ESDM/DTT
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Traditional Behavioral Interventions
Therapists teach skills in a one-on-one setting with a predetermined response.
Highly prescribed teaching structure.
May break skills down into small steps.
Repetitive teaching in a controlled environment.
Positive reinforcement of desired behaviors while working to minimize “undesired” behaviors.
May represent principles of operant and/or classical conditioning.
Social-Pragmatic Developmental Interventions
The therapist follows the child’s lead.
Therapist fosters initiation and spontaneity.
Reinforcement of contingent responses.
Implemented as part of naturalistic communication.
Emphasizes the “how” and “why” of communication in everyday interactions.
Follows a natural developmental process.
Contemporary Behavioral Interventions
Recognizes the value of traditional behavioral and other developmental approaches.
Value of giving children choices, sharing the communication opportunity, and using preferred activities and materials.
May combine approaches to meet the needs of the child and family.
Naturalistic Developmental Behavioral Interventions (NDBIs)
Embed strategies in everyday activities
Encourage engagement and motivation by responding to the child’s cues.
Focus on Joint Attention
Early Start Denver Model
designed for 12-60 months of age
from no language skills to skills at 48 month level (4)
play based activities to promote socializ ation
parents are highly involved
Core features of ESDM
naturalistic ABA strategies
prompt, behavior, some sort of interaction (instead of reward)
sensitivity to developmental norms
480 question assessment
extensive caregiver involvement
focus on shared affect/interaction
shared engagement
language and communication embedded in everyday activities
Core principles
naturalistic teaching
Uses everyday activities and routines to teach skills.
Makes learning more relevant and enjoyable!
Could increase motivation.
joint attention
focus on building child’s ability to share attention and activities
developmental appropriateness
Tailored to the child's developmental level.
Activities suitable for age and skills.
Helps parents/caregivers to understand the child’s skills.
family involvement
The family is a key member of the team and should be involved in all sessions.
Focus on warm, positive interaction.
Learn strategies to support skills at home.
Operant conditioning
ESDM uses operant conditioning as a behavioral technique
Reinforcement of positive behaviors through social interaction and praise.
Can help to shape behavior
Can promote communication and interaction
Experiential learning
This approach is hands-on.
Encourages active participation, exploration, and skill acquisition.
Focus on what the child is interested in and build the strategies around it.
We can still control the materials presented within the environment.
Discrete trial training
can teach any learner
can teach a variety of skills, help maintain and/or generalize skills
based on ABA principles
highly structured intervention
Discrete trial training
Breaks skills down into smaller steps and explicitly teaches them.
The goal is for learners to consistently provide the desired response and to generalize the response to other situations.
Teacher provides reinforcement and/or consequences for responses.
Treatment focuses on building toward behavioral cusps or “the integration of subskills that lead to substantial changes”
Can help to promote skills in a a highly structured setting.
4 key components DTT
Discriminative Stimulus
Response
Consequence
Intertrial Interval
Discriminative stimulus
A specific cue that signals to the learner that the behavior is expected.
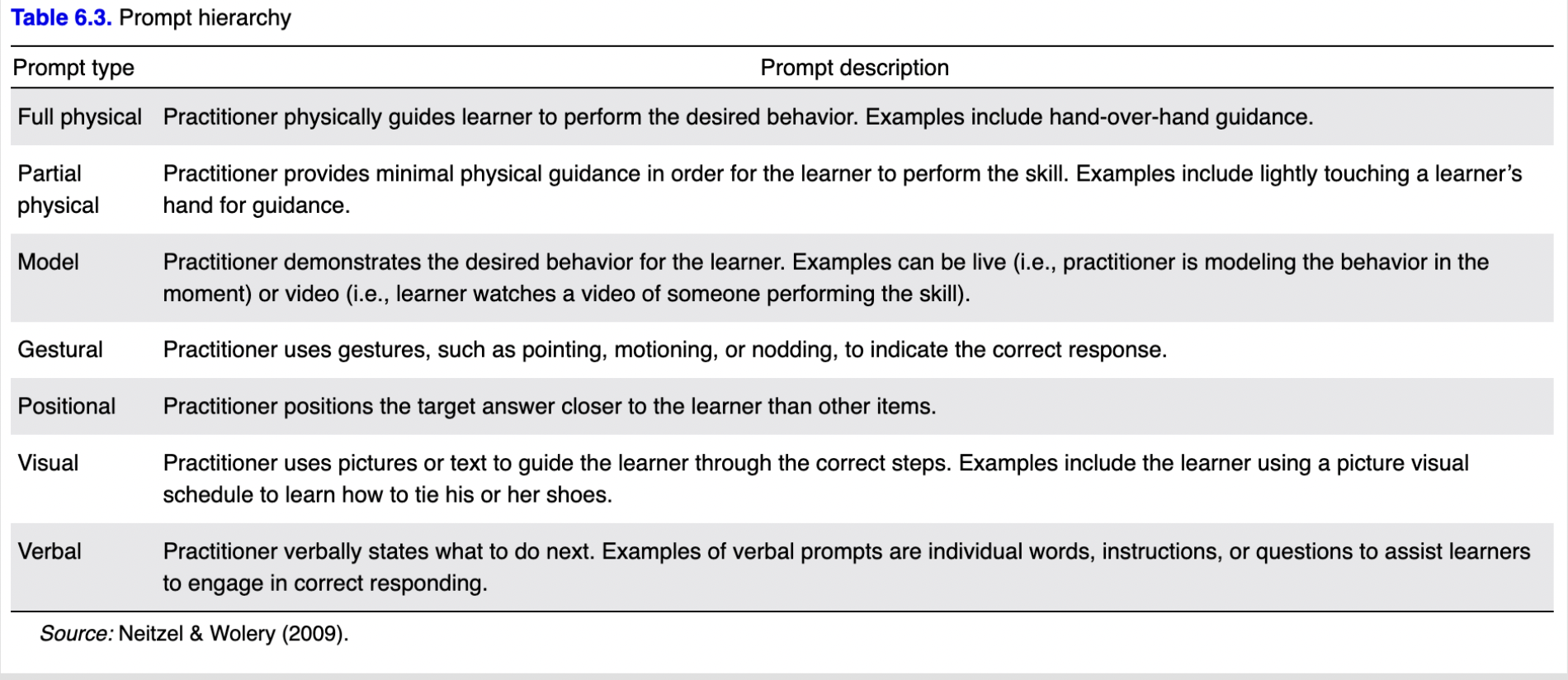
Learned may need an additional prompt to provide a correct response.
Fading of prompts will occur with the goal of independent performance of a skill.
Response and consequence
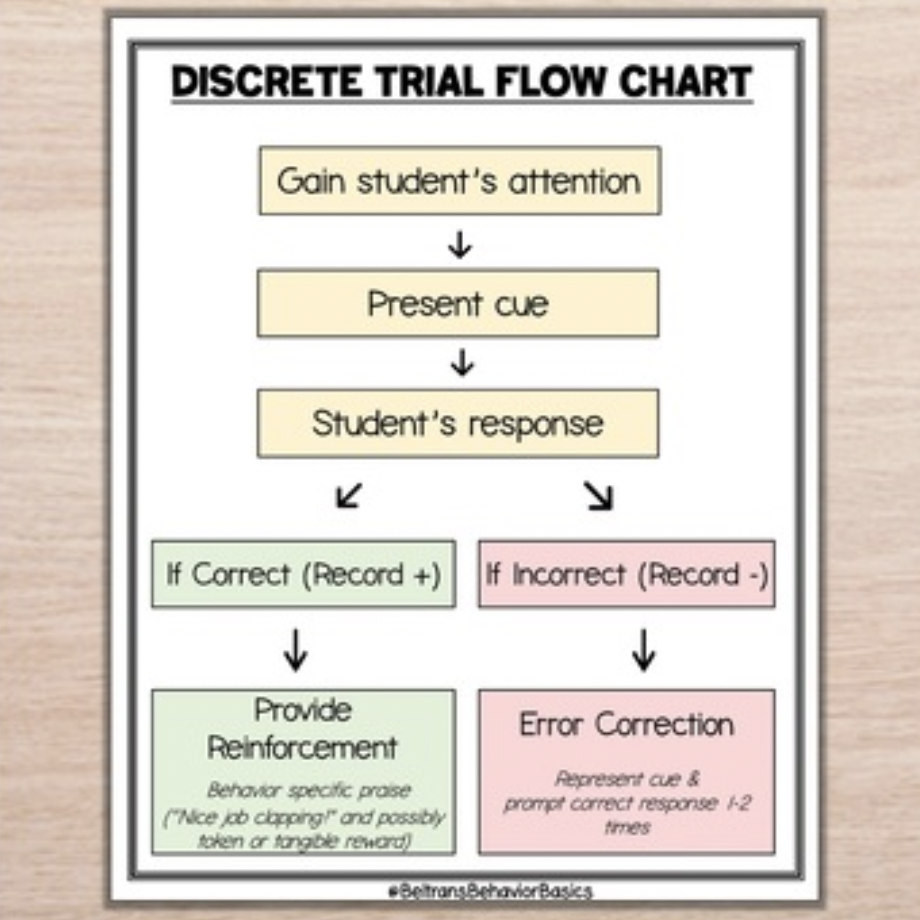
The response is the learned behavior or action following the instructional cue.
The learners response is scripted and anticipated.
The consequence is the feedback or reinforcement provided by the therapist.
The learners response is either reinforced or error correction is provided.
Reinforcers should be delivered immediately!
Discrete Trial flow chart
Intertrial Interval
The amount of time between the conclusion of one discrete trial and the beginning of the next.
Usually represented by the number of trials per minute.
Stimuli may be presented repetitively or randomly.