Study Guide F (test 2)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What are formed elements?
erythrocytes, leukocytes, and plateles
Why are they called “formed elements” instead of cells?
b/c mature erythrocytes contain neither nuceli nor organelles and platelets are merely fragments broken off from a larger cell
The production of blood is known as _____________________________ and takes place in the _________________ ____________________ __________________
hematopoiesis
embryonic period of development
ALL blood cells arise from a stem cell known as the _________________
hemocytoblasts
Production of RBC is known as ______________________ and it is stimulated by the hormone __________________
erythropoiesis and is stimulated by EPO (erythropoietin
Note that there are several precursor cells and that the ________ is ejected
nucleus
What cell is the immediate precursor to the RBC that completes maturation while circulating in blood vessels?
reticulocytes
The production of WBC is known as ___________
leukopoiesis
The production of platelets is known as _________________
thrombopoiesis
Small pieces break off the ____________________ to form platelets
megakaryocytes as they stretch they are called proplatelets
Why is a RBC not technically considered to be a cell?
b/c mature RBC lack nucleus and organelles
Describe the shape of erythrocytes
biconcave disc
What is hemoglobin?
red-pigmented proteins that transports O2 and CO2
Describe the structure of hemoglobin
consists of 4 protein molecules called globins
2: alpha
2: beta
contain 4 heme group: organic compound ring w/ 4 Fe2+ as center
Where does oxygen bind on hemoglobin?
binds to the Fe2+
Where does carbon dioxide bind on hemoglobin?
binds to globin proteins as blood moves through systemic capillaries and is release as blood moves through capillaries of the lungs
What organ produces the majority of EPO in erythopoiesis?
kidney
What stimulates EPO production (primary stim.)?
decrease in blood O2 levels
What is the life span of erythrocyte? Why is is fairly short?
~120 days, b/c as they lack a nucleus and organelles cannot sythen proteins or repair it self
What happens to the globin portion when hemoglobin is destroyed?
globin: broken down into free aa to be used to form new proteins
Most of the Iron is __________ for future RBC production
recycled
Describe what happens to the heme group and pigments involved in erythrocyte destruction
heme group: iron is removed from heme and transported into stroage. Heme is converted by macrophages into biliverdin → bilirubin and causes a chain reaction:
bilirubin released into blood and taken out of the blood by the liver. the liver then transports bilirubin into the small intestine as a components of bile to facilitate digestion. The small intestine also converts bilirubin into urobilinogen which either creates the brown pigment in feces or absorbed back into blood converted into urobilin that is exerted by the kidneys
What are the 2 groups of surface antigens that determine blood type?
ABO group and Rh protein
What are the 2 antigens that determine ABO group?
A and B
Which antigen are found on each ABO blood type?
Type A: surface antigen A only
Type B: surface antigen B only
Type AB: both surface antigen AB
Type O: neither surface antigen
What are the 2 types of antibodies that recognize A and B antigens?
anti-B and anti-A
Which antibodies are found in the blood of individuals with each ABO blood type?
type A: anti-B in plasma
Type B: anti-A in plasma
Type AB: neither in plasma
Type O: both anti-A/B in plasma
Note that a person does not have an _________ that binds to the antigens on their RBC. Why?
antibody
why: b/c the antibody react with the surface antigen A and B
What is the antigen that determines the Rh factor?
antigen D
What is Rh postive
antigen D is present
What is Rh negative
no antigen D is present
What is required for anti-D antibody production in Rh neg. individuals?
when exposed to Rh positive blood
What can occur if incompatible blood is given during a blood transfusion? What is the result?
antibodies in the plasma bind to surface antigens of transfused erythrocytes causing clumps = agglutination
clumped erythrocytes can block blood vessels which prevents normal circulation of blood. eventually some rupture = hemolysis
What is hemolytic disease of newborn (HDN)?
when the mother has been exposed to anti-D and the antibodies cross the placenta
When does (HDN) occur?
during pregnancy when the mother has been previously exposed to Rh + blood
How can HDN be prevented?
giving Rh - special immunoglobins btwn 28-32 weeks b/c the immunoglobinds bind to fetal erythrocyte surface antigens to prevent the mother’s immune system from recognizing anti-D and stimulating to produce anti-D antibodies
What are the 2 classes of leukocytes?
granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophil, basophil
agranulocytes: lymphocyte, monocyte
What distinguishes the 2 classes of leukocytes?
presence or absence of secretory vesicles in the cytosol
What are granulocytes?
contains secretory vesicles (specific granules)
Describe the cytosol and nucleus of neutrophils
cytosol: contain specific granules
nucles: multilobed
What is the primary function of neutrophils?
phagocytize bacteria
Describe the granules and nucleus of eosinophils
granules: reddish/pink-orange
nucles: bilobed
What are important functions of eosinophils
phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes and allergens
release chemical mediators to destroy parasitic worms
Describe the appearance of basophils
blue purple circle
nucleus: bilobed
cytosol: deep blue/violet specific granules
What 2 chemicals are released by basophils and what is the function of each?
histamine: vasodilator and increases capillary permeability
heparin: anticoagulant
Describe agranulocytes
absent specific granules
Describe the appearance of lymphocytes
round or slightly indented
nucleus: usually darkly stained
What are 3 types of lymphocytes?
T/B lymphocytes and NK cells
What is the function of T-lymphocytes
manage/direct immune response
What is the function of B-lymphocytes
stimulated to become plasma cells and produces antibodies
What is the function of NK cells
attack!
Which WBC’s are most abundant?
Neutrophil
What WBC is least abundant?
basophil
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
Neutrophil (most abundant)
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
Eosinophil
Basophil (least abundant)
What is leukopenia?
reduced # of leukocytes
What is leukocytosis?
slightly elevated leukocyte count
What is a differential WBC count? How is it helpful clinically?
measures the amount of each type of leukocyte in the body to see if any are immature
this can help diagnose disease
What is the general function of platelets?
aid in hemostasis
What is hemostasis?
stoppage of bleeding
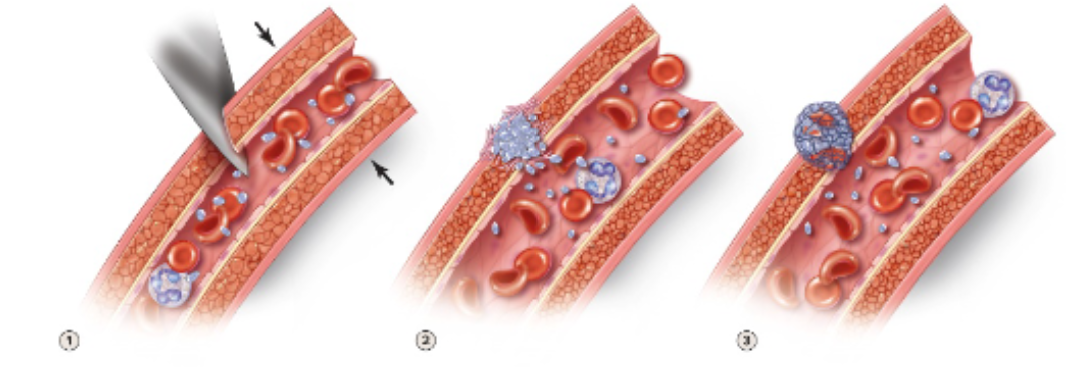
What are the three stages of hemostasis?
1. vascular spasm from trauma
2. platelet plug formation
3. coagulation (fibrin strands)
Describe vascular spasm and its benefits
the constriction of a blood vessel to limit blood loss
What do the platelets stick to in a damaged blood vessel?
platelets stick to the exposed collagen fibers
The plateles release chemicals that attract other platelets. Is the neg or positive feedback?
positive feedback
Platelets also release chemicals that ___________ _________ spams and initiate ___________ and are thus involved in all stages of hemostasis
prolong vascular
clotting
What substances prevents platelets from sticking to healthy portions of blood vessels?
prostacyclin
What is the 3rd stage of coagulation?
the clot is formed
A network of which protein composes a blood clot?
fibrin
What is the precursor to fibrin ?
derived from soluble fibrinogen
Which ion is necessary for blood clot formation?
Ca
What triggers the intrinsic pathway?
damage to inside of vessel
What triggers the extrinsic pathway?
damage to tissue outside vessel
he intrinsic pathway and extrinsic pathway merge into the ________________ pathway
common pathway
What is the name of the enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin?
thrombin
What is the precursor to thrombin?
prothrombin
How does the sympathetic NS help to compensate for blood losses over 10%?
bringing increase vasoconstriction of blood vessels, increased heart rate/force of contraction
What is clot retraction?
when actinomyosin contracts and squeezes the serum out of the developing clot making the clot smaller as the vessel walls are pulled together
What is fibrinolysis?
the destruction of fibrin framework
Where is blood produced in young children?
more bones in the body
long bones
Where is blood produced in adults?
spine, hips, ribs, skull, sternum
What is anemia?
percentage of erythrocytes is lower than normal or O2 carrying capacity of blood is reduced
Why are older individuals more prone to anemia?
because the red bone marrow is placed with fat as individuals continue to age causing the decrease in the ability to deliver O2 to body cells
less erythrocytes circulating
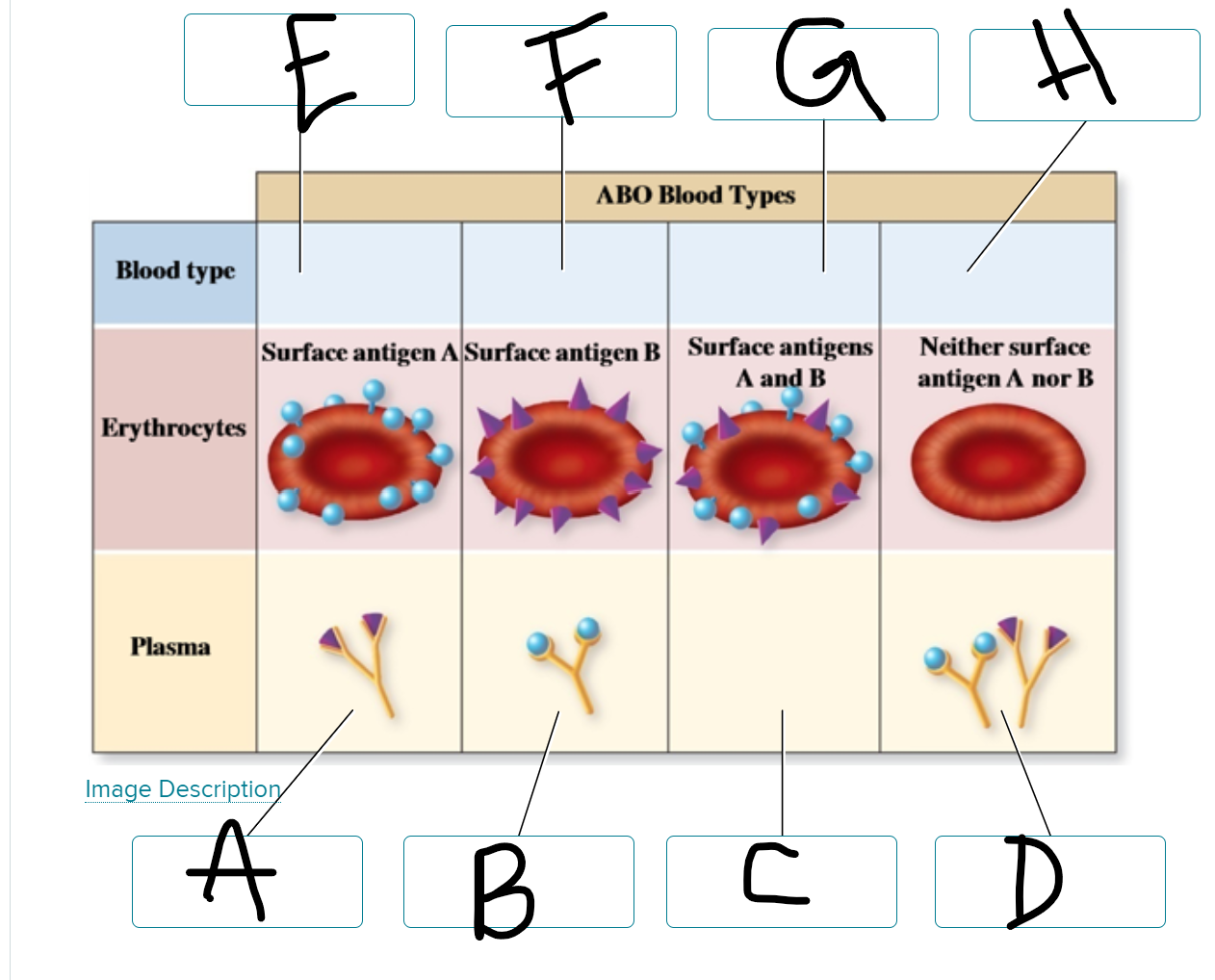
A: anti-b
B: anti-a
C: neither
D: both
E: type A
F: type B
G: type AB
H: type O
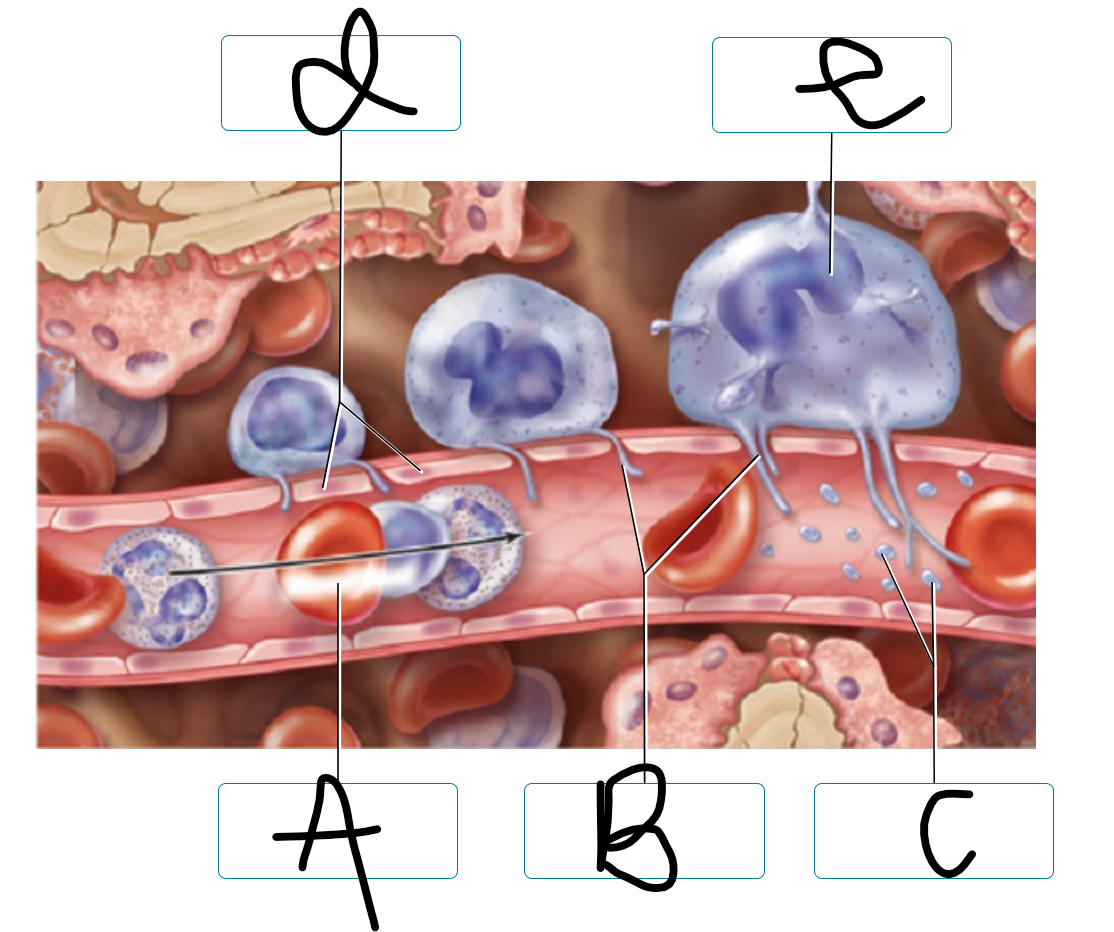
a: erythrocyte
b: proplatelets
c: platelets
d: endothelial cells
e: megakaryocyte
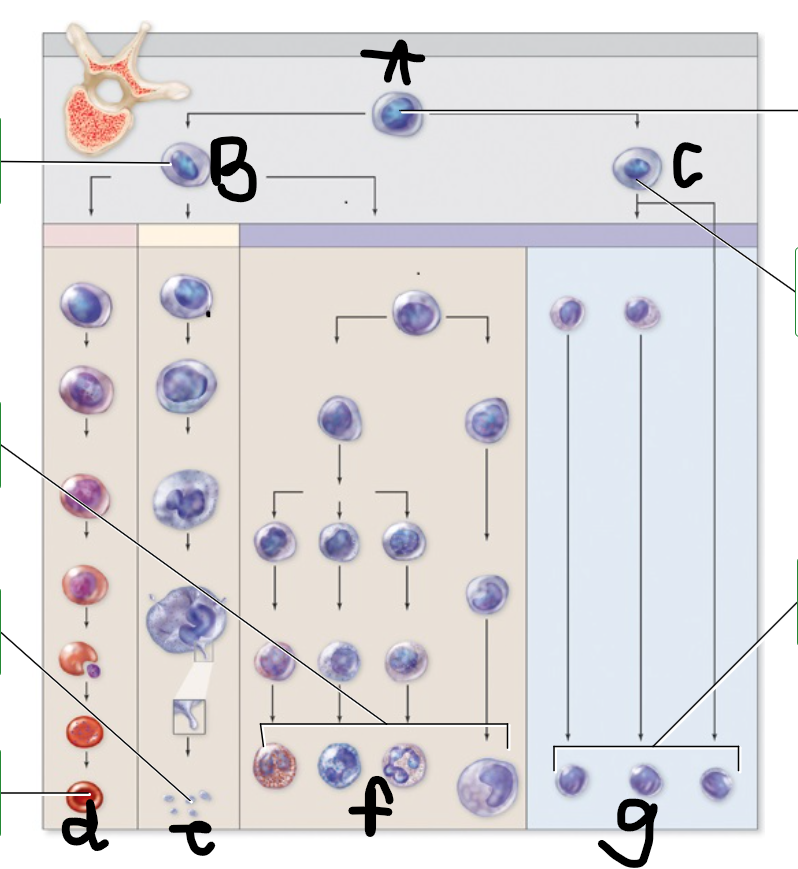
A: hemocytoblast
b: myeloid stem cells
c: lymphoid stem cell
d: erythrocyte
e: platelets
f: granulocytes and monocyte
g: lymphocytes and NK cell
Which cells are Granulocytes?
eosinophil, neutrophil, basophil
Which cells are agrnulocytes?
plasma cell, macrophage, monocyte, T/B-lymphocytes
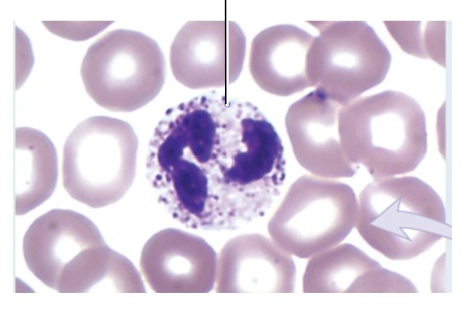
Neutrophil
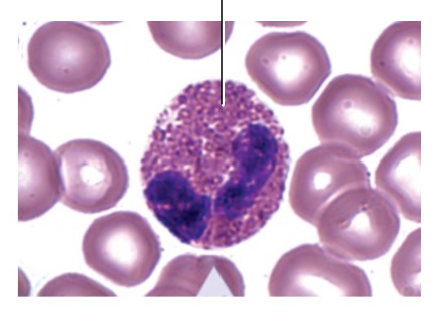
eosinophil
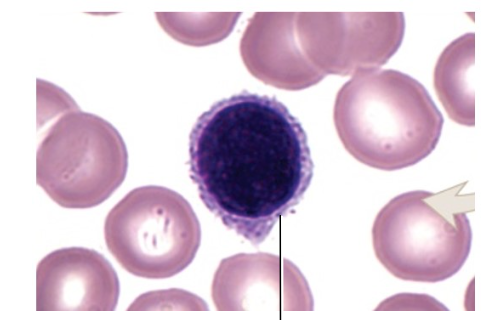
lymphocyte
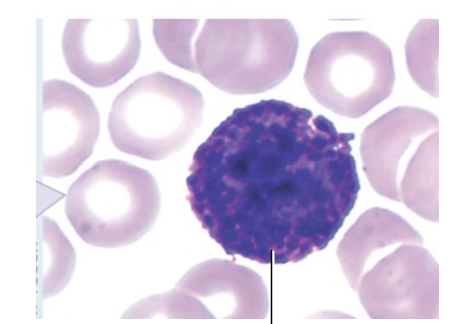
basophil
Coagulation is described as
“clotting”
includes intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms
includes a vast enzymatic cascade of proteins produced by the liver
LAST STAGE OF HEMOSTASIS
conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
Platelet plug formation is described as
involves endothelial collagen exposure and disruption of prostacyclin
2nd stage in hemostasis
degranulation and serotonin, thromboxane A2, and ADP
Vascular spasm is describes as
the first stage in hemostasis and involves vasoconstriction
What leukocyte:
releases histamine, which promotes inflammation
basophil
What leukocyte":
the cytoplasm is a thin ring around the nucleus
lymphocytes
What leukocyte:
contain cytoplamsic granules that stain bright red with eosin
esoinophils
What leukocyte:
most common type of WBC
Neutrophils
What leukocyte:
Nuclei have up to 5 lobes
neutrophils
What leukocyte:
enlarge and become macrophages which engulf foreign substances
monocytes
What leukocyte:
contain large cytoplasmic granules that stain dark blue or purple with basic dyes
basophils