Intro to Antimicrobial Resistance
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://tinyurl.com/3ajxjj6p
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are antimicrobials?
name some examples (think about what antimicrobials are used to treat)
medicines used to prevent and treat infections in humans, animals and plants
including: antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiparasitics
what is antimicrobial resistance (AMR)?
(when does it occur)
= occurs when microbes change over time and no longer respond to medicine. making infections harder to treat, & increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
(microbes = bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites)
describe the antimicrobial resistance issue using TB as an example
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that causes TB in humans. infects the lungs.
it is highly transmissible but can be treated w/ antibiotics. the overuse of antibiotics has caused multidrug resistant strains to develop and spread, limiting treatment options & accounting for half a million infections annually.
which are the main group of pathogens that are considered to be of high concern due to their increasing resistance to antibiotics?
(hint: ESCAPE)
Enterococcus faecium
Staphylococcus aureus
Clostridioides difficile
Acinetobacter baumannii
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Enterobacter spp.
why is AMR a global threat? (what does it threaten)
progress in healthcare, food production, and life expectancy
food & agriculture production
balance of microbial community in soil
composition of microbial community in aquatic ecosystem. disrupting the food web
In 2019, there were an estimated _ million deaths associated with bacterial AMR, including ____ million deaths directly caused by AMR bacteria
~4.9 million
~1.3 million
The cost of AMR to ____ and ____ is significant as it affects productivity of patients or their caretakers through prolonged hospital stays and the need for more expensive and intensive care
national economies
health care systems
how does AMR develop (4 steps)
- high number of bacteria, some of them have resistance
- antibiotic kills all bacteria, inclding the ones that protect the body from infection
- resistant bacteria can now grow and multiply w/o competition
- some bacteria can transfer the resistance to other bacteria, creating more problem
innate vs. acquired resistance
- innate = innate ability of bacteria to resist a class of antibiotics
- acquired = naturally susceptible microbe acquiring resistance to the drug. (may be genetic or non-genetic
what are the 2 ways in which bacteria can acquire resistance via the genetic pathway
mutation or gene transfer
what are the 2 ways that bacteria can genetically transfer resistance genes to each other
- horizontal gene transfer (transformation, transduction, conjugation)
- vertical gene transfer (replication)
describe how conjugation works
- donor donates one strand of its plasmid to the recipient
describe how transformation works
new cell taking up DNA fragments from old dead cell
describe how transduction works
- virus infects bacteria & injects its own DNA
- when the new virus is made inside the bacteria, it accidentally take up part of the bacteria DNA with it as well
- the new virus w/ bacteria DNA infects a new bacteria & inject that DNA (transduced cell)
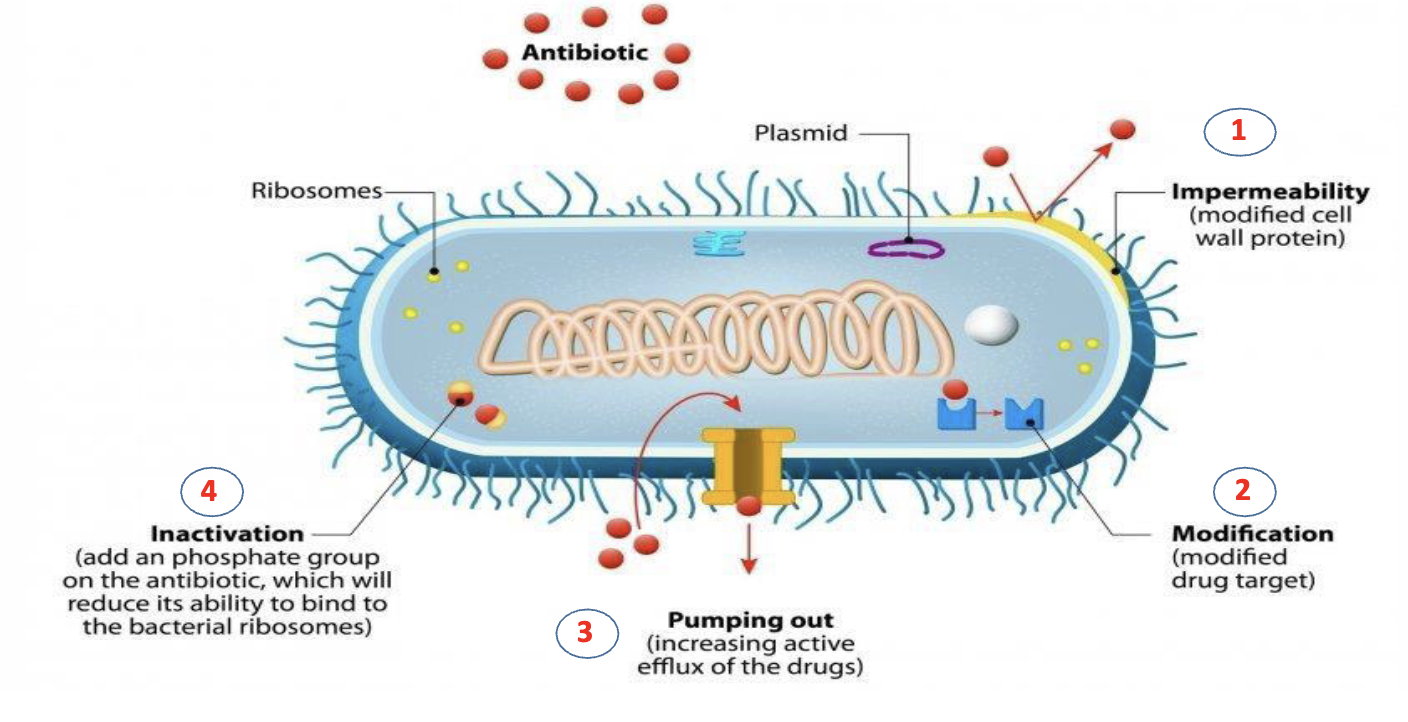
What are the 4 mechanisms through which bacteria develop resistance to antimicrobials (how do they stop responding to the drugs)
limiting uptake of a drug (cell wall protein modification)
modification of a drug target (changing shape of drug receptor)
active efflux of a drug (pumping out the drop)
inactivation a drug (adding phosphate group to the drug, making it unable to bind to bacterial ribosome)
what are the 4 drivers of AMR?
inappropriate use of antibiotics
in human medicine
in veterinary medicine
lack of hygiene & infection prevention & control strategies
political conflicts, equity, & human mobility
give 2 examples of inappropriate use antibiotics in vet med
- antibiotic misuse in livestock & fish
- therapeutic & prophylactic (growth promoters)
what does the WASH infrastructure refer to
water, sanitation, hygiene
what are the 4 factors that contribute to AMR (who are associated with increase in AMR)
- environment
- drug related factors
- patient related factors
- physician/prescriber
explain how environmental factors may contribute to AMR
- populations density & overcrowding
- poor sanitation
- increase community acquired resistance
- ineffective infection control program
- increasing national & international travel
- widespread use of antibiotics in animal husbandry & agriculture
explain how drug related factors can contribute to AMR
- quality of the antimicrobials
- misuse
- over-the-coutner availability of the drugs
- irrational dose & combo of the drugs
- substandard drugs
explain how patient related factors can contribute to AMR
- poor adherence to drug regimens (e.g. not completing the entire course)
- poverty
- lack of sanitation
- lack of education
- self-medication
- misconception
explain how physician & prescriber factors can contribute to AMR
inappropriate use of drugs
increase empiric poly-antimicrobial use (broad spectrum drugs)
overuse of antimicrobials
inadequate dosing
lack of current knowledge & traning
what are the 7 steps to fighting AMR
- coordination
- regulatory framework
- reduce need & promote prudent use of antibiotics
- improve surveillance
- advocate & communicate
- build capacity & provide training
- address knowledge gaps & research needs
Name examples of organization & plans/actions in fighting AMR
- GAP
- WAAW
- tripartitie joint secretariat on antimicrobial resistance
- GLASS
- global research & development setting for AMR
GAP
= global action plan on antimicrobial resistance
WAAW
world antimicrobial awareness week
GLASS
global antimicrobial resistance & use surveillance system
under the "one health" approach, what are the 6 key areas for fighting AMR
knowledge
use of drugs
reducing the need for drugs
public awareness
research
stakeholders
strengthen Knowledge: thru surveillance & research
optimize Use of antimicrobials: in humans & animals
reduce incidence of infection: thru effective Sanitation
improve Awareness & understanding of AMR thru effective communication, education & training
promote Research on AMR
strengthen partnership & foster engagement of relevant stakeholders
what percentage of the antibiotics used in livestock produce are unnecessary
2/3
how can AMR in animals spread to humans? (4 ways)
- foodborne
- manure
- environment
- occupational
what can vets do fight AMR?
working with pet owners, farmers & vets
implement efficient prevention strategies
promote efficient use of antibiotics
maintaining records
preventing environmental contamination
keeping knowledge up to date
limitations in AMR research & data
- number of sites recruited to compile AMR data is limited
- sites have access to human data only
- AMR data from animal & environment are limited
- focus on farm animals (not enough data on wildlife)