Epithelial Tissue (Revised)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Last updated 11:42 AM on 10/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
4 Types of Tissue
- epithelial -muscle
-connective -nervous tissue
-connective -nervous tissue
2
New cards
Tissue
group of similar cells that together carry out a specific job
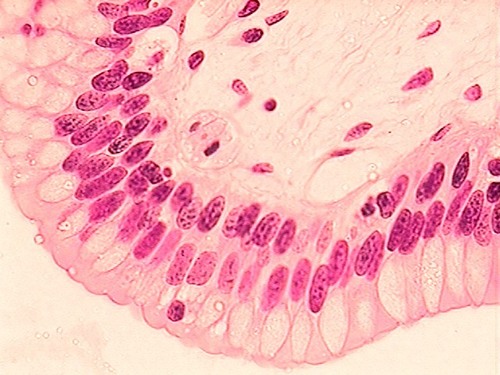
3
New cards
Histologist
Study of tissue
4
New cards
Pathologist
studies the diseases of cells and tissues

5
New cards
Cellularity
more cells than matrix
6
New cards
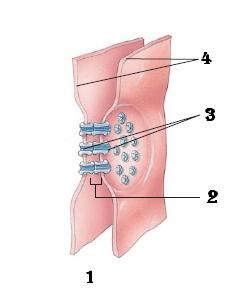
Junctions
Anchor cells together so it can remain in a continuous sheet
7
New cards
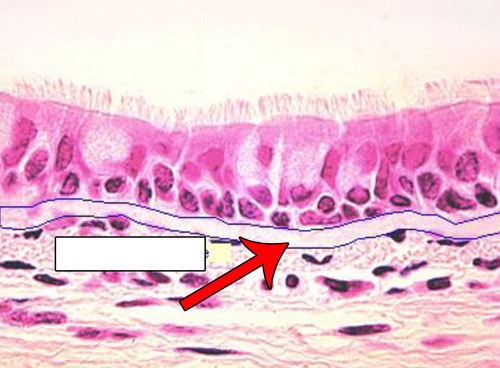
Basement Membrane
bottom of epithelial tissue that has glycoproteins and reticular fibers
8
New cards
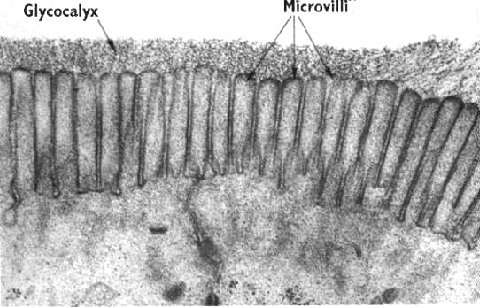
Microvilli
increases surface area for absorption
9
New cards
Avascular
no blood vessels
10
New cards
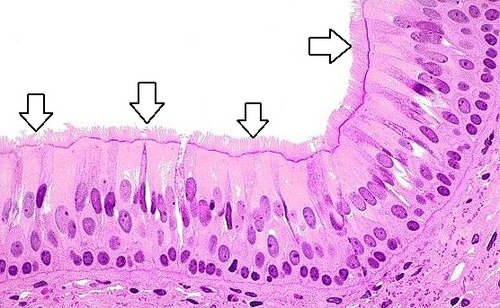
Cilia
sweepers and cleaners
11
New cards
Simple Squamous
- diffusion, permeability, filtration, slick
- Lungs, heart, blood vessel, kidneys
- Lungs, heart, blood vessel, kidneys
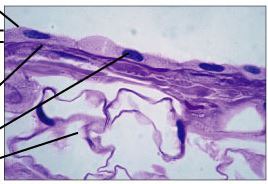
12
New cards
Simple Cuboidal
-one layer
-secretes
-glands
-secretes
-glands
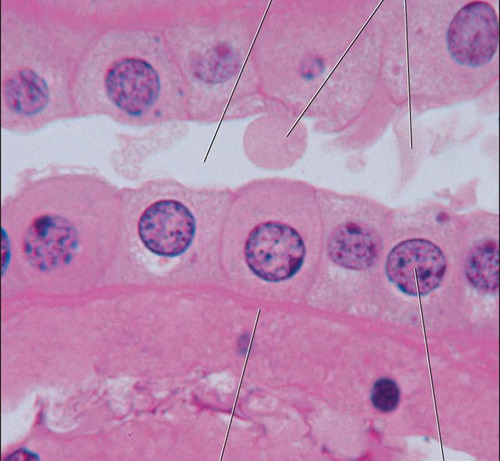
13
New cards
Endocrine Glands
secretes hormones directly into blood
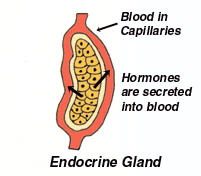
14
New cards
Exocrine Glands
products are carried by a duct to a hollow organ (digestive enzymes) or out of body (sweat)
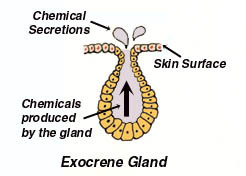
15
New cards
Simple Columnar w/ microvilli
- absorption of nutrients
-intestines
-intestines
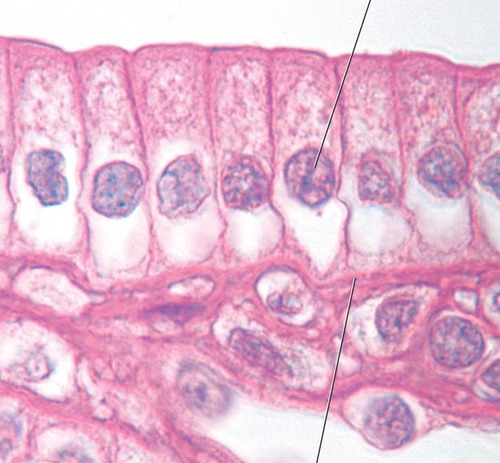
16
New cards
Simple Columnar w/ cilia
- sweeps eggs
-fallopian (uterine) tube
-fallopian (uterine) tube
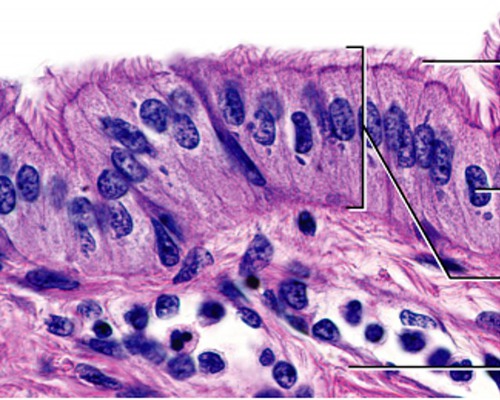
17
New cards
Pseudostratified Columnar
-secretes mucus, sweeps out debris
-upper respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, bronchioles)
-upper respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, bronchioles)
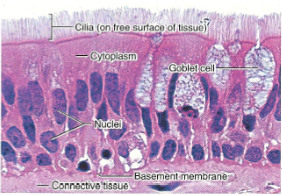
18
New cards
Goblet Cells
Single cell gland that secrete mucus
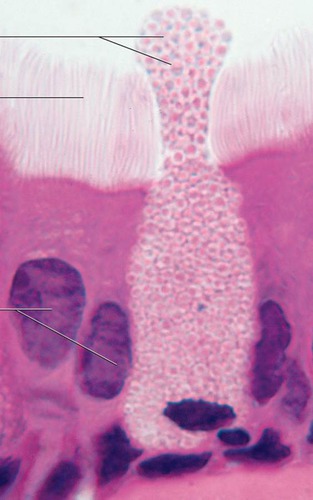
19
New cards
Stratified Epithelium
-more than one layer, classified by top layer
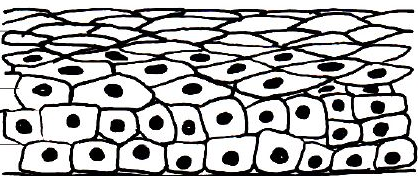
20
New cards
Stratified Squamous
-takes friction, is a barrier, protects from fluid loss
-Esophagus, skin, mouth
-Esophagus, skin, mouth
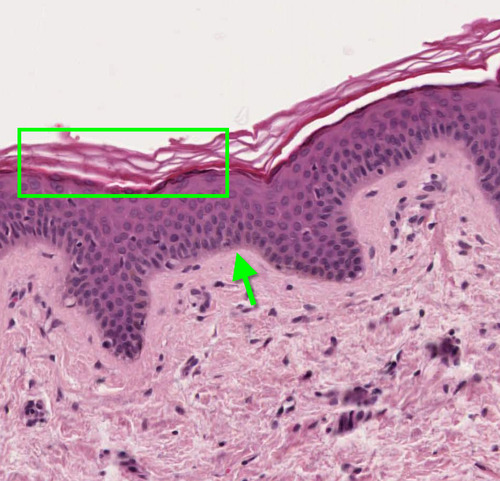
21
New cards
Connective Tissue
Type of tissue that stratified squamous sits on top of
22
New cards
Mitotic Cells
Cells in the stratified squamous tissue that regenerate (mitosis)
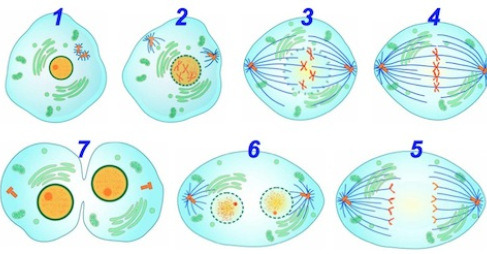
23
New cards
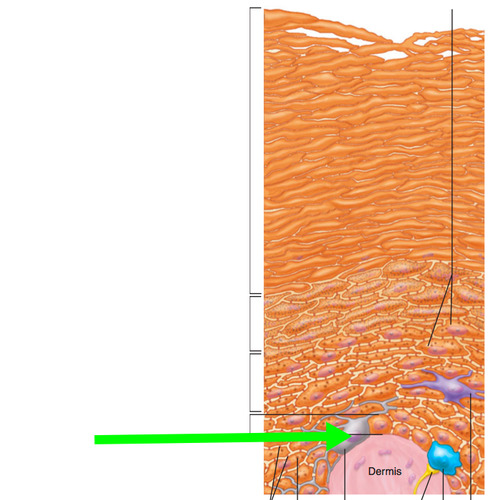
Melanocytes
make and release melanin
24
New cards
melanin
skin, eye, and hair pigment

25
New cards
Keratin
waterproof protective top layer of skin
26
New cards
Stratified Cuboidal
-layered
-secretes
-glands
-secretes
-glands
27
New cards
Desquamification
Friction causing top layer of stratified squamous cells to fall off
28
New cards
Transitional Epithelium
-stretch to squamous shape (full) to cuboidal (empty)
- urinary bladder
- urinary bladder
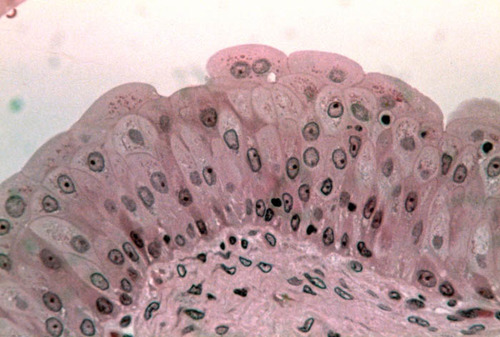
29
New cards
Stratified Columnar
- protection
- surrounds sphincter muscles, at end of stomach
- surrounds sphincter muscles, at end of stomach