section 1 chapter 2 amount of substance oxford aqa
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
reltive atomic mass
weighted average mass of an atom of an element, taking into account its naturally occurring isotops. in comparison to 1/12 the relative atomic mass of a carbon 12 atom

relative molecular mass
mass of a molecule compared to 1/12 the relative atomic mass of a carbon 12 atom

why is carbon 12 the standard
when a mass spectrometer was used on carbon 12 1/12 of carbon 12 is exactly 1 hence is the standard used by all chemists
what term is used for ionic compounds because they do not exist as molecules
relative formula mass
how does the Mr and the mass correlate
if Mr = x
then mass =x grams
e.g helium= 4 so the mass is 4 g
the avogadro constant and how to calculate the number of moles using the constant
the number of atoms in 12g of carbon 12
the number of particles in a mole
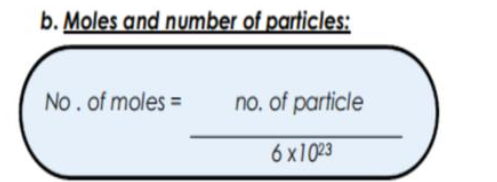
how to calculate mass using Avogadros constant and the Ar

how to calculate moles
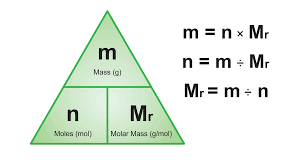
how to calculate concentration using volume and moles
units
concentration mol/dm³
n=mol
volume= dm³
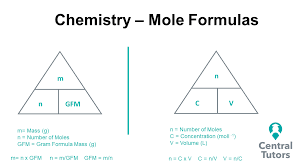
the ideal gas equation
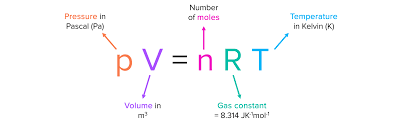
gas equation given room temperature and pressure
what is the empiricle formula
the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms of each element present in a compound
how to find the empiricle formula
find the masses
find the number of moles
convert the moles into whole number ratios
molecular formula
actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the compound
e.g C2H6(molecular) is CH3 (empiricle)
how tofind the units of the empiricle formula using the molecular formula
divide the relative molecular mass by the relative mass of the empiricle formula

stoichiometry
the ratio in which the reactants react and the products are produced in simple whole numbers
spectator ions
ions that do not take part in the reaction
how to write an ionic equations
An ionic equation shows only the ions or other particles taking part in a reaction, without showing the spectator ions
step 1 Write the chemical equation
STEP 2: Rewrite by separating the soluble ionic compounds into their dissociated ions
step 3 Cancel out common ions, which are the spectator ions
STEP 4: Write the net ionic equation for neutralisation
atom economy
The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product

Economic, ethical and environmental advantages for society and for industry of developing chemical processes with a high atom economy.
A high % yield does not always mean the reaction is efficient.
The higher the % atom economy, the cheaper the process
The higher the % atom economy, the less wasteful the process.
