Fundamentals Marine Fisheries Midterm
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Systematics/Taxonomy
study of the diversity, relationships, and evolution of organisms and how to put names on them
Fisheries
Study related to human use of aquatic organisms
Catch
total number of organisms caught
Target catch
number of intended targets caught
Incidental/Bycatch
number of unintended organisms caught
Discards
The organisms you don’t keep
Landings
Number of fish kept and brought to port
Effort
Time spent fishing and the resources used in the process
Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE)
Fish caught in a chunk of time
Catchability Coefficient (q)
the relationship between the catch rate and the true population size
Stock
a population of fish within a certain area that can reproduce and sustain itself
Recruitment
the addition of new individuals to a fish stock through reproduction or immigration
Cohort
a group of fish born in the same year or season, often used in population studies to assess growth and survival
Fishery Dependent Data
data collected from fishing activities that provide information on stock status and catch rates
Fishery independent data
data collected through scientific surveys and assessments that do not rely on commercial fishing activities, used to estimate fish populations and ecosystem health
Carrying capacity
the maximum number of individuals that an environment can sustain without negative effects on the ecosystem
Maximum sustainable yield
highest theoretical yield that can be continuously taken (on average) from stock under existing environmental conditions without significantly affecting the reproduction process
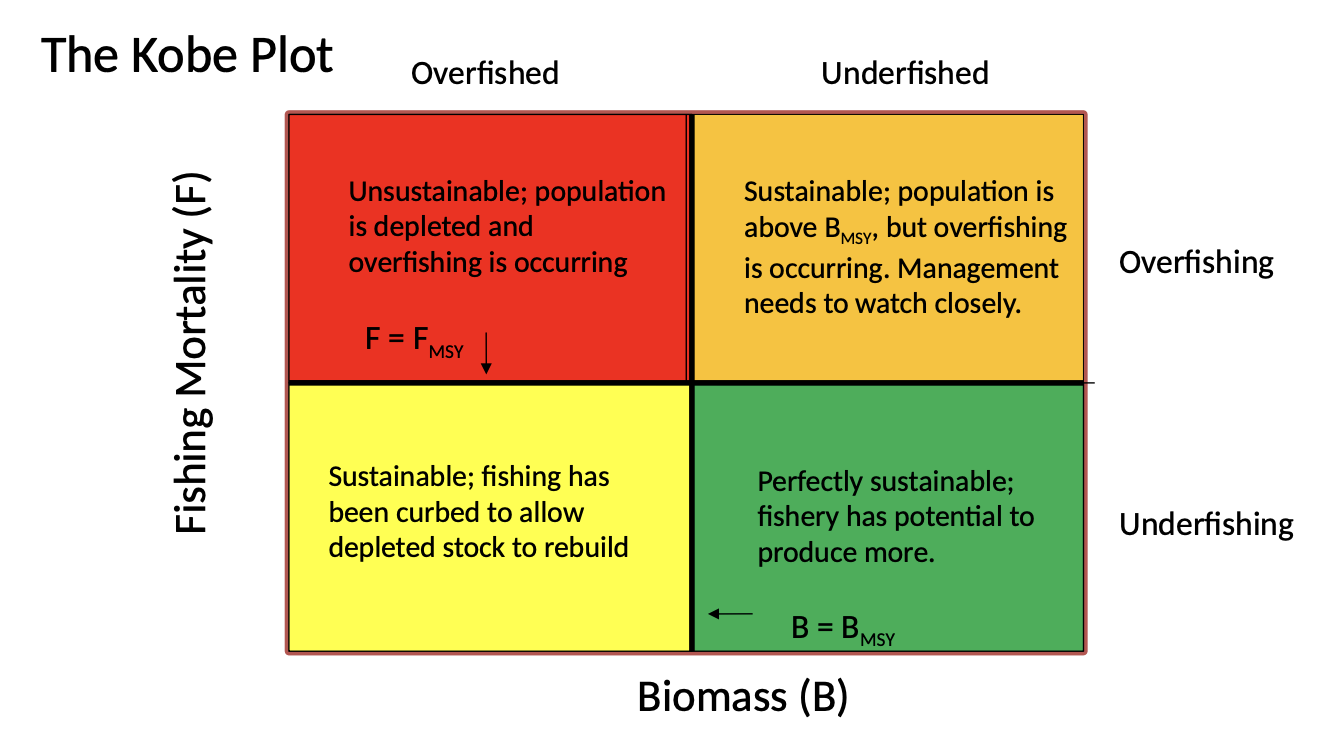
Overfished
A stock exploited to a degree that there reproduction and MSY is jeopardized
Overfishing
A stock having a higher harvest rate than rate that produces its MSY
Kobe Plot
Upwelling
A spatially and temporally limited movement of nutrient-rich, cooler waters into the euphotic zone. 25% of fisheries catch comes form 5 upwellings that are 5% of the oceans surface
Types of upwelling
wind induced (gulf of Panama), island or seamount (Galapagos), wind/current (eastern boundary currents), monsoonal (somali), equitorial divergence, divergence of open ocean or currents
Primary production
heterogeneous in space and time, requires sunlight, requires nutrients. Photosynthetic organisms are the base of food webs
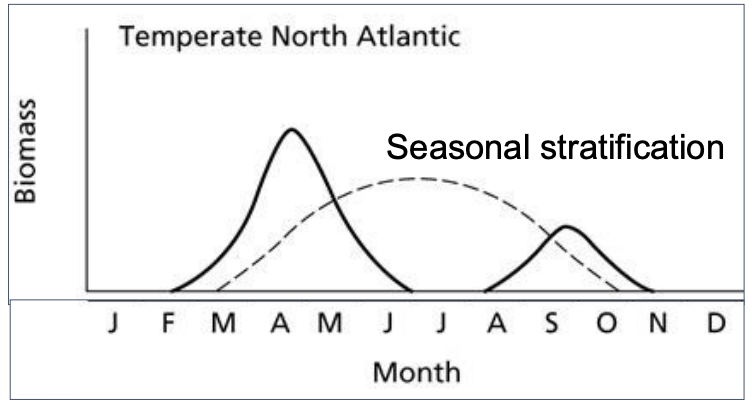
North Atlantic Spring Bloom
Clupeoid fishes
Herrings, anchovies, shads, sardines, pilchards, menhaden. Synapomorphies: scutes, swim bladder connections. Life history characteristics: rapid growth, short lived, early maturity, high fecundity, schoolers, pop size can vary greatly. Often boom and bust fisheries.
Passive Gear
Target species move to the gear. E.g. gill nets, long line, fyke and pound nets, traps, pots
Active Gear
Gear that is moved to the target species (propelling or towing). Trawls, dredged, harpoons
Demersal Fisheries
Multi-species fisheries, bottom associated, in waters over the continental shelf, often 20+ species vulnerable to the fishing gear, can assess but not manage stocks/species individually
Gadiformes
Cods, hakes, grenadiers. Earlyish maturation, high fecundity, schoolers.
Atlantic Cod fishery
Super old. Collapsed hard in the 70s. Whoopsies
Hypotheses for Atlantic Cod Fishery Collapse
overfishing and slow govt response, ability to catch fish efficiently at low abundance, failure to recognize spawn/recruit relationship, lack of accounting to increasing efficiency of effort, increased discarding and non reporting of small fish, overestimates of stockproductivites/underestimates of fishing mortality
Pelagic fishes biological characteristics
Most are top level predators, feed on smaller fishes and squids, high metabolic rates, several species maintain elevated temperatures in some body regions
Pelagic fishes (minus sharks) life history characteristics
High fecundity, broadcast spawning over large geographic area, rapid growth, most species reach sexual maturity at 2-4 years, can be relatively long lived (6-20+)
Major pelagic species
Tunas, wahoo swordfish, billfishes, scimbriformes, mahi mahi, lamnidae, carcharhinidae
Atlantic bluefin tuna fishery
centuries old, rapid buildup of overfishing, major reforms in 2010
Growth overfishing
When fish are harvested before they reach the size where yield per recruit is optimized
Deepsea Fisheries and Shark Fisheries
long lived, slow growing, late age at maturity, low fecundity, typically boom and bust due to mismanagement, more like mining (exploit and move on)
Orange Roughy Biology
generalist body form, slow growing, old at first maturity, max age 100+, winter spawning aggregations around seamounts, low fecundity, single batch spawners,
Sharks and Rays biology
1000+ species, slow growing maturity at 15+, low fecundity (1 or 2 year reproductive cycles, few pups per cycle), long lived 25+
US Shark Fisheries
Small until 1970s then got big, fins highly valued, quickly became overfished, shark finning banned in US
General status of stocks for Shark fisheries
landing records not good, many species with greatly reduced biomass, very long rebuild time
Chesapeake Bay Fishes
~350 species, freshwater to marine habitats, tolerant of wide range of temperature and salinities, many transient species, many are commercially and recreationally important
Take homes from the 202 ASMFC stock assessment
Adult mortality for coastline metapopulation unknown, juvenile mortality unknown for all systems, coastwide metapopulation considered depleted based on the decline in coastwide landings
American Shad age shift
1998-2005 age 5 most abundant, increase in average age due to increase in older individuals
2016-2021 average age increases because decrease in age 5s
Blue Catfish
Invasive. 2011 Resolution of the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission: potential negative effects on other managed species. All practicable efforts should be made to reduce population levels and ranges of invasive blue catifsh
Eastern Oyster biology
bivalve mollusk, feeds on phytoplankton, aggregate to form reef structure, grow to ~20cm, max age 20-25 years, broad environmental tolerance, protandric hermaphrodites, mature age 1, spawn late spring through early fall, female fecundity 20-30 million per spawn
Eastern oyster fishery
Large in 1800s through mid 1900s, overfishing as far back as late 1800s, patent tongs hand tongs and oyster dredge common, fishery decimated by diseases (MSX and Dermo)
Haplosporidium nelsoni
Parasitic protist agent of MSX, known since 1959 in Chesapeake bay, likely introduce from pacific oyster shipments, not directly transmissible among oysters
Perkinsus marinus
agent of dermo, basal dinoflagellate, known since 1940s in Chesapeake, directly transmissible among oysters,
Oyster Management today — Public Grounds
annual estimates of abundance of oysters, license limit, rotational harvest + shell repletion, gear type and time restricitons, oyster sanctuaries, restoration to increase footprint of extant reefs with alternate substrates, Stock Management Advisory Committee
Oyster management today - private grounds
Traditional culture menthods, spat on shell, increased interest in containerized aquacultre
Eastern Oyster fishery since 2000s
Increase in catch, oysters developed tolerance to perkinsus, increased recruitment ~2008, rotational harvests implemented in 2007. Biggest impediment — oysters living less long, not contributing to shell base as much, illegal harvesting more prevalent
Sea scallop biology
20-120meters, max age ~20 years, max size ~9 inch shell height, Planktonic then settlement life phase, separate sexes, females mature in 1st or 2nd year, spawn in fall, George’s bank gyre entrains larvae, juveniles mobile adults not as much, fast growing
Sea scallop fishery
Most valuable wild scallop fishery, was most valuable fishery in VA, most valuable single species in US in 2007, major gear scallop dredge
Scallop fishery management
Overfished in 1990s, limited access program implementd in 1994, effort reduction, limitations on crew size, gear restrictions (increase in cull ring size). Part of annual catch contributes to the Research Set Aside, money from RSA used to fund research. money also set aside to fund Observer program
Sea scallop closed area rotational management
Implemented 2004, elephant trunk was first area closed, closure protected 2 massive year classes, remained closed for 3 years then controlled re opening
Blue crab biology
Western atlantic, tolerate wide range of temperatures, prefer estuarine salinities, eat bivalves shrimp plant matter detritus etc, important prey and predator, relatively short lived ~2 or ~3 years
Blue crab life cycles
lots of stages, both in bay and open ocean. mating occurs may to october in brackish water. females store spermatophores
Blue Crab Fishery
Chesapeake bay with 1/3rd of US blue crab catch, pot fishery, winter dredge fishery (current moratorium), peeler crab/soft shelled crab fishery, recreational fishery.
Blue crab management
minimum size, limited entry implemented in 2008, effort reduction. Spawning sanctuary. Chesapeake bay stock assessment committee uses VIMS winter dredge survey as indicator of stock status.
Blue crab stock status
in 2024 evaluated to NOT be overfished. However, low recruitment and high male exploitation still concerning. Continued precautionary management recommended