Hypothesis Testing
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
When do you know that you need to use one tailed hypothesis testing?
if the alternative hypothesis is H1: p> … or H1: p<…
When do you know that you need to use two tailed hypothesis testing?
if the alternative hypothesis is H1: p≠0
(i.e. if something is different or not the probability from before)
I throw a coin 10 times. For what number of heads might you conclude that the coin is biased towards heads? Why?

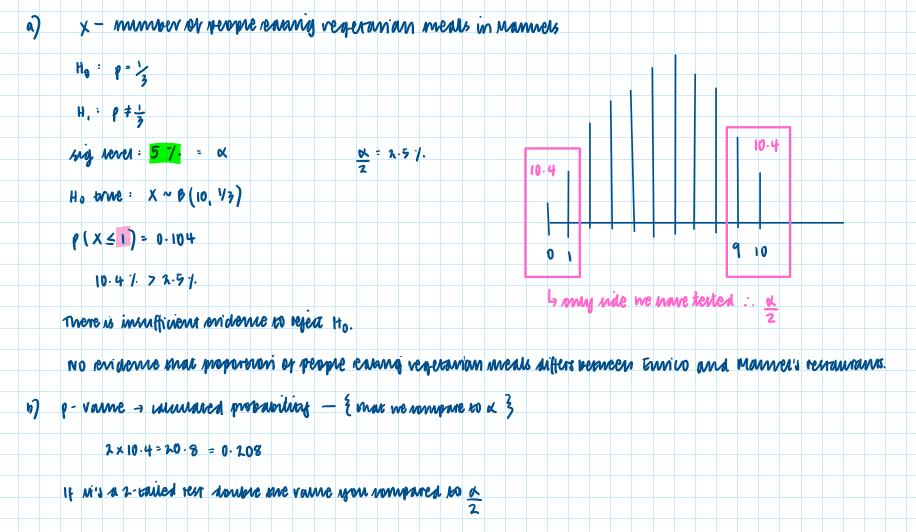
Over a long period of time it has been found that in Enrico’s restaurant the ratio of non-vegetarian to vegetarian meals is 2 to 1. In Manuel’s restaurant in a random sample of 10 people ordering meals, 1 ordered a vegetarian meal.
a) using 5% significance level, test whether or not the proportion of people eating vegetarian meals in Manuel’s restaurant is different to that in Enrico’s restaurant.
b) State the p-value of this test.
Remember, sometimes you need to find the expected value. This is found by multiplying the sample size by the probability (E(X)= np). If the observation is larger, then use X>or equal to that. If the observation is smaller, then use X<or equal to that.
Critical Regions: What is a tip to find the upper region?
first find the probability that exceeds (1-sign level)
then add one onto the x-value
also remember to halve the significance value
How can you calculate the actual significance level?
the actual probability that the observation falls in the critical regions (remember that when it is a two tailed test you have to add the two together)
