Ch 8: Global Marketing-Extended version
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
globalization
the processes by which goods, services, capital, people, information, and ideas flow across national borders
Components of a Country Market Assessment
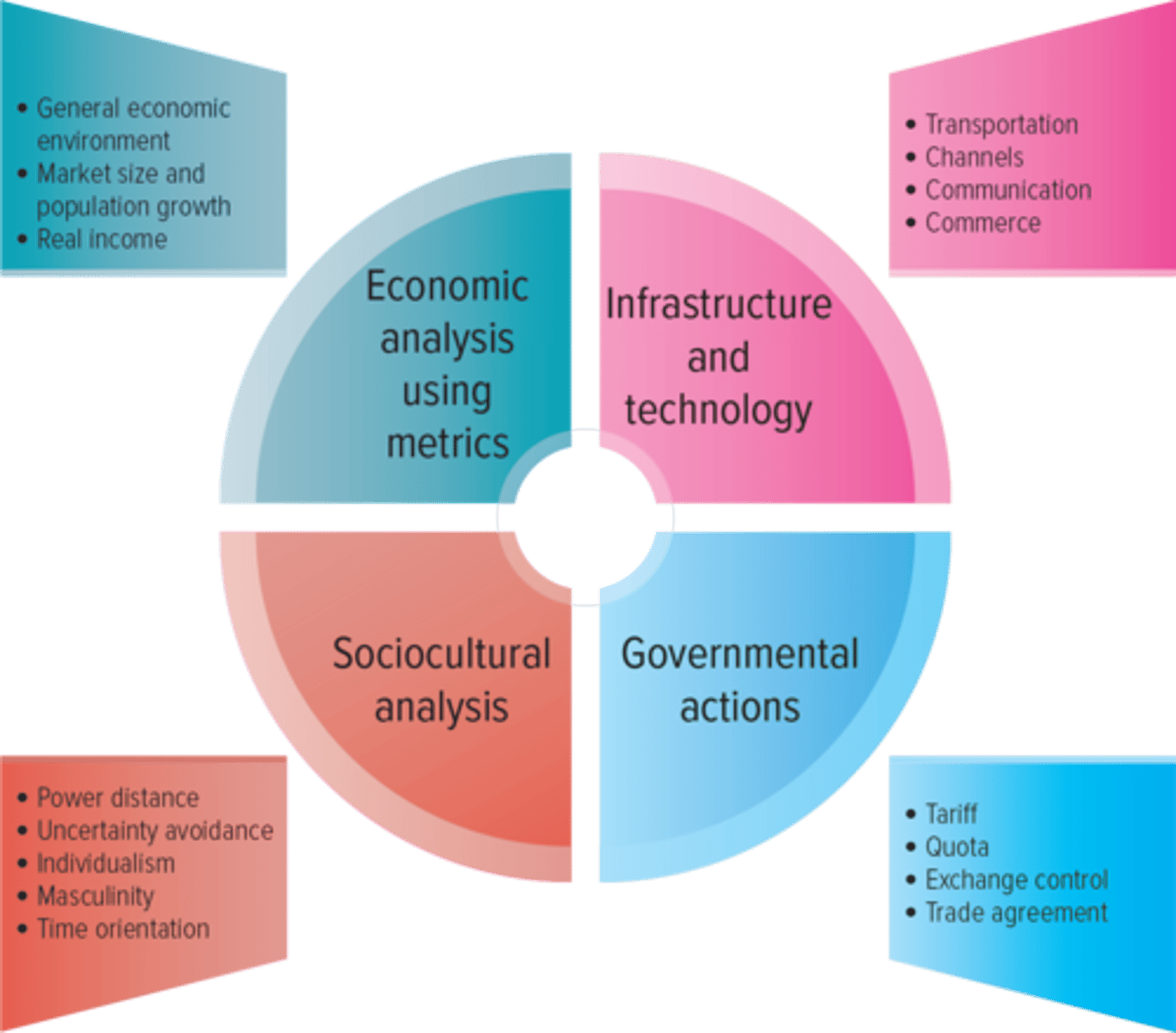
Economic Analysis Using Metrics
- the greater the wealth of people in a country, the better the opportunity a firm will have in that particular country.
- three major econ factors using well established metrics: the general economic environment, the market size and population growth rate, and real income
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating the general Economic environment
- healthy economies provide better opportunities for global marketing expansions
- to determine the market potential for its particular product or service, a firm should use many metrics it can obtain (metric: relative imports and exports)
- - metrics help marketers understand the relative wealth of a particular country, though they may not give a full picture of the economic health of a country because they are based solely on material output
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating the general Economic environment:trade deficit
An excess of imports over exports
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating the general Economic environment:trade surplus
when a country exports more than it imports
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating the general Economic environment: GDP and GNI
- most common way to gauge the size and market potential for an economy, and therefore the potential the country has for global marketing, is to use standardized metrics of output
--- Gross domestic product: (GDP) market value of the goods and services produced by a country in a year
--- Gross national income: (GNI) consists of GDP plus the net income earned from investments abroad (minus any payments made to nonresidents who contribute to the domestic economy)
--- U.S. firms that invest or maintain operations abroad count their income from those operations in the GNI but not the GDP
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating the general Economic environment: PPP
- Purchasing power parity (PPP): if the exchange rates of two countries are in equilibrium, a product purchased in one will cost the same in the other if expressed in the same currency
- Big Mac Index employs PPP to assess the relative econ buying power among nations. Use this to compare buying power (what consumers can afford)
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating Size and Population Growth Rate
- Firms must consider uneven pop growth and distribution of populations
- strong growth rates in BRICS econ
- population is denser in urban areas (impacts delivery)
- many less developed nations are rabidly growing while more developed countries are zero or negative growth
- the countries with the highest purchasing power today may become less attractive in the future for many products and services because of stagnated growth
--- long supply chains, in which goods pass thru many hands, are often necessary to reach rural populations in less developed countries and therefore add to the product's cost
Economic Analysis Using Metrics: Evaluating Real Income
- firms can make adjustments to an existing product or change the price to meet the unique needs of a particular country market (more common for lower priced consumer goods
- bottom of the pyramid: consumers earn very low wages-> large, lower income population that still wants and needs consumer goods but cannot pay the prices that the fewer, wealthier consumers in more developed nations can
- more expensive product manufacturers make downward adjustments to their prices in countries where the incomes of their target markets cannot support higher prices
Analyzing Infrastructure and Technological Capabilities
What is infrastructure and what are the 4 key elements of infrastructure
- Infrastructure: basic facilities, services, and installations needed for a community or society to function, such as transportation and communications systems, water and powerlines, and public institutions such as schools, post offices, and prisons
- 4 key elements of a country's infrastructure: transportation (system to transport goods thruout markets and to consumers), distribution channels (deliver products in a timely manner and at a reasonable cost), communications (media access so consumers can find info abt the products and services), and commercial infrastructure (legal, banking, and regulatory systems allows markets to function)
Analyzing Governmental Actions
- influence firm's ability to sells g and s bc they often result in laws or other regulations that either promote the growth of the global market or close off the country and inhibit growth
Analyzing Governmental Actions: Tariffs
- Tariff/Duty: tax levied on a good imported into a country; intended to make imported goods more expensive and less competitive with domestic products, which in turn protects domestic industries from foreign competition
- might be imposed to penalize another country for trade practices that the home country views as unfair
- tariffs artificially raise prices and lower demand
- benefit domestically made products bc they reduce foreign competition
Analyzing Governmental Actions: Quotas
- Quota: designates a maximum of a product that may be brought into a country during a specified time period
- quotas reduce the availability of imported merchandise
- benefit domestically made products bc they reduce foreign competition
Analyzing Governmental Actions: Exchange Control
- Exchange control: regulation of a country's currency exchange rate, the measure of how much one currency is worth in relation to another
- A designated agency in each country, the central bank, sets the rules for currency exchange
- prices are lower in the country of origin bc there are no customs or import duties to pay, and international transportation expenses are less than domestic ones
- As economies and currencies continue their constant rising and falling relative to one another, marketers must keep revising their pricing strategies to reflect the current international conditions
Analyzing Governmental Actions: Trade Agreements, trading bloc, and RTAs
- - Marketers must consider the trade agreements to which a particular country is a signatory or the trading bloc to which is belongs
- Trade Agreement: intergovernmental agreement designed to manage and promote trade activities for specific regions
- Trading bloc: consists of those countries that have signed a particular trade agreement
- Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs) have faced recent challenges but amount for over half of international trade
Analyzing Sociocultural Factors: Culture
- culture exists on two levels: visible artifacts (behavior, dress, symbols, physical settings, ceremonies) and underlying values ( thought processes, beliefs, and assumptions)
- businesses find it more difficult to understand the underlying values of a culture and appropriately adapt their marketing strategies to them
- Culture affects every aspect of consumer behavior: why ppl buy, who is in charge of buying decisions; and how, when, and where people shop
Analyzing Sociocultural Factors: Hofstede's cultural dimensions
- tool that helps assess country's culture
1. Power Distance
2. Uncertainty avoidance
3. Individualism
4. Masculinity
5. Time Orientation
6. Indulgence
Power Distance
willingness to accept social inequality as natural (U.S. low)
Uncertainty Avoidance
the extent to which the society relied on orderliness, consistency, structure, and formalized procedures to address situations that arise in daily life. (U.S. high)
Individualism
perceived obligation to and dependence on groups (collectivism) (U.S. high)
Masculinity
the extent to which dominant values are male oriented. A lower masculinity ranking indicates that men and women are treated equally in all aspects of society; a higher masculinity ranking suggests that men dominate in positions of power (U.S. high)
Time Orientation
short vs long term orientation/ A country that tends to have long term values long term commitments and is willing to accept a longer time horizon (U.S. short term)
Indulgence
the extent to which society allows for the gratification of fun and enjoyment needs or else suppresses and regulates such pursuits (U.S. high)
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries
- changes in tech, especially communications, have been a driving force for growth in global markets for decades
- greatest change facing the global community has been the growth and expansion of BRICS: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa
- companies looking for new economies to move to
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries: Brazil
- long a regional powerhouse, Brazil's ability to weather, and even thrive during, economic storms has transformed it into a global contender
- 12th largest econ
- significant econ progress in early 200s, and recession in 2015
- recovery was rocky, but B's govt implemented a variety of reforms to boost its econ growth
- expanded literate population and the impositions of social programs have half of population enter middle/C class
-structural limitations of its reforms; rate of econ growth is slowing, due to some ineffective state policies, a downturn in the domestic labor market, and its inability to address global inflation and supply bottlenecks
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries: Russia
- formersoviet union, Russia has undergone multiple ups and downs
- 2010s: improve trade relations with other countries and became apart of WTO
- Russian invasion of Ukraine
- middle class is affluent and well educated; has strong demand for imported products during previous econ growth; thruout this Russia relied on energy exports
- invasion: countries imposed sanctions on russian goods to express solidarity with Ukraine and limit russias funding
- EU imposed 8 separate sanctions
- Russia is producing less natural gas and crude oil
- resilient to the sanctions; ongoing energy exports
- domestic econ consequences for military draft; ppl are fleeing to avoid the draft
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries: India
- one of the worlds fastest growing markets
- youngest populations in the world; adapting global attitudes while living in growing urban centers and shopping at large malls
- well educated is fluent in english, skilled workforce holds great attraction to firms
- retail environment lacks modern supply chain mngt
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries: China
- foreign occupation, civil unrest, major famine, and strict one-party communist regime in 20th cent
- 1978: market oriented economic dev-> rapid gains
- today: low levels of econ and personal freedom, but has econ growth
- large population and econ development have helped china attain the highest global retail devel index (GRDI); total retail sales in china are now close to the US
- thriving e commerce precense
- wants to achieve common prosperity
- unequal econ distribution
-wants to now focus less on manufacturing and rela estete and more on digital products
- reduced investments in exports and focusing on domestic markets
The Appeal of the BRICS Countries: South Africa
- newest addition to brics
- one of africas largest econ
- small pop and gdp
- achieved highley developed commercial standards, with a good transportation infrastructure and it also provides unique insights into other markets of subsaharan africa
- setbacks bc of apartheid which put down black majority
Global Entry Strategies
- many firms actually follow a progression in which they begin with less risky strategies to enter their first foreign markets and more to increasingly risky strategies as they gain confidence in their abilities and more control over their operations
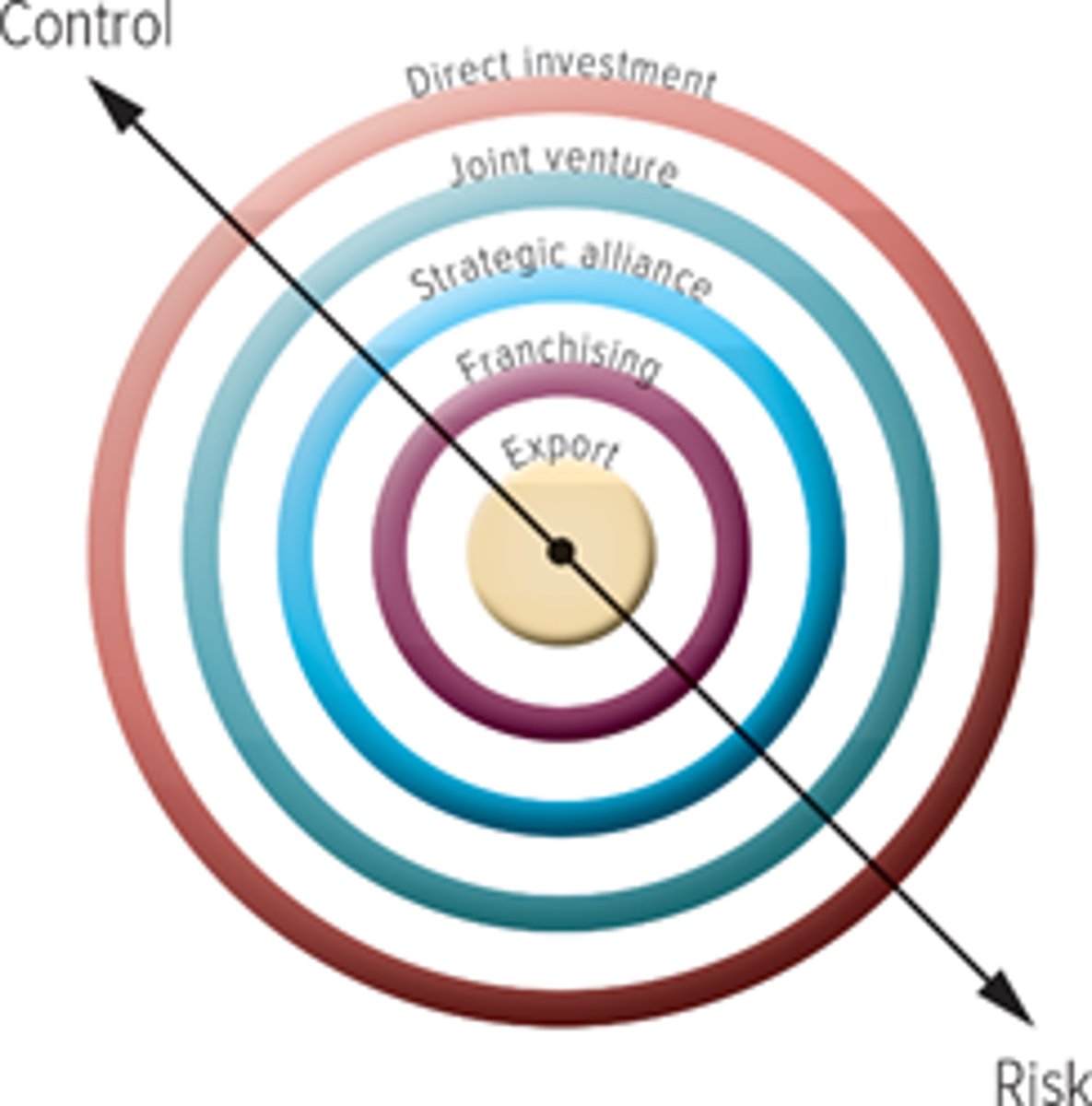
Global Entry Strategies: Exporting
- Exporting: producing goods in one country and selling them to another
- least financial risk, but allows for only a limited return to the exporting firm
- global expansion begins when a firm receives an order for its product or service from another country; little risk bc it has no investment in people, capital equiipment, buildings, or infrastructure
- difficult to achieve economies of scale when everything has to be shipped internationally
Global Entry Strategies: Franchising
- Franchising: contractual agreement btwn firm and indiv, the franchisor and another firm or indiv, the franchisee
- A franch contract allows the franchise to operate a business using the name and business format developed and supported by the franchisor
- when it engages in franchising, the firm has limited control over the market operations in the foreign country, its potential profit is reduced bc it must be split with the franchisee and once the franchise is established, there is always the threat that the franchise will break away and operate as a competitor under a diff name
Global Entry Strategies: Strategic Alliance
- Strat alliances: collaborative relationships btwn independent firms, though the partnering firms do not create an equity partnership; they do not invest in one another
- allied comp inc their chances of reaching new customers
Global Entry Strategies: Joint Venture
- joint venture: firm entering a market pools its resources with those of a local firm
- ownership, control, and profits are shared
- in addition to sharing financial burdens, a local partner offers the foreign entrant greater understanding of the market and access to recourses such as vendors and real estate
- some countries require joint ownership of firms entering their domestic markets
Global Entry Strategies: Direct Investment
- direct investment: req a firm to maintain 100% ownership of its plants, operation facilities, and offices in a foreign country, often thru the formation of wholly owned subsidiaries
- req the highest level of investment and exposes the firm to significant risks, including the loss of its operating and/or initial investments
- a dramatic econ downturn (natural disater/war) can inc a foreign entrant's risk
- in certain markets potential risks are outweighed by high potential rewards-> none of the potential profits must be shared with other firms
- DI offers the firm complete control over its operations in the foreign country
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy
includes two components:
(1) determining the target markets to pursue
(2) developing a marketing mix that will sustain a competitive advantage over time
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Target Market (STP) Why would it be more or less difficult than Domestic STP
- Global Segmentation, targeting, and positioning: more difficult than domestic STP
1. firms considering a global expansion have more difficulty understanding the cultural nuances of other countries
2. subcultures within each country also must be considered
3. consumers often view products and their role as consumers differently in different countries A product, service, or even a retailer often must be positioned differently in diff markets
- still need to monitor econ and social trends to protect their position within the market and adjust products and marketing strats to meet global market needs
- selecting global target markets is complicated for several reasons: sub-cultures, cultural nuances, cultural view of product and consumer roles, different positioning, and adaption
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Target Market (STP): Global product or service Strategies- Three potential global strats
1. Sell the same product or service in markets in both the home country (where the firm's parent comp is) and the host country (the country in which the parent comp has expanded beyond the host company)
2. sell a product or service similar to that sold in the home country but include minor adaptions for products sold in the host country (global localization)
3. sell totally new or different products or services in the host country than in the home country
- the strat a firm chooses depends on the needs of the target market
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Target Market (STP): Global product or service Strategies- Same product or service, similar product or service with a minor adaptions, and totally new product or service
- Same product or service: most typical method of introducing a product outside the home country is to sell the same product or service in other countries
- similar product or service with a minor adaptions: some products req only small changes to appeal to consumers in a new country
- Totally new product or service: the level of econ development and cultural tastes also affects global product strat bc they relate directly to consumer behavior
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Global Pricing Strategy
- determining the selling price in the global marketplace is difficult
- competitive factors influence global pricing in the same way they do home-country pricing, but bc a firm's products or services may not have the same positioning in the global marketplace as they do in their home country, market prices must be adjusted to reflect the local pricing structure
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Global Supply Chain Strategies
- global supply chains are complex as they involve wholesalers, exporters, importers, and different transportation systems
- the additional intermediaries typically add cost and ultimately inc the final selling price of a product
- the number of firms with which the seller needs to deal to get its merch to the consumer determines the complexity of a supply chain
- in most less devel countries, manufacturers must go thru many types of supply chains to get their products to end users, who often lack adequate transportation to shop at central shopping areas or large malls-> consumers shop near their homes at family owned retailers
Choosing a Global Marketing Strategy: Global Communication Strategies
- major challenge is identifying the elements that need to be adapted to be effective in the global marketplace
- Differences in lang, customs, and culture complicate marketers ability to communicate with customers in various countries
- even with these differences, many products and services serve the same needs and wants globally with little or no adaption in their form or message