advanced research methods
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Key issues in research methods
how do we know what to test?
Popper (1972) argued that research begins when a problem is identified and further suggested that there are: 1. causal observations
previous research
test statistic (e.g., t-value)
variance explained by the model/ variance not explained by the model= effect/error
Alpha value
0.05
Beta value
0.20
effect size
an attempt to address for Type I errors in hypothesis testing, quantifying the strength of the relationship between variables or the magnitude of treatment effects.
power analysis
attempt to control for Type || error
tells us the statistical power associated with a particular test
two approaches
a priori
post-hoc
Research integrity
honesty
accountability
professional courtesy and fairness
good stewardship
Replication crisis
Ioannidis (2005) raised concerns about research findings within the literature
Open science collaboration (2015) found that 36% could be replicated
and highlighted the importance of replicating studies to ensure the reliability and validity of research outcomes.
Advanced issues in experimental research
hypothesis
a testable prediction about the relationship between variables.
validity
The extent to which a test measures what it is intended to measure.
internal validity
The degree to which an experiment accurately establishes a causal relationship between variables, free from confounding influences.
threats to validity
Maturation effect: ppt’s behaviour changes over time naturally
history effect: something changes about the ppts circumstances that influence the variables
Testing effects: merely having been tested before may change how they do the post-test
types of control groups
passive
active
wait list
Advanced issues in survey design
reliability
test-retest
inter-rater reliability
inter-method reliability
internal consistency reliability
multiple regression
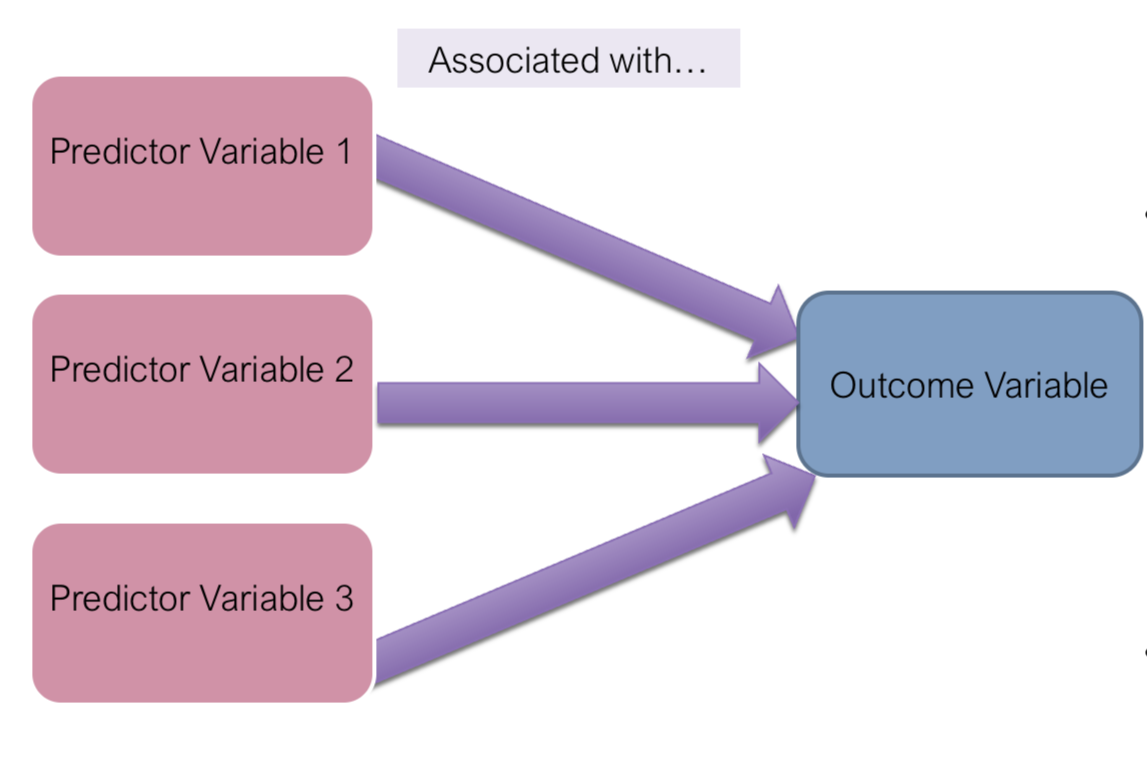
multiple regression
forced entry
predictors based on previous research and theory
all variables forced into the model at the same time
hierarchical regression
predictors based on previous research
The researcher decides the order in which the predictors are entered into the model
stepwise method
based on maths rather than previous research/ theory
both forward/backwards method
The computer programme selects the predictor that best predicts the outcome and enters it into the model first
Independent errors
for any two observations the residual points should not correlate, they should be independent
to identify if this causes an issue conduct a durbin-watson test
hierarchical multiple regression
Hierarchical multiple regression
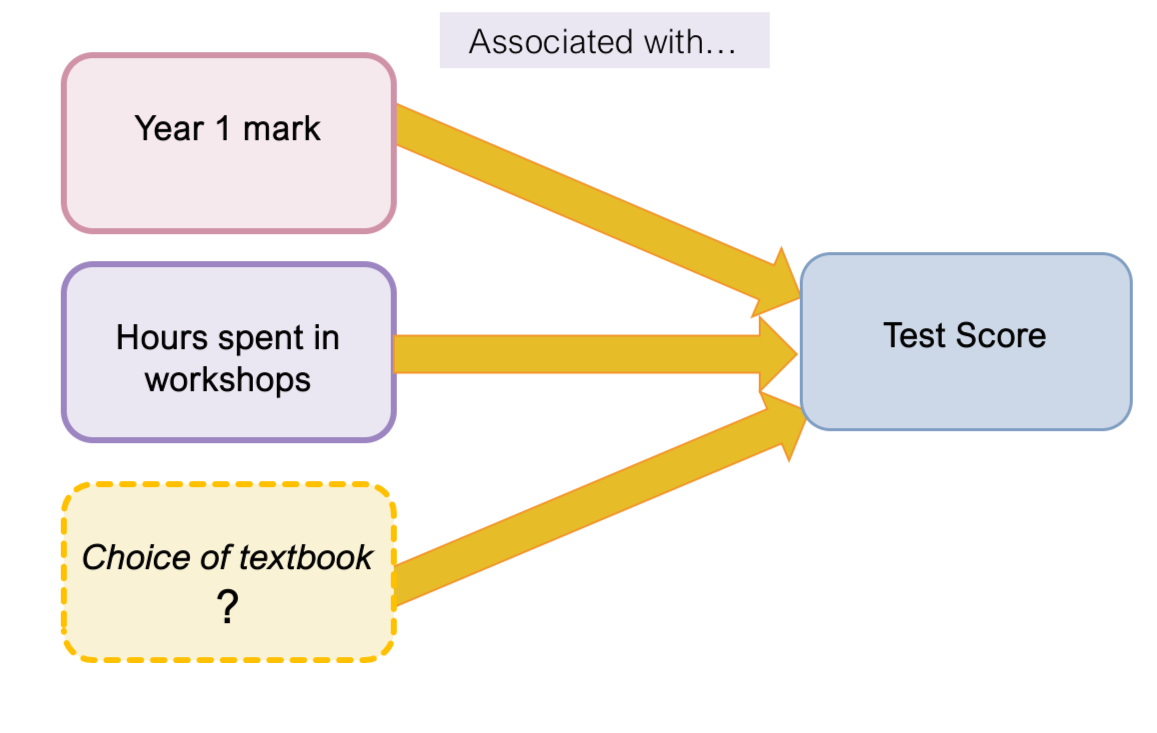
dummy coded
if it has 3+ categories
how to dummy code
Identify how many levels a variable has
Number of columns, number of conditions - 1
Columns should only have 0’s and 1’
two-way mixed anova & non-parametric data
Kurskal-Wallis Test
IVs with 3 or more conditions
between-subjects design
Friedman test
IVs with 3 or more conditions
within-subjects design
Mann-Whitney U test
for IVs with 2 conditions
between-subjects design
Wilcoxon test
For IVs with 2 conditions
within-subjects design
Post-hoc Kruskal-Wallis
between subjects
3+ conditions
followed with post-hoc Mann-Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction
Post-hoc Friedman
within subjects
3+ conditions
followed by post hoc wilcoxon test with Bonferroni correction
Post-hoc mann-whitney
between subjects
2 conditions
used as a post hoc test following analysis using kurskal-wallis test
Post-hoc Wilcoxon
within subjects
2 conditions
used as a post hoc test following analysis using a Friedman test
ANCOVA
what does the C in ANCOVA stand for
Analysis of Covariance
what is a covariate
Other variables that may influence results
how does covariates influence ANOVA results
f= variance between conditions/ variance within conditions
why include covariates
reduces within-group ‘error’ variance
Controlling for the influence of the covariates on the DV
ANCOVA assumptions
linear relationship between the covariate and the DV at each level of IV
Homogeneity of regression slopes
Independence of the covariate and experiment effect
MANOVA