Cell Division
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are chromosomes made up of?
Chromosomes consist of DNA molecules combined with proteins.
Chromosomes contain genes which provide the instructions for ________ _________.
protein synthesis
What is a gene?
A section of DNA which codes for a protein.
How many chromosomes are found in the nucleus of human body cells?
46
How many chromosomes are found in the nucleus of gametes?
23
How are chromosomes arranged in the nucleus of a body cell?
Arranged in pairs - 46 chromosomes form 23 pairs.
What is the first main stage of the cell cycle? (Not describe)
Replication of DNA and synthesis of organelles
What is the second main stage of the cell cycle?
Mitosis
What is the third main stage of the cell cycle?
Division of cell
Importance of mitosis: Produces additional cells for _____ and ______.
growth, repair
Importance of mitosis: Mitosis produces ________ cells which all have the same _______ information.
identical, genetic
Describe the first stage of the cell cycle
Longest stage
cells grow and increase in mass
replicate DNA
synthesise more organelles (eg. mitochondria, ribosomes).
Describe the second stage of the cell cycle
Each chromosome in a pair is pulled to opposite poles of the cell, then the nucleus divides.
Describe the third stage of the cell cycle
The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide - two identical daughter cells are produced.
What is a stem cell?
An unspecialised cell which is capable of differentiating into other cell types and capable of self-renewal.
What is the function of stem cells in embryos?
Embryonic stem cells can replicate themselves and differentiate into many other types of cells.
What conditions could embryonic stem cells treat?
Paralysis and diabetes
How would embryonic stem cells be able to treat conditions?
By dividing to replace damaged cells.
What is the function of stem cells in adult bone marrow?
Adult stem cells can differentiate into several cell types to replace dead or damaged tissues.
Bone marrow stem cells can form many _________ types of ______ cell.
different, blood
What is the function of stem cells in plant meristems?
They can differentiate into any cell which is required by the plant.
Meristem stem cells retain the ability to __________ into any type of plant cell throughout their ________.
differentiate, lifespan
What is therapeutic cloning?
A cloning method where an embryo is produced with the same genetic makeup as the patient.
The stem cells which originate from the embryo will not be ________ by the patient’s _______ _______, so can be used to treat certain medical conditions.
rejected, immune system
Advantages of cloning plants using meristem stem cells: Can prevent rare plants from becoming ______.
extinct
Advantages of cloning plants using meristem stem cells: Can produce ________ plants for research.
identical
Advantages of cloning plants using meristem stem cells: Can produce _____ numbers of plants with a favourable ___________.
large, characteristic
Issues associated with the use of stem cells: Many embryonic stem cells are sourced from _______ embryos - some people have an ethical/religious _________.
aborted, objection
Issues associated with the use of stem cells: If donor stem cells do not have a similar _______ makeup to the patient, an ______ response could be triggered.
genetic, immune
Issues associated with the use of stem cells: Adult stem cells infected with _______ could transfer infections to patients.
viruses
Issues associated with the use of stem cells: Development of stem cell therapies is slow, ________ and difficult.
expensive
Cancer is caused by changes in cells that result in uncontrolled cell division. Before a cell begins to divide, its DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. Describe one other change that occurs in a cell before the cell begins to divide.
There is an increase in the number of sub-cellular structures.
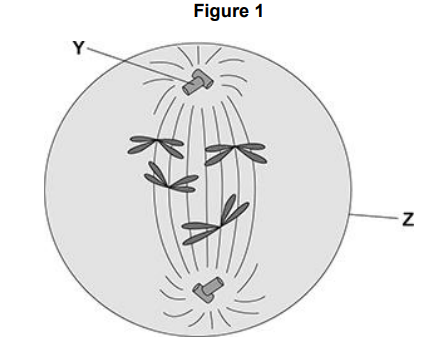
Figure 1 shows a cell during one of the stages of cell division. Name structure Z in Figure 1.
Cell membrane
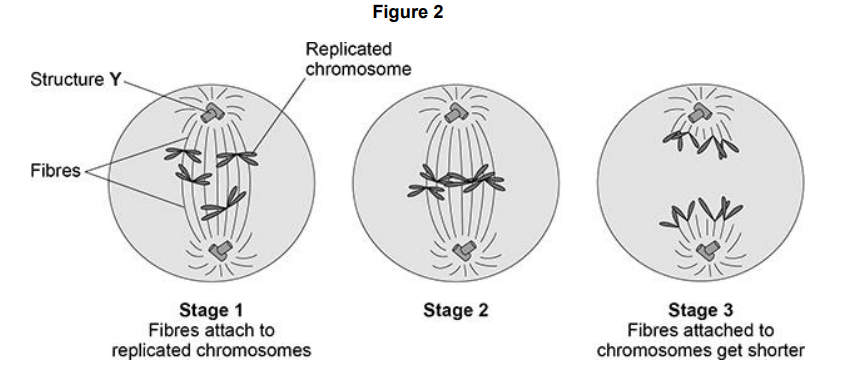
Figure 2 shows some of the stages of cell division. Some cancer drugs prevent cell division. Drug X prevents the fibres from attaching to the replicated chromosomes in stage 1. Explain why a cell cannot complete division when affected by drug X.
Chromosomes cannot be pulled by the fibres to each end of the cell so the nucleus cannot divide.
Give the reason why a drug that stops cell division helps to treat cancer.
The tumour cannot grow.
Describe how mitosis produces two genetically identical cells.
Chromosomes are replicated. The replicated chromosomes are pulled apart. Cytoplasm divides into two cells. The set of chromosomes in each new cell are identical to each another.
Name the process by which stem cells form specialised cells.
Differentiation
Which process makes two identical new body cells for growth and repair?
Mitosis
Name the chemical which the genetic material is made from.
DNA
A cell divides to form two new cells every 24 hours. How many days will it take for the original cell to divide into 8 cells?
3
What is one section of genetic material on a chromosome called?
Gene
Stem cells are cells which have not yet been specialised to carry out a particular job. Bone marrow cells are one example of stem cells. Explain how a transplant of bone marrow cells can help to treat medical conditions.
Bone marrow cells differentiate into many other types of cell. So they will cure diseases where cells are damaged.
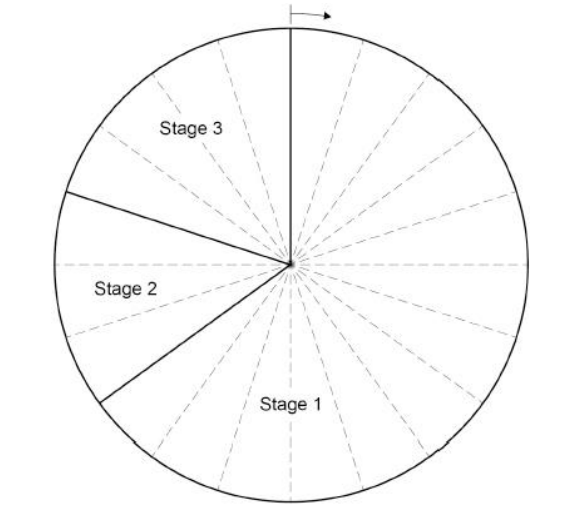
The chart below shows a cell cycle. What percentage of the time for one cell cycle is represented by stage 2 and stage 3 together?
35%
Name two conditions that could be treated using regenerated human tissue.
Paralysis and diabetes
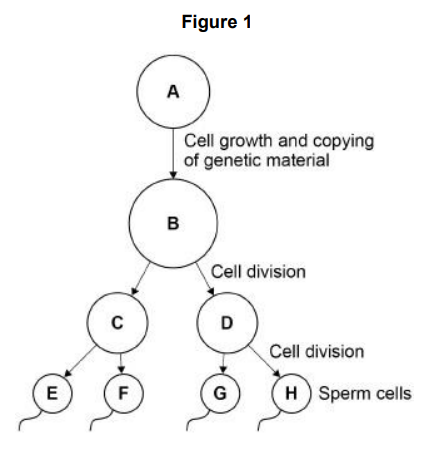
Figure 1 shows the production of sperm cells in humans. Cell A is a normal body cell. How many chromosomes are there in cell A?
46
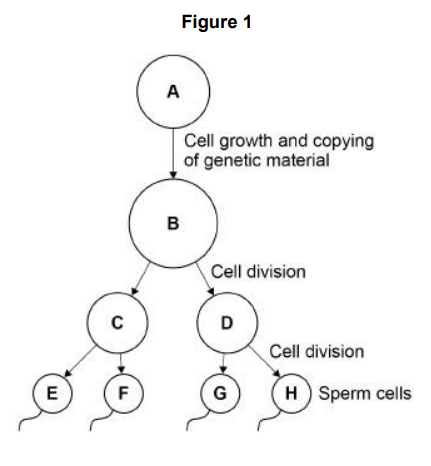
Figure 1 shows the production of sperm cells in humans. What is the mass of DNA in cell E?
Half the mass of the DNA in cell A
Sometimes there are errors in copying the genetic material. What term describes an error in the genetic material?
Mutation
A woman has three children, aged 4, 6 and 9 years. Why are the children not genetically identical?
They have genes from two parents.
In sexual reproduction, a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell to form a new single cell. An embryo develops from the single cell. The cell divides three times to produce the embryo. How many cells are there in the embryo after three cell divisions?
8
Chromosomes are copied during the cell cycle. Where are chromosomes found?
Nucleus
What is the name of a section of a chromosome that controls a characteristic?
Gene
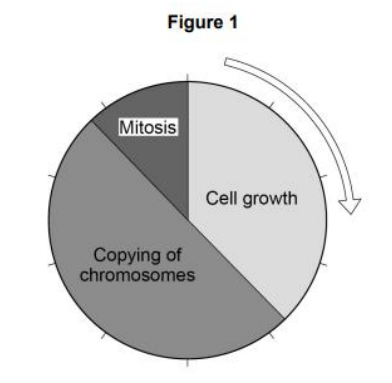
Figure 1 shows information about the cell cycle. Which stage of the cell cycle in Figure 1 takes the most time?
Copying of chromosomes
During mitosis cells need extra energy. Which cell structures provide most of this energy?
Mitochondria
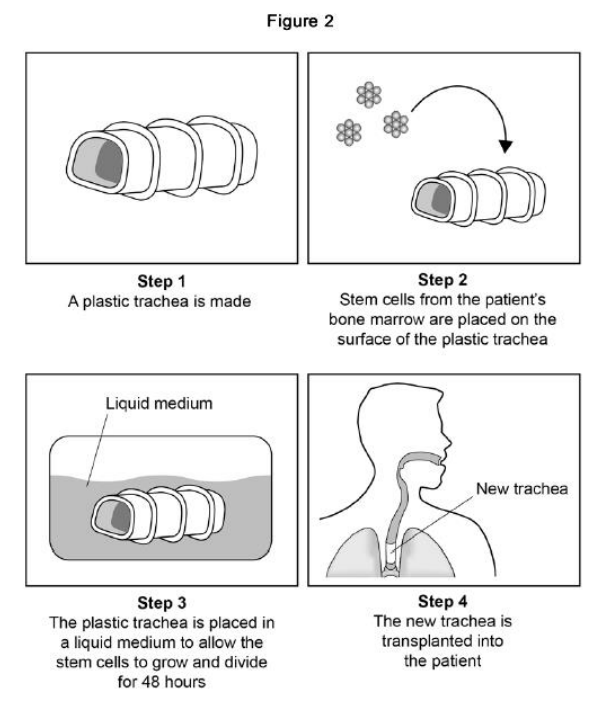
Scientists can treat a patient’s tumour by replacing the trachea with a plastic trachea. The plastic trachea has a layer of the patient’s own stem cells covering it. Figure 2 shows the procedure. In Step 3 the cells are left for 48 hours to divide. Name the type of cell division in Step 3.
Mitosis
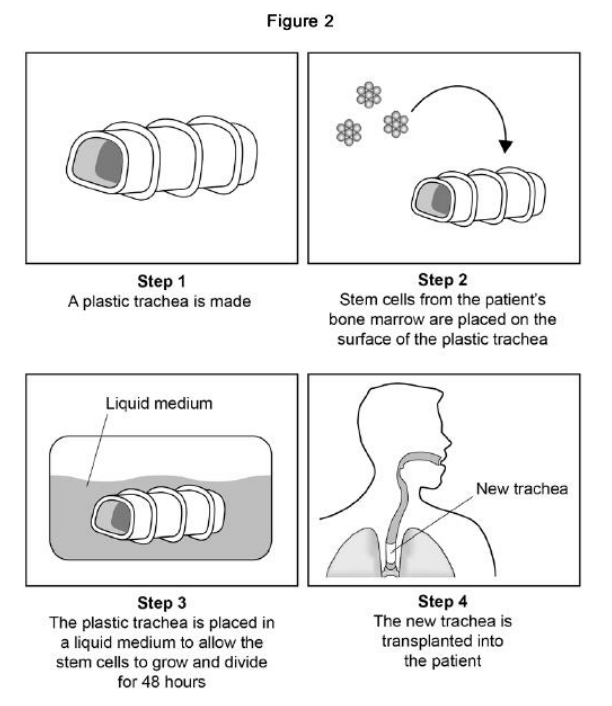
Scientists can treat a patient’s tumour by replacing the trachea with a plastic trachea. The plastic trachea has a layer of the patient’s own stem cells covering it. Figure 2 shows the procedure. In Step 3 the cells are given oxygen and water. Name two other substances the cells need so they can grow and divide.
Glucose, Amino acids
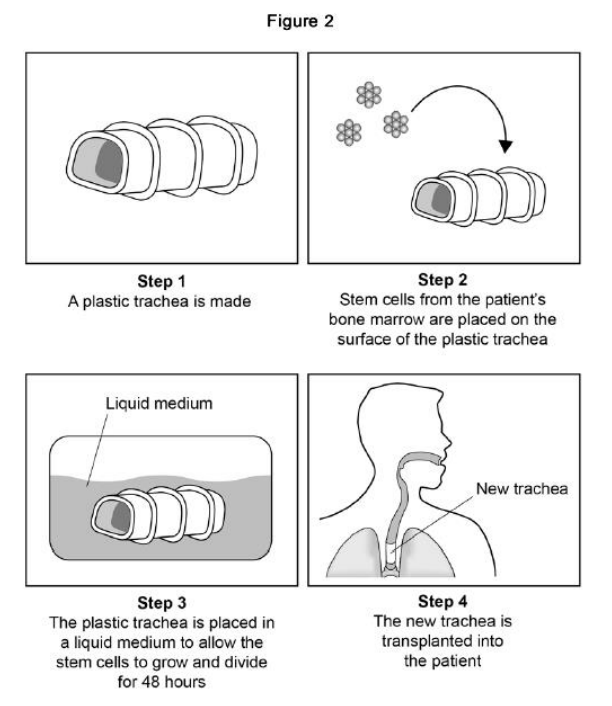
Scientists can treat a patient’s tumour by replacing the trachea with a plastic trachea. The plastic trachea has a layer of the patient’s own stem cells covering it. Figure 2 shows the procedure. Give two advantages of using the stem cell trachea compared with a trachea from a dead human donor.
No need for immunosuppressant drugs, No need to wait for a donor.
Stem cells can be obtained from human embryos. Evaluate the use of stem cells from a patient’s own bone marrow instead of stem cells from an embryo. Give a conclusion to your answer.
Using stem cells from a patient’s own bone marrow avoids ethical issues since the patient can give consent, and the procedure is safe, tried and tested. There is no risk of embryo harm or destruction. However, bone marrow stem cells can only treat a few diseases because they aren’t pluripotent. Embryonic stem cells can develop into any type of cell and could potentially treat more diseases, but their use raises ethical concerns and destroys embryos. Bone marrow stem cells are safer and more ethical, but embryonic stem cells have greater potential for treating a wider range of diseases.