Head and Neck: Ear Anatomy and Pathologies
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Inspecting the auricle
Looking at auricle and surrounding tissue for: Deformity, lumps, lesions
Any appliances?
Any pain/discharge/inflammation?
Pressure on tragus = OE
Pressure on mastoid process = OM
Otitis Externa
Infection causing pain and swelling in ear canal.
Otitis Media
Middle ear infection, indicated by mastoid pressure pain.
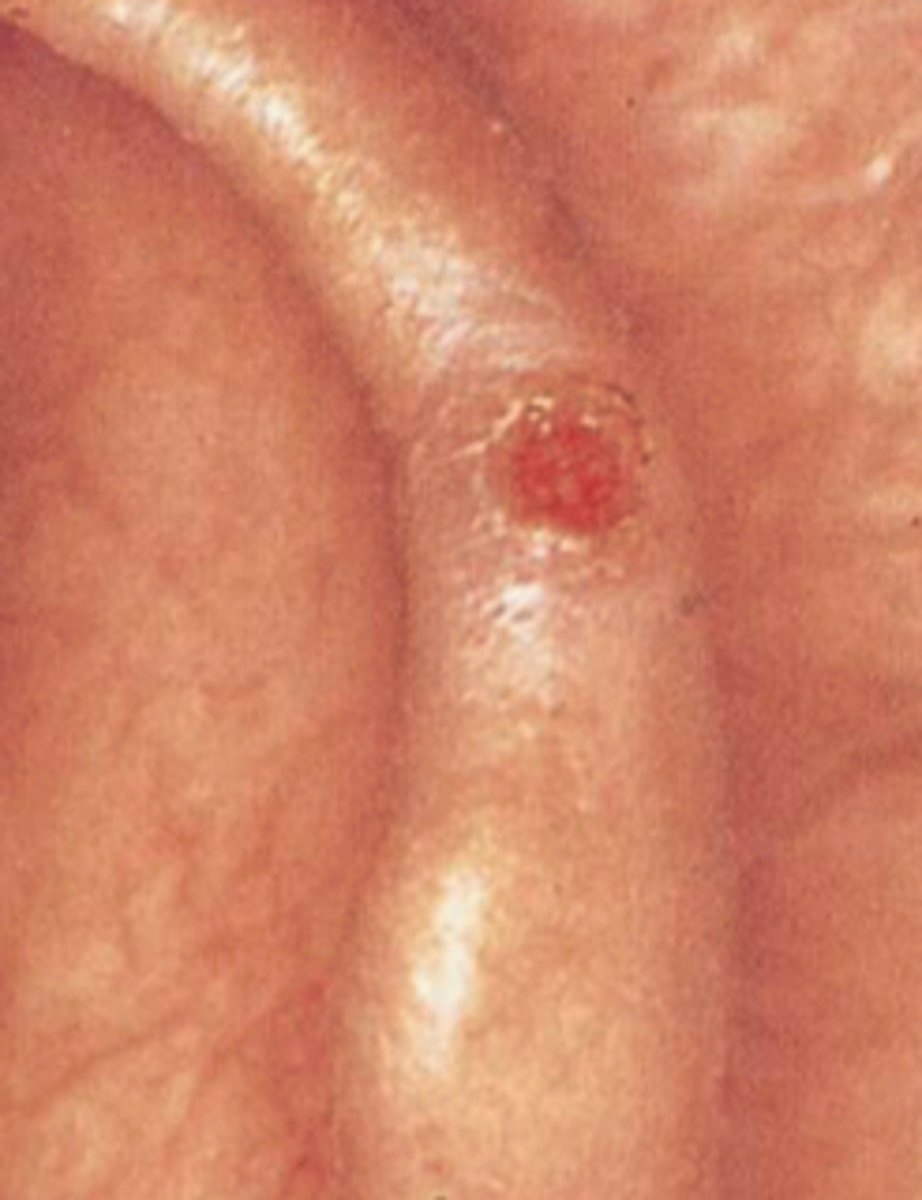
Chondrodermatitis Helicis
Chronic inflammatory lesion
Starts as a painful, tender pustule
Helix or antihelix
May ulcerate or crust dt influence
Distinguish from carcinoma via biopsy
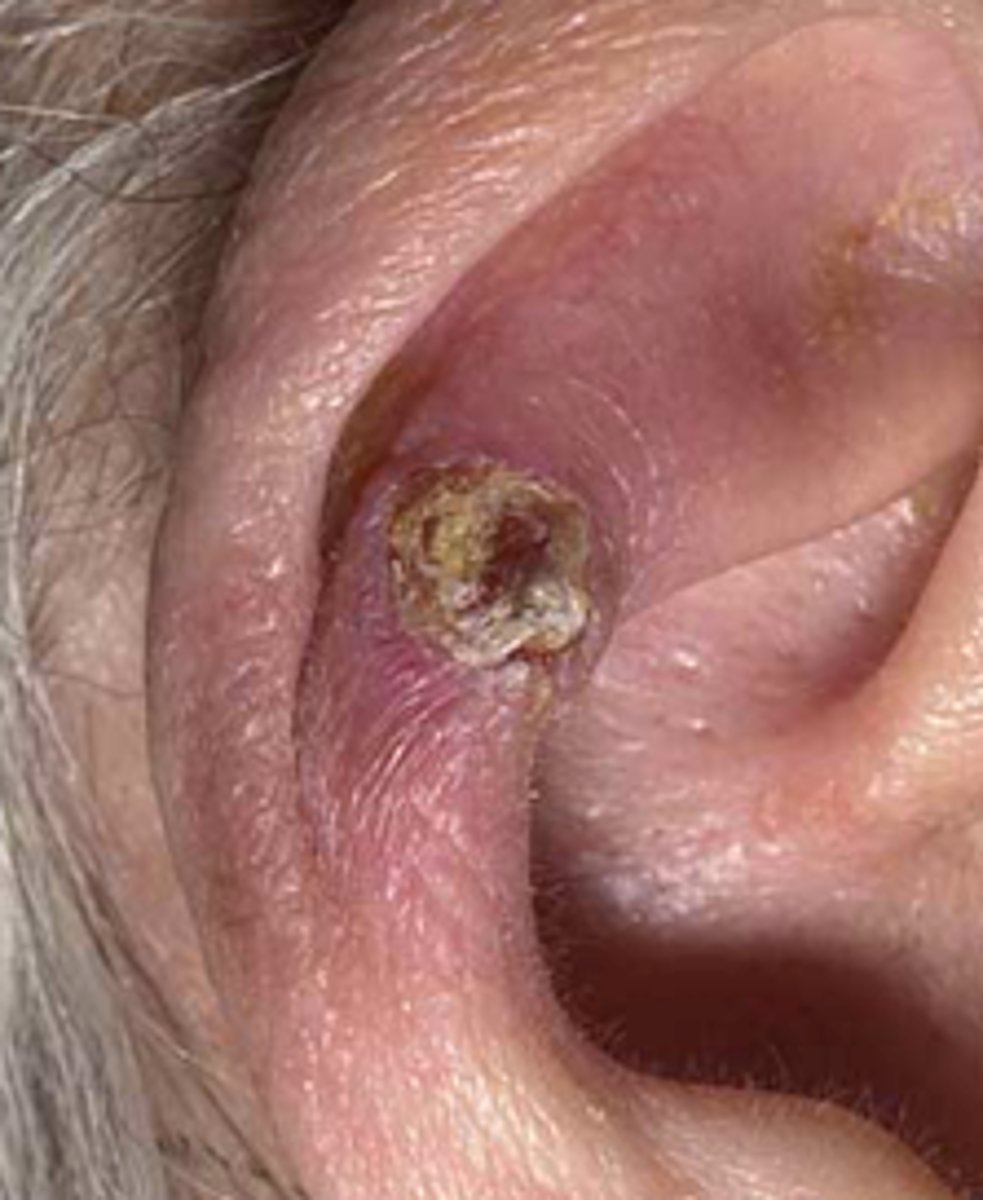
Ear Carcinoma
Basal/Squamous cell carcinoma or malignant melanoma
Common in fair skin
Possible growth & ulceration
NB - biopsy
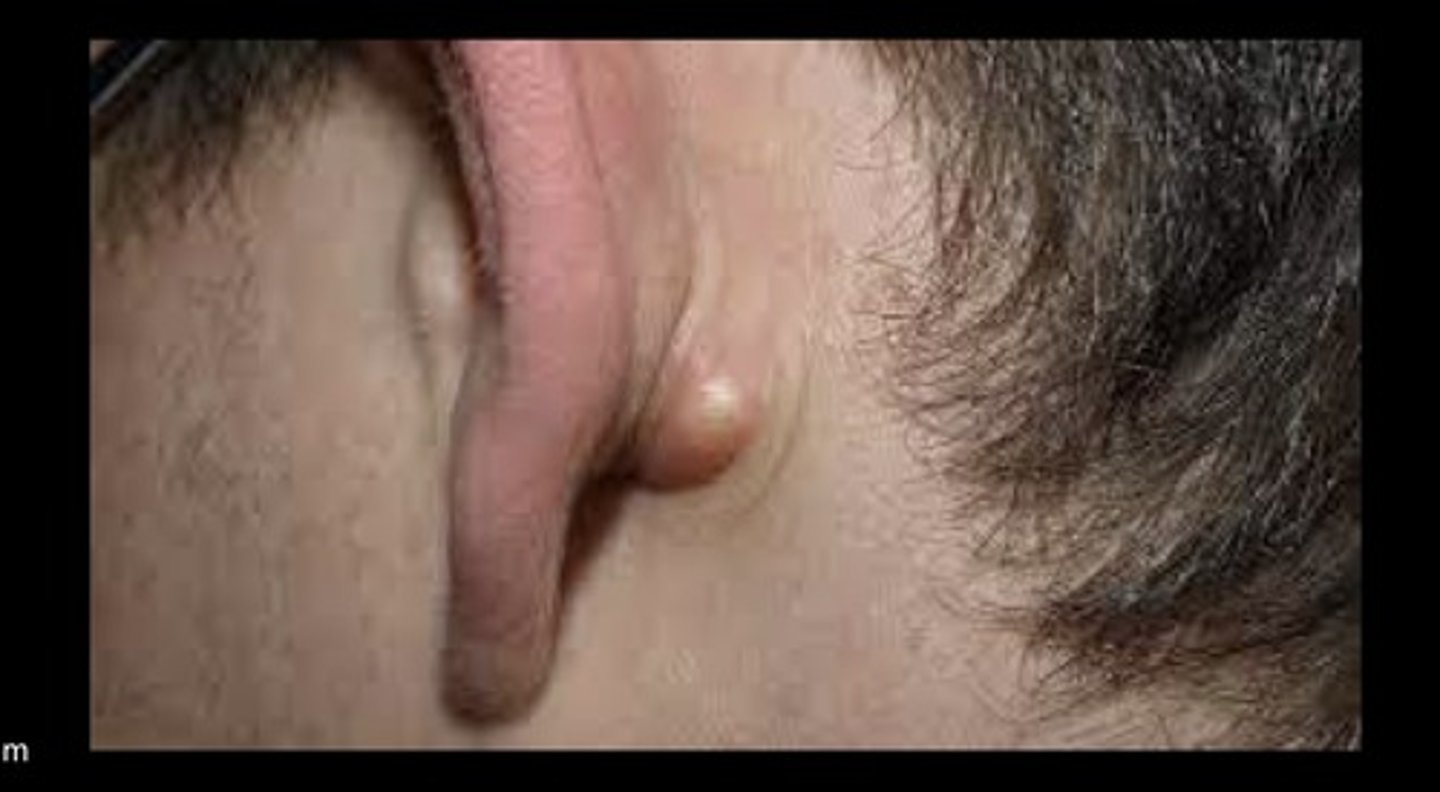
Cutaneous Cyst (Sebaceous cyst)
Benign, closed, firm sac, dome shape lump
In dermis, attached to epidermis
Possible inflammation
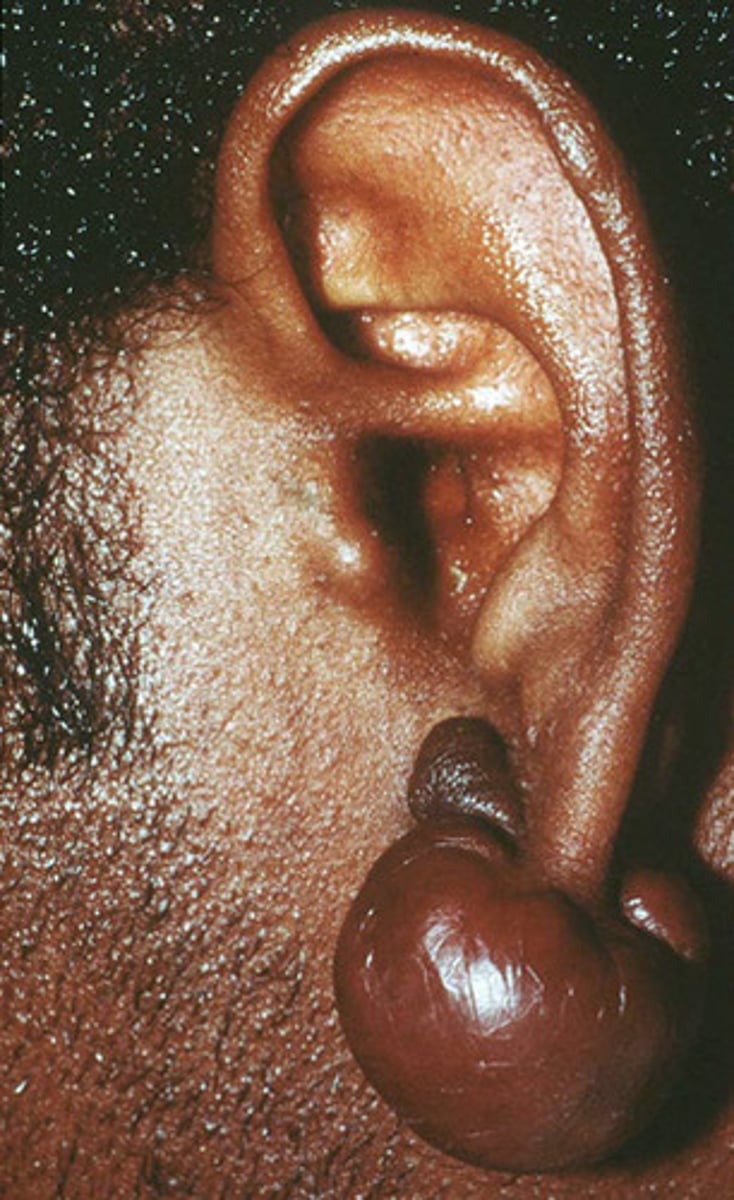
Keloid
Overgrowth of scar tissue
Dt: Trauma
On ear lobe/cartilaginous area
On/around area of trauma
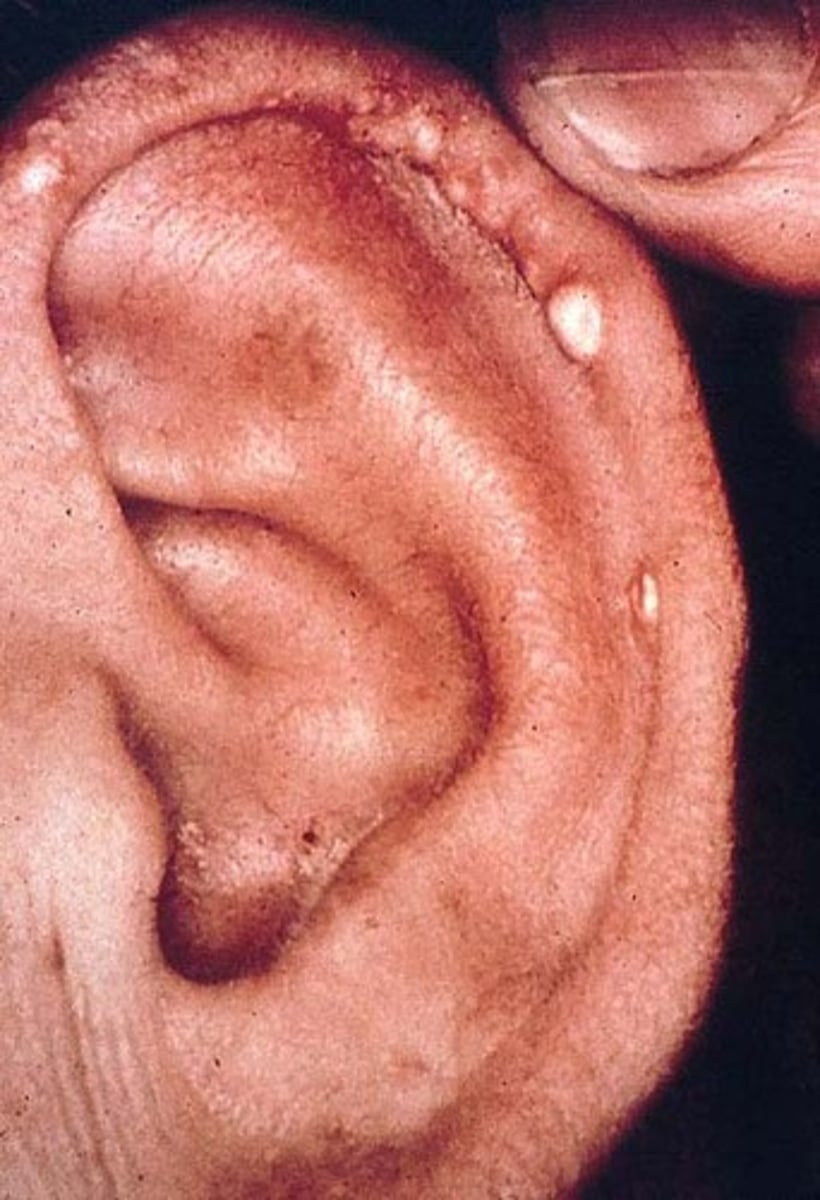
Tophi
Uric acid crystal deposit - dt chronic tophaceous gout
Hard nodules on helix/antihelix
May discharge - white chalky crystal
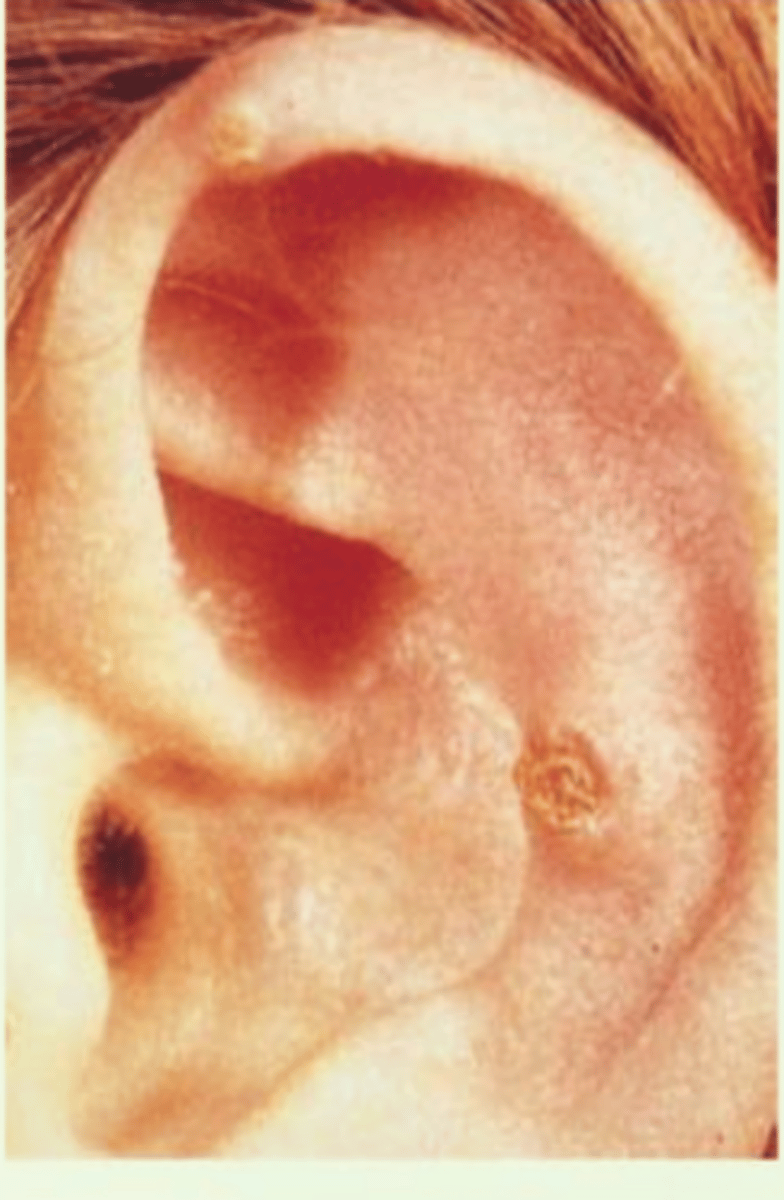
Rheumatoid Nodules
Small lump on helix/antihelix
Associated with chronic RA
Possible ulceration
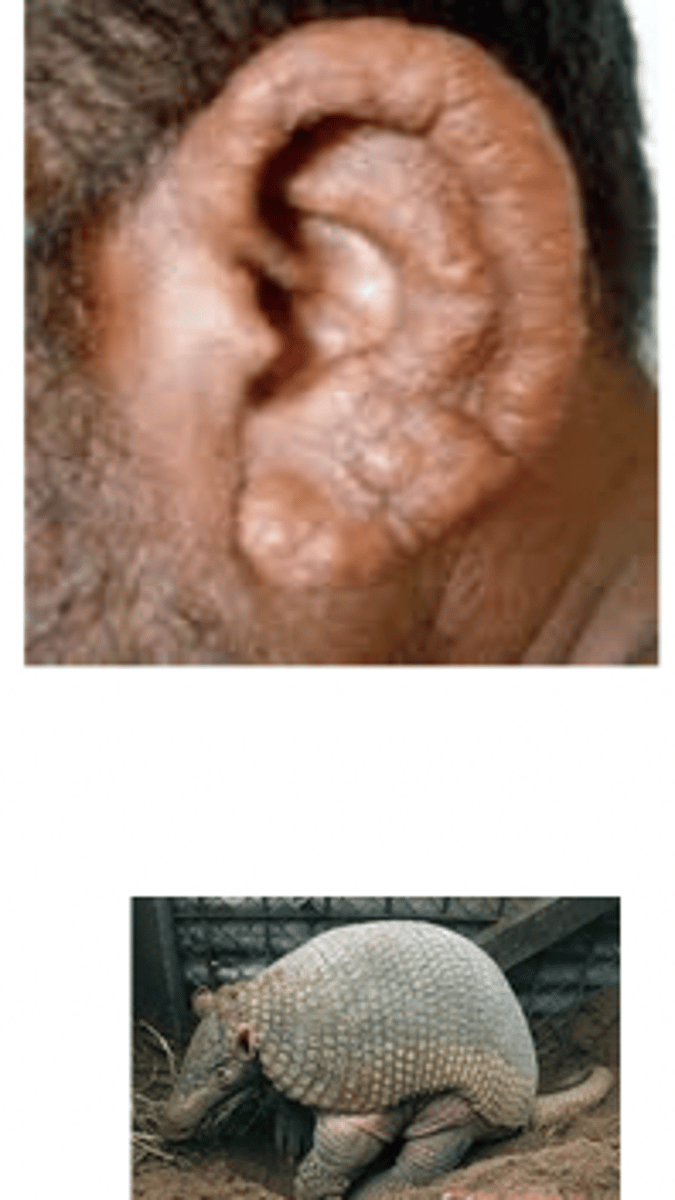
Lepromatous Leprosy
Multiple papules and nodules dt chronic infection
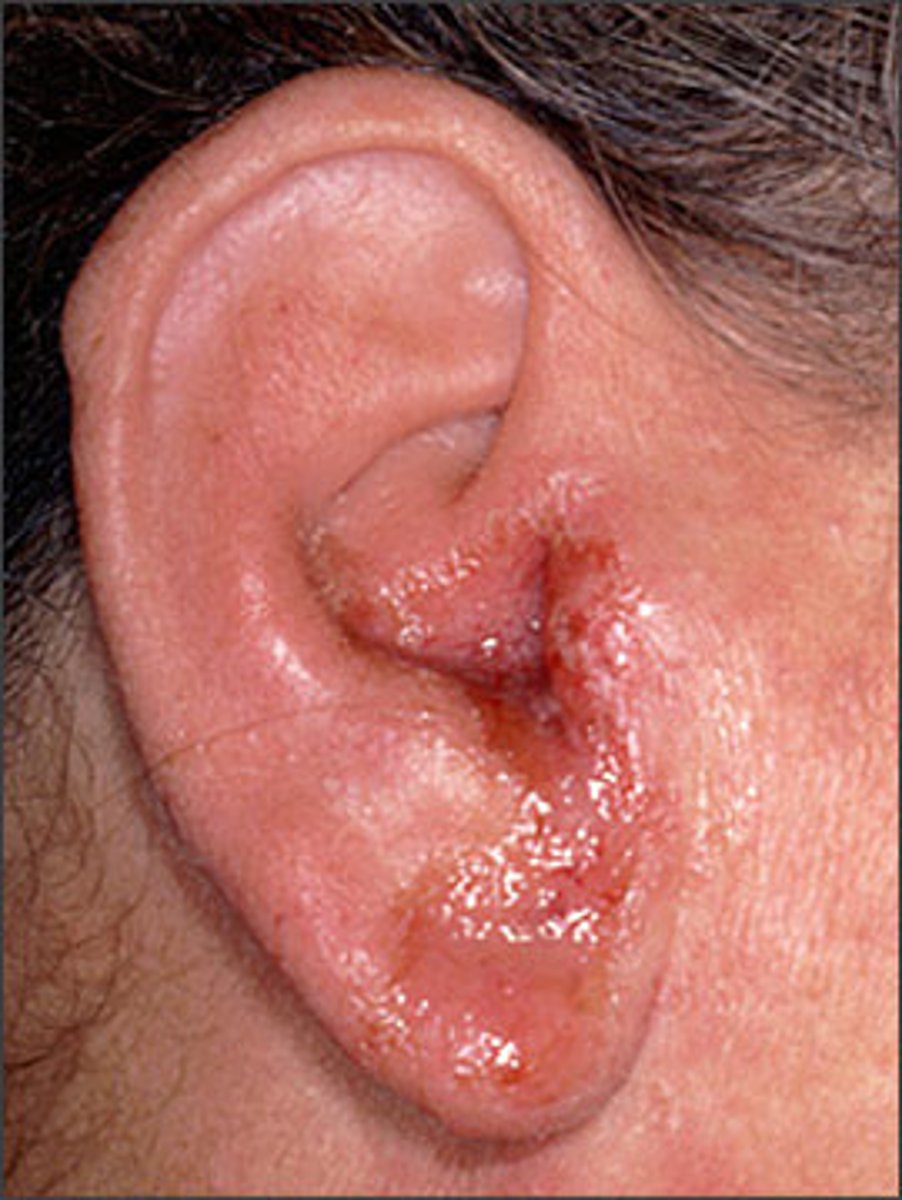
Acute Otitis Externa
"Swimmers ear"
Skin of ear is swollen and tender
Auricle and meatus is narrowed, moist, and red
Hard to see TM
Cx's:
Trauma (fingernail, bobby pins)
Moisture (swimming)
Chronic Otitis Externa
Red, itchy, thickened skin with keratin debris in canal.
Ear Drum inspection
1. Colour - pinkish-grey
2. Contour
3. Cone of light - 4 or 8 'o' clock
4. Handle of malleus
5. Short process - white elevation
6. Pars flaccida - superior
7. Pars tensa - inferior
8. Incus - can see shadow
9. Umbo - COL fans ant. & inf.
10. Circumferential & manubrial blood vessels
Red reflex of ear
Dilation of blood vessels supplying tympanic membrane
Follows prolonged examination
Mimics acute OM
NB - beware of false +ve
Exostosis
Hard round outcroppings
Along auditory meatus
Multiple - usually bilateral
Slow growing
Asymptomatic - rare to occlude meatus
Risk factors:
Bony external canal stimulation with cold water
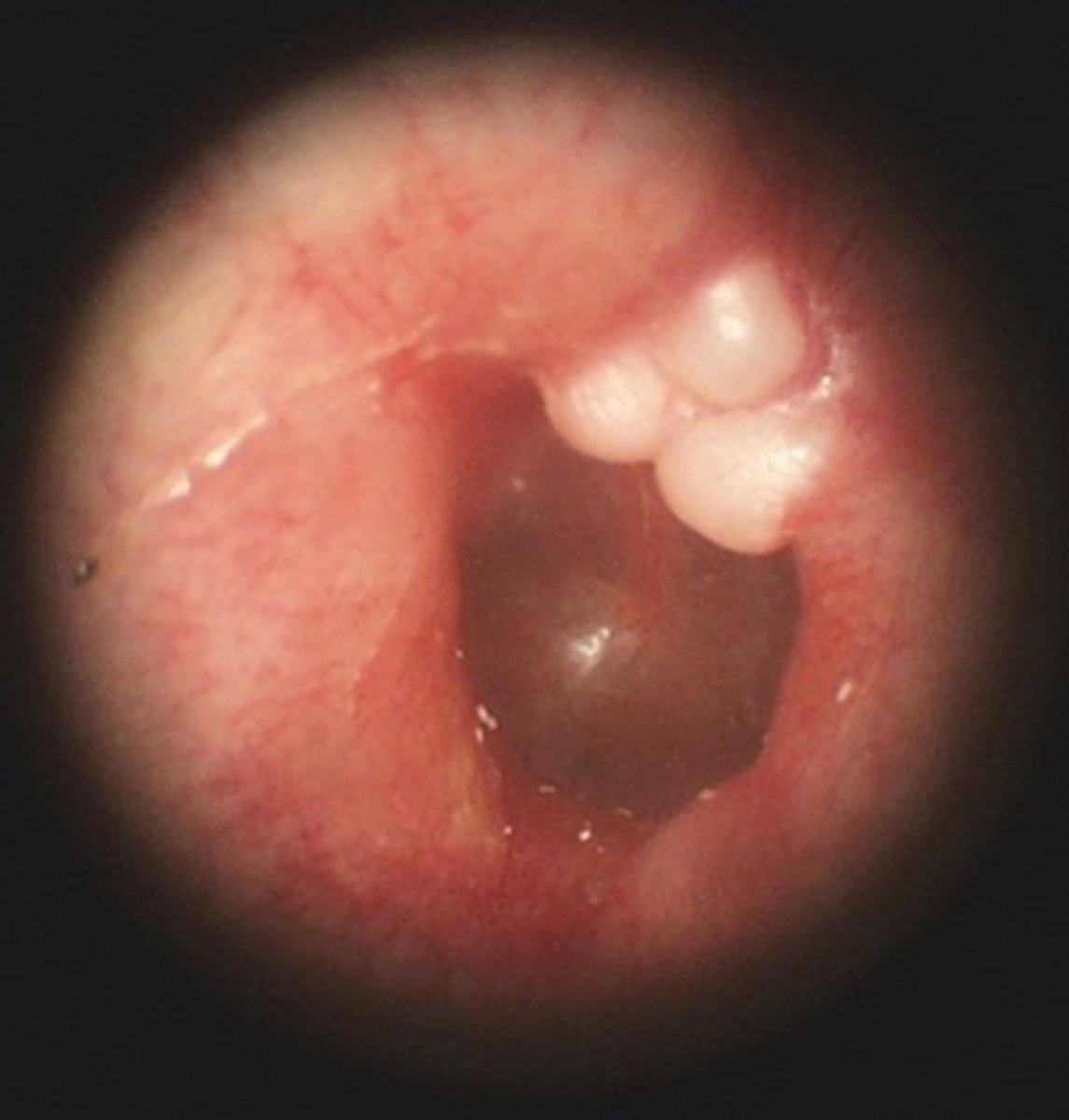
Foreign Body
Varied
Causes conductive HL
May result in:
Secondary OE
TM or occicle damage
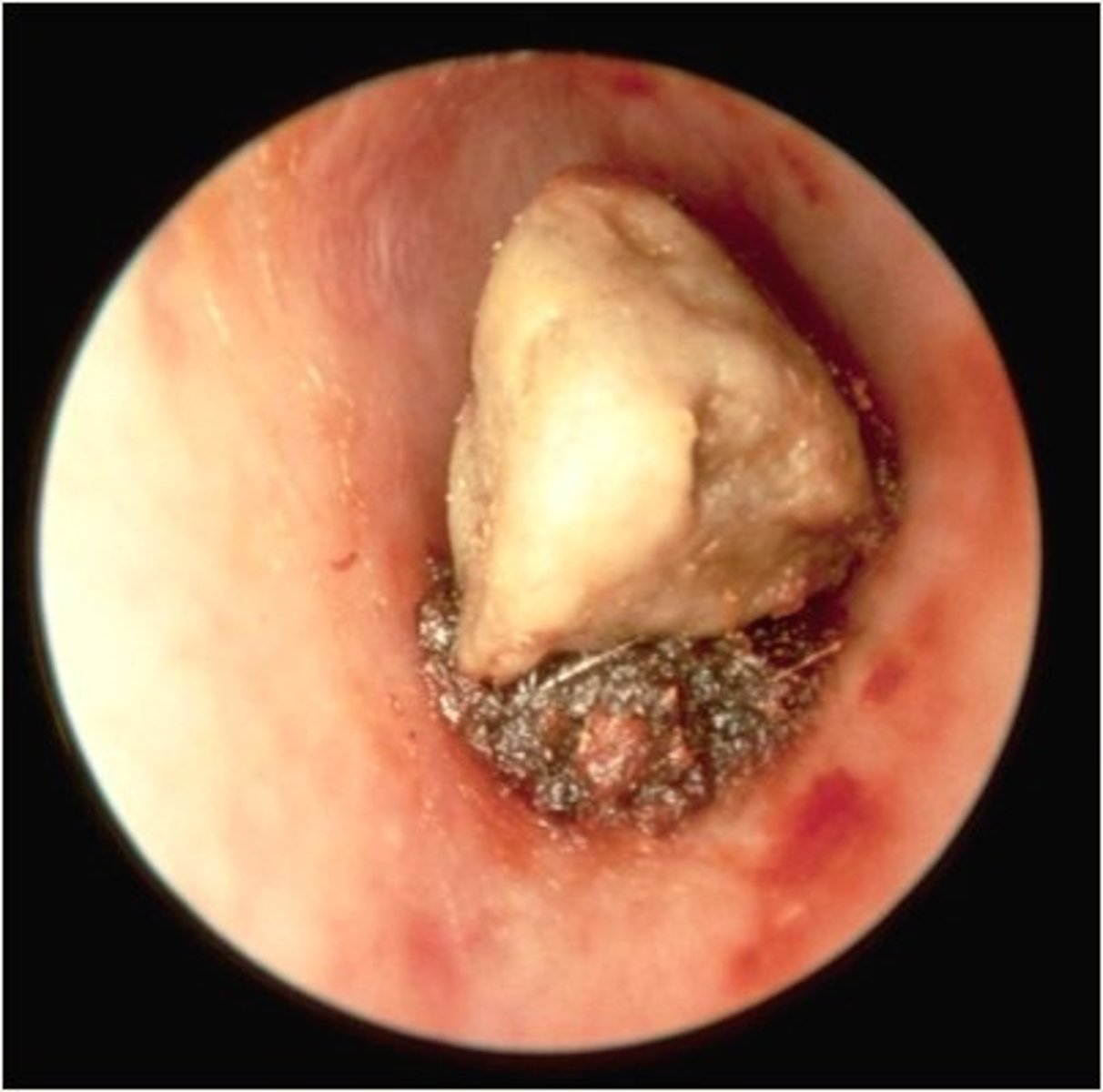
Cerumen Impaction "Wax impaction"
Build up over time (asymptomatic)
Occludes all structures pos. to site
Causes:
Conductive HL
Otalgia
Fullness
Itching
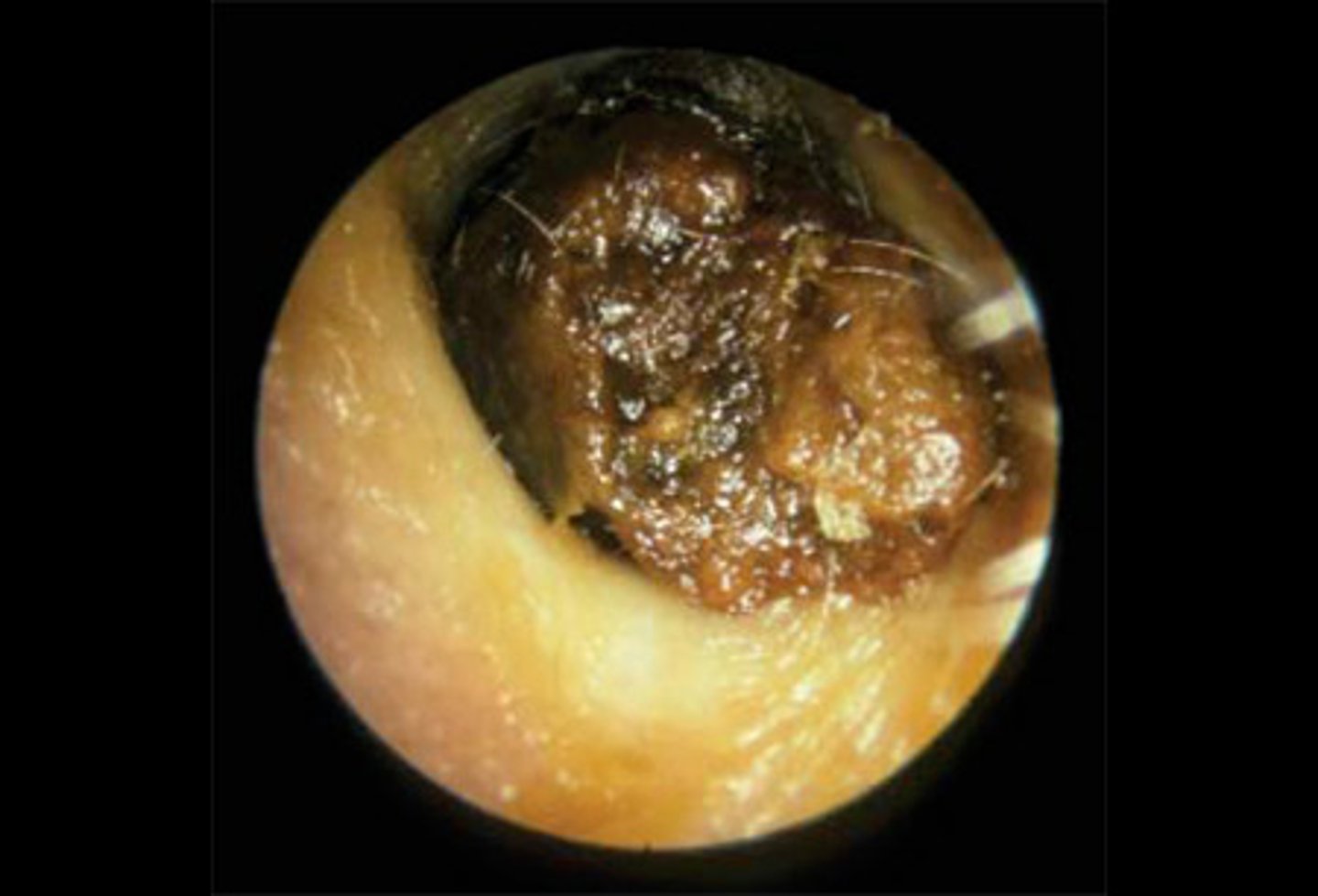
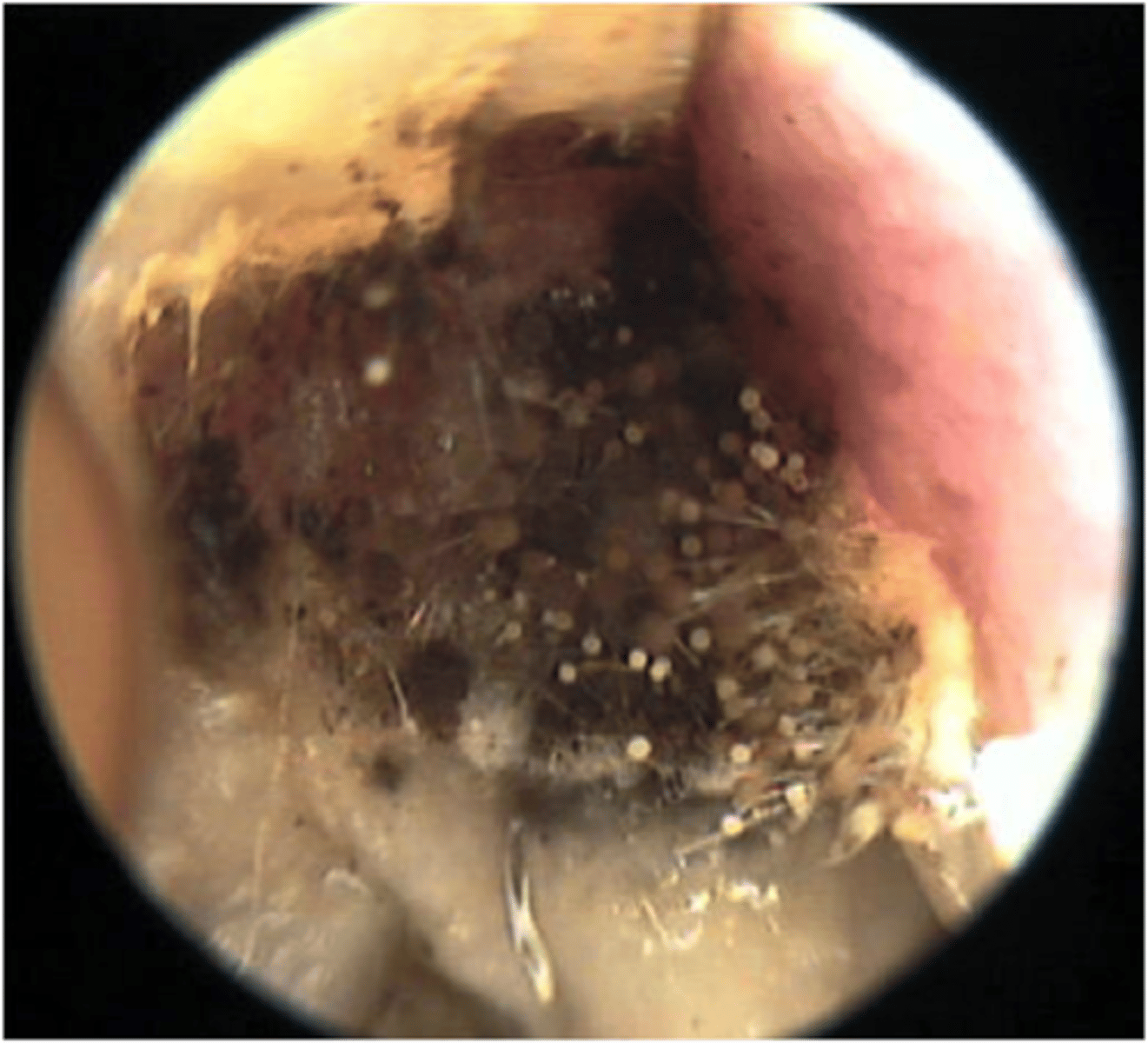
Otomycosis
Fungal infection
White coloured thick debris
Fluffy appearance (Mycelium growth)
Underlying skin is red, tender, & swollen
Acute Otitis Media
Bacterial infection
After URTI
Common in children
Red, bulged TM
Possible perforation (pus)
-
Sxs:
Otalgia
Fever
Conductive HL
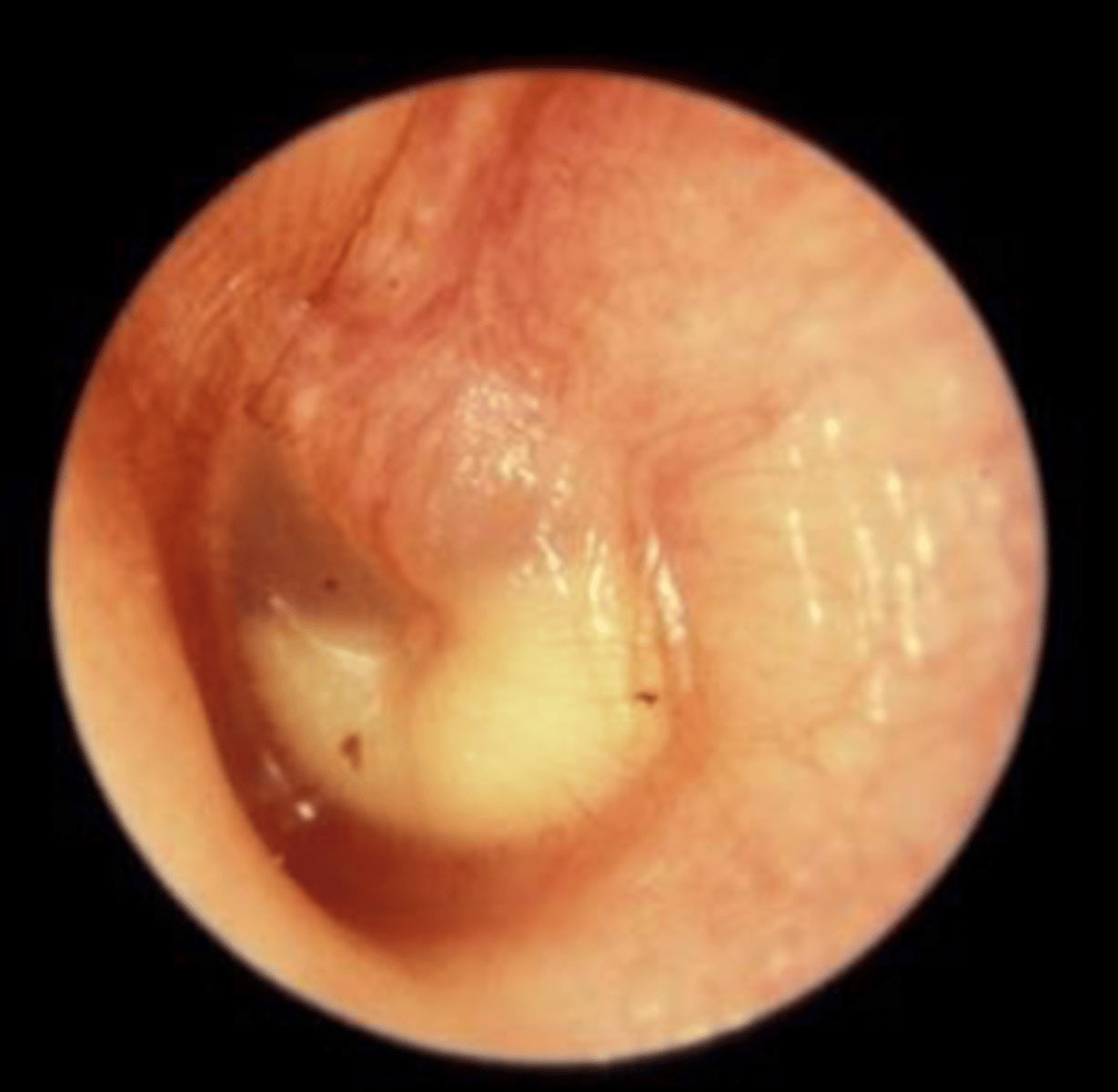
Atrophic OM (Retracted drum)
Pulled medially
Malleolar folds tight and outlined
Short process protrudes & prominent
Handle of malleus pulled inward - looks horizontal
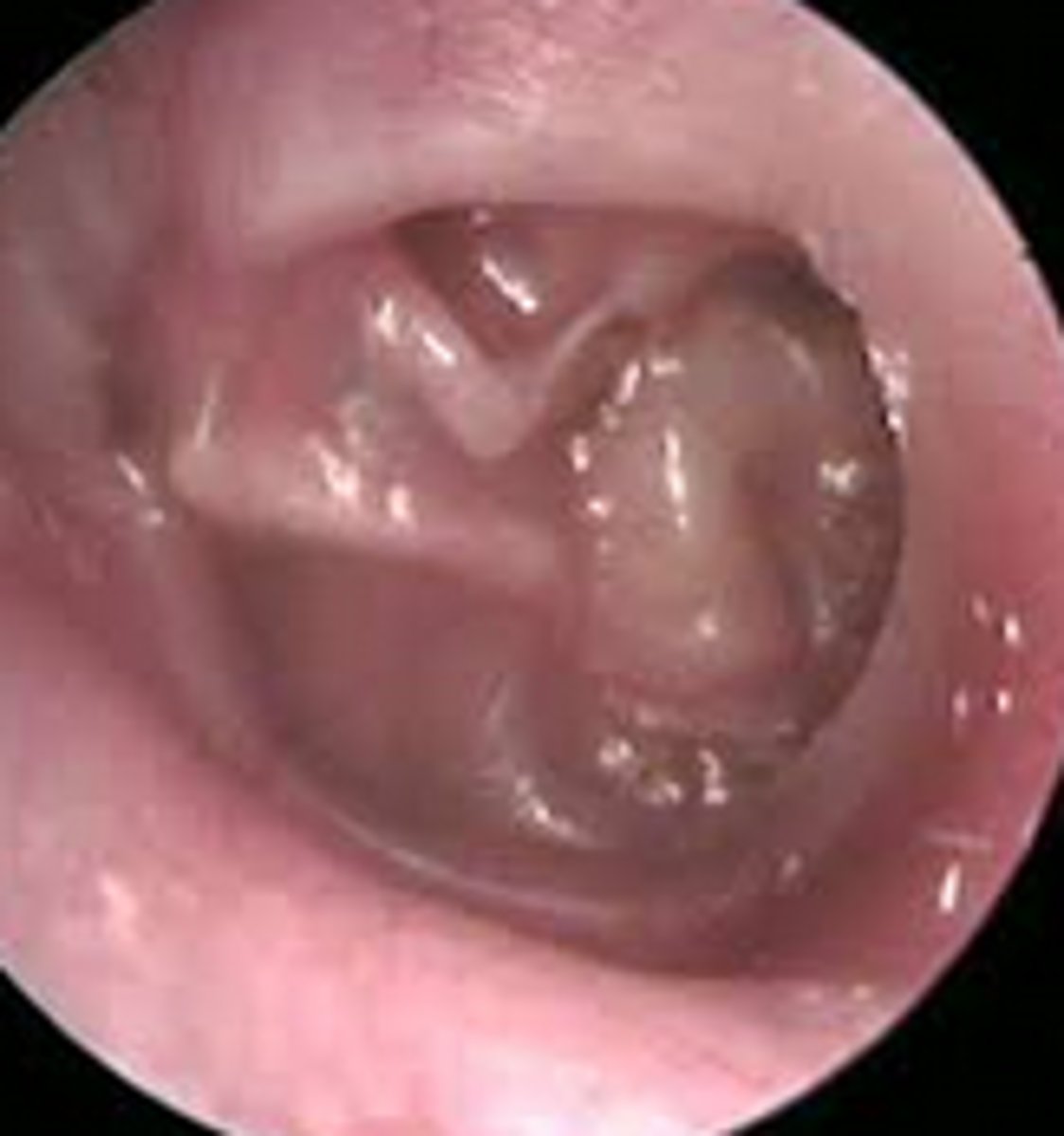
Serous Effusion
Causes:
Viral URTI
O. Barotrauma
Eustachian tube cannot equalise air pressure in middle ear with outside ear
~
Air is absorbed & replaced with serous fluid (amber colour) - NB
~
Sxs:
Fullness/Popping
Mild conductive HL
Otalgia
~
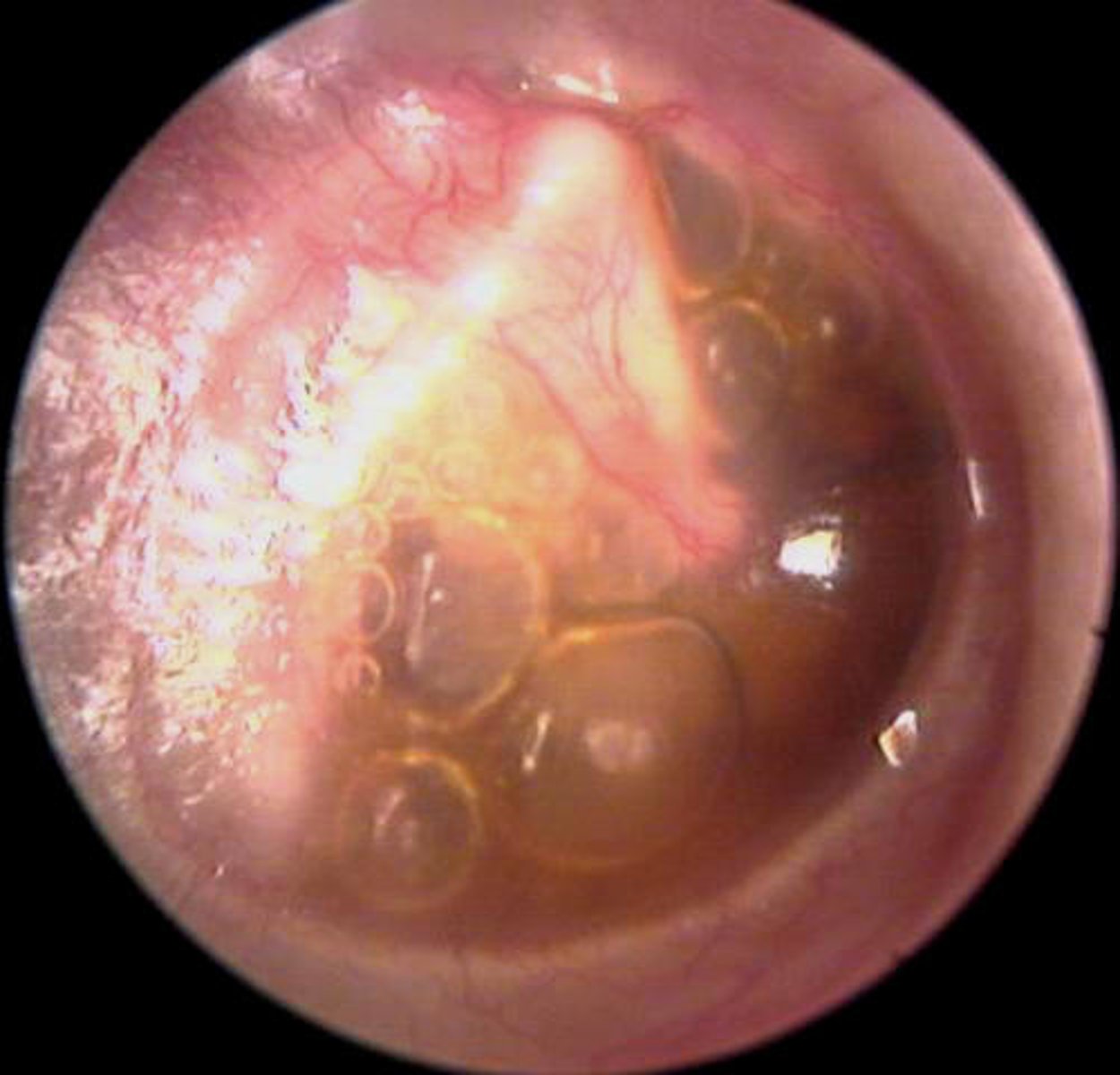
Perforated Drum
Holes in eardrum from:
Infection
Trauma
~
Classed as:
Central
Marginal
~
Scarring causes loss of landmarks
Heals in tympanosclerosis
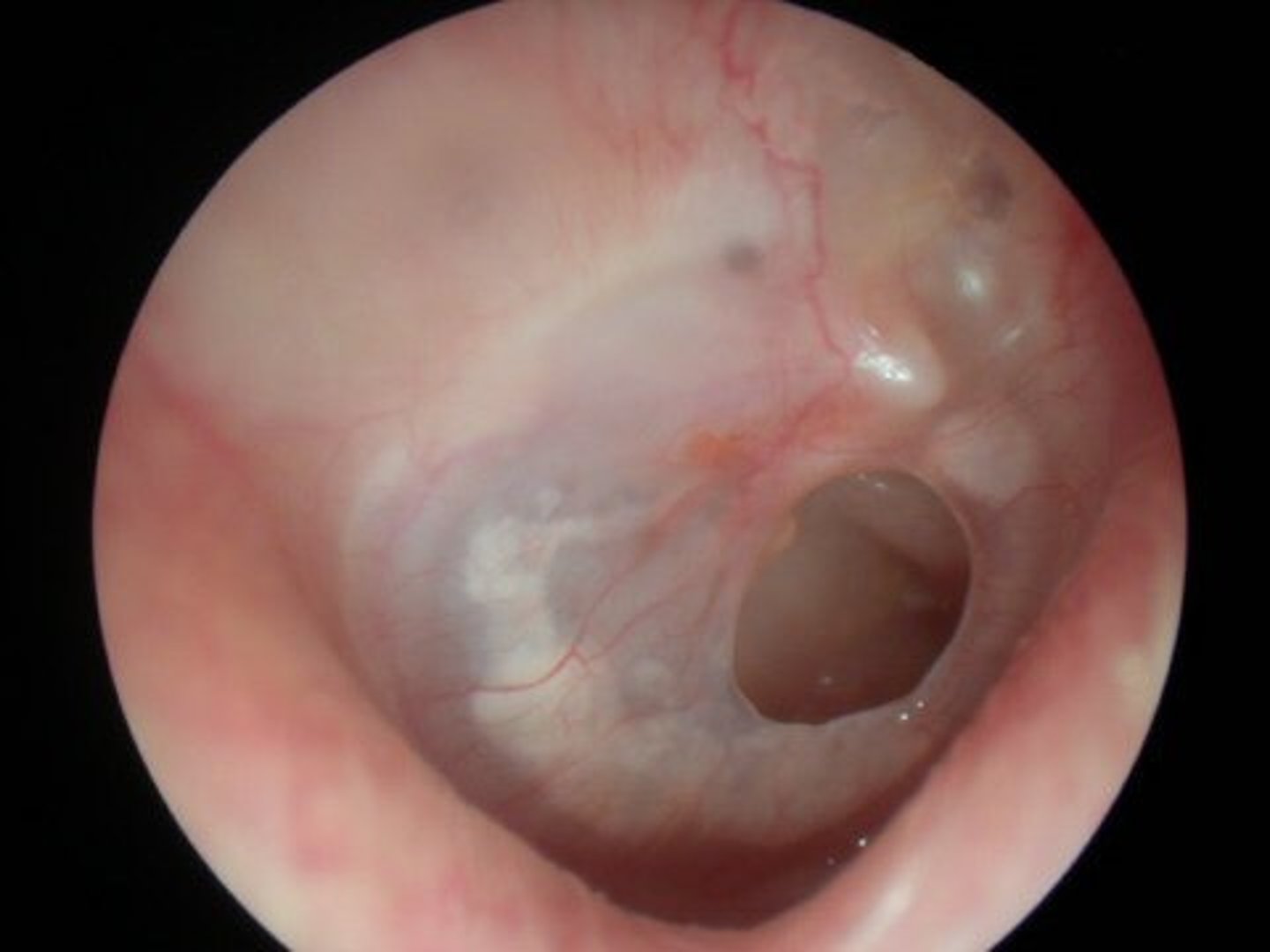
Traumatic perforated drum
Dt: Variety - e.g. blast injury
Any shape/size - small, clean cut
Generally along pos. pars tensa
Possible fresh blood visible
Spontaneous healing
Infected perforated drum
Follows OM
Pressure build up ruptures TM
Irregular edges
Pars tensa/flaccida
Otorrhea along meatus
(Discharge characteristics - volume, frequency, colour, consistency, odour, blood streaked)
Tympanosclerosis
Deposition of hyaline material in TM layers - follows perforated TM
"Hyalinization"
Large, chalky, white patches with irregular margins
Usually doesn't impair hearing
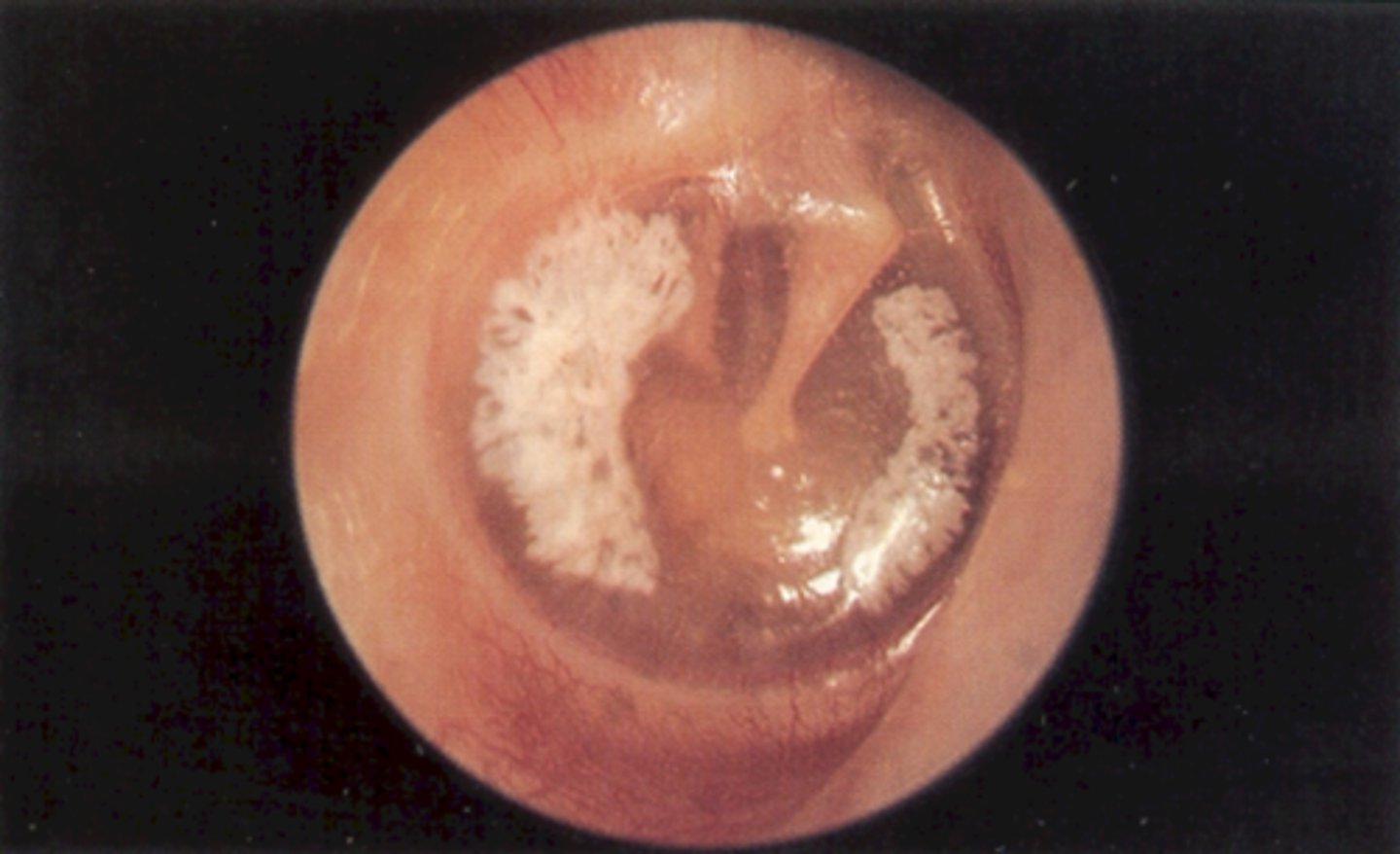
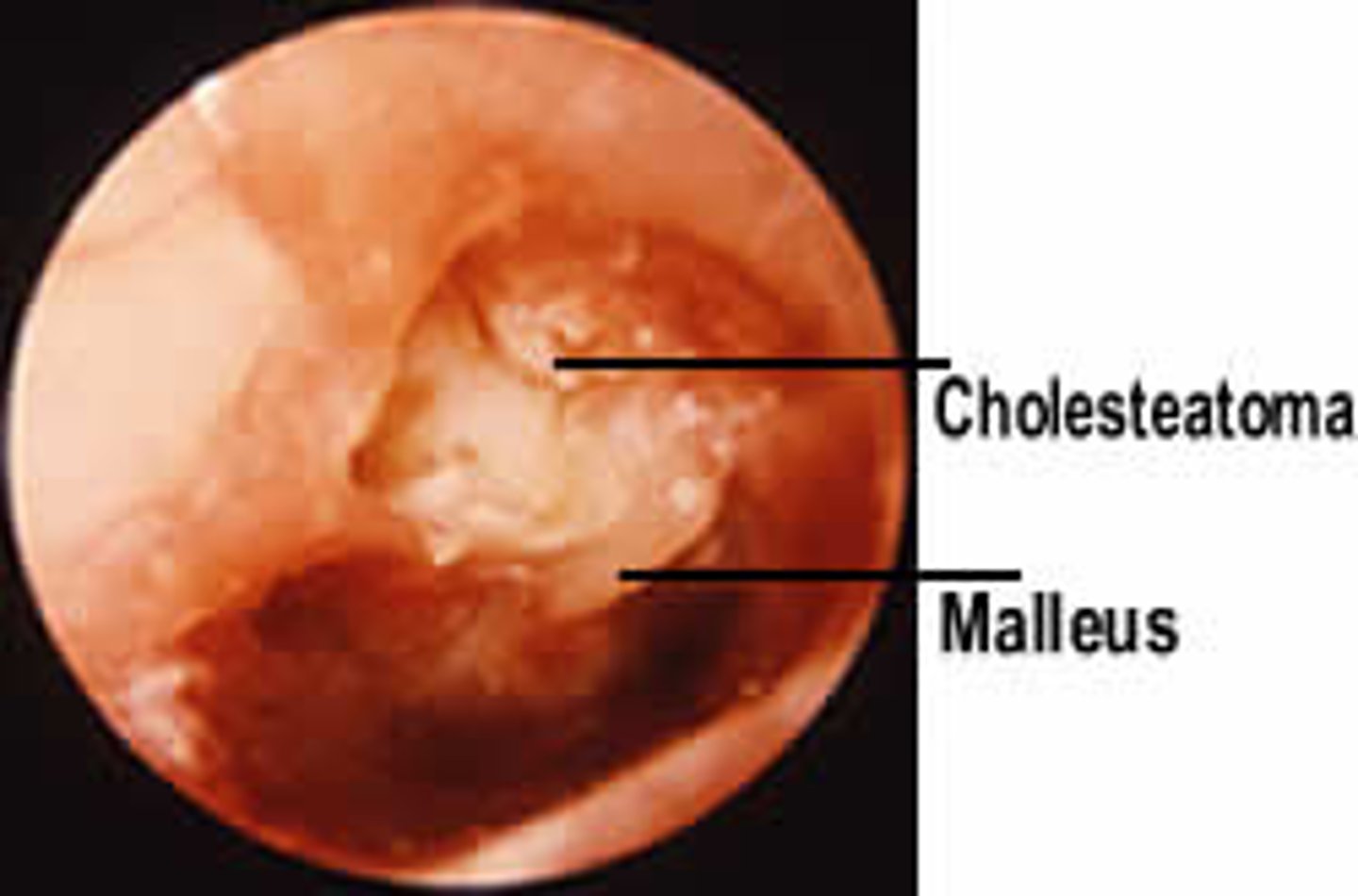
Cholesteatoma
Skin cell build up in middle ear
Cyst like growth
Congenital or dt chronic OM
Sxs:
Discharge
No pain or HL
Meniere's Disease
Endolymph build-up affecting vestibular system of the ear
Sxs:
Vertigo, tinnitus, dizzy, temp. HL
Unilateral
Episodes (20 mins - 24 hrs)
Drop attacks
Confused with labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis
Viral/Bacterial inner ear infection
Swelling both branches of vestibulocochlear nerve or labyrinth (affects balance and hearing)
Sxs:
Dizzy, vertigo, N&V, LOB, tinnitus
Possible nystagmus and blurred vision
Risk factors:
URTI
Smoking
Alcohol
Meds
Stress
Diagnosis = Rule out other cx of sxs
Vestibular battery test
Vestibular Neuritis
Mimics labyrinthitis
Swelling of 1 branch of vestibulocochlear nerve (vestibular portion only - affecting balance)
Sxs:
Dizzy
Vertigo
N&V
LOB
Difficult concentration
No auditory sxs
Whisper Test
Estimate hearing by whispering into one ear.
Weber Test
Test for lateralization of sound perception.
Rinne Test
Compare air and bone conduction of sound.
AC>BC : N = Sensineural HL
BC>AC = Conductive HL
Sensineural HL
Disorder of inner ear or cochlear nerve
Upper tone of words disproportionately lost
Hearing worse in noisy environment
Speaks loudly (can't hear voice)
Can't see problem
Onset middle - later years
Weber = lateralises to good ear
Rinne = Positive AC>BC
Cx:
Sustained exposure to loud noise, drugs, inner ear infections, trauma, tumour, presbycusis
Conductive HL
Disorder of external/middle ear
Minor sound distortion
Hearing better in noisy environment
Speaks softly
Can normally see abnormality in ear canal
Onset in childhood & young adult up to 40
Weber = lateralises to bad ear
Rinne = Negative - BC>AC or BC=AC
Cx:
Ear canal obstruction, OM, perforated drum, otosclerosis
Common ear related complaints
✓Otalgia
✓Muffling or distortion of hearing
✓Hearing loss/deafness
✓Tinnitus
✓Discharge
✓Masses or lesions
Referrals
ENT specialist
Audiologist
Speech and hearing therapist