Restrictive Lung Disease
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Restrictive lung disease
Are characterized by either a reduction in lung compliance or increased external pressures around the lungs limiting lung inflation during inhalation (decreased quantity of air moved in and out of the lungs with each breath)
fluid collection/overload, abnormal thoracic anatomy
What external factors that can cause restrictive lung disease?
loss of lung compliance due to thickening/fibrosis or lungs lose their ability to stretch
What intrinsic factor can lead to restrictive lung disease?
TLC decreased, FEV1 decreased, FVC decreased, FEV1/FVC normal/increased
What does your spirometry look like in a restrictive lung disease
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
What is the most common idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) that is a restrictive lung diseases with diffuse lung scarring and is linked to recurrent cycles of epithelial cell injury and dysregulated repair?
smoking, comorbid autoimmune, long term fume/particle exposure
What are some associated risk factors of IPF?
spirometry, CXR, Chest CT
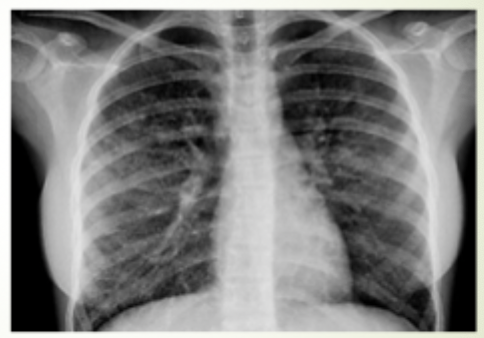
A 65 y/o male presents to the clinic with progressive dyspnea and a dry cough that has appeared over the last 6 months. Patient reports he is a past smoker, but has quit. Patient denies, fever, fatigue, and muscle/joint pain, dry mouth, and hair loss. On physical exam you note bibasilar crackles. What do you want to order?
IPF, Lung biopsy
Okay so the imaging comes back for our patient with progressive dyspnea and a dry cough that has appeared over the last 6 months. Spirometry shows a restrictive pattern, CXR shows increased reticular markings and ground glass, and the chest CT shows honey comb changes and ground glass opacities? What are you thinking and what could you use to completely confirm your diagnosis?
lung biopsy
What is the gold standard for a definitive diagnosis of IPF (TBH you can skip this if you imaging is conclusive)?
Nintedanib, pirfenidone, lung transplant, supportive care
Okay so for our IPF homie what is our treatment plan?
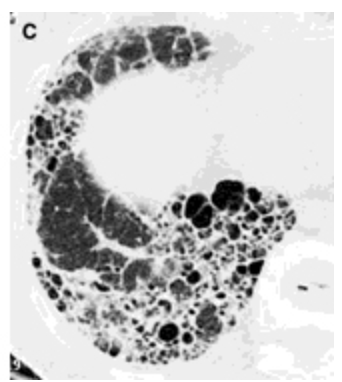
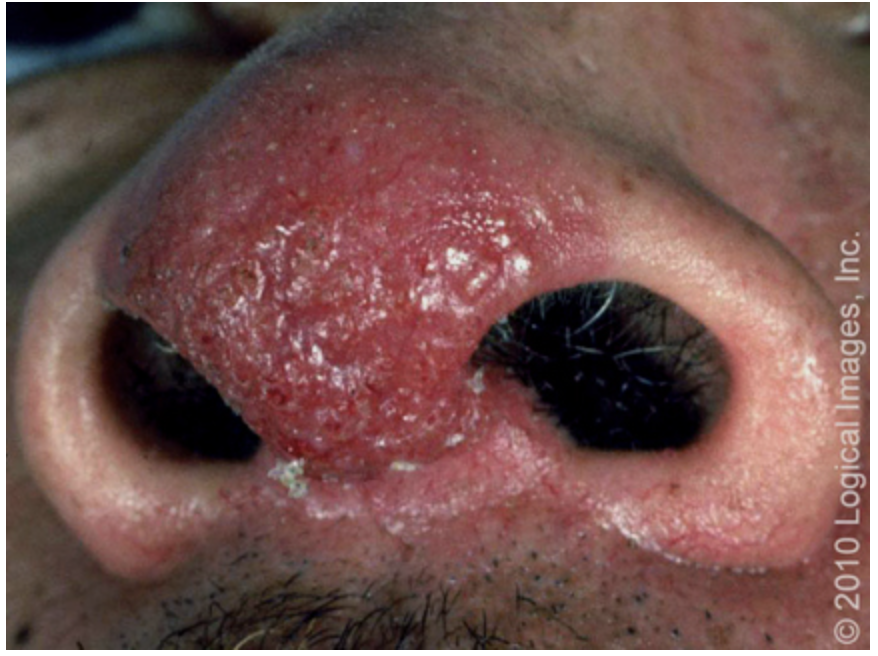
Sarcoidosis
A 35 y/o African American male presents to the clinic for a dry cough and dyspnea. He also reports pleuritic chest pain, fever, night sweats, and that he has loss 20 pounds without trying. On a physical exam you note bluish-red papules/nodules/plaques on the nose and ears and crackles/rales on auscultation of the lungs. CBC shows leukopenia and anemia. ESR is elevated. CMP shows an extremely high calcium. What alarm bells are ringing?
non-caseating tissue granulomas
What is the pathological hallmark of sarcoidosis
Lupus pernio, Erythema nodosum (nonspecific), maculopapular trunk lesions
What skin changes might you see with sarcoidosis?
Dry eyes, anterior uveitis, iritis, retinitis,
What eye issues might you see with sarcoidosis (can progress to blindness)?
Granulomatous infiltration, lymph node enlargement
What changes in the lymph nodes might you see with sarcoidosis?
granulomatous disease, hepatomegaly, hepatitis
What changes in the liver might you see with sarcoidosis?
anemia, leukopenia, splenomegaly
What changes in the bone marrow and spleen might you see with sarcoidosis?
Stroke like symptoms due to granulomatous lesions in brain
What changes in the CNS might you see with sarcoidosis?
granulomatous lesions progress to CHF/arrythmias
What changes in the heart might you see with sarcoidosis?
nephritis
What changes in the kidneys might you see with sarcoidosis?
progressive arthritis and joint pain
What changes in the joints might you see with sarcoidosis?
hypercalcemia (low PTH, high vitamin D)
What electrolyte imbalance can occur as a result of sarcoidosis?
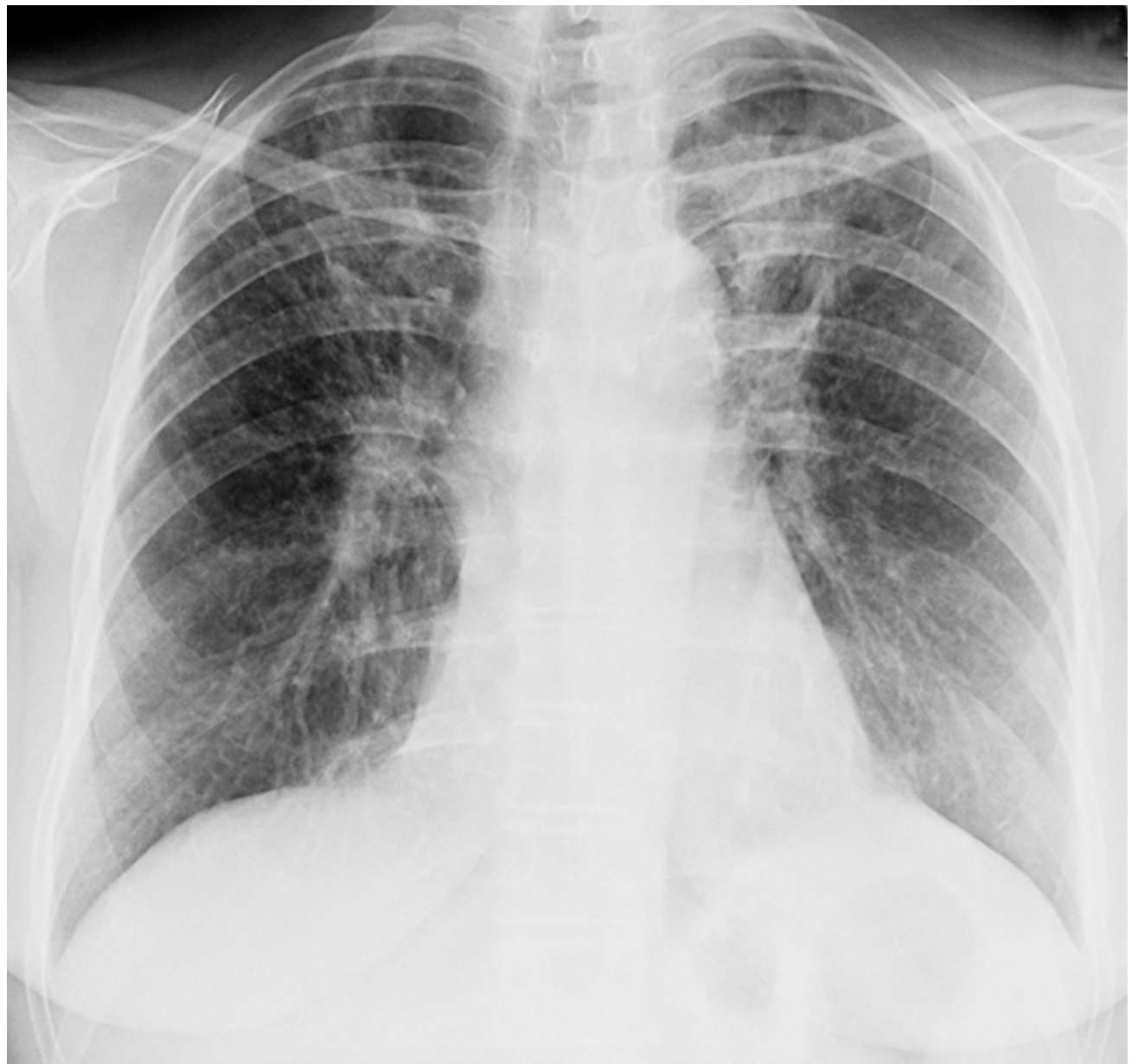
bilateral hilar adenopathy, reticular infiltrates/nodular, cavitary lesions
What are you going to see in a CXR that give off the vibes of sarcoidosis?
restrictive
Sarcoidosis is what type of lung disease?
rules out infection/malignancy
What is the point of a biopsy in a sarcoidosis workup?
symptomatic (dyspnea), multisystem involvement, increasing CXR opacities, extrapulmonary disease
What are indications for treating sarcoidosis?
Oral corticosteroids (prednisone)
1st line treatment for sarcoidosis?
Immunosuppression (methotrexate)
2nd line treatment for sarcoidosis (used for failed treatment or those intolerant of 1st line)?
pulmonary HTN, respiratory failure, myocardial sarcoidosis
Complications of sarcoidosis?
pneumoconiosis
A class of chronic, fibrotic lung diseases caused by inhalation of inorganic particles
remove exposure, symptomatic treatment, monitor for COPD
General approach to treating pneumoconiosis
asymptomatic, increased COPD risk
Characteristics of simple CWP (coal workers pneumoconiosis)
sterile necrotic (caseating) cavitary lesions
What is the MAJOR characteristic of complicated CWP?
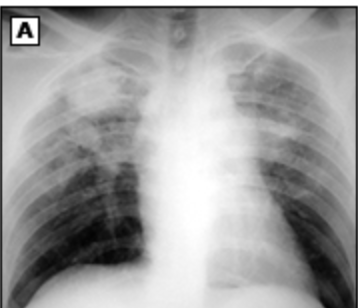
silicosis
What pneumoconiosis is due to extensive or prolonged inhalation of free silica and results in eggshell calcification of the periphery/outer layer hilar lymph nodes?
simple
What form of silicosis is normally asymptomatic with no negative functional effects
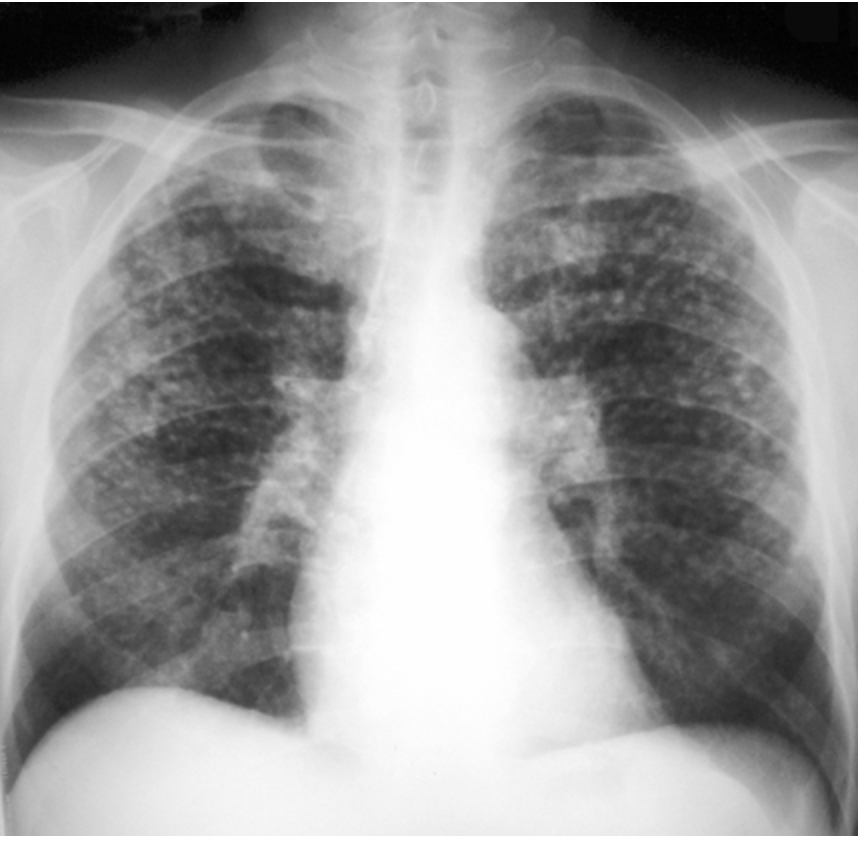
Complex
What form of silicosis has large conglomerate densities of nodules in the upper lungs and patients become symptomatic with dyspnea?
TB (get those PPDs and CXRs)
What is a common complication of silicosis?
Asbestosis
A form a pneumoconiosis that is due to prolonged (10-20 years) exposure to asbestos fibers common in shipyard/construction workers
Asbestosis
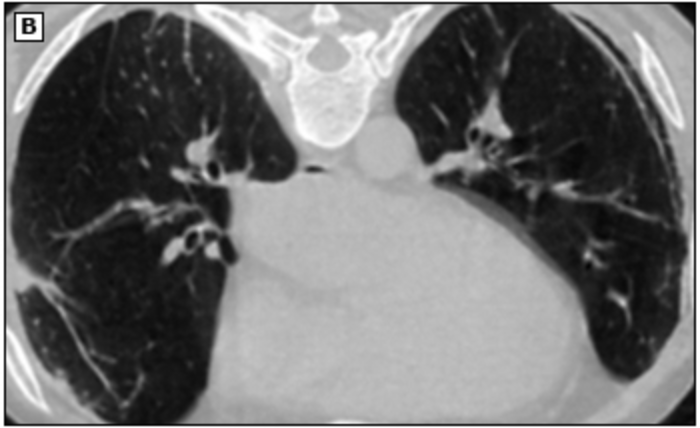
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for worsening dyspnea. While collecting a history, he notes that he used to work construction back in the 80s. On a physical exam you note inspiratory crackles, digital clubbing and and cyanosis. CXR shows thickening/calcification along the parietal pleura and lower lung fields (diaphragm/cardiac border). What are you thinking?
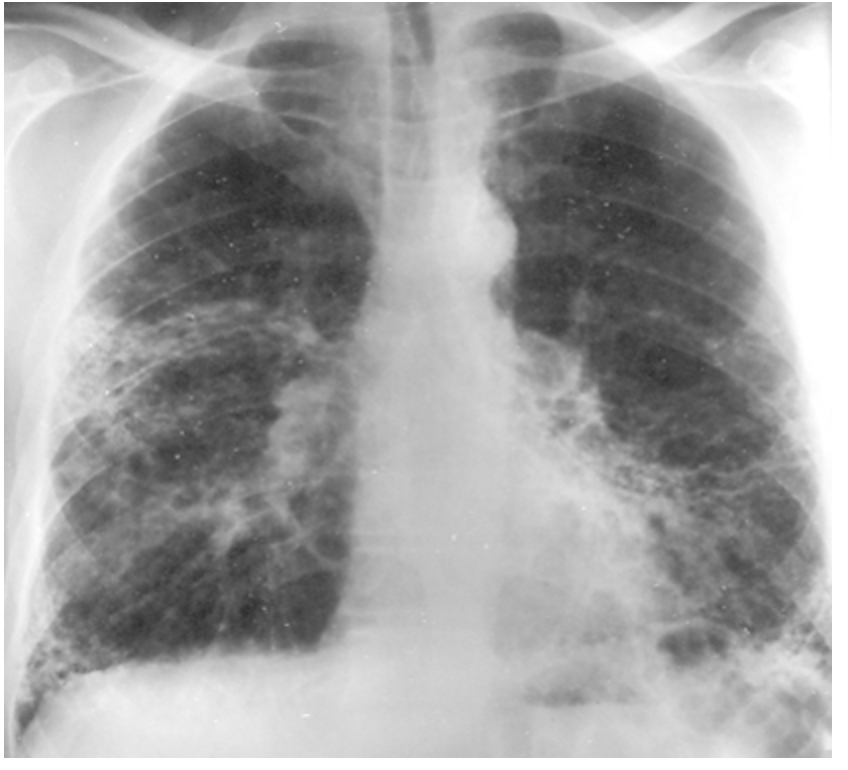
Chest CT
What is the imaging of choice for diagnosing abestosis?
linear streaking, honeycomb changes, pleural plaques
What are you going to see on a chest CT positive for asbestosis?
lung cancer, mesothelioma
What are some complications of abestosis?
E-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI)
What type of lung injury tends to effect male patients under 35 and is associated with diacetyl (popcorn flavorings), THC, nicotine, vitamin E, and delivery device problems?
Supportive care, empiric antibiotics, systemic steroids
An 18 y/o male presents to the ER for SOB and chest pain. Patient also reports N/V/D, cough, and chills. In your history you discover that your patient loves a mango juul. Vitals are stable with the exception of a fever 101.4, 123 bpm, and 89% O2sat on RA. CXR shows bilateral ground glass. How are you managing this patient?