HIV I: History and Epidemiology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
AIDS
-caused by 2 retroviruses: human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2)
-both are result of multiple cross-species transmission events of simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs) naturally infecting African non-human primates
-HIV causes AIDS by depleting CD4+ T lymphocytes, weakening the immune system and increasing risk of opportunistic infections & malignancies
-while the greatest depletion of CD4+ T lymphocytes occurs at the time of primary HIV infection, it takes several years for most patients to develop AIDS and its associated signs/symptoms
-no cure or vaccine
-antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of disease and may lead to normal life expectancy
finding the underlying cause
-initially, there were many hypotheses, both infectious and non-infectious (toxins, autoimmunity)
-unlike standard outbreak investigations, AIDS presented unique challenges as it was characterized by clinical signs that developed years after the initial exposure had occurred
retroviruses
-after discovery of reverse transcriptase from animal oncogenic RNA viruses in 1970, significant interest in role of retroviruses in human malignancies
-efforts to identify these viruses in humans initially unsuccessful
-HTLV-I as first identified human retrovirus
-HTLV-I: shown to be the cause of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), and tropical spastic paraparesis (TSP)
retrovirus investigators suspected a viral etiology of AIDS because
-specific targeting of CD4+ lymphocytes was identical to HTLV-I
-were animal models in which retroviruses caused cancers and an AIDS-like wasting syndrome
-HTLV-I was transmitted through blood and sexual activity consistent with the hypothesized transmission of AIDS
-cases of AIDS in patients with hemophilia who had received only filtered clotting factors eliminated the possibility that any particular casual microorganism that was larger than a virus
establishing causal links between HIV and AIDS
-HIV was repeatedly isolated from patients with AIDS, including those from different origins
-virus was found to be highly tropic to CD4+ T lymphocytes
-readily reproducible antibody test was developed that was sensitive and specific for the development of AIDS
-demonstrated that patients with mutations in the co-receptor CCR-5 were immune to HIV-1 infection
-later, it was observed that AIDS could be prevented when administering medications that could prevent HIV replication
viral archeology
-HIV-1 sequences pre-dating the recognition of AIDS could be crucial in defining the time of origin and the subsequent evolution of these viruses in humans
-discredited origin theories: smallpox vaccination, HBV vaccination, oral polio vaccination, other conspiracy theories
HIV subtypes and viral evolution

prehistory of HIV
-importance of DRC60: highly divergent from ZR59, which was most closely related to the ancestor of subtype D
-demonstrates that group M HIV-1 strains had already undergone substantial diversification by 50 years ago
-ZR59 and DRC60 within the group M phylogeny indicate that the various subtypes already existed 50 years ago
-based on analyses, first HIV-1 group M virus entered human populations between 1902 and 1921
-HIV-1 was spreading between humans for 60-80 years before AIDS was first recognized in 1981
where did HIV come from in 1910?
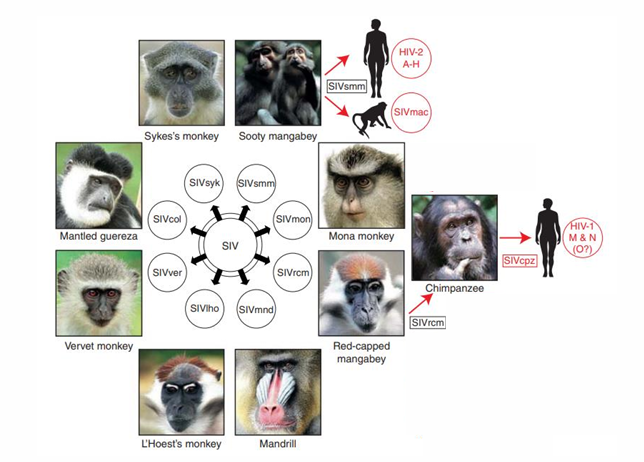
SIVcpz: the precursor to HIV-1?

effects of colonialism
-rapid establishments of towns, cities, and other colonial stations
-development of seaports, railroads, and other infrastructure
-large influx of European workers
-disruption in cultures/traditions of native populations
-increase in sexual encounters
-increase in STIs, particularly genital ulcer diseases
-impaired immunity of native populations from malnutrition, forced labor
-increase in medical interventions, including non-sterile injections
-increase in demand for bushmeat
early human transmission

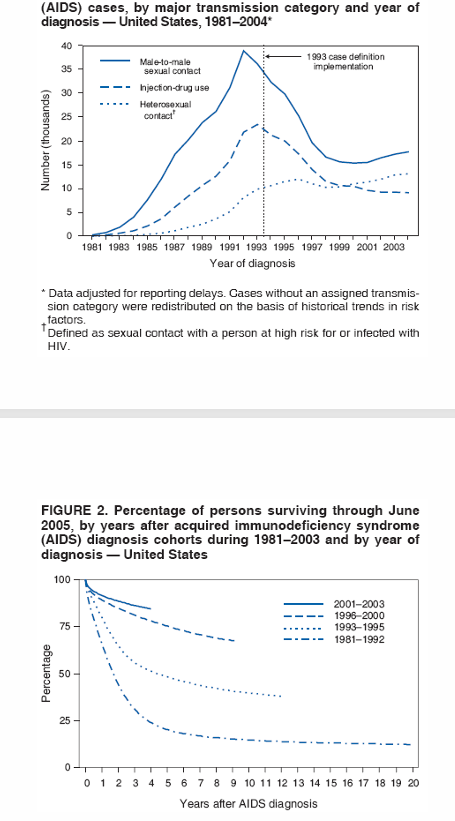
early AIDS epidemic
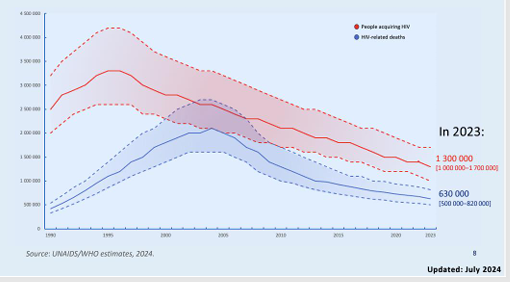
____ in number of people acquiring HIV and HIV-related deaths, globally over time
-decline
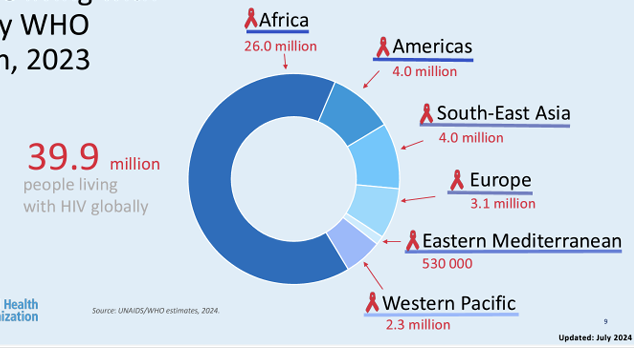
people living with HIV by WHO region, 2023
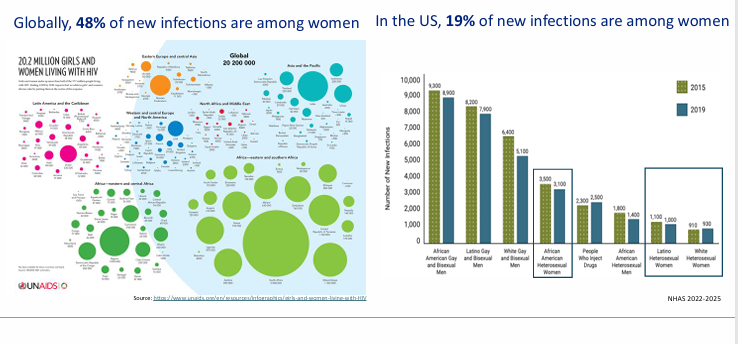
____ are disproportionately affected by HIV
-minoritized women
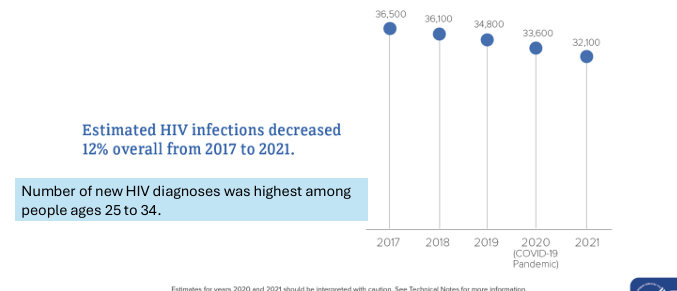
estimated HIV infections in the US over time
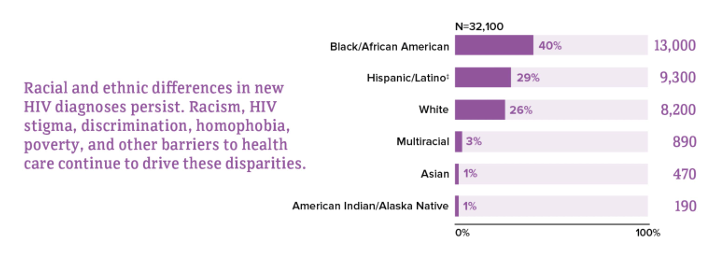
differences in estimated HIV infections by race/ethnicity
global goals to end HIV by 2030
-rates of new infections and deaths are not falling rapidly enough to meet 2030 target

how do we get to the targets?

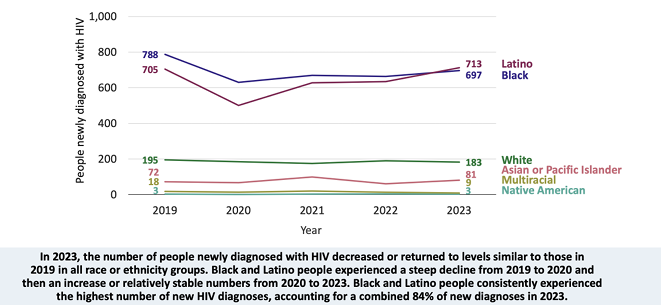
number of new HIV diagnoses in NYC by race or ethnicity, 2019-2023