Comp Sys Fund Quizzes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
When a process is waiting for an I/O operation to complete, what is the state of the process?
-new
-ready
-waiting
-running
-waiting(blocked)
Which of the following best describes the function of the short-term scheduler?
admits new processes to the system
selects the next process from the ready queue to run on the CPU
swaps processes in and out of memory
handles process termination
selects the next process from the ready queue to run on the CPU
The Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) must save the state of the process before executing. Which of the following is NOT typically saved?
Stack Pointer
Mouse position
Instruction Register(IR)
Program Counter(PC)
Mouse position
Interrupts create events T/F
False
When an interrupt occurs, the CPU immediately stops the current instruction and jumps to the ISR. T/F?
False
Throughput is defined as the time between the submission of a process and its completion. T/F?
False
The mean time between failures (MTBF) measures the average time a system operates without interruption. T/F?
True
Suppose a system has the following process completion times: Process A arrives at 0 and finishes at 3, Process B arrives at 2 and finishes at 7, Process C arrives at 4 and finishes at 10. What is the average turnaround time?
4.66
A server is available 99.9% of the time in a year. Approximately how many hours is it down in one year?
8.76 - answer was 9 with margin of .5
A computer system is running three processes:
Process A is waiting for a user to click a button,
Process B is reading data from the disk,
Process C is currently using the CPU.
Suddenly, the user clicks the button for Process A. What is the most likely sequence of events that will happen next?
The system ignores the click until Process C finishes all its work.
Process A immediately starts running, interrupting Process C, and Process B is terminated.
Process B is paused, Process A and C both run at the same time.
The CPU finishes the current instruction for Process C, saves its state, and then switches to Process A if it has higher priority.
The CPU finishes the current instruction for Process C, saves its state, and then switches to Process A if it has higher priority.
Explain the difference between CPU utilization and throughput using an example from everyday life (e.g., a kitchen, a classroom).
hY
If we roll a six-sided dice two times, what is the probability of getting a sum of two dice equal to five (5)?
0.33
0.5
0.11
0.25
0.11
The service time of a process follows Poisson's distribution.
T/F
False
Which of the following is the correct formula for the probability of event A given event B (conditional probability)
Pr[A U B] / Pr[A]
Pr[A ∩ B] / Pr[B]
Pr[A] + Pr[B]
Pr[A ∩ B] / Pr[A]
Pr[A ∩ B] / Pr[B]
We have options to buy one of the two cars. Car 1 is brand new with an engine life-expectancy of 5 years. The Car 2 has been in use for 2 years, with a life expectancy of 5 years. The probability of engine failure is higher after 3 years for a used car. T/F
False
If a fair die is tossed, what is the probability of getting an even number?
1/2
If the average number of arrivals at a store is 4 per minute, what is the probability that there are exactly 2 arrivals in one minute? (Answer up to 2 digits after the decimal)
0.14
For a random variable X representing the number of heads in 3 coin tosses, what is the probability that X = 2?
3/8
1/8
4/8
2/8
3/8
What does the simulation "clock" represent in a discrete-event simulation?
The number of arrivals
The current simulated time in the system
The number of events processed
The number of customers in the system
The current simulated time in the system
If the ready queue has 2 processes from time 6 to 8, and 1 process from time 8 to 11, what is the total accumulated process time in the ready queue during this interval?
7
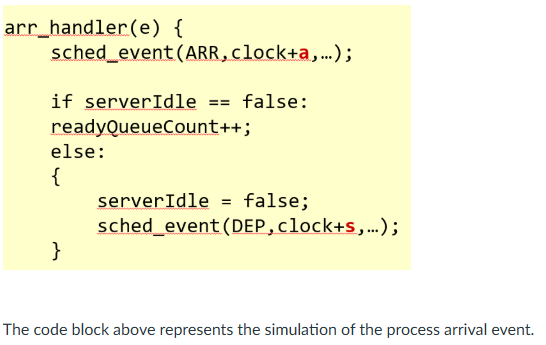
T/F
True
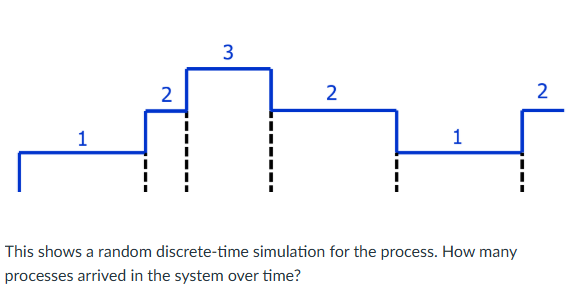
4
In the FCFS scheduling algorithm, we pause the running process when another process comes into the system. T/F?
False
To increase the availability, we must perform vertical integration. T/F?
False
In a real-time system, latency is not an important issue.
T/F?
False
In the Shortest Job First (SJF) algorithm, we consider both the service time and the arrival time to determine the next process for execution. T/F?
False
Multilevel queue scheduling allows different queues to use different scheduling algorithms. T/F?
True
If a process has waited 10 units and has a service time of 5 units, what is its response ratio (R)?
3
Cache Hit/ Cache Miss is related to which of the following concepts?
Hard Affinity
Non-preemptive
Preemptive
Soft Affinity
Hard affinity
soft affinity
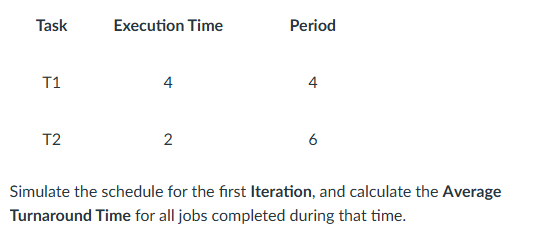
5.5
Task set: (4, 1.5), (3, 2.5). If we apply the RM scheduling algorithm to this Task Set, will we be able to meet all deadlines?
NO
Task parallelism is more efficient because it can be scaled better than Data Splitting. T/F?
False
We can solve the Data Race issue with the help of Synchronization. T/F?
True
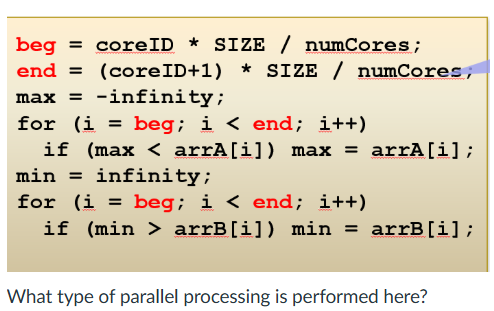
Data-Oriented
Task-Oriented
Data-oriented