VET-125 - Ch 5 - Hematologic & Immunologic
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Blood functions
Temperature regulation, pH balance, nutritional & hormone transport, waste disposal, & immune response
Blood components
RBCs, WBCs, platelets, & plasma
Plasma
Fluid portion of the blood that contains suspended cells; about 55% total blood volume
90% water, 10% dissolved constituents (protein, hormones, lipids, enzymes, salts, carbs, vitamins, electrolytes, & waste)
Serum
Fluid portion of blood with fibrinogen removed (liquid left after clotting)
RBC production
In red bone marrow
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment
Hemoglobin concentration is roughly what percentage of PCV in most pets & domestic animals?
33%
Anemia
Disorder characterized by reduced numbers of RBCs; various causes
Three broad categories = decreased production, increased destruction (eg. immune related), & inappropriate loss
Classified as 2 types = regenerative & nonregenerative
Treatment is aimed at correcting the primary problem & supporting the patient
What is the most common cause of anemia?
Hemorrhage from trauma
Hemorrhagic anemia
Anemia caused by hemorrhage aka blood loss
Hemorrhagic anemia treatment
Should consist of controlling hemorrhage & volume replacement
— blood transfusions (platelet rich), steroid therapy (less common now), & avoid additional trauma
Hemorrhagic anemia other info
With acute blood loss, the hematocrit doesn’t reflect severity of the problem, & as a fluid shift occurs to compensate for blood loss, shock may result
— may act fine otherwise, then go into shock abruptly
Thrombocytopenia accounts for many cases of generalized bleeding
What are the best areas to check for signs of bleeding?
Gingiva, inner ear pinna, lower ventral abdomen, & eyes
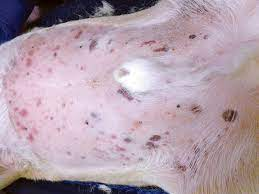
Petechiae (pinpoint) & ecchymoses (larger) aka petechial & ecchymotic hemorrhages; dotted or speckled bruising caused by bleeding into the skin, may be caused by bleeding disorders such as IMTP
Iron-deficiency anemia
Iron & hemoglobin lost with external bleeding results in altered RBCs with decreased life spans
Iron-deficiency anemia causes
Possibly chronic external blood loss such as fleas, internal parasites (commonly hookworms), gastric ulceration, & bleeding neoplasms
Iron-deficiency anemia treatment
Correcting cause of blood loss & iron supplementation for 30-60 days
Hemolysis
Destruction of RBCs
Hemolytic anemia
Immune components attach directly or indirectly to the RBC membrane & alter its structure
— in attempt to regain homeostasis, the body removes these cells
Hemolytic anemia causes
Dogs = appears related to underlying inflammatory process
Cats = most common cause is hemobartonellosis (Mycoplasma haemofelis)
— FeLV may stimulate immuno-hemolytic disease
Hemolytic anemia signs
Exercise intolerance, pale mucous membranes, tachycardia, & icterus if severe
Hemolytic anemia treatment
Suppression of immune system (steroids) & supportive therapy; transfusion if hematocrit declines to life-threatening; Doxycycline (antibiotic) for hemobartonellosis
Anemia from blood-borne parasites
Hemobartonellosis (Mycoplasma haemofelis)
— epicellular bacterial parasite attaches to the RBC membrane, resulting in immune related hemolysis
— most common cause of hemolytic anemia in cats
Babesia canis & B. gibsoni = babesiosis
— hemolytic anemia in dogs
— transmitted by brown dog tick
Cytauxzoon felis = cytauxzoonosis
— Protozoan found in southern US, responsible for fatal disease in cats
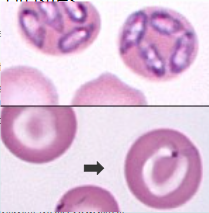
Babesia sp. (top = B. canis, bottom = B. gibsoni)
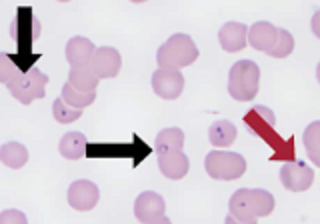
Found in cats
Cytauxzoon felis
Toxin-induced anemia aka Heinz body anemia
Most common cause in dogs = onion toxicity
Acetominophen (tylenol) toxicity in dogs & cats (especially fatal in cats) results in methemoglobinemia (brown blood) & anemia
Heinz body
Changes in RBC that may be seen as large eccentric pale structures within feline RBC or as multiple small structures within canine RBC
Which lab abnormality is frequently seen with acetaminophen toxicity in cats?
Methemoglobinuria (brown urine)
Also brown-colored mucous membranes
Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (IMHA)
Specific cause unknown, but accelerated RBC destruction occurs because of the presence of antibodies that attach to RBC membrane
Antibodies may attach directly to cell membrane, to a microorganism, or drug that has previously been bound to membrane receptor sites
Adherence of antibodies activates the complement system, causing agglutination & hemolysis
IMHA risk factors
Most commonly in dogs 2-8 years; 4 times more prevalent in females
Breeds = poodles, old english sheepdogs, cocker spaniels, & irish setters
IMHA signs
Pale mucous membranes, anorexia, listlessness, weakness, tachycardia, tachypnea, icterus, hepatomegaly, & splenomegaly
IMHA diagnosis
CBC, agglutination test, direct combs, & direct immunofluorescence assay (detects antibodies against immunoglobulin)
CBC = leukocytosis, neutrophilia with left shift, regenerative anemia, & spherocytes
IMHA treatment
Aimed at improving tissue oxygenation & managing immune response
Glucocorticoids, cyclosporine, & azathioprine
— protectants from gastric ulceration side-effect from these = omeprazole, cimetidine, misoprostol, & sucralfate
Heparin = prevent thromboembolism or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
IMHA prognosis
Guarded
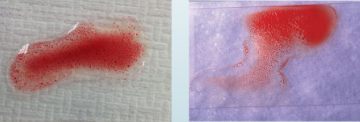
Agglutination test; 1 drop anticoagulated blood + 1 drop saline, if antibody molecules are present then agglutination will be observed
Thrombocytes
Shortly after vascular injury, platelets become active & stick together, forming a platelet plug that blocks the vessel & prevents hemorrhage
Chemicals contained within thrombocytes are also necessary for the activation & maintenance of blood clotting cascades
Should you scrub puncture site to clean off blood?
No because it will disturb clotting; only dab to clean
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMTP)
Occurs when platelets become coated with antibodies or complement-antibody complexes
Destruction may occur in spleen, bone marrow, or liver
IMTP causes
Cause unknown
Some drugs associated with this condition = sulfonamide, chlorothiazide, arsenicals, digoxin, & quinidine
IMTP risk factors
Dogs 5-6 years; females twice as likely
IMTP signs
Epistaxis, petechial & ecchymotic hemorrhages, weakness, & lethargy
Epistaxis
Nose bleeds
IMTP diagnosis
Rule out differential, bone marrow exam, & clinical signs with response to treatment
IMTP differential diagnosis
Other causes of thrombocytopenia such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), lymphoma, & myeloproliferative disease
IMTP treatment
Immunosuppressive drugs (prednisone, azathioprine, cyclosporine, etc. & platelet rich transfusions), splenectomy in refractory cases, & spay females to decrease hormonal stress
IMTP prognosis
Guarded to favorable; relapses may occur
As platelets decline to what level, then what happens?
< approx. 30,000, bleeding problems develop
Hematocrit is aka what?
Packed cell volume (PCV)
Neutrophil
Granulocyte; predominantly phagocytic cells, active in inflammation response
Basophil
Granulocyte; contain histamine & heparin, involved in immune response & blood clotting
Eosinophil
Granulocyte; involved in allergic responses & parasitic infections
Monocyte
Agranulocyte; predominantly phagocytic cells, active in inflammation response
Lymphocyte
Agranulocyte; B & T types; identify & neutralize invaders
T-Lymphocyte
Active in cell-mediate immune responses; recognize & destroy invaders
Nature killer & cytotoxic t-cells are active against tumor cells
B-Lymphocyte
Make up the humoral immune response (antibodies); produce antibodies specifically designed to destroy invaders & activate mechanisms that also aid in destroying invaders
Ehrlichia canis origin
First recognized in the U.S. in 1963; gained prominence due to large losses of military working dogs stationed in Vietnam
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) transmission
Saliva from ticks (E. canis = brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus) & blood transfusions
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) acute phase signs
Lymphadenopathy, edema of the limbs & scrotum, dyspnea, ocular & nasal discharge, depression, anorexia, fever, & weight loss
— scrotal edema more suspicious of this condition, especially with known tick bite or potential exposures
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) chronic phase signs
Anterior uveitis, retinal hemorrhages, bleeding tendencies, severe weight loss, debilitation, & abdominal tenderness
Ehrlichiosis (E.canis) diagnosis
Hematology = thrombocytopenia (most common sign), pancytopenia, anemia, positive Coombs test, increased serum proteins, & organism found on blood smear
Serology = SNAP 4Dx plus test & immunofluorescent antibody test (IFA)
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) treatment
Doxycycline (antibiotic)
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) prevention & prognosis
Tick control products
Generally good, reinfection may occur
Ehrlichiosis (E. canis) other info??
Multiplies within mononuclear cells, both circulating & fixed (liver, spleen, & lymph nodes), which can infect other organs
Results in vascular endothelial damage, platelet consumption, RBC destruction, & bone marrow suppression resulting in aplastic anemia
Dogs unable to mount an adequate immune response become chronically infected
What is the most common diagnostic finding in dogs with Ehrlichiosis?
Thrombocytopenia
Aplastic anemia
Blood disorder where bone marrow doesn’t produce enough blood cells (including RBCs, WBCs, & platelets)
von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Most common inherited disorder of hemostasis (aka clotting disorder)
In healthy dogs, the von Willebrand clotting factor (vWF) promotes platelet clumping, but in affected dogs the gene causes a decrease or absence of vWF & results in a bleeding disorder
In most dogs, inheritance is autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance, so dogs that carry this gene will demonstrate varying severity of bleeding tendencies
vWD risk factors
Identified in 54 breeds; in U.S. overrepresented in german shepherds, doberman’s & labs
vWD signs
Easy bruising & prolonged bleeding during estrus, venipuncture, etc.
vWD diagnosis
Buccal mucosal bleeding time (BMBT) > 4 minutes, decreased vWF in plasma, DNA confirmation of gene defect, & positive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
vWD treatment
Bleeding episodes managed with plasma or cryoprecipitate infusion
Desmopressin acetate to control bleeding during surgery
What is recommended before surgery in dogs that carry the gene for vWD?
Buccal mucosal bleeding time (BMBT) assessment
Feline lymphoma
Accounts for 90% of all feline hematopoietic tumors
Multicentric disease is the most common form
May be classified by location or extent of disease
Feline lymphoma causes & risk factors
FeLV (70%), average presentation at 4 years (multicentric)
Canine & feline lymphoma signs
Depend on location & size of tumors
Enlarged peripheral lymph nodes, dyspnea, anemia, vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, & weight loss
— 85% of cases in dogs involve regional or generalized lymphadenopathy
Canine & feline lymphoma diagnosis
Fine needle aspirate (FNA) or surgical biopsy = cytology
Canine & feline lymphoma treatment
No cure
Goal of therapy is to induce remission, improve comfort, & prolong life
Chemotherapy, which some protocols have up to 80% remission rates in cats & up to 90% in dogs
Canine lymphoma
Malignant lymphoma (aka lymphosarcoma) is the most common hematopoietic tumor in dogs
Canine lymphoma risk factors
Boxers, mastiffs, basset hounds, st. bernards, & scottish terriers
Radiation or Chemotherapy
Body surface area is a more accurate method of dosing toxic materials; doses are in mg per square meter
Negative side effects = anorexia, vomiting, leukopenia, renal toxicity, & hemorrhagic cystitis
— leukopenia is a concern because decreased immunity can cause dangerous secondary infections & patient may be unable to continue therapy
When was FIV first isolated?
1987
Are free roaming males or females at greater risk for FIV?
Males; 1.5-3x more likely than females
What cells does FIV affect?
Lymphocyte
Lymphopenia, loss of memory cell function, & decrease in antibody production for T-cell-stimulated lymphocytes leave the cat open for opportunistic infections
What must be looked at to determine if an anemia is regenerative or non-regenerative?
Absolute reticulocyte count
What is the tick vector responsible for the spread of canine ehrlichiosis (E. canis)?
Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus)
What might a buccal mucosal bleeding time (BMBT) > 4 minutes in a healthy, young Doberman indicate?
von Willebrand disease (vMD)
True or false? Few cats with feline lymphoma will test positive for FeLV.
False
List some drugs that are useful in the treatment of canine lymphosarcoma
Prednisone, cytoxan, l-asparaginase, vincristine, & doxorubicin
True or false? According to the new protocols for vaccination, all cats should be vaccinated for FIV
False, vaccination may result in positive tests in the future, making it more difficult to distinguish actual infection versus vaccine-induced antibodies
What is the main disadvantage to vaccinating young cats for FIV
Vaccinated cats will test positive in the future, so it will be difficult to determine if they contracted the disease prior to being vaccinated or not
When dosing toxic drugs, which method should be used instead of by weight?
Body surface area
What is Haemobartonella felis now called?
Mycoplasma hemofelis
Animals demonstrating intravascular hemolytic disease will have what color plasma?
Red