14-Cold War, Independence Movements and Decolonization
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

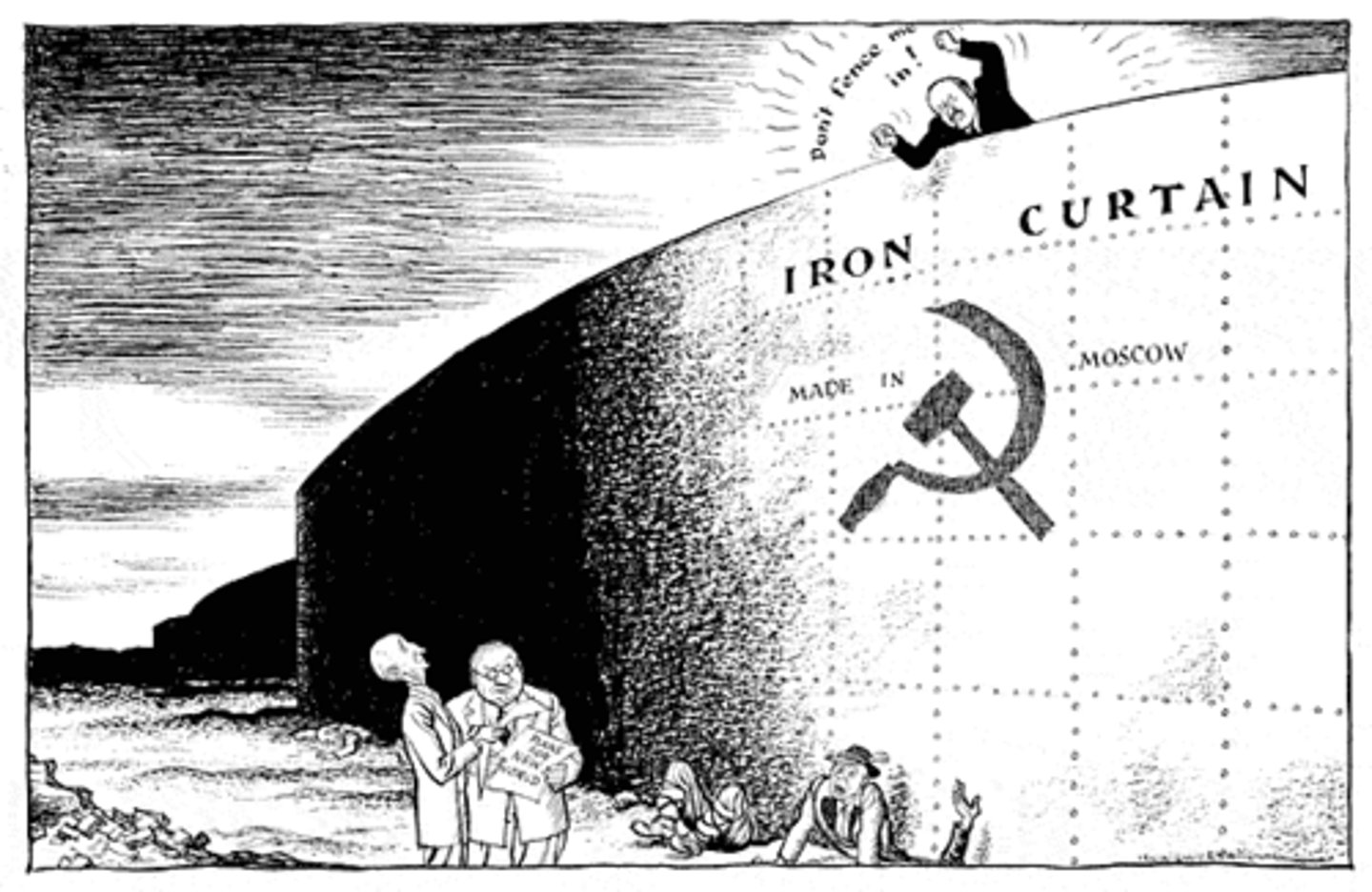
Iron Curtain
A political barrier that separated the communist and free world in Europe. Term created by Winston Churchill.

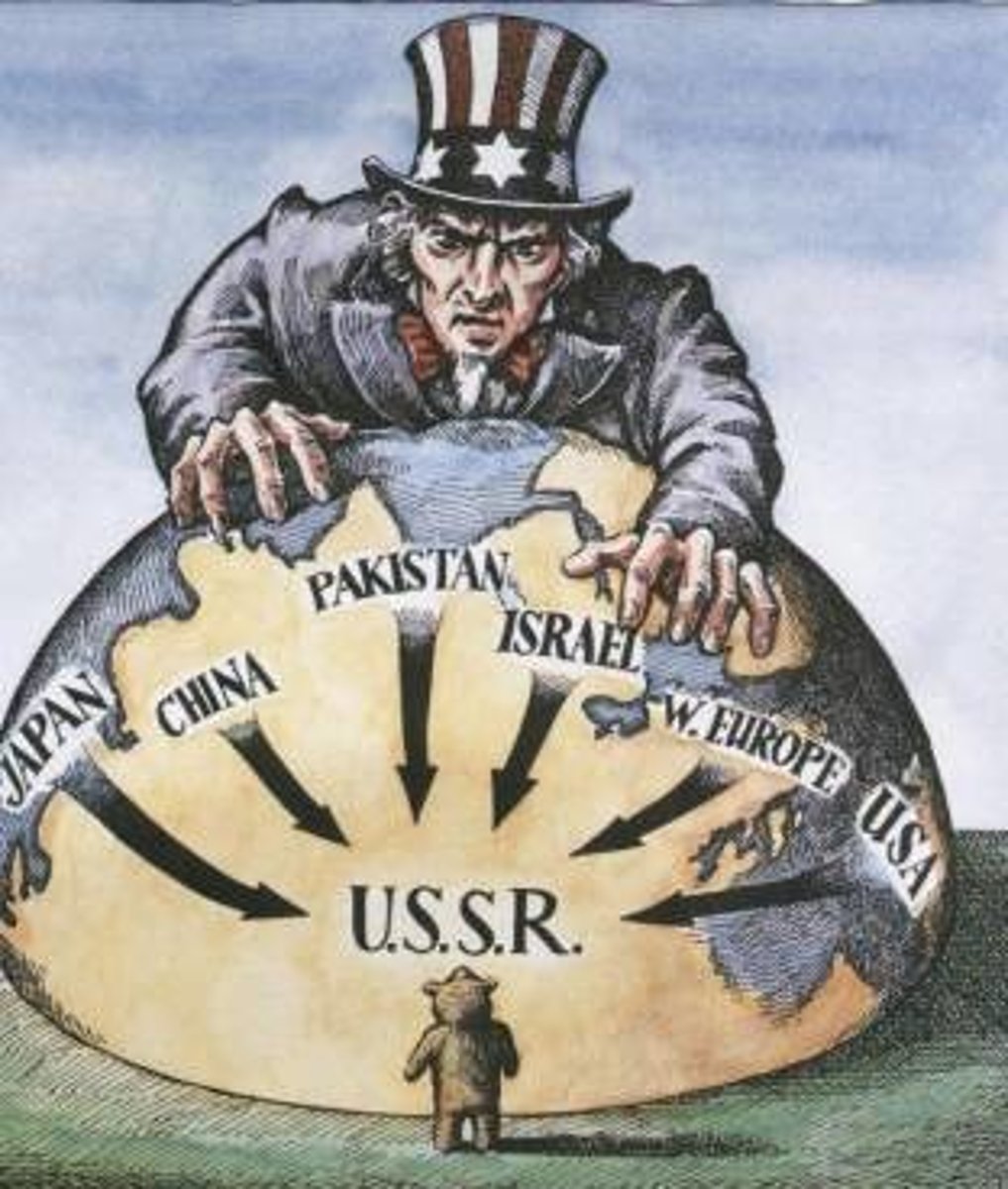
Containment
American policy of resisting further expansion of communism around the world
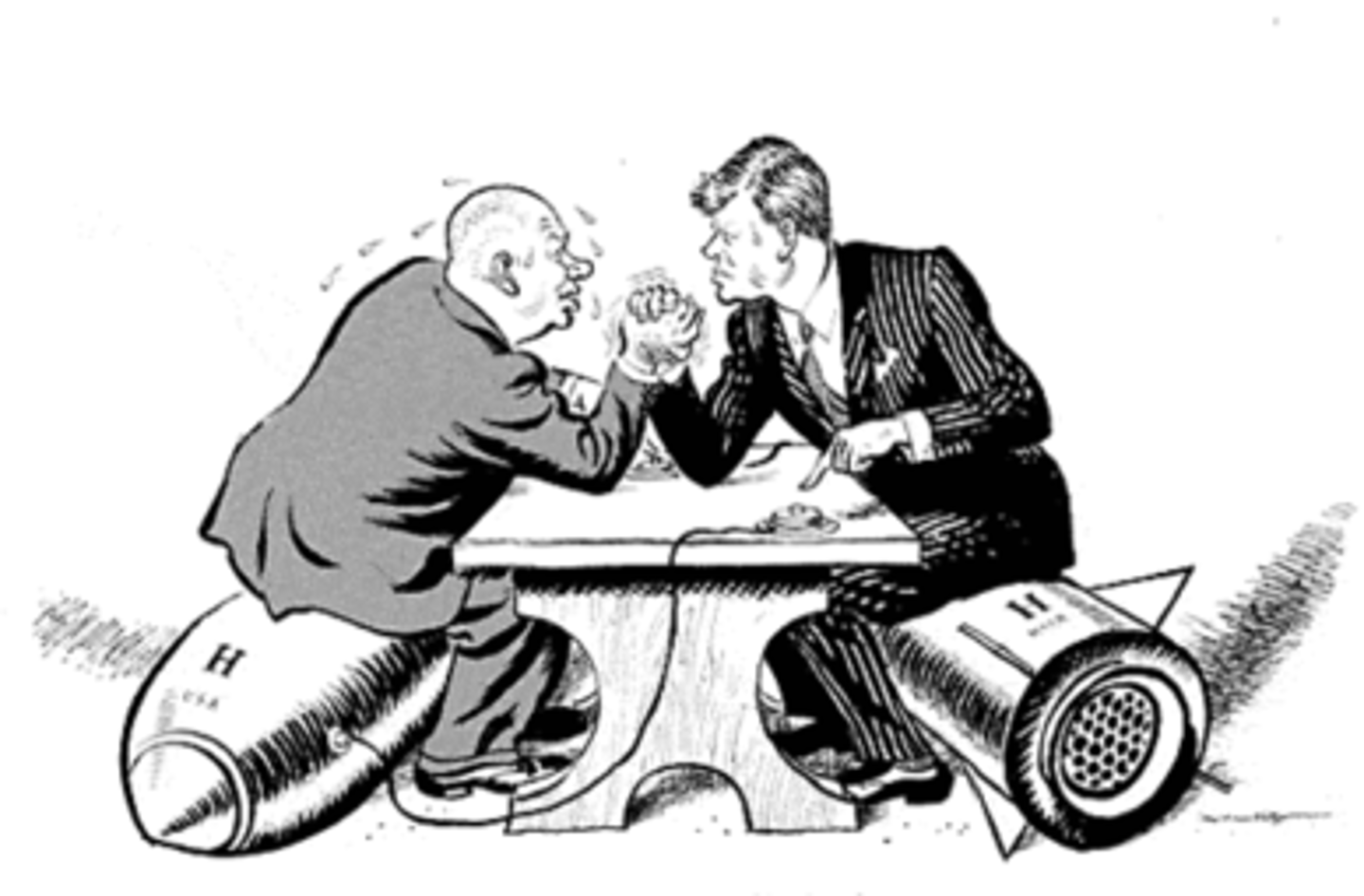
Brinkmanship
Threaten nuclear retaliation to get the other side to back down.

Taiwan
About 100 miles off China's southeastern coast, the Chinese Nationalists fled here to escape the communists. Protected by the United States
Red Guards
the Radical youth of the Cultural Revolution in China starting in 1966.

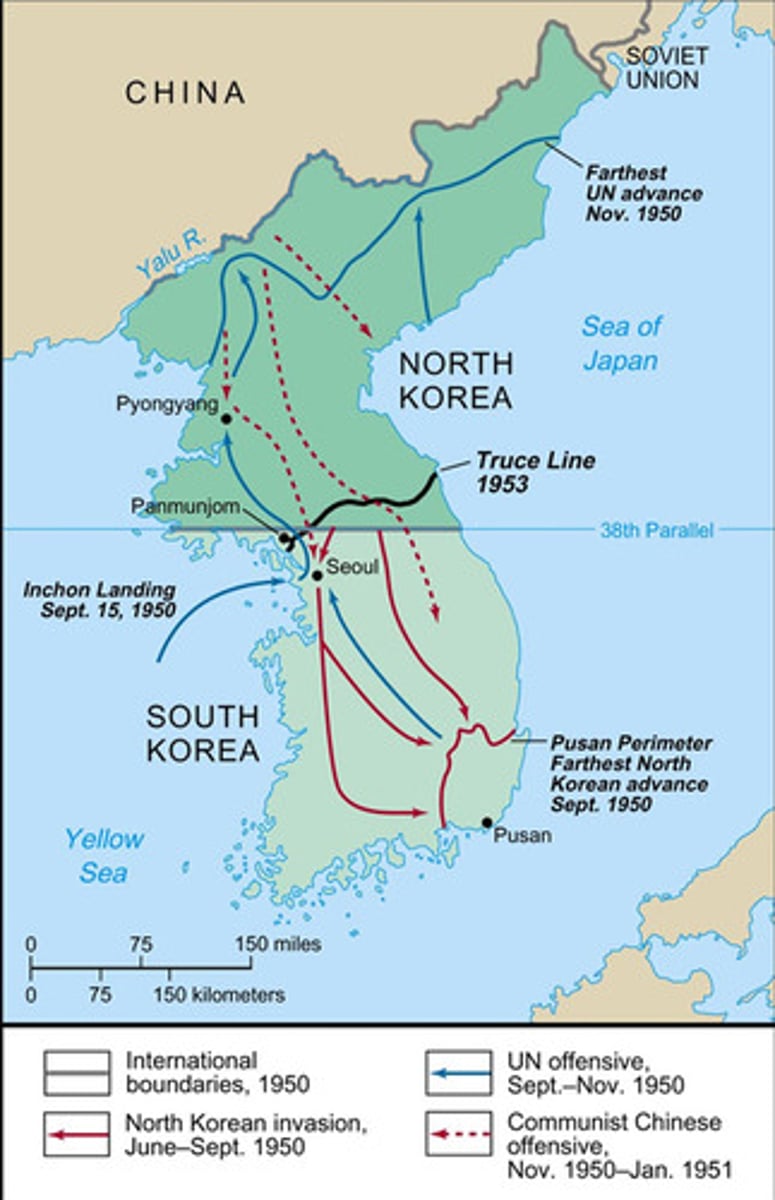
Korean War (1950-1953)
North Korea (aided by USSR) fighting to take over South Korea (Aided by US). Ended in a ceasefire and established the 38th parallel.
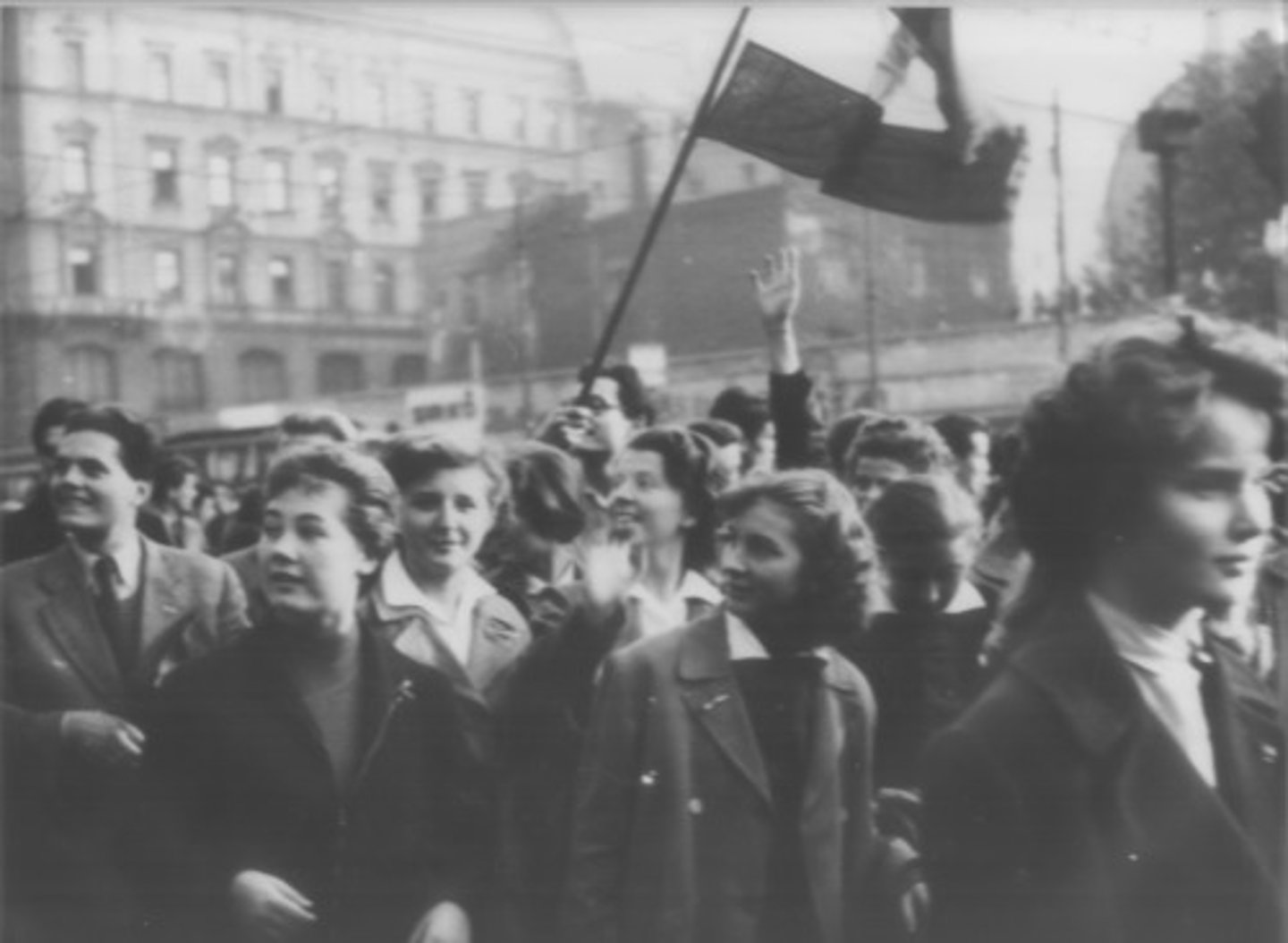
Hungarian Revolution of 1956
An attempt by Liberals in Hungary to overthrow the Soviet-backed Communist leadership of the country.

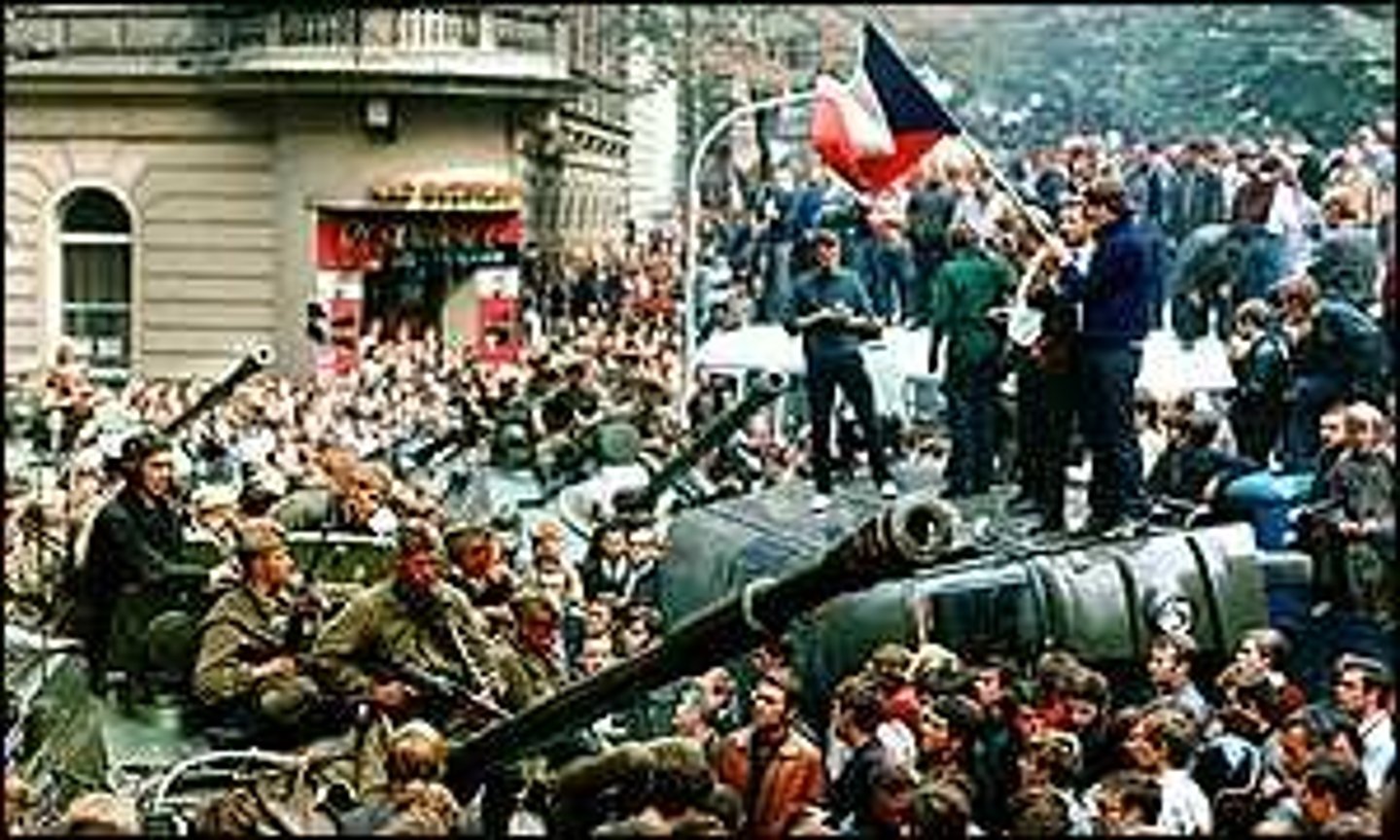
Prague Spring (1968)
a failed attempt to overthrow communism in Czechoslovakia; crushed by Soviet troops

Afghan War
Failed attempt by USSR to take over Afghanistan - expense/negative public reaction hurt USSR communists - US supported Afghan guerillas

Perestroika
A policy initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev that involved restructuring of the social and economic status quo in communist Russia towards a market based economy and society

Boris Yeltsin
President of the Russian Republic in 1991. Helped end the USSR and force Gorbachev to resign.

Fall of the Iron Curtain
In 1989 many nations of the Eastern Soviet Bloc overthrew their communist dictatorships and established free governments. Symbolic end was the Fall of the Berlin Wall.

Hong Kong
A British colony in China, received after the first Opium War and returned to China in 1997
Capitalism
An economic system in which private individuals and corporations control the means of production and use them to earn profits.

Communism
An economic and political system based on one-party government and state ownership of property.

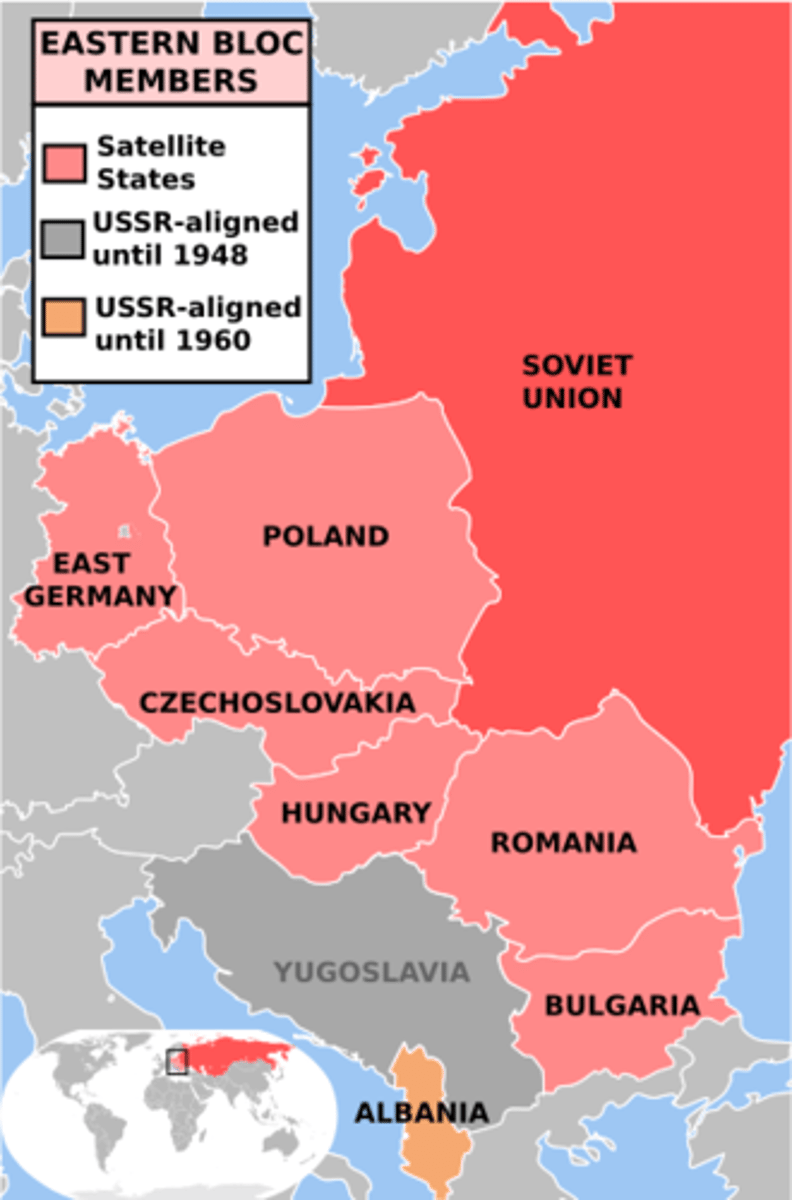
Satellite Nations
A country that is dominated politically and economically by another nation.
Truman Doctrine
A U.S. policy, announced by President Harry Truman in 1947, of providing economic and military aid to Turkey and Greece.

Marshall Plan
T the United States supplied economic aid to European nations to help them rebuild after World War II.

Berlin Airlift
A 327-day operation in which U.S. and British planes flew food and supplies into West Berlin after the Soviets blockaded the city in 1948.
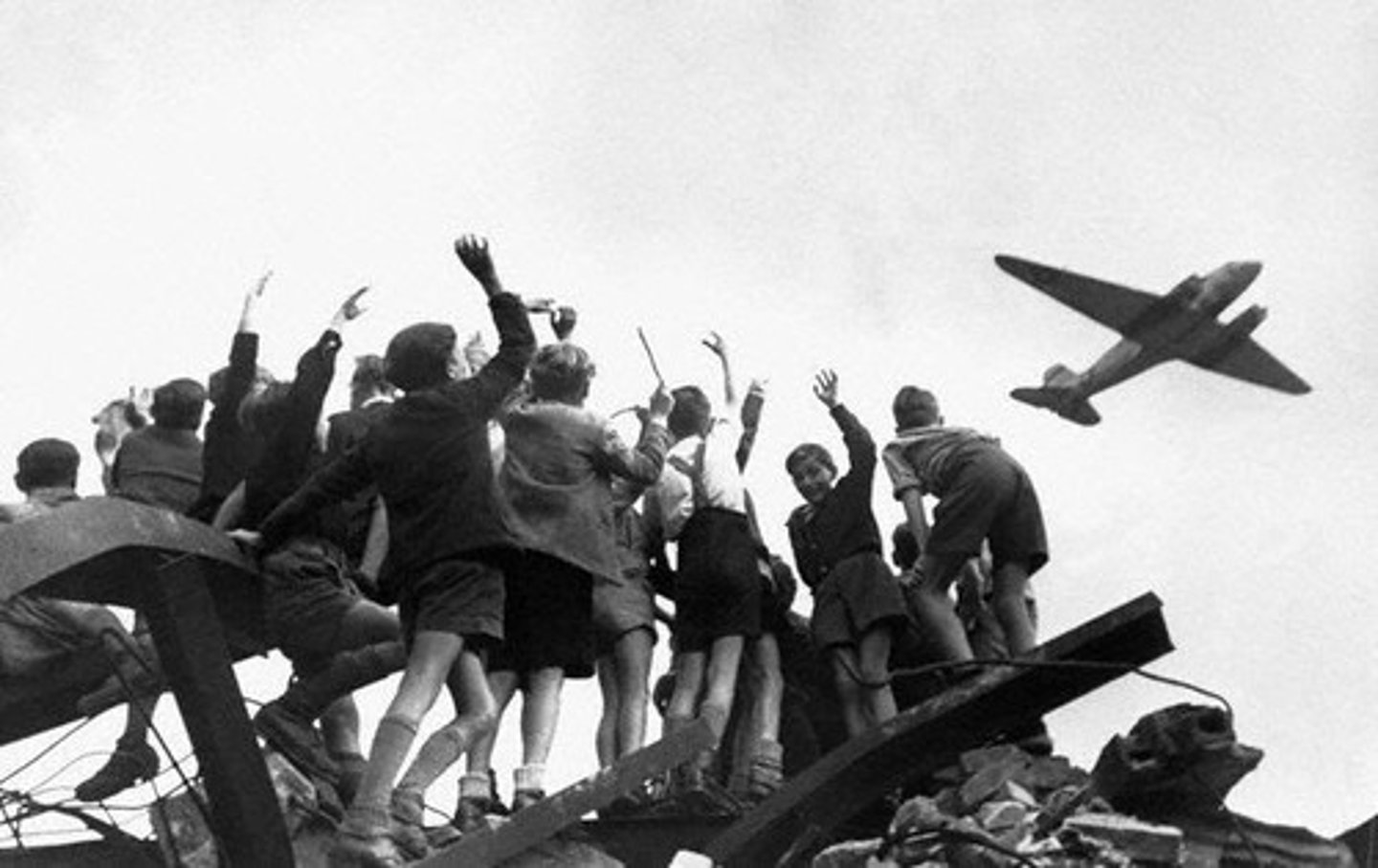

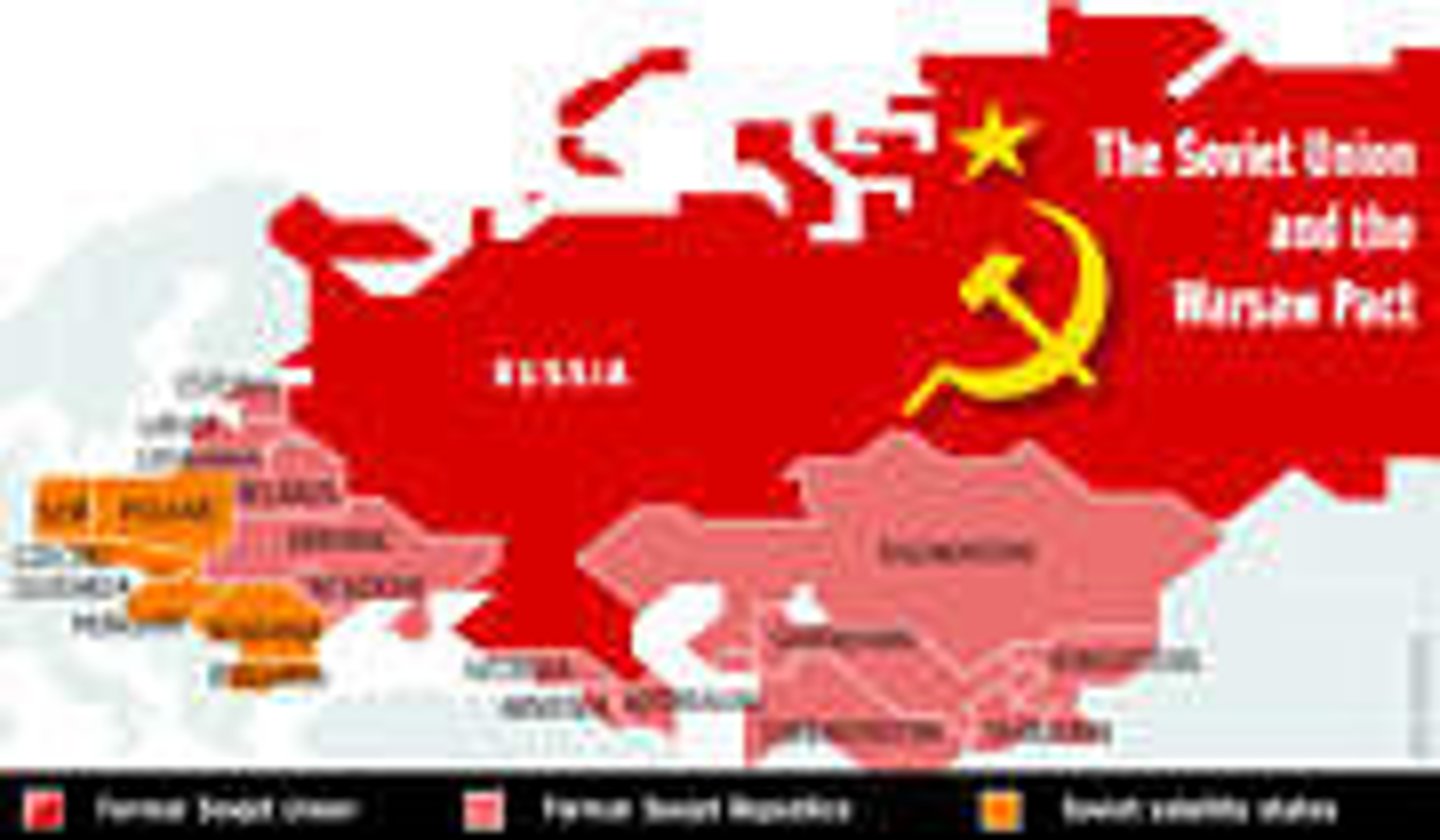
Warsaw Pact
A Military alliance formed in 1955 by the Soviet Union and its Eastern European satellites.
Bay of Pigs
Failed CIA operation in April 1961to overthrow Castro and take over Cuba using Cuban exiles.
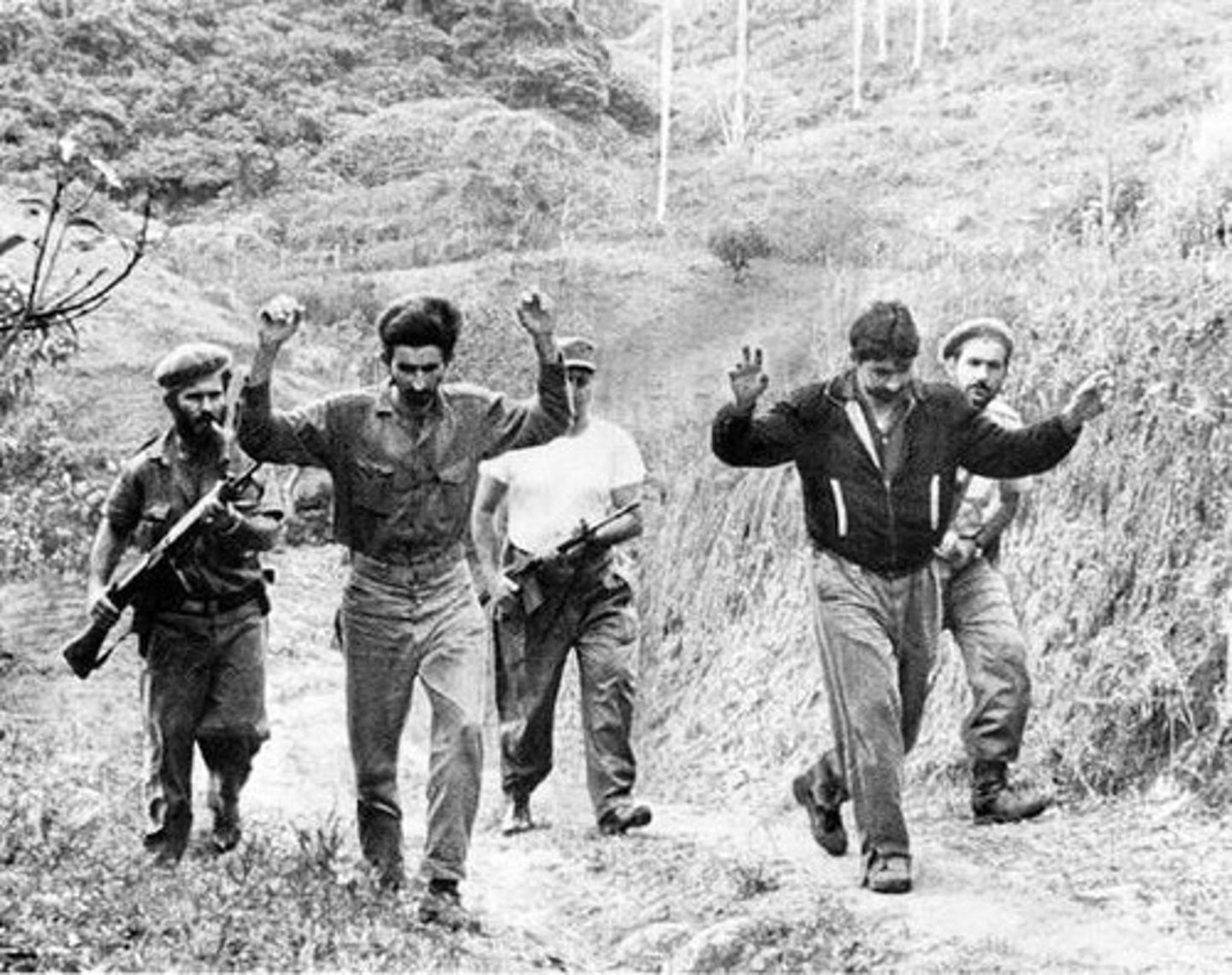

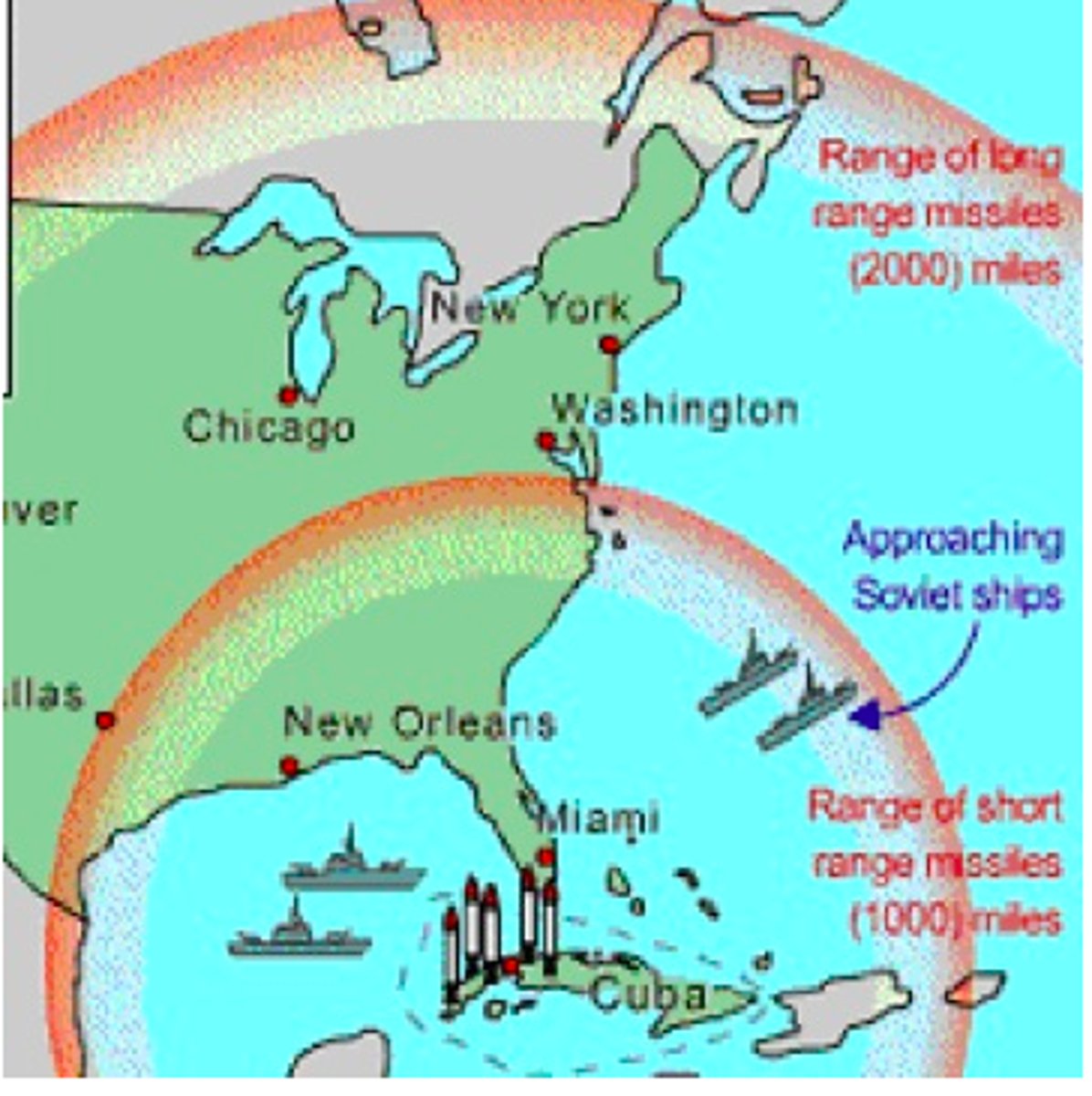
Cuban Missile Crisis
13 Day period in October 1962 when Soviet nuclear missile were pointed at the United States in Cuba.
Mao Zedong
Communist leader of China who comes into power in 1949.

MAD
Mutually Assured Destruction: the idea that the superpowers had so many nuclear weapons that they would completely destroy each other in a war
Cold War
Conflict started in 1949 between superpowers, U.S. and Soviet Union.

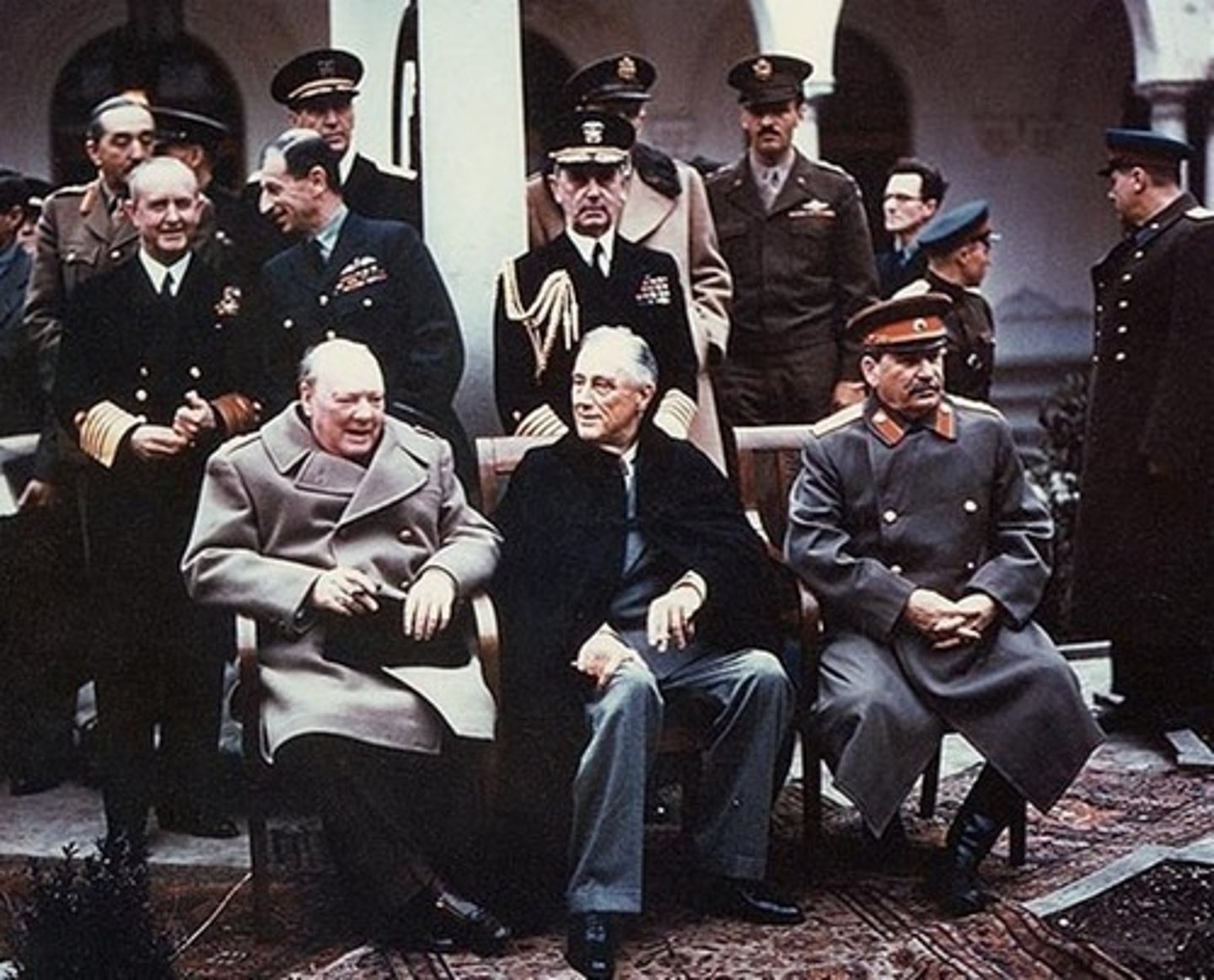
Yalta Conference
Meeting of leaders from U.S. (FDR), Britain (Churchill) and Soviet Union (Stalin) in 1945 before end of WWII.
Made plan for post-war to divide Germany.

Great Leap Forward
Mao's plan to modernize China with a focus on agriculture and industry.

Cultural Revolution
Revolution led by the Red Guards under Mao.
Goal to establish a society of peasants and workers that are all equal.
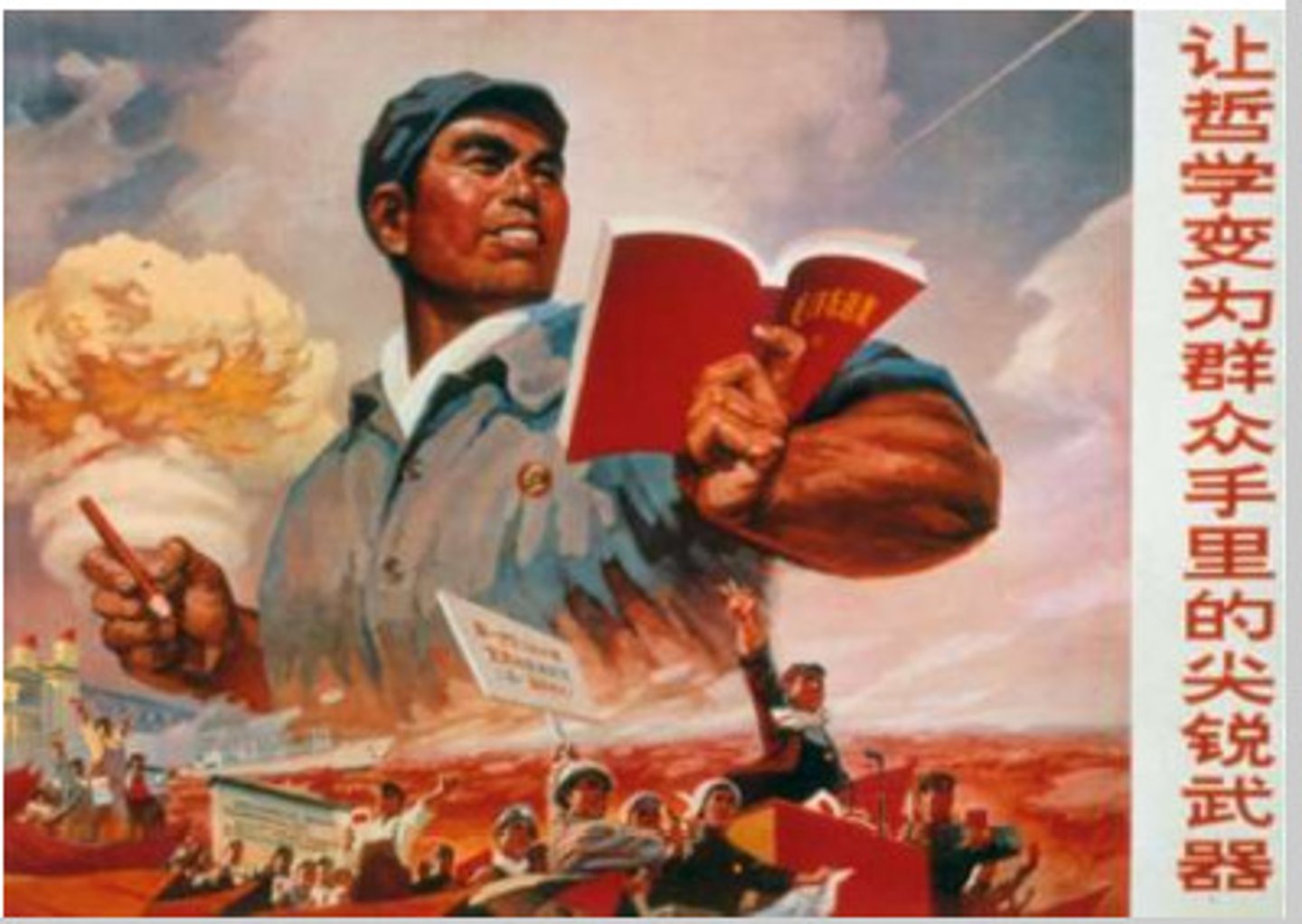

Tiananmen Square
Student protest for democratic reform in China in 1989 for more policies that would allowed more economic freedom.

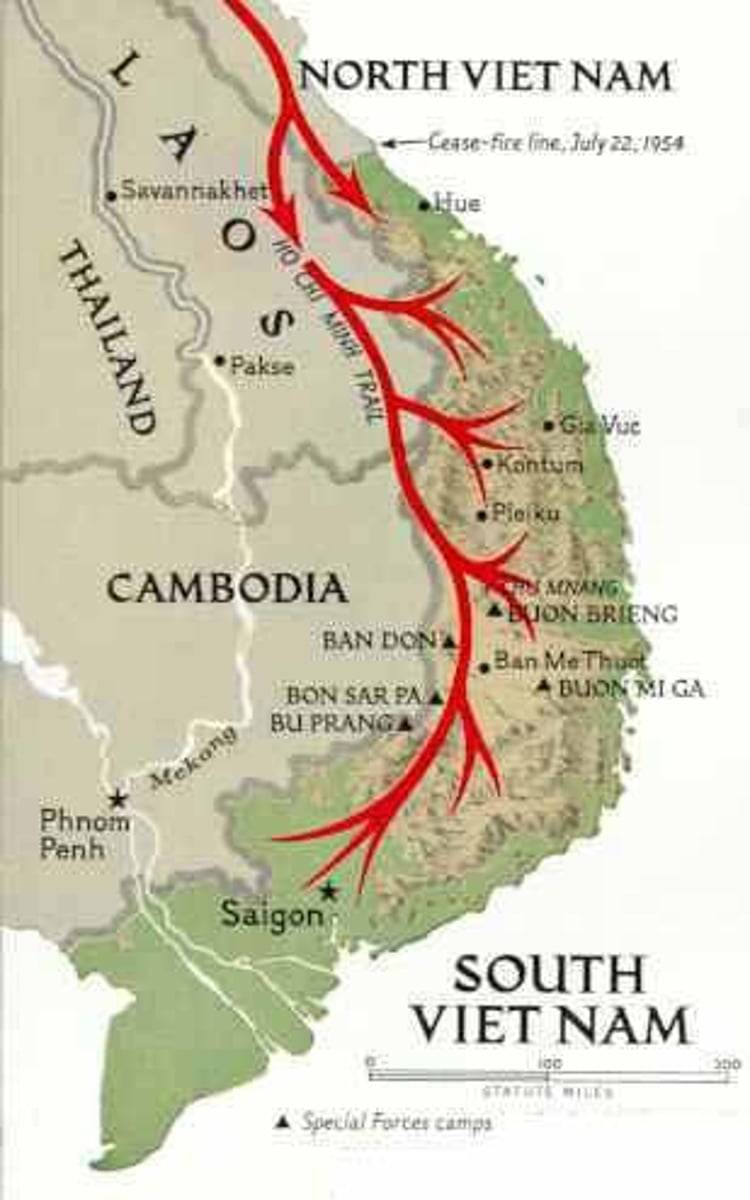
Vietnam War
Country divided between communist north (Ho Chi Minh & Vietcong & supported by China & Soviet Union) and south (Ngo Dinh Diem -dictator & U.S.). Another example of a proxy war
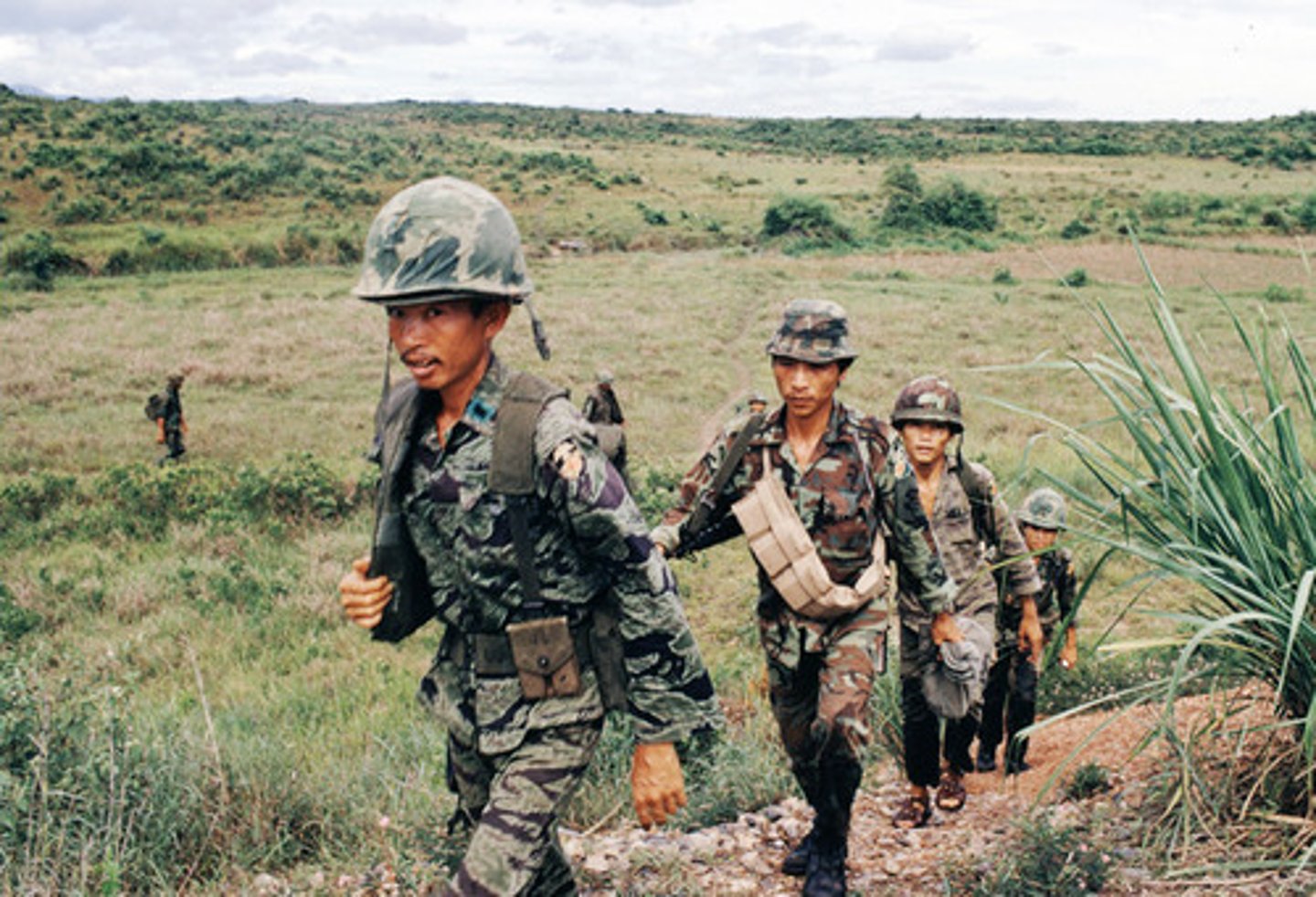

Ho Chi Minh
Leader of the Vietnamese independence movement from France and later the leader of the communists Democratic Republic of Vietnam.
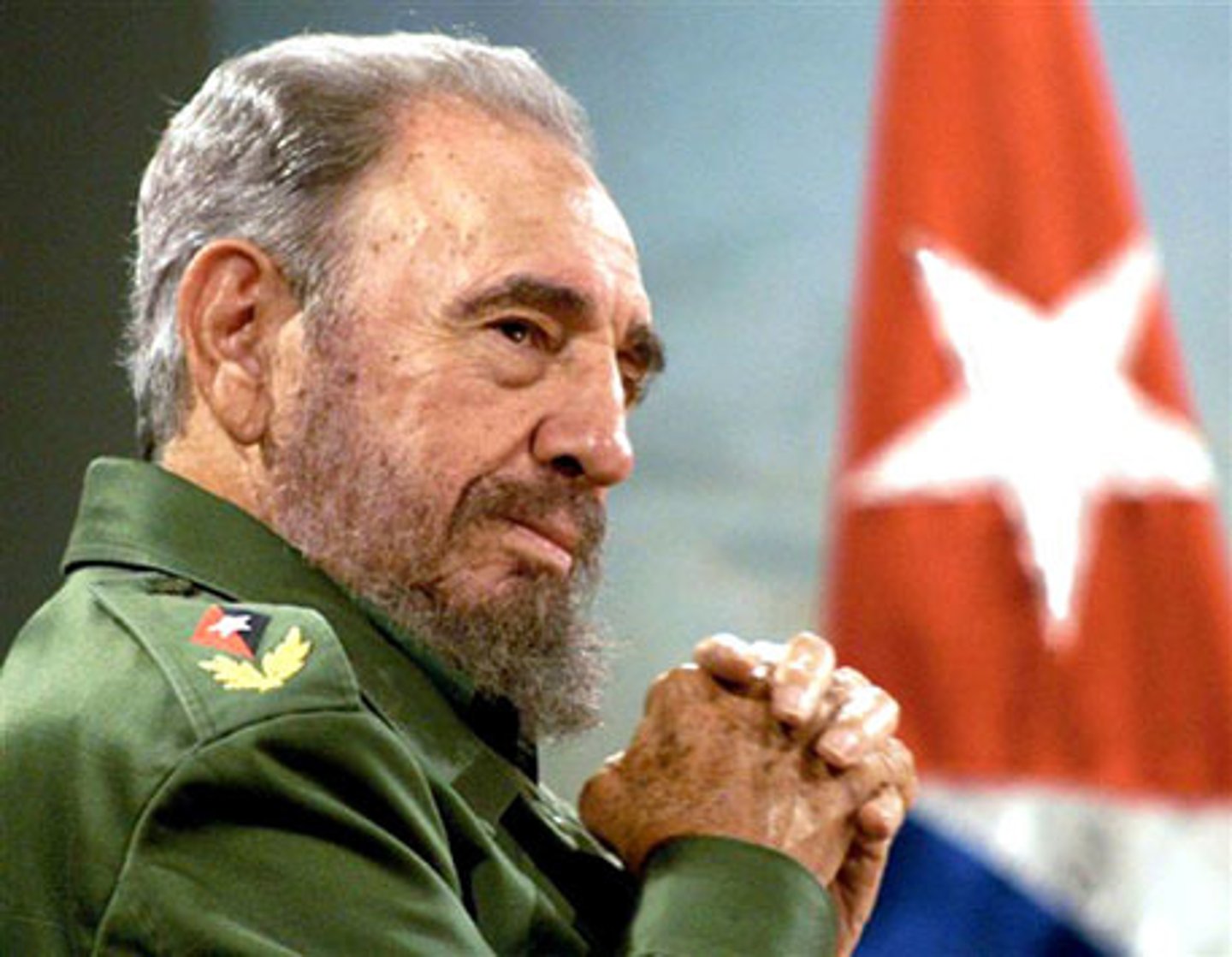
Fidel Castro
Leader of revolution in Cuba and later become communist dictator.

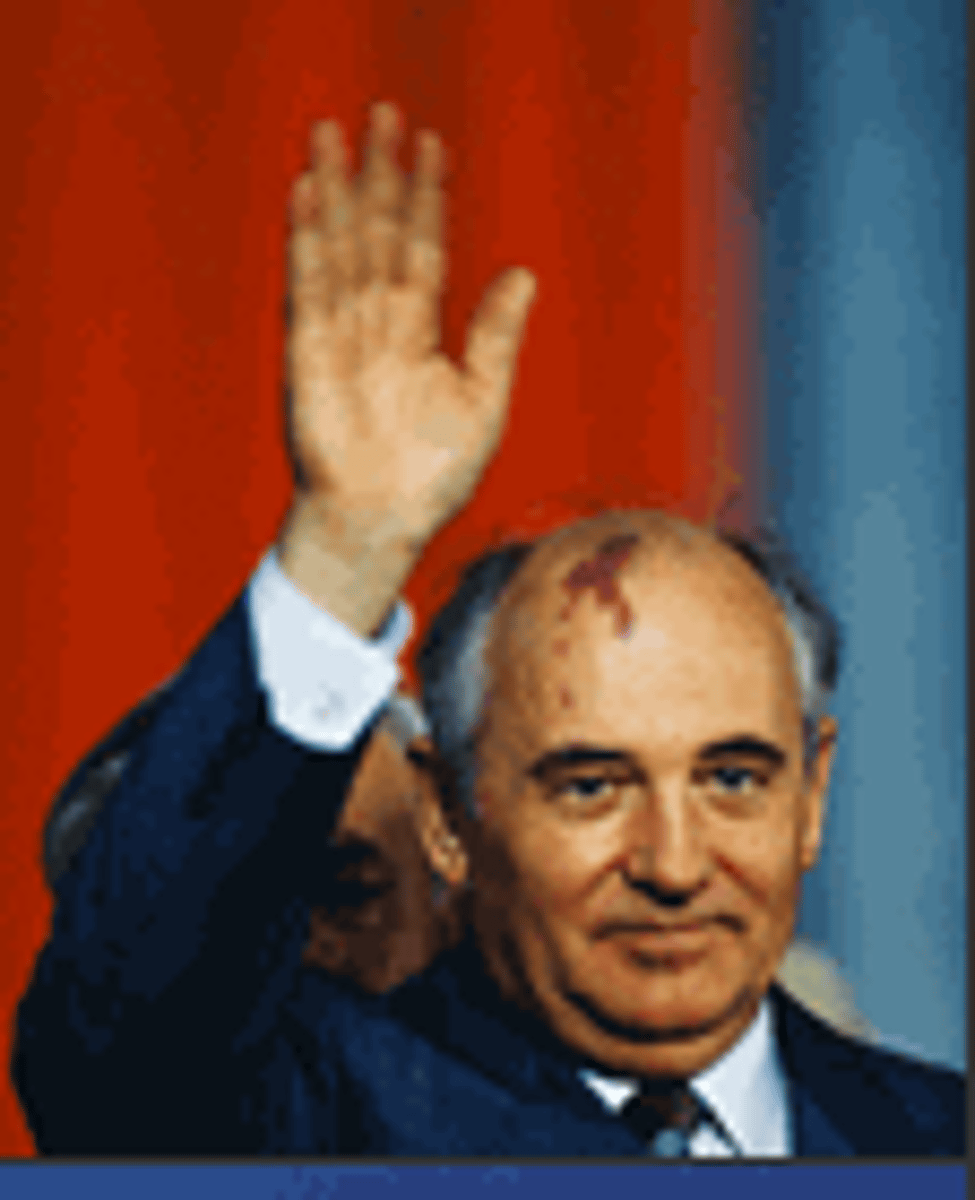
Mikhail Gorbachev
General Party Secretary and Leader of the Soviet Union in 1985. His reforms led to the breakup of the Soviet Union and eventually the end to Communist Russia.

Glasnost
Means openness.
Reform under Mikhail Gorbachev to create more freedom and openness both socially and politically in the U.S.S.R.

Solidarity Movement
Movement in Poland in response to Soviet Communist control and Gorbachev's reforms.

In 1947, India gained its independence from what country?
Britain
What 3 countries were formed when India was partitioned?
West Pakistan, East Pakistan, and India
What religious/ethnic group was to live in West and East Pakistan?
Muslims
What religious/ethnic group was to live in India?
Hindus
Today, West Pakistan is the nation of ...
Pakistan
Today, East Pakistan is the nation of ...
Bangladesh
Who used civil disobedience and passive resistance to lead the Indian independence movement?
Mohandas Gandhi
The right of a nation to choose its own type of government without outside influence?
Self-determination
As African nations became independent following WWII, they came under the control of what two superpower countries?
USSR and US
Following WWII, the mandates were granted their independence. What new nation-state was created when Palestine was partitioned?
Israel
Israel is the nation-state for what religious/ethnic group?
Jews (Judaism)
This Jewish grandmother became Prime Minister of Israel. She led Israel to increase its land holdings through war.
Golda Meir
Which group of people have been displaced by the expansion of Israel?
Palestinians
Israel declares itself independent in ...
1948
Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO)
An organization founded in 1974 that declared Israel "illegal, null, and void"
Dropping of the atomic bomb
US drops two atomic bombs on Japan, one in Hiroshima, and the other was Nagasaki. Both devastated the cities, killing thousands and forcing Japanese surrender
Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
A 1949 defense alliance initiated by the US, Canada, and 10 Western European nations
U2 Incident
the downing of a U.S. spy plane and capture of its pilot by the Soviet Union in 1960
Sputnik (1957)
First man-made satellite put into orbit by the USSR. This caused fear in the US that the Soviets had passed them by in science & technology and the arms race.
War in Bosnia
Serbs attacked Bosnia in 1992 and took over 70% of their territory; Serbs conducted ethnic cleansing against Muslim Bosnians-killing 250,000.
SALT I
Treaty signed in 1972 between the U.S. and the USSR. This agreement limited the number of missiles in each nation and led to the SALT II discussions and a slowdown of the arms race between the two countries.
Chinese Communist Revolution
A political revolution in China led by Mao Zedong. After several years of fighting the Kuomintang, the communists won control of the country in 1949.
Star Wars (SDI)
Reagan's defensive program; laser beams and satellites would shoot down USSR missiles
Khemer Rouge
Ruled in Cambodia. Unleashed a genocide of anyone who had ties to previous Cambodian governments. Killed over 2 million Cambodians in labor camps.
Irainian hostage crisis
a diplomatic standoff between the United States and Iran that lasted for 444 days before hostages were released.
Creation of Israel (1948)
Was founded as a response to the Holocaust in addition to the Diaspora of the Jewish people. The U.N. divided the land between Palestinians and the Jewish people with Jerusalem as an international city.