Group 1 and metallic bonding
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Why are alkali metals stored under oil?
Because they react very vigorously with oxygen and water, including moisture in the air
General equation for the reaction of Alkali Metals with oxygen
Metal + Oxygen --> Metal oxide
What is the balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with oxygen? (Include state symbols)
4Na(s) + O2(g) --> 2Na2O(s)
General equation for the reaction of alkali metals with water
Metal + Water --> Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
What is the balanced equation for the reaction of potassium with water? (Include state symbols)
2K(s) + 2H20(l) --> 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
Why do all the Alkali Metals react in a similar way with water?
They all have 1 electron in their outer shell
What would you observe when lithium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (4 points)
Lithium moves slowly on the surface of the water
Fizzing
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
What would you observe when sodium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (5 points)
Sodium moves quickly on the surface of the water
Fizzing
Sodium melts to form a ball
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
What would you observe when potassium metal reacts with water containing universal indicator solution? (6 points)
Potassium moves very quickly on the surface
Fizzing
Potassium melts to form a ball
A lilac flame
The metal gets smaller and eventually disappears
Universal indicator turns purple
Why does the universal indicator turn purple?
An alkaline solution of the metal hydroxide is formed
Which ion causes the solution to become alkaline?
The hydroxide ion (OH-)
What is the trend in reactivity down Group 1
Reactivity increases as you go down the group
Why does reactivity increase down Group 1?
Down the group, the number of electron shells increases.
The outer electron is therefore further away from the nucleus and is lost more easily. There is more shielding as you go further down the group.
How would the reaction of Caesium with water compare with that of Potassium?
Much more vigorous reaction. The hydrogen gas is produced extremely quickly and ignites. Explosive.
Group 1 melting points
Decrease as you go down the group
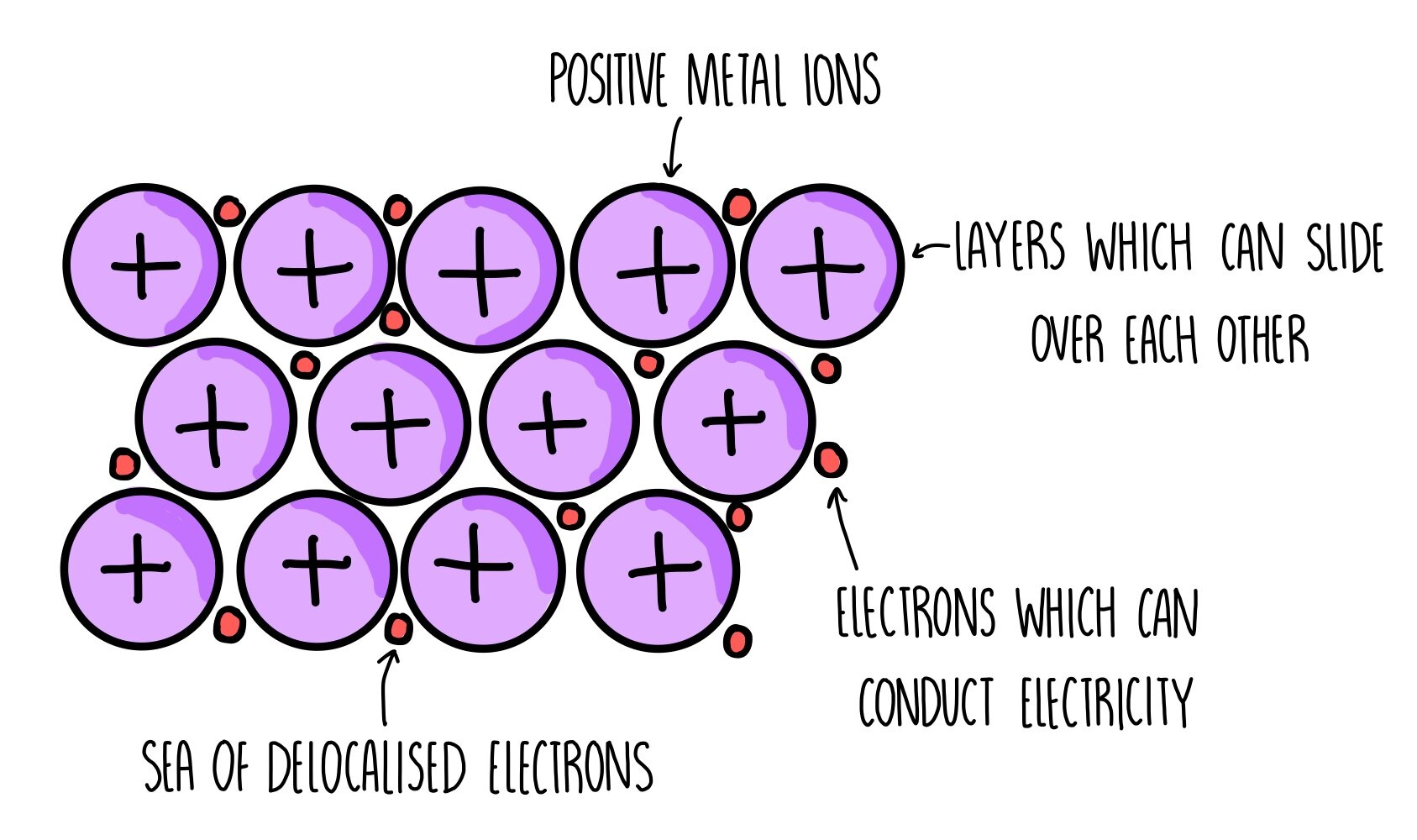
Metallic Bonding
The electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons.
Positive ion
Cation
Metallic Bonding Structure
Giant metallic lattice
Metal melting and boiling points
High.
The attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons is very strong so a lot of thermal energy is required to break the bonds.
Metal conductivity
Conductive in solid or liquid.
They contain delocalised electrons which are mobile, and free to move and carry charge.
Are metals malleable and ductile?
Yes.
This is because the metal ions are arranged in a regular lattice structure in layers which can slide over each other when a force is applied.