U.S. Income, Wealth, and Poverty: Sociological Perspectives and Policy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is wealth defined as in the context of income inequality?
The value of assets owned by a household at a point in time.
Which has a greater impact on income inequality: individual choices or broader social factors?
Broader social and structural factors.
How does wealth affect life chances?
Wealth provides access to goods and services and preserves economic divisions.
What is the World Bank's definition of poverty?
Living on less than $2.15 per day.
What are the two types of poverty mentioned?
Absolute poverty and relative poverty.
What is the poverty threshold based on?
The cost of a minimal food diet multiplied by three.
What does the Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM) adjust for?
Current spending patterns for food, clothing, shelter, and utilities, and geographic differences in housing costs.
Who are the largest group living in poverty in the United States?
White people.
What demographic is most affected by poverty?
Children living in poverty.
What is the Functionalist Perspective on poverty?
Poverty is a product of social structures and legitimizes dominant norms.
According to the Conflict Perspective, how is inequality maintained?
Inequality is systematically created and maintained through economic position and power dynamics.
What does the Feminist Perspective highlight about poverty?
Bias against women is reproduced, and there is a distinction between deserving and undeserving poor.
What is the Interactionist Perspective's view on poverty?
It emphasizes social inequity and the culture of poverty, shaped by media narratives.
What are the consequences of poverty related to food?
Food insecurity and lack of access to adequate nutrition.
What challenges do low-income families face regarding housing?
Housing affordability and the risk of eviction leading to instability.
How does social class affect health outcomes?
Social class determines life expectancy, with lower classes facing hazardous work conditions.
What was the New Deal's contribution to welfare policy?
It created assistance programs to help those in need.
What is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)?
A tax relief program that strengthens family self-sufficiency.
What is a significant criticism of the current poverty calculation?
It is outdated and does not accurately reflect modern living costs.
What does the health-inclusive poverty measure (HIPM) aim to address?
It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of poverty by including health factors.
What is the significance of the 2023 Federal Poverty Guidelines?
They provide a benchmark for determining eligibility for federal assistance programs.
What is the role of the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)?
To assist food-insecure individuals and families in accessing adequate nutrition.
What does the term 'working poor' refer to?
Individuals who are employed but still live below the poverty line.
What is the impact of the War on Poverty?
It aimed to reduce poverty rates and improve living conditions for low-income families.
What is the purpose of poverty guidelines?
To determine eligibility for federal programs based on income levels.
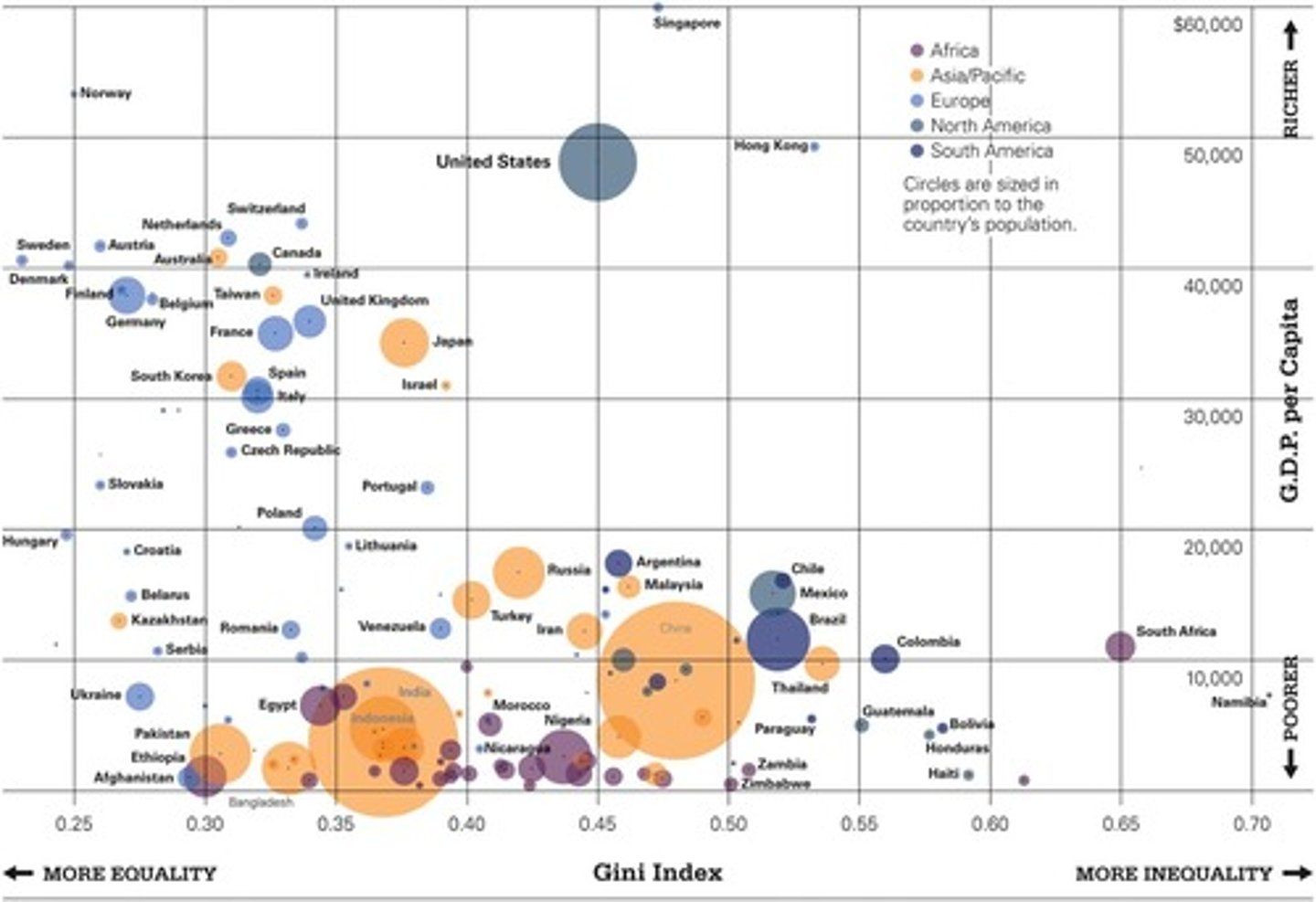
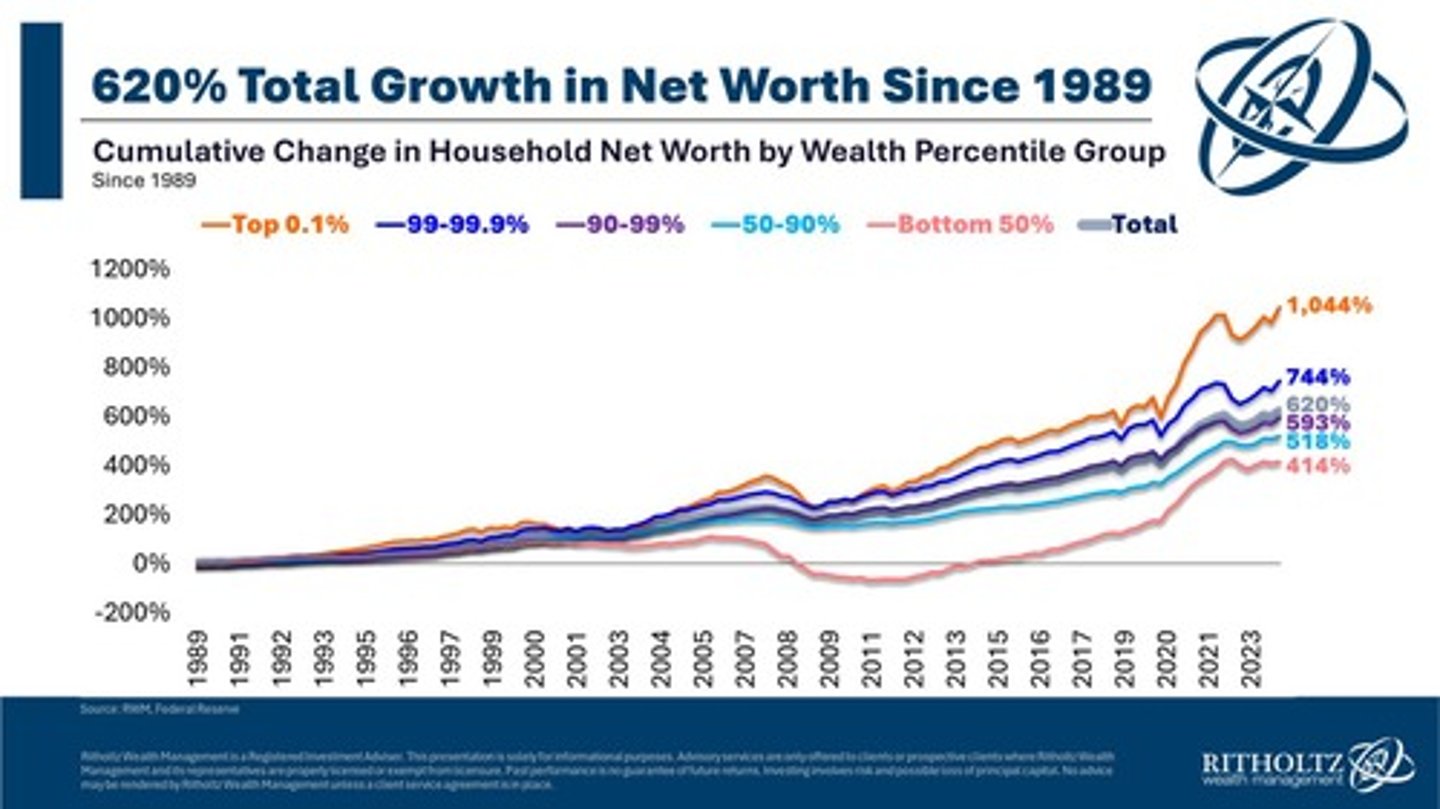
How does wealth inequality differ from income inequality?
Wealth is more unequally distributed than income, affecting access to resources.