Bio - D.1.1 DNA Replication
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Why DBA replication is needed
production of gametes - sex cells during meiosis
Growth + repair of tissue - mitosis
Semi - conservative
Replication of DNA - one old + one new strand
When cell = ready to divide - 2 strands of double helix = seperate
Each of original strands acts as template for the creation of a new strand
new strands = assembled through complimentary base pairing
DNA Replication
Unwinding + unzip double helix with enzyme HELICASE
Unzips to position called replication fork
Nucleotides base pair through complementary base pairing
DNA Polymerase joins together nucleotides - strong phosphodiester bonds
DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides in 5’ to 3’ direction
Double strand reforms a double helix
Polymerase chain reaction
Used for making copies of DNA artificially
Used to amplify/make millions of DNA copies
Taq polymerase = heat resistant version of DNA polymerase
PCR = Cloning DNA at rapid speed
Temperature used instead of enzymes to break H bonds - 95 degrees
Gel Electrophoresis
Fragments of DNA move in electrical field and are separated
Separation = based on size/mass
Sample of DNA = placed on wells ong el
Electrical current = passed across gel
DNA = negatively charges - when electrical current is passed through
DNA fragments move to positive electrodes
Large Fragments move slow
Small fragments move quicker
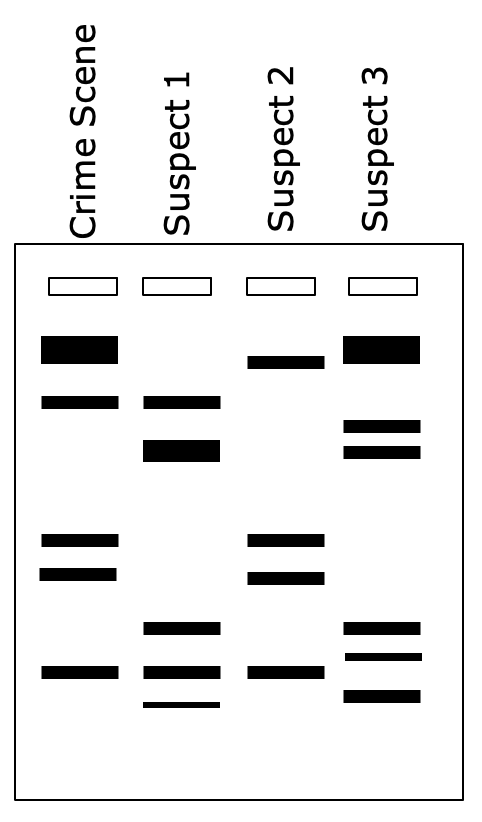
Gel electrophoresis used in DNA profiling
Used to differentiate between individuals
Technique can be used for:
Forensic crime investigations - see if suspects DNA match DNA on scene
Parentage issues
Animal breeding
Disease detection
HL - DNA replication
Takes place during S section of interphase
5’ to 3’
Antiparallel strands
Replication begins at sites ‘origin of replication’
Helicase attaches + unzips and unwinds - breaks hydrogen bonds
Gyrae keeps DNA strands separated
RNA Primase synthesises small amount of RNA primer (will be changed to DNA)
DNA polymerase III can only join Nucleotides in 5’ to 3’
only nucleotides can join to 3’ end called leading strand
On other side DNA polymerase works away from replication fork
Create small fragments - Okazaki fragments - Lagging strand
Several primers - one between each fragment
Enzyme Ligase joins okazaki fragments to form one continuous DNA molecule
DNA polymerase I replaces RNA primer with DNA
DNA polymerase 3 can check its work and repair mismatched bases