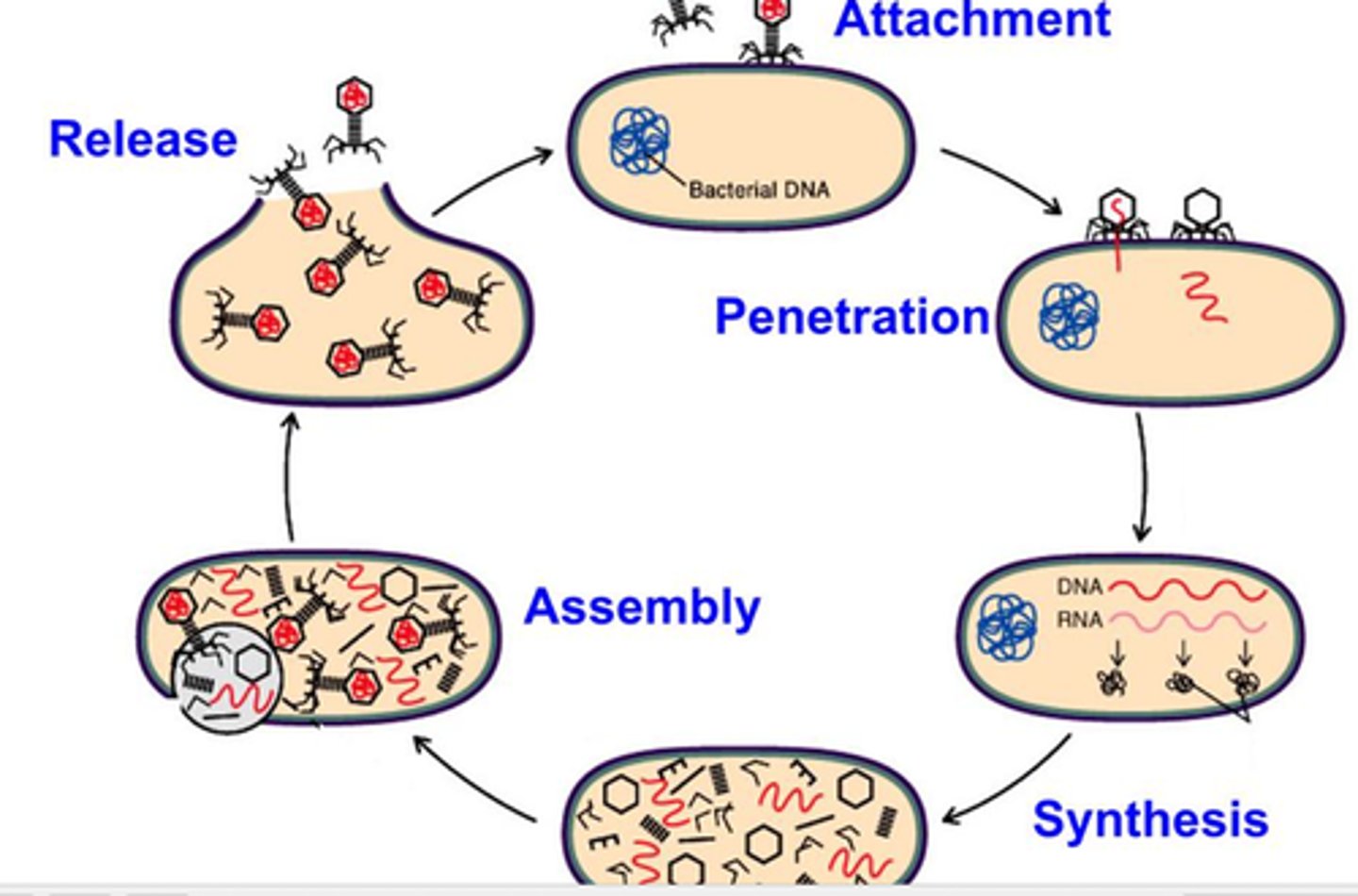
Attachment
Virus attaches to the surface of animal host cell
Entry
Virus DNA enters host cell through endocytosis or fusing with plasma membranes of the host cell
Uncoating
Breakdown or removal of the capsid of the virus; genome is completely released and viral genes are able to transcribe replicate()
Replication
Host cell is used to copy viral single-stranded RNA, double-stranded RNA or single stranded DNA; information on how to produce virus is encoded
Assembly
Newly created virus parts self-assemble into new virions
Maturation
Final change in structure of the capsid within a immature virion results in an infectious virus particle
Release
Cell host releases new virions into the extreacellular environment
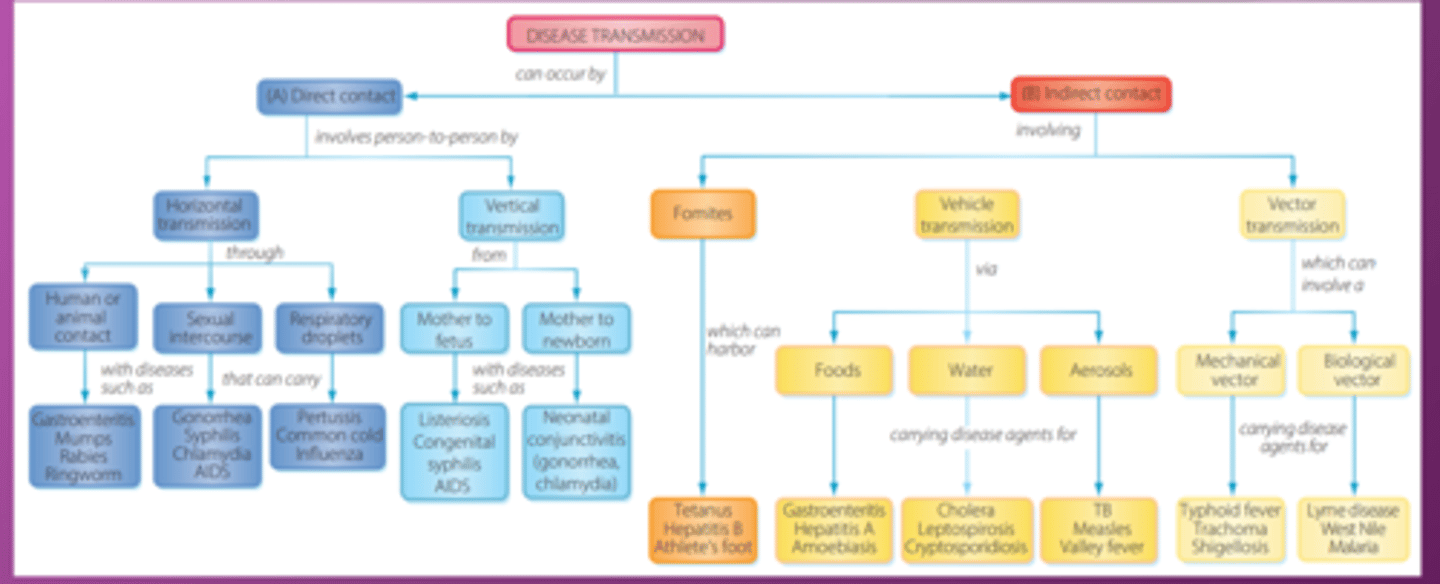
Direct mode of transmission
physical contact between an infected person and new host
Indirect mode of transmission
No physical contact
Modes of Transmission
Retina
receives image formed by the lens and converting it into chemical and nervous signals
Blind Spot
Where optic nerve enters part of eye that is devoid of rods and cones and is insensitive to light
Sclera
White external layer of eyeball
Vitreous Humor
Substance that fills the eyeball behind the lens
Lens
Focuses light on the retinaA
Acqueous humor
fluid that fills the space between the lens and cornea
Tapetum
Mainly found in animals, refracts visible light back through the retina
Pupil
Admits light into the interior of the vertebrate eye
Cornea
Covers iris and pupil and admits light into the interior
Iris
Excludes the entrance of light except through the pupil, determines eye color.
Conjunctivitis
Also called pink eye, an infection of the conjunctive that causes inflammation. Eyes are red and itchy, and may water or have a thick discharge
Loiasis
Also called African eye worm, periodic appearance of itchy but not painful swellings, especially near joints, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, and worm crawls over the surface of the over in the conjunctiva
Onchocerciasis
River blindness, a disease with symptoms including impaired vision or blindness caused by recurring conjunctivitis and infection of the cornea and sclera
Trachoma
An infection that can cause vision impairment and blindness when the eyelid and eyelashes scratch and damage the cornea
Traumatic Iridodialysis
Eye injury where the iris detaches from the structure behind it, irregularly shaped pupil, eye pain, and blurry or impaired vision. Can result in glaucoma.