Thalamus Definitions & Terms: Biology Study Guide
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
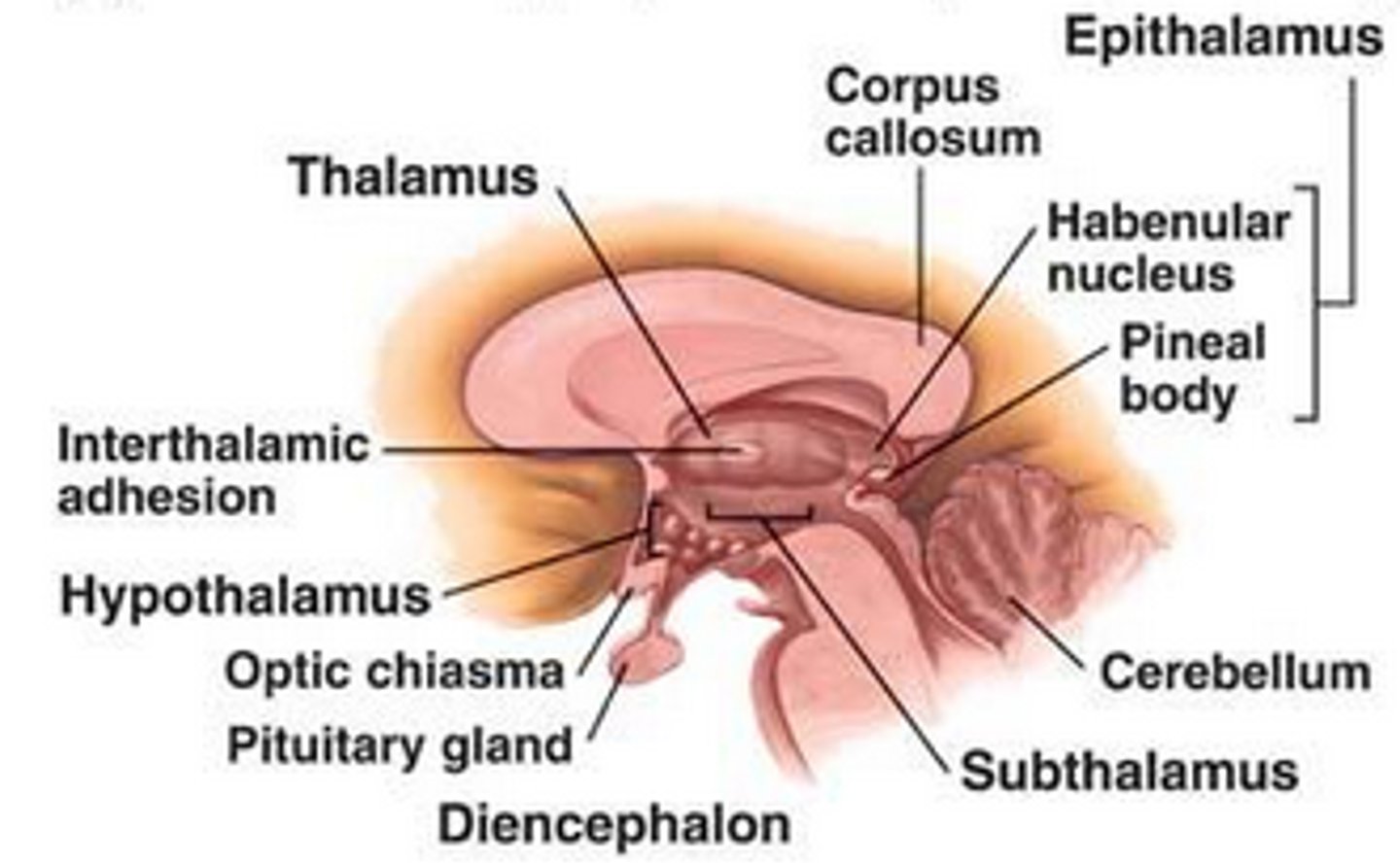
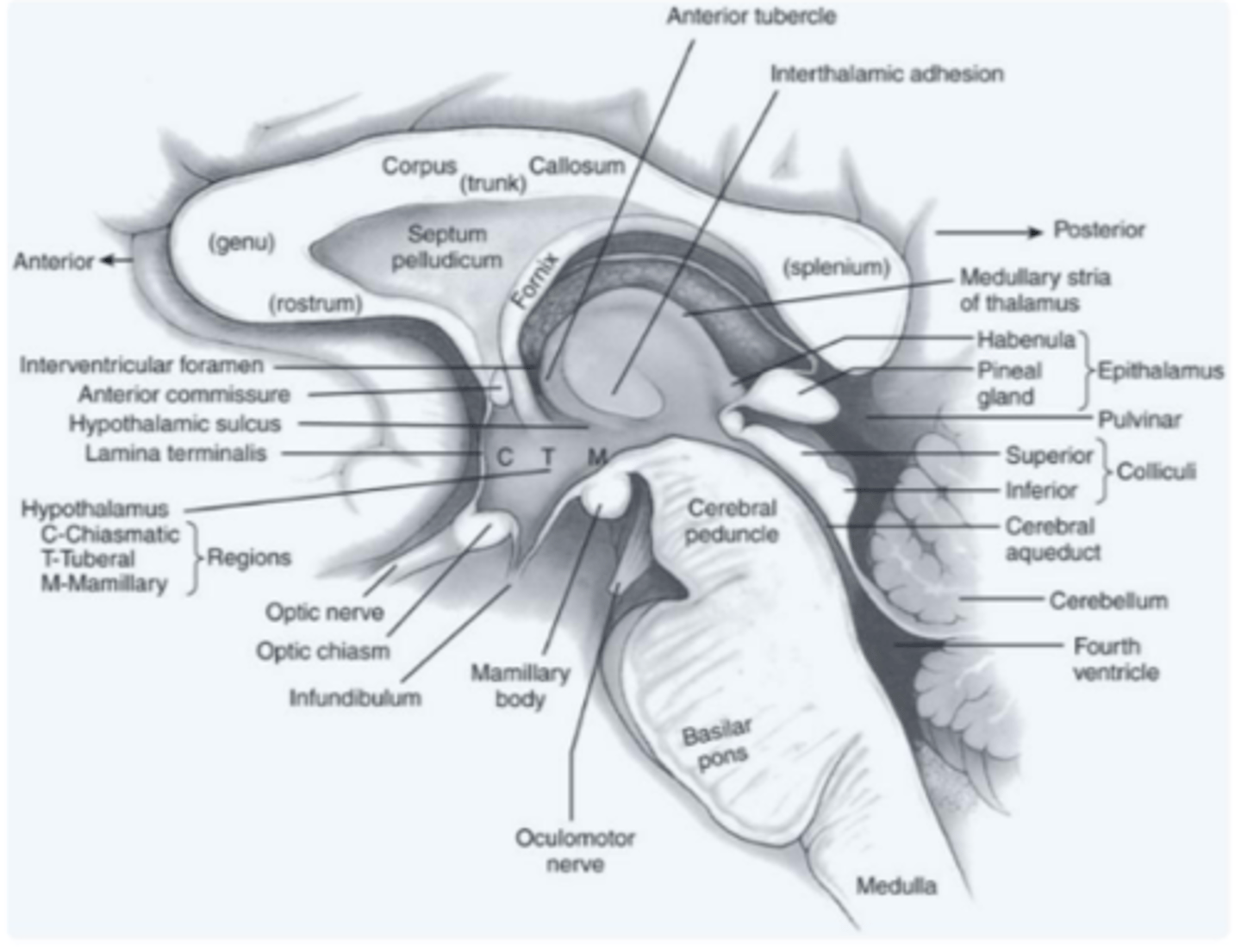
components of the diencephalon
includes the epithalamus, subthalamus, hypothalamus and thalamus
function of the diencephalon
receives/disperses widespread sensory, motor and limbic connections
What does the epithalamus contain?
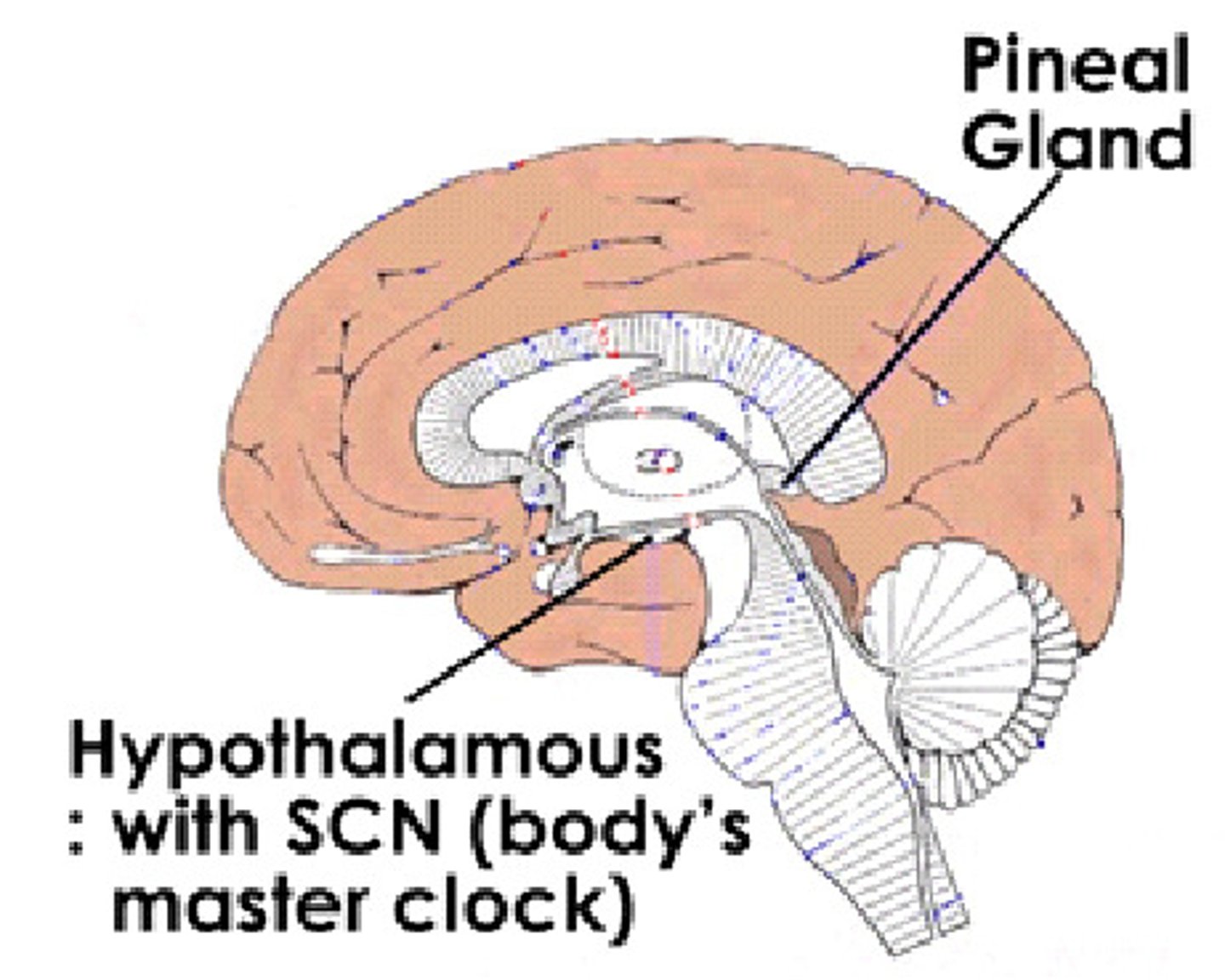
region of the diencephalon that contains the habenula and the pineal gland
pineal gland
endocrine gland found in the epithalamus that is associated with seasonal (reproductive) cycles and secreting melatonin
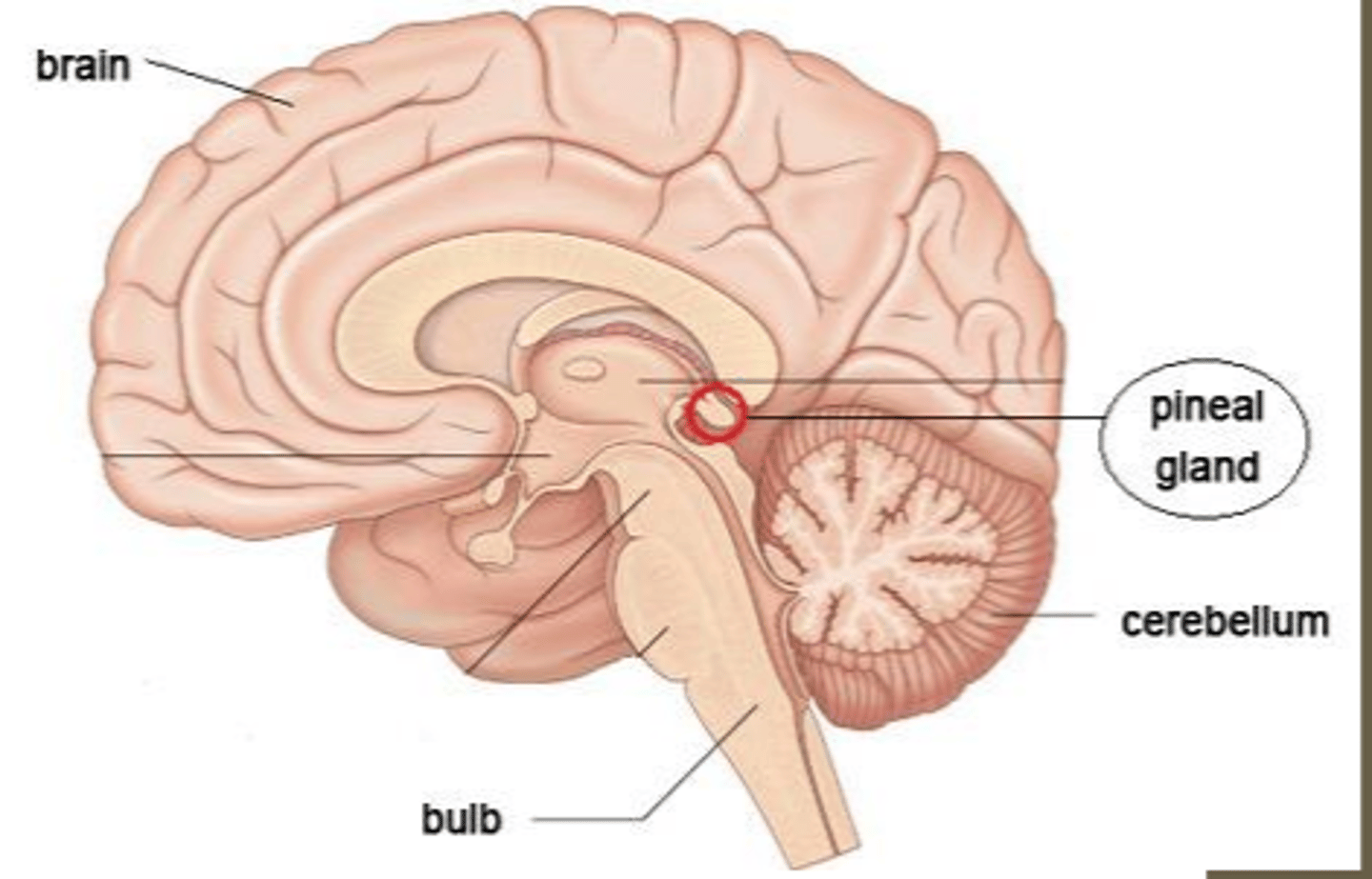
when does the pineal gland secrete melatonin
at relatively high rates during darkness
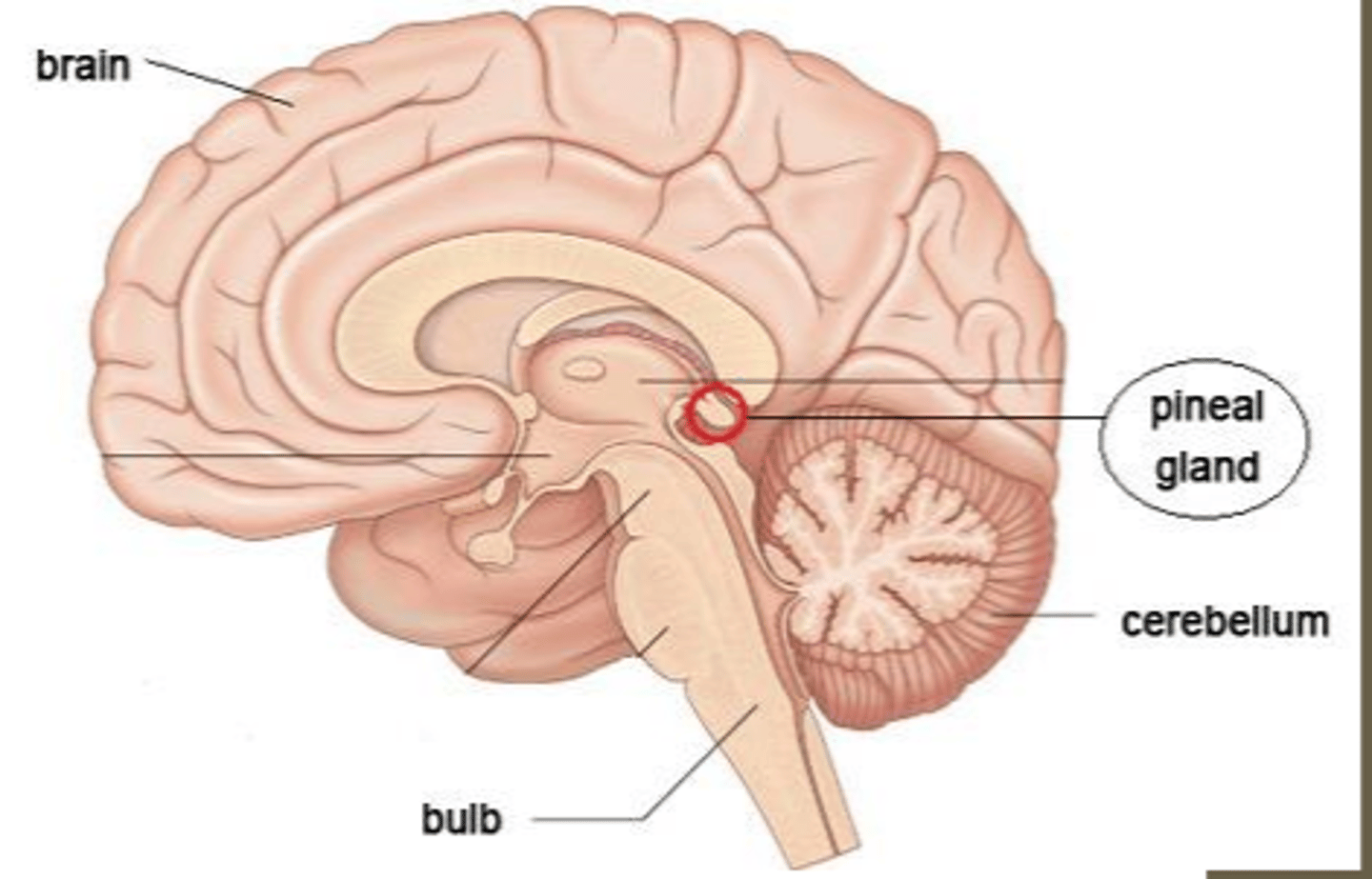
function of melatonin
important in the regulation of the circadian rhythm, including sleep-wake cycles
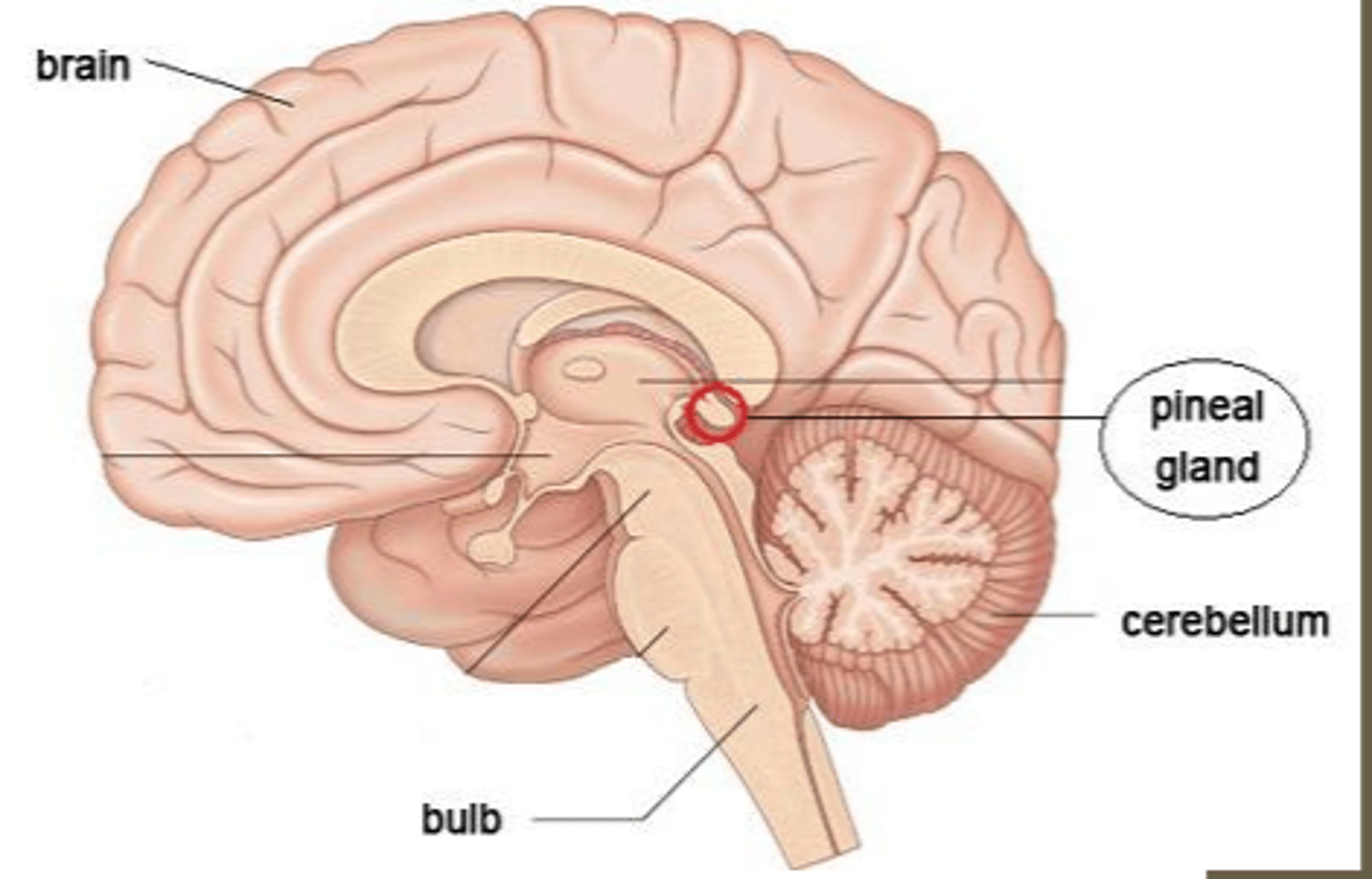
What do pineal tumors cause?
pineal tumors can result in compression of the midbrain, sexual dysfunction and abnormal regulation of circadian rhythm
consequences of compression of the midbrain with pineal tumors
can result in hydrocephalus if the cerebral aqueduct is occluded and it can impact the eye
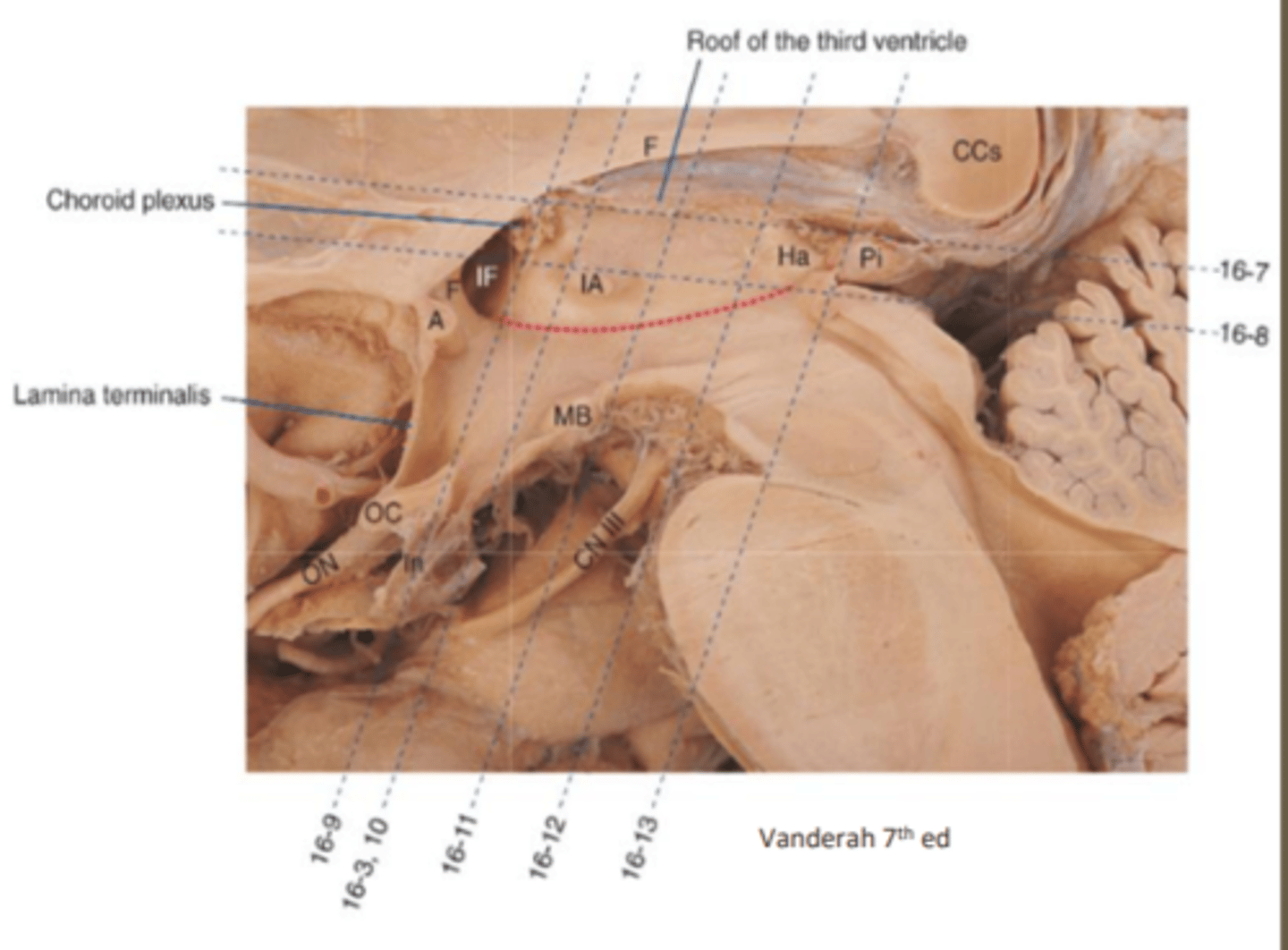
how can pineal tumors impact the eye?
compression of the midbrain can impair both CN III, IV, and VI because they are found at the Midbrain as well as the colliculi/pretectal area which can result in various deficits in eye movements and pupillary reactions
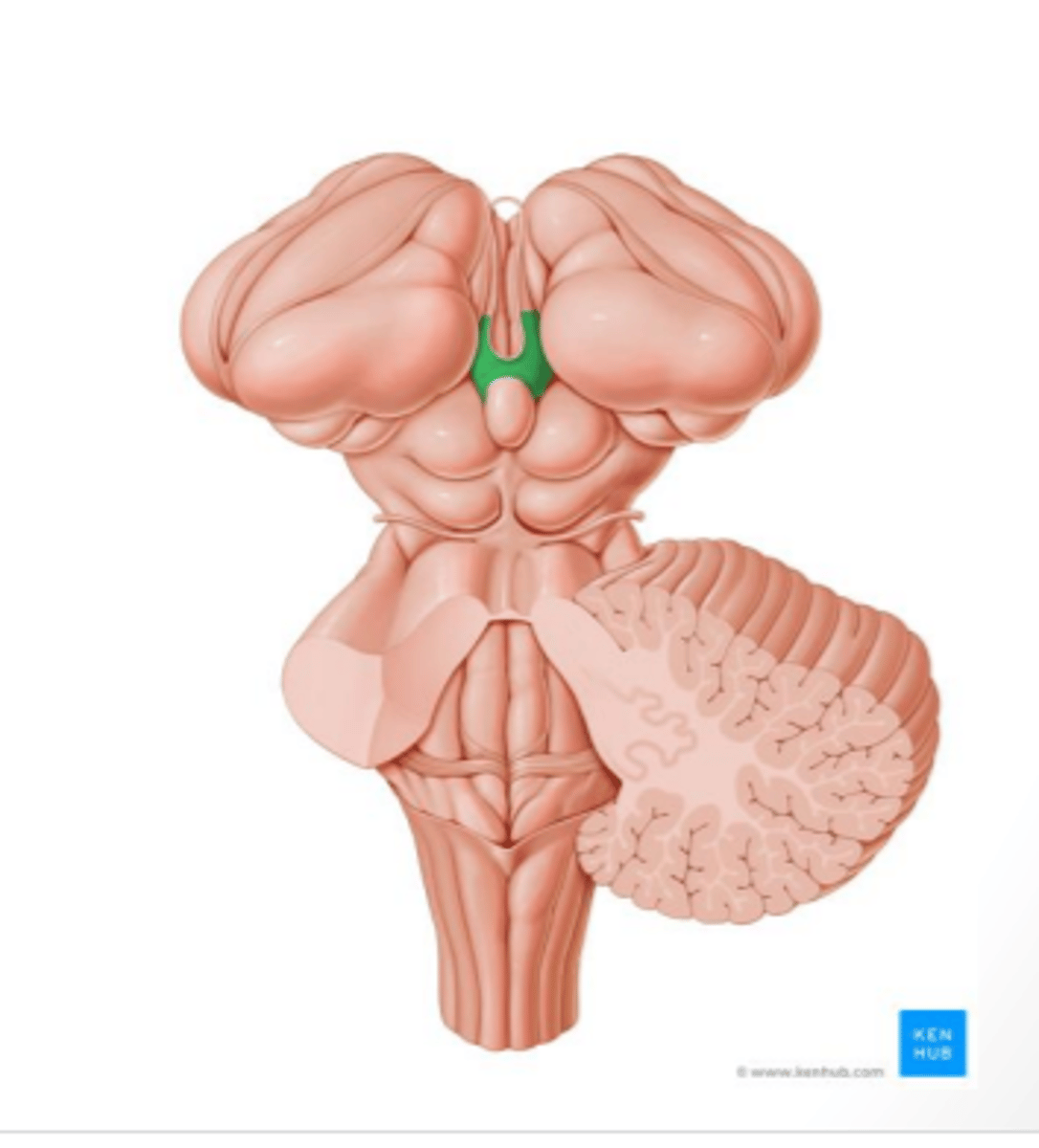
habenular nuclei
component of the epithalamus that is located rostrally to and on each side of the pineal gland that functions to regulate the release of biogenic amines (neurotransmitters) from the reticular formation
-plays a large role in assigning "reward value" to stimuli
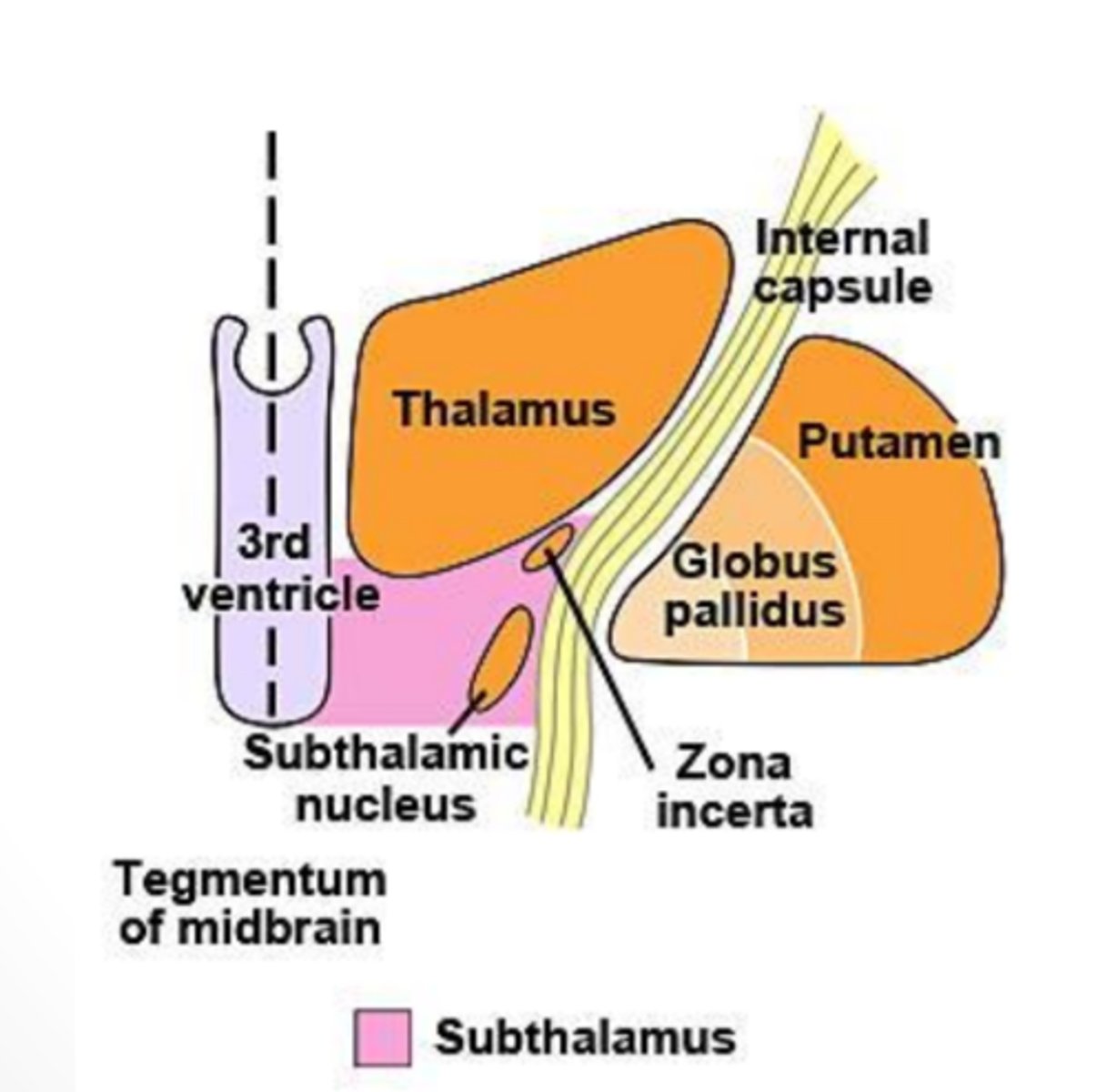
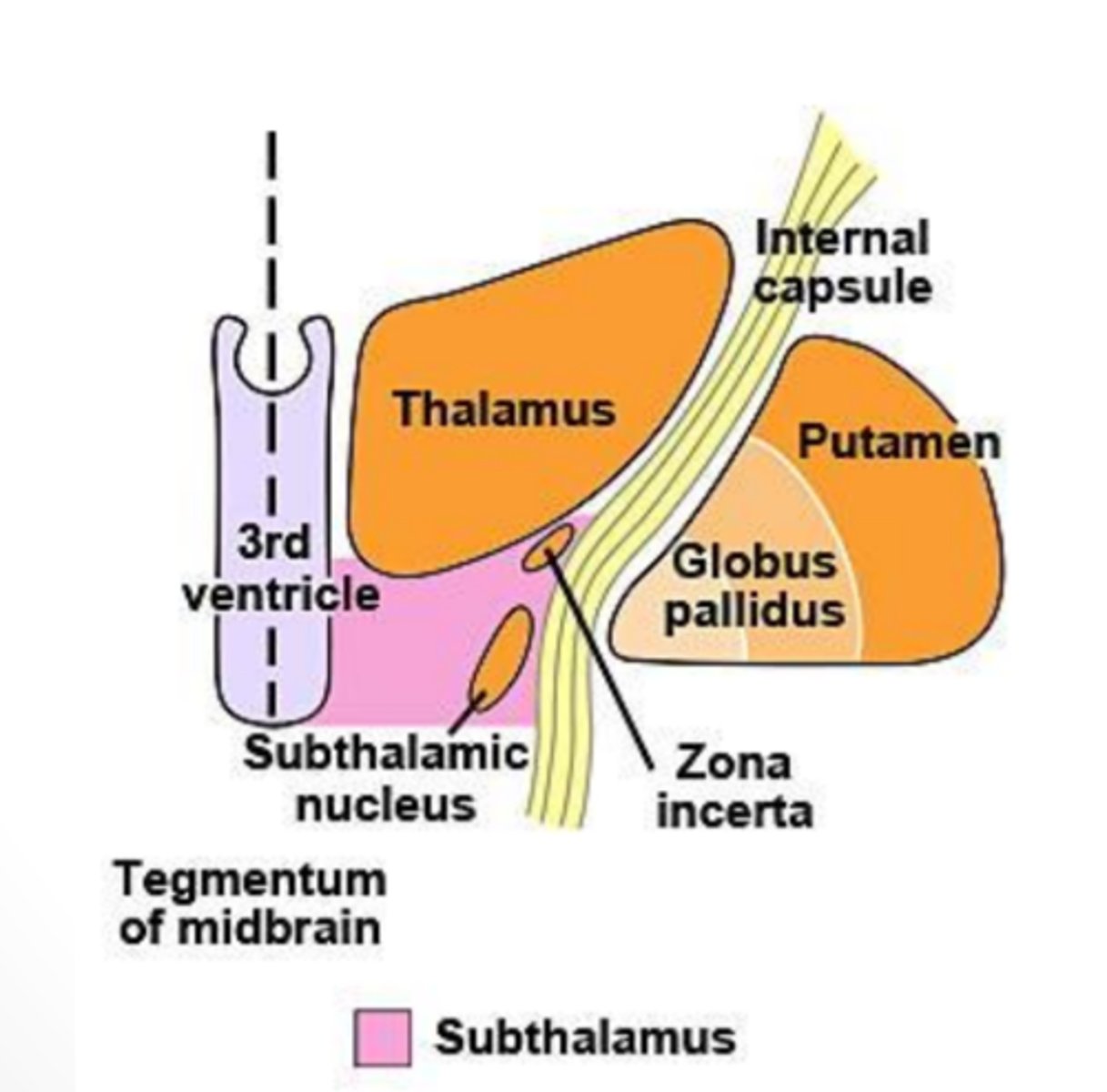
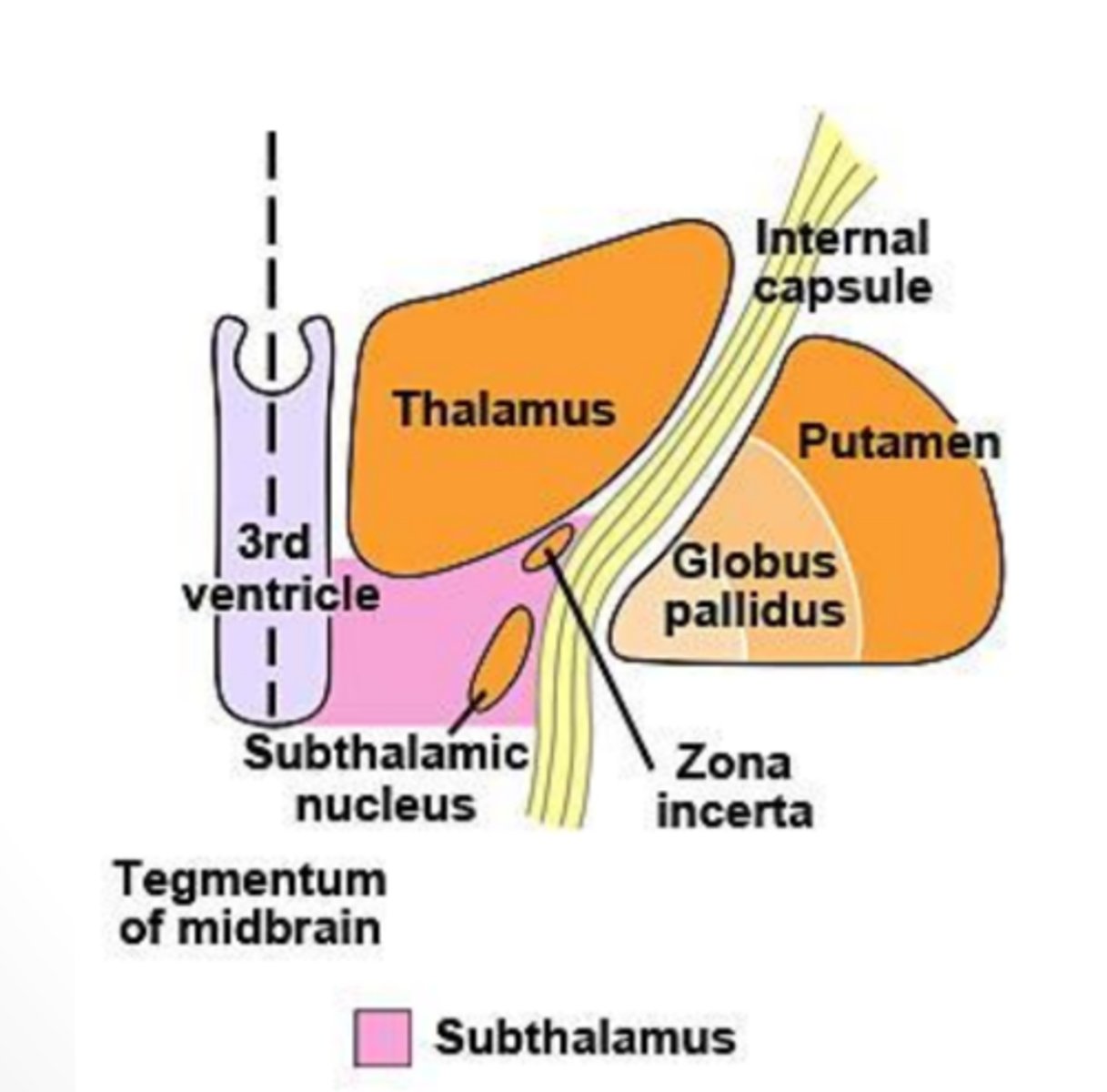
What does the subthalamus contain?
region of the diencephalon that consists of both the subthalamic nucleus and the zona incerta
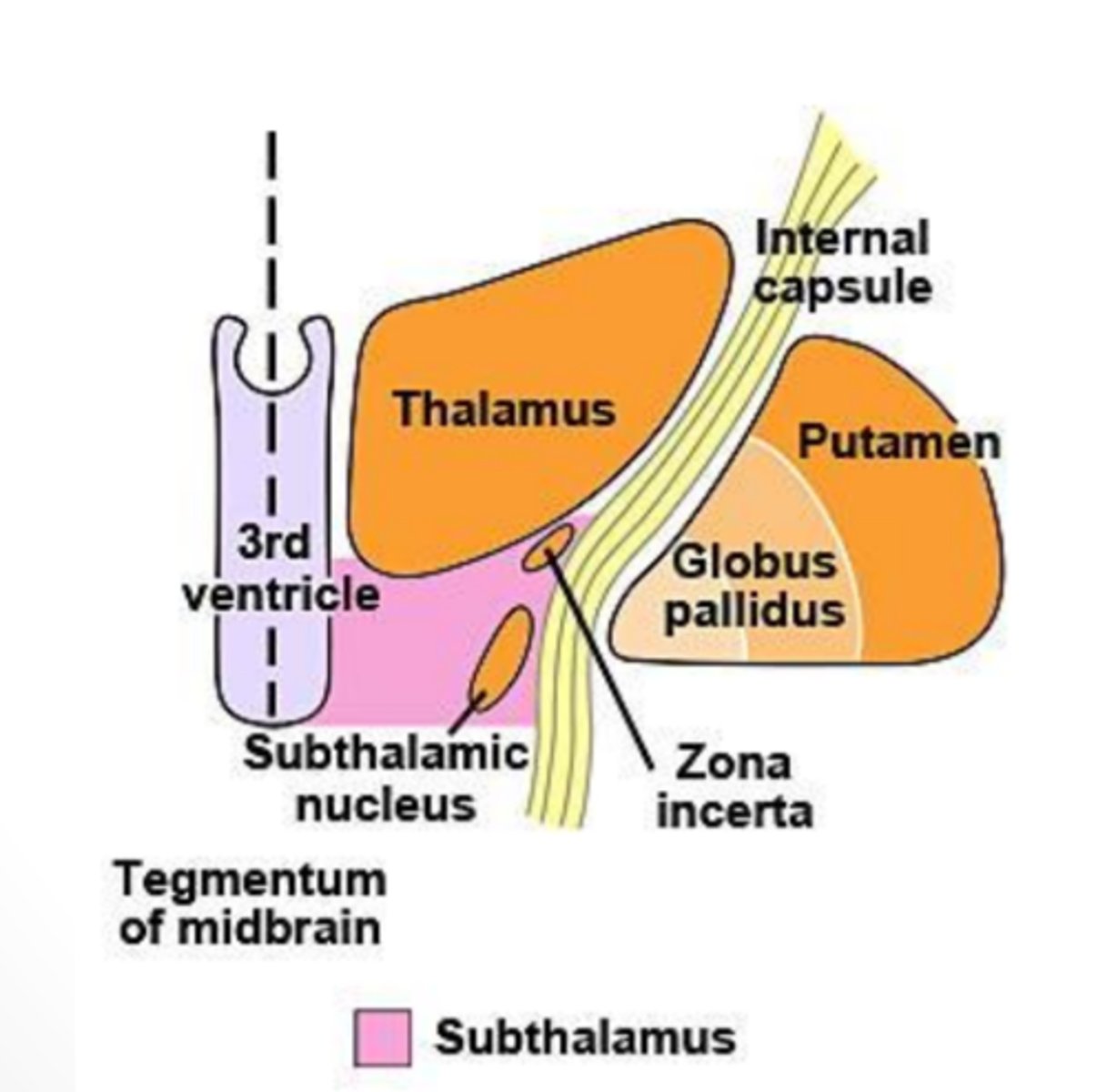
subthalamic nucleus
lens-shaped, bioconvex structure interconnected with basal nuclei that is important in movement
-component of the diencephalon
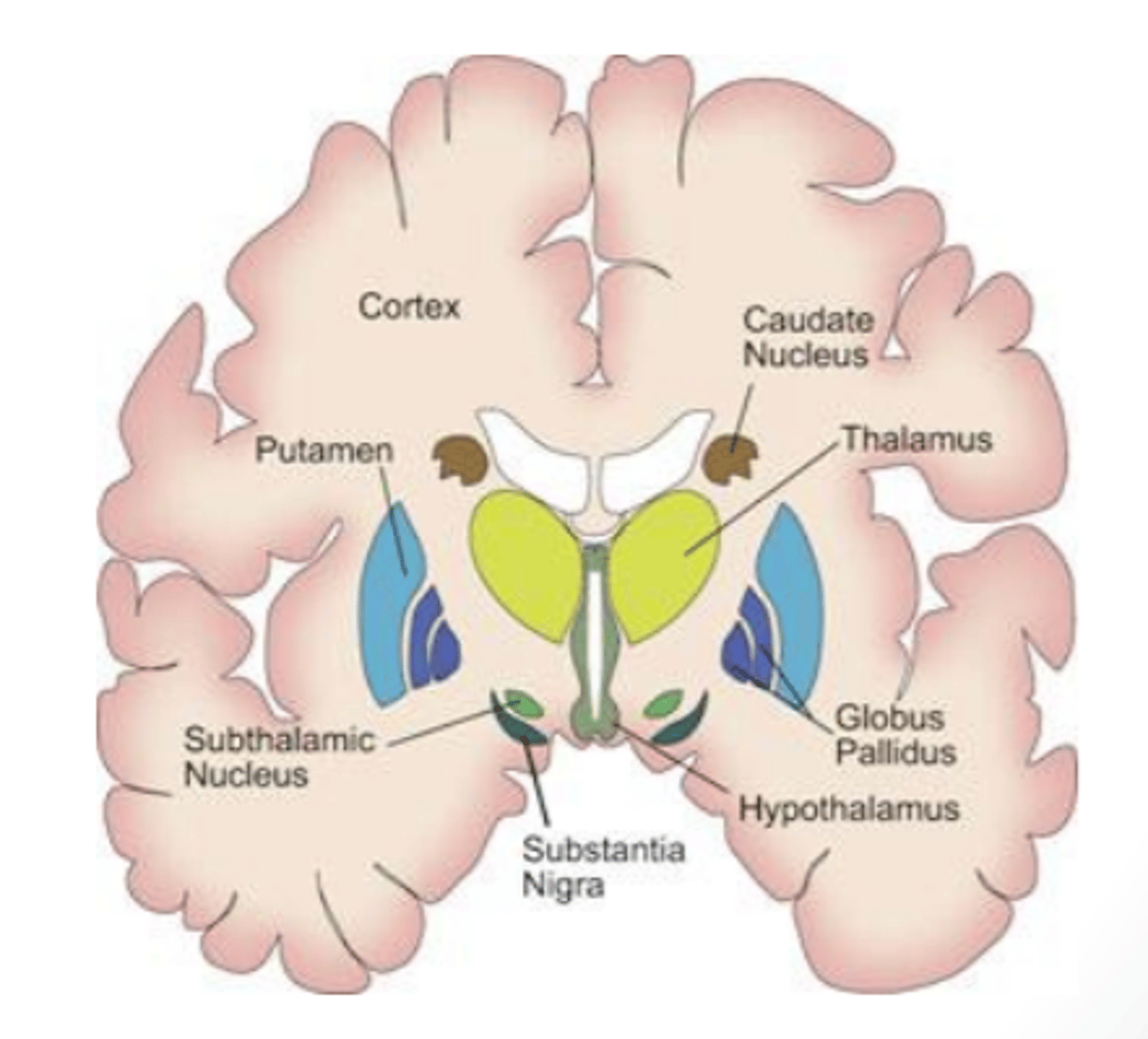
zona incerta
small mass of gray matter found between the subthalamic nucleus and the thalamus that projects widespread connections and receives collateral branches from almost all fibers going to the thalamus
what region of the subthalamus sends direct projections to the cerebral cortex?
the zona incerta
function of the zona incerta
it is largely unknown besides sending/receiving projections
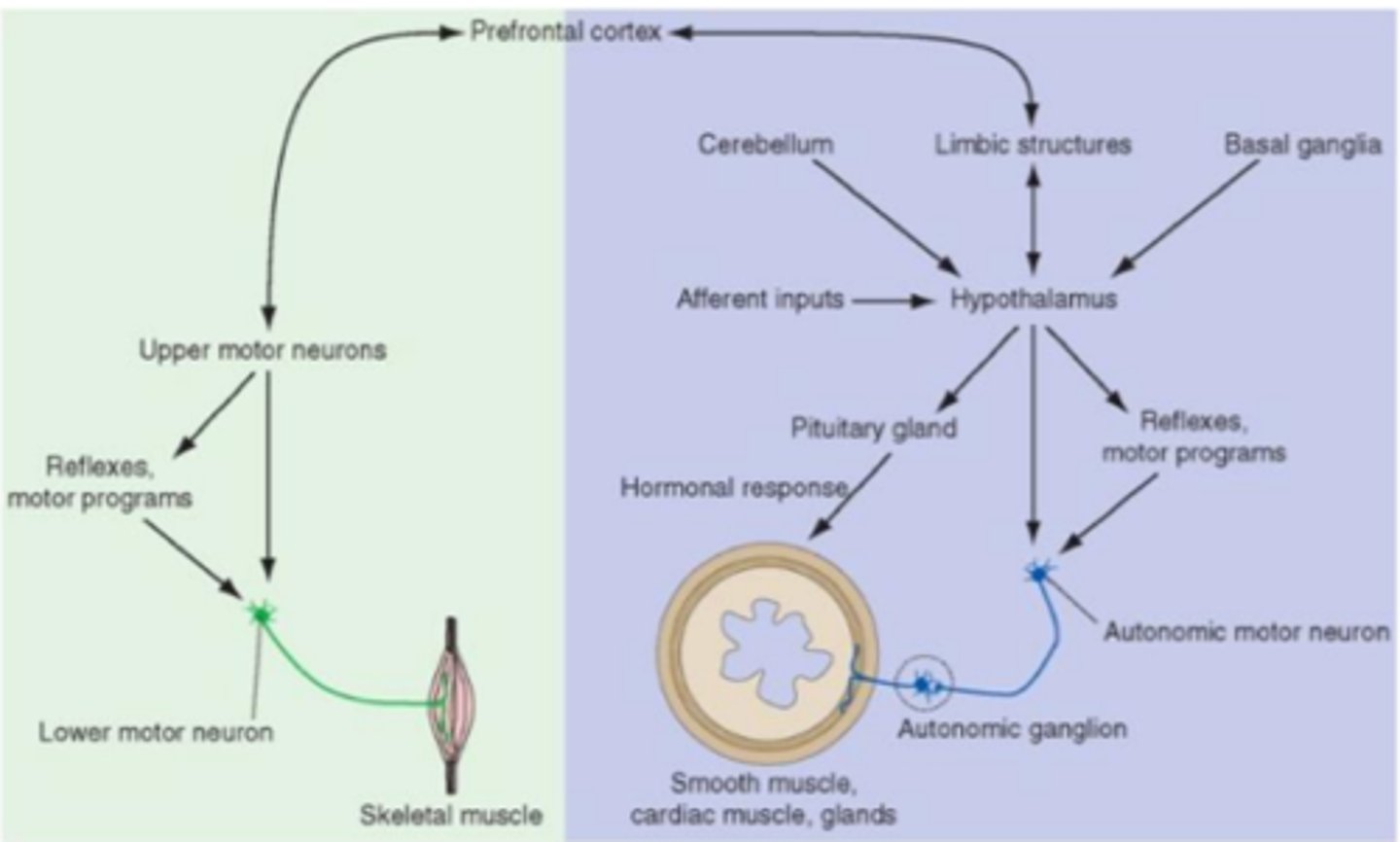
function of the hypothalamus
functions to maintain our internal environment in a physiological range (homeostasis) as well as act as a nodal point in pathways concerned with autonomic, endocrine, emotional and somatic functions
divisions of the hypothalamus
it is divided into a number of nuclei and areas that each have distinctive connections
-further subdivided in longitudinal and medial-lateral directions
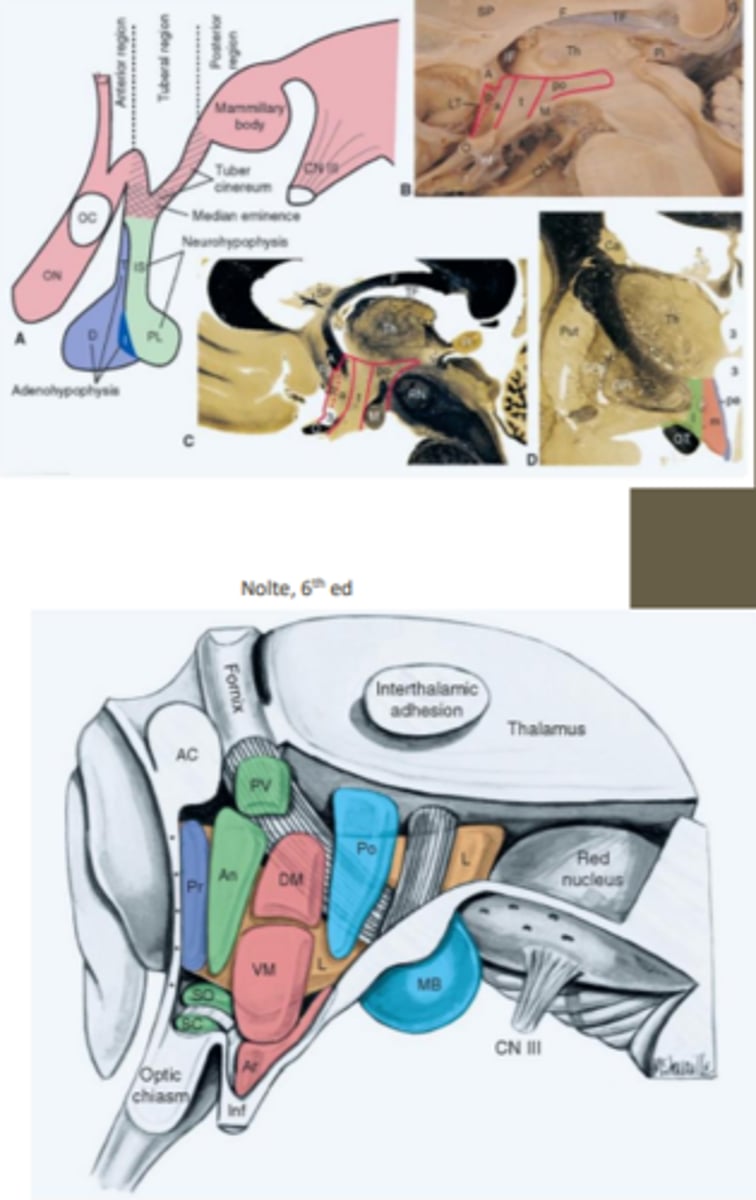
longitudinal subdivisions of the hypothalamic nuclei
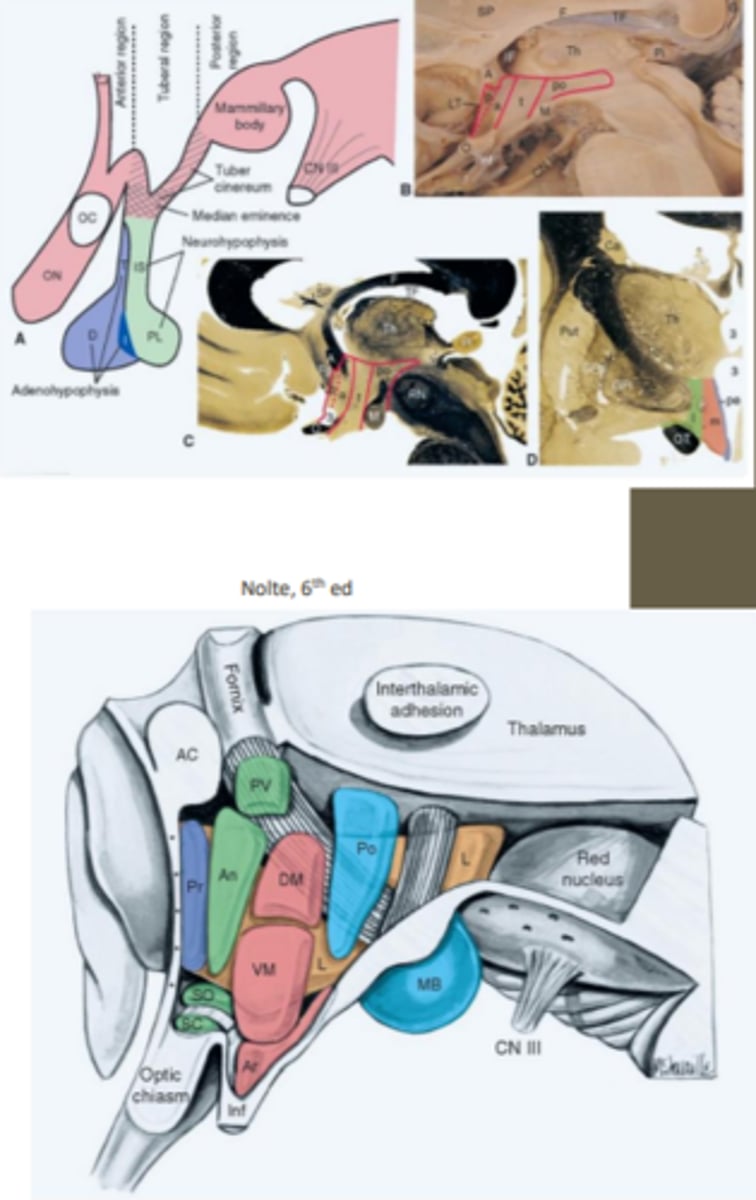
consists of anterior, tuberal and posterior regions
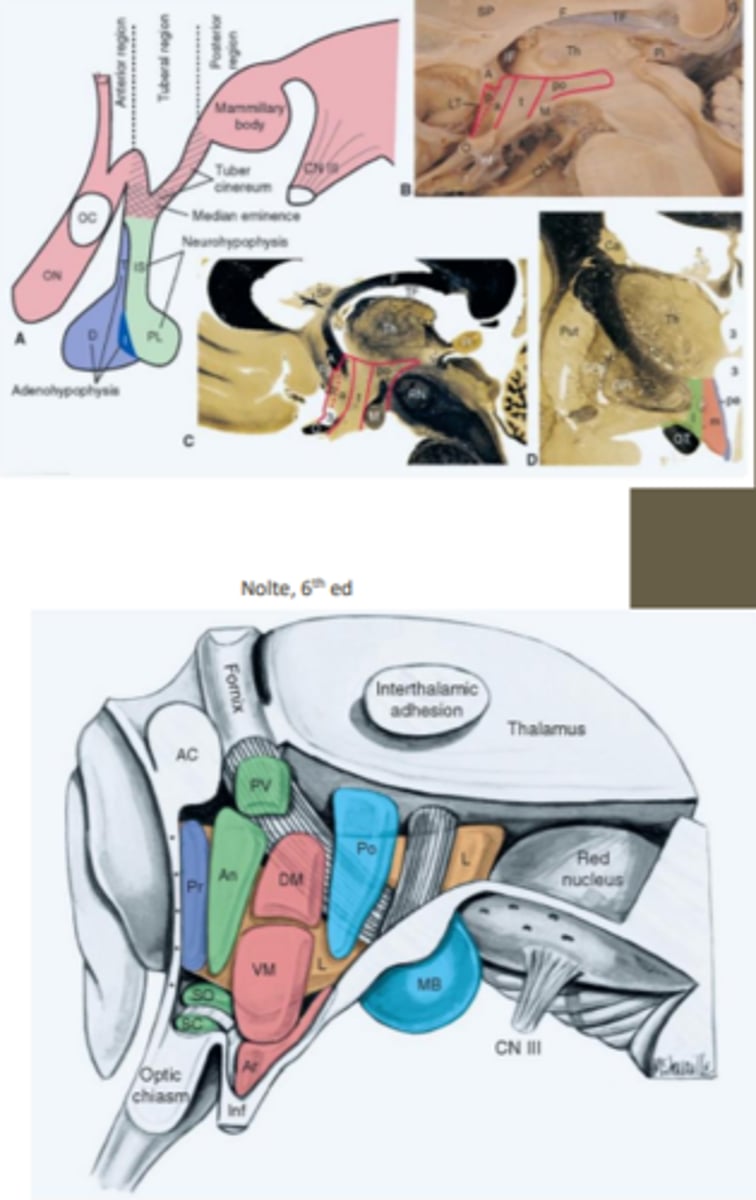
medial-lateral subdivisions of the hypothalamic nuclei
consists of periventricular, medial and lateral divisions/zones
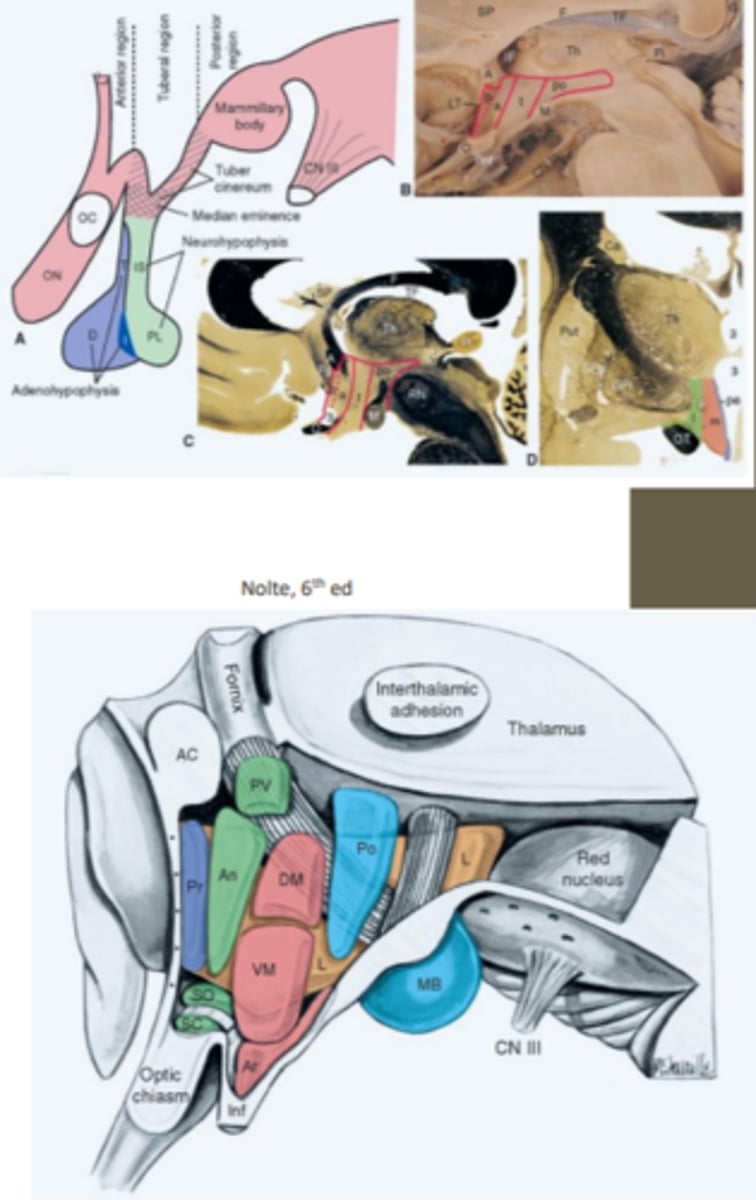
periventricular zone
region of the hypothalamic medial-lateral subdivision that contains a number of nuclei including the superchiasmatic nucleus
superchiasmatic nucleus
functions as a "master clock" for circadian rhythms as it contains lots of receptors for melatonin as well as connects with the retina
what structure is often disturbed when the hypothalamus is damaged
CN II due to the "closeness" of the hypothalamus to the optic chiasm
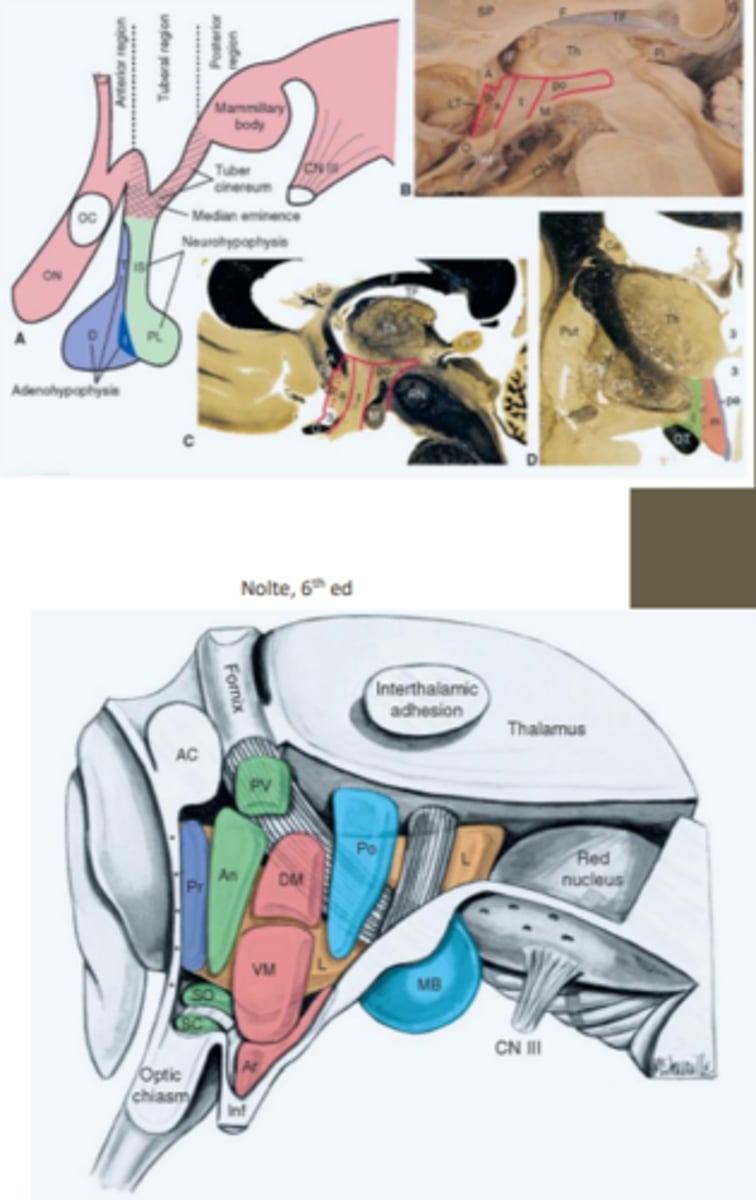
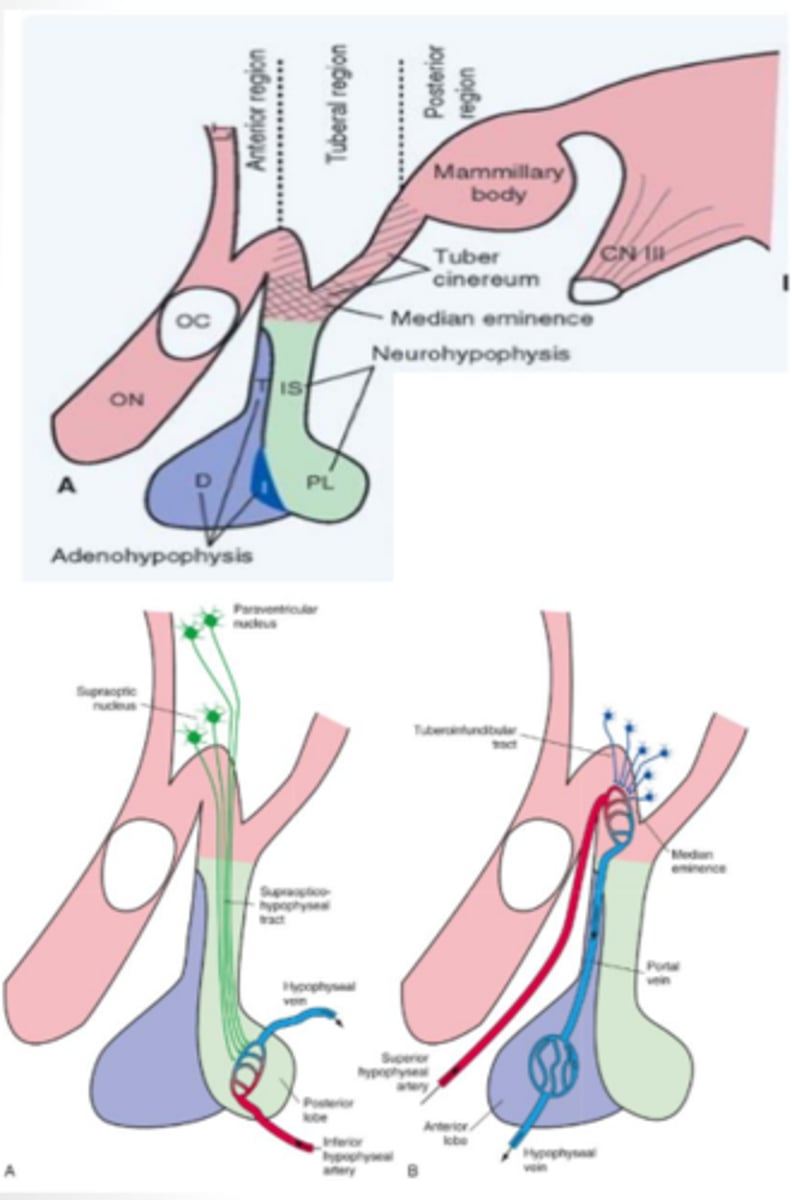
pituitary gland
pea sized gland attached and controlled by the hypothalamus that has separate control systems for each of its two (anterior/posterior) lobes
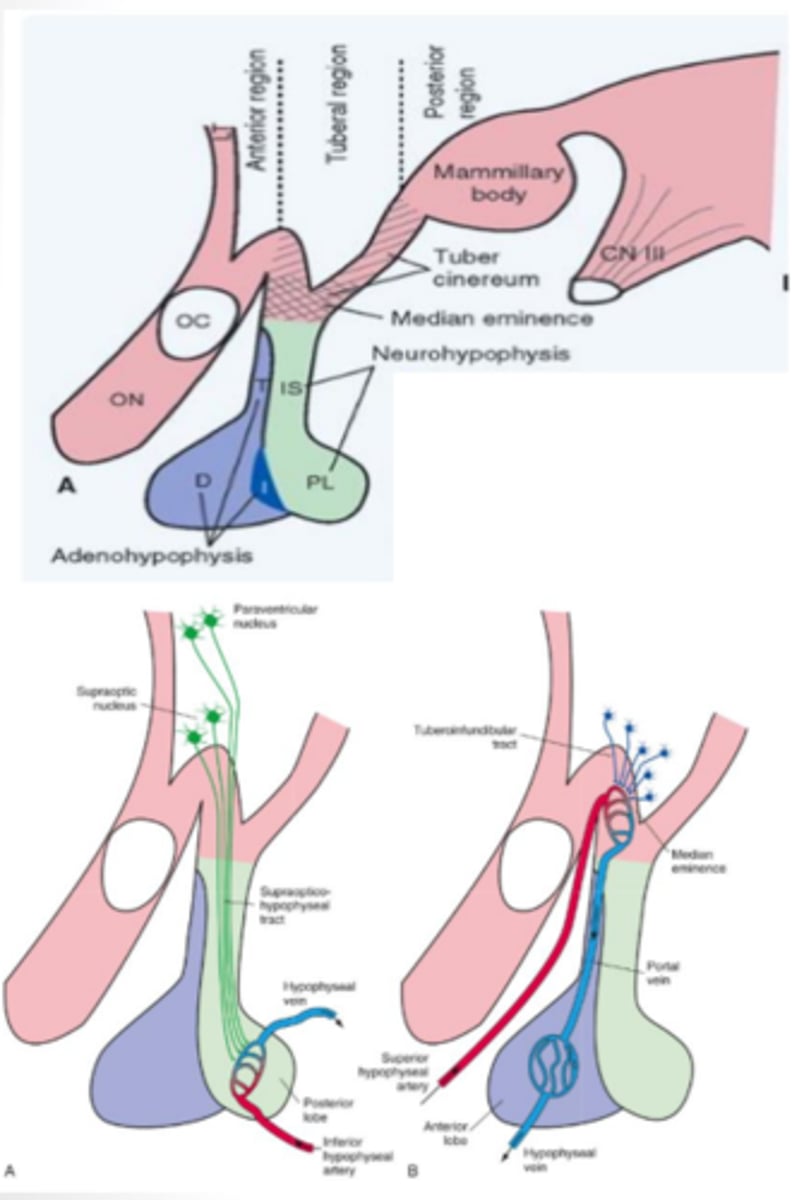
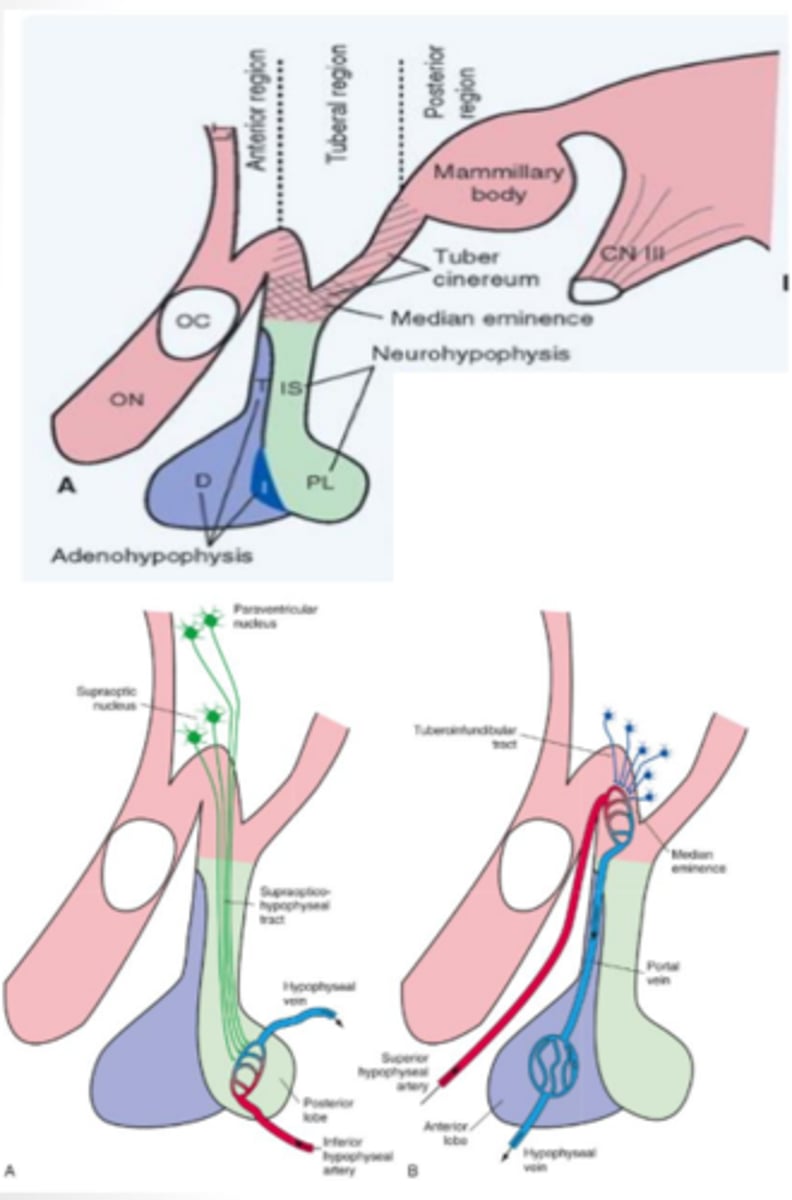
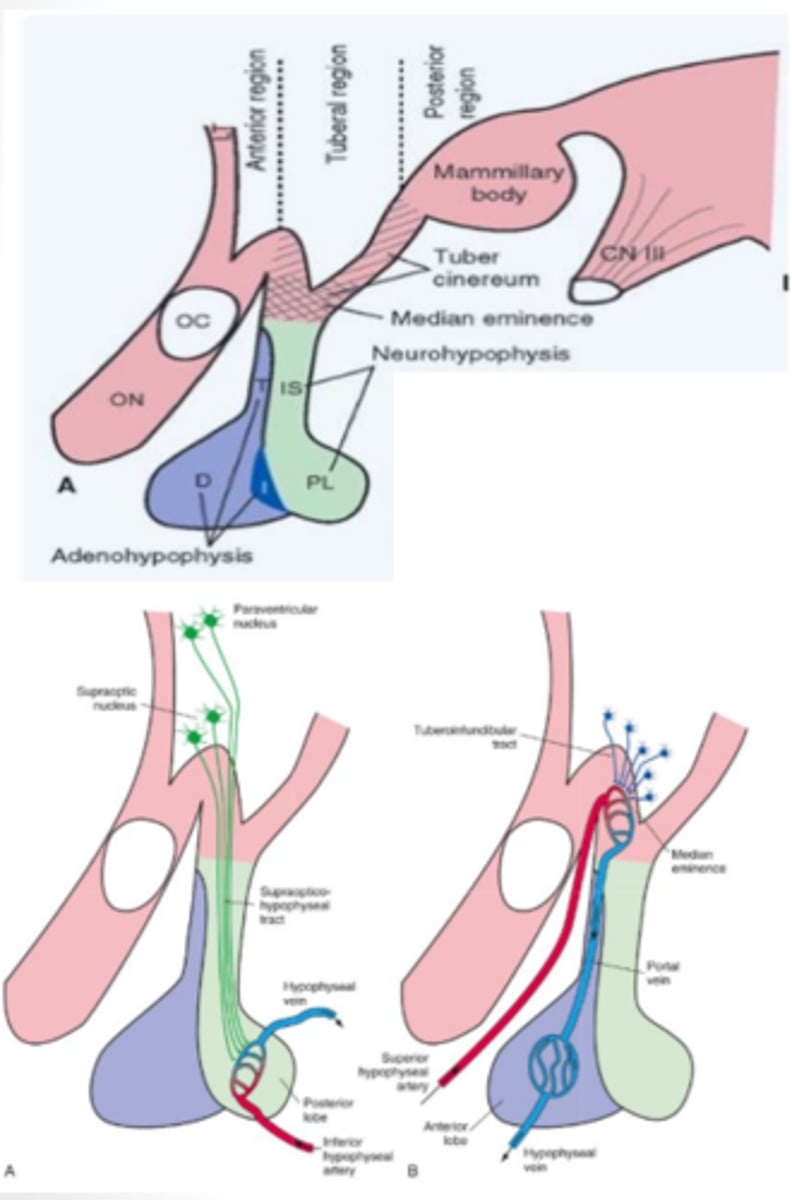
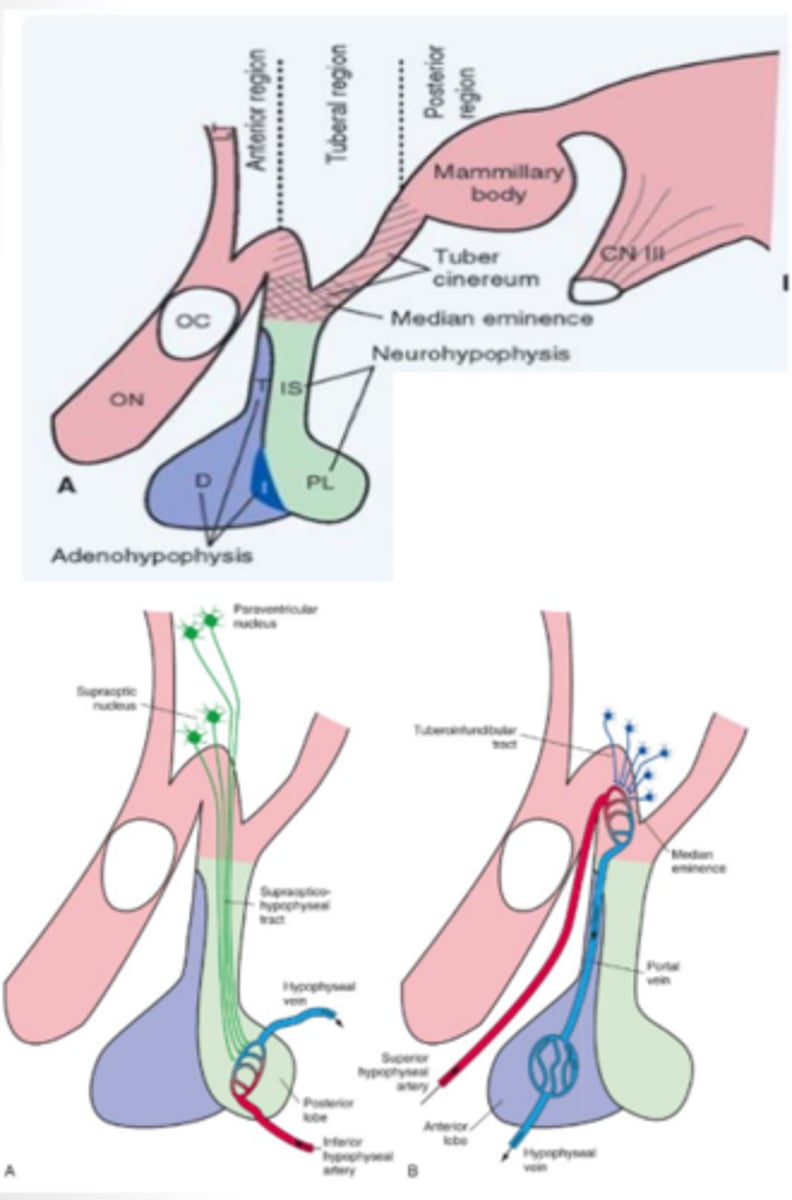
What does the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) of the pituitary gland contain? What does it produce?
developed from the outgrowth of the diencephalon and contains both the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei that function to produce antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin
what is another name for the antidiuretic hormone produced in the pituitary gland?
ADH/vasopressin
Function of ADH
hormone produced in the pituitary gland that functions to increase water reabsorption in the kidney
oxytocin function
birth hormone produced in the pituitary gland that functions to contract the uterus and produce milk and smooth muscle
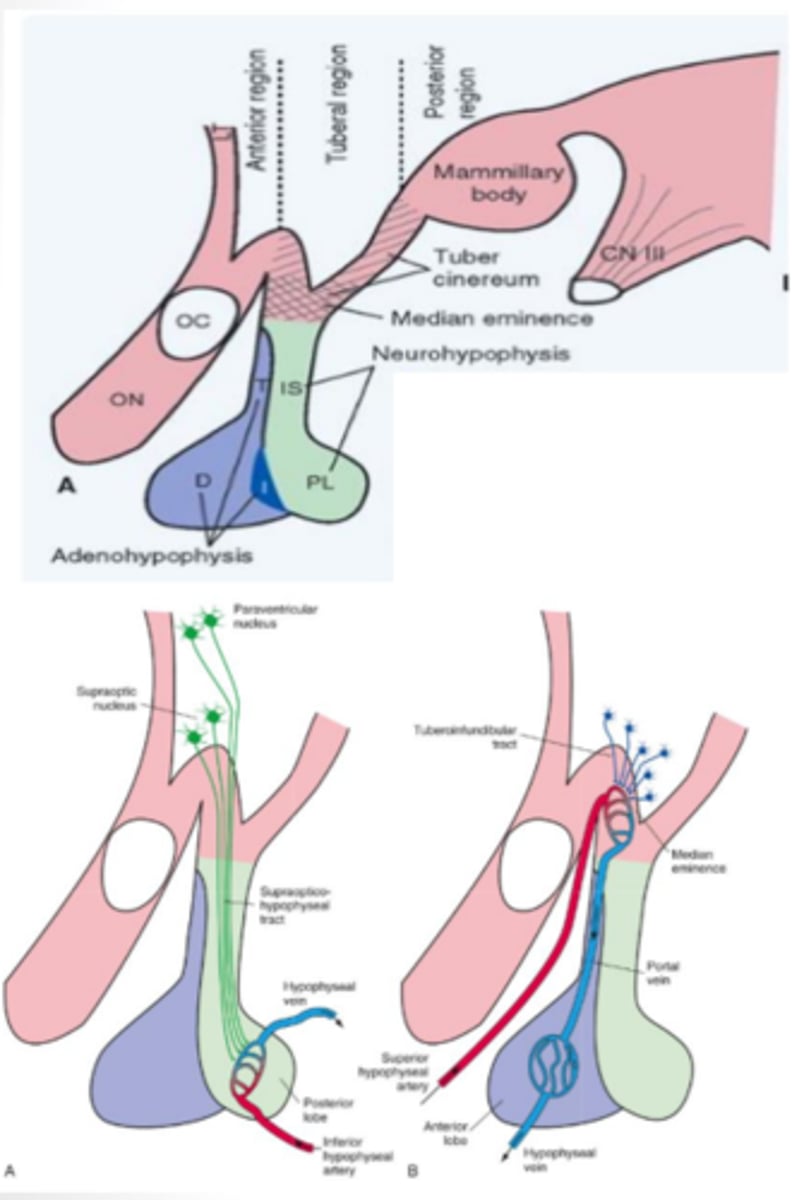
anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) of the pituitary gland function
developed from the roof of the mouth and contains vascular links that secrete a multitude of releasing/inhibiting hormones
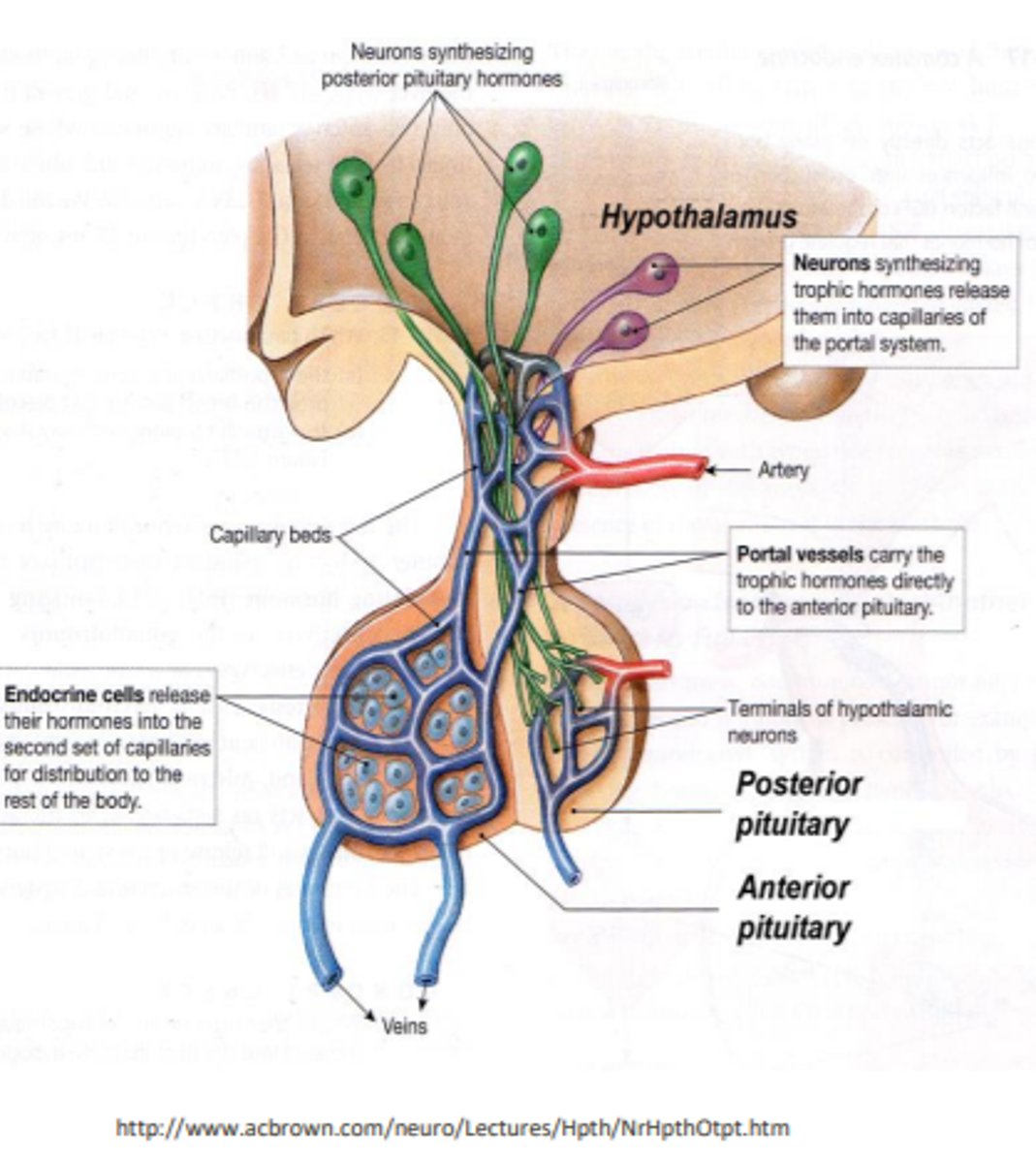
output from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
the anterior lobe secretes trophic hormones that stimulate the release of other hormones from the anterior pituitary gland
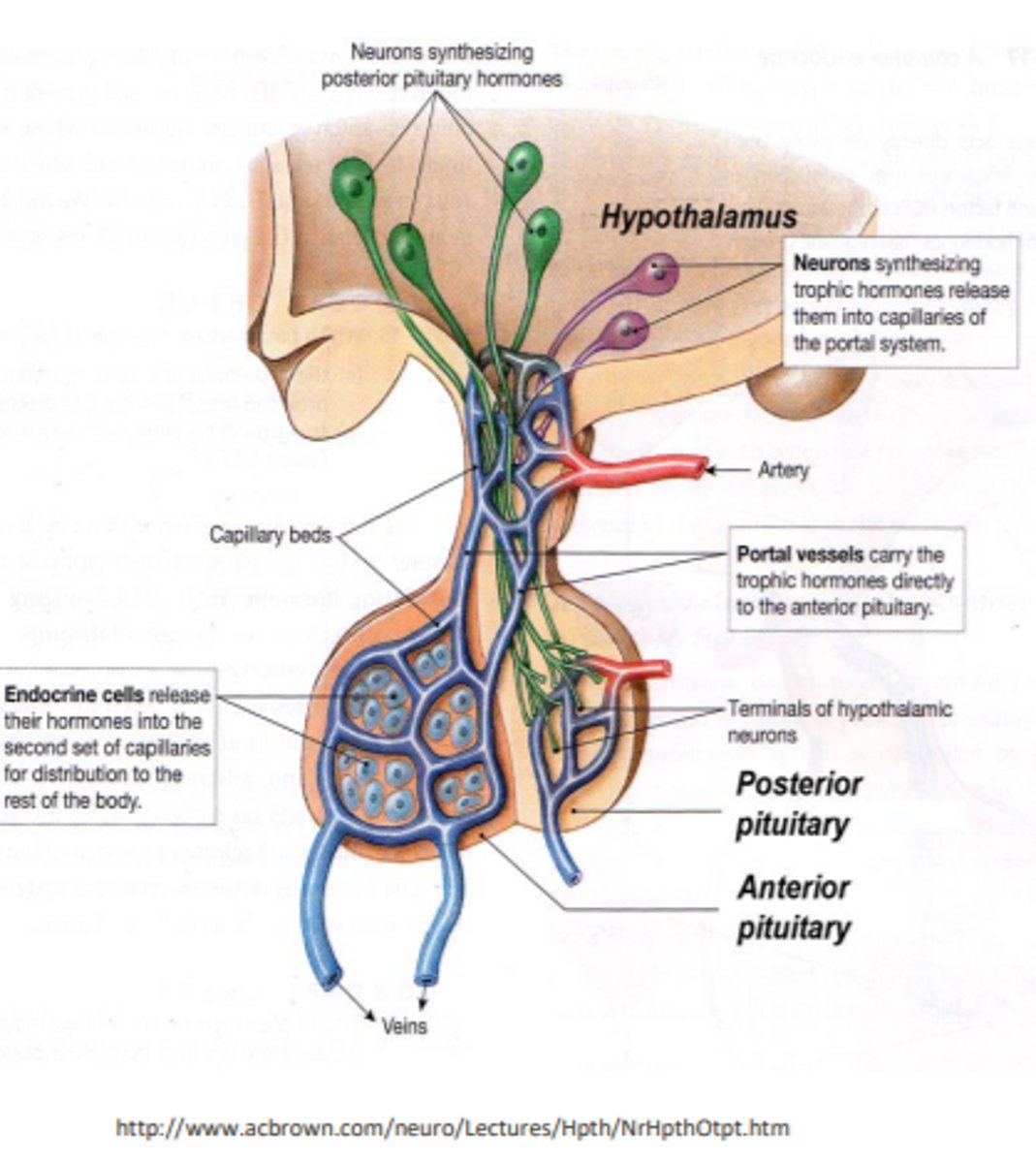
what hormones are found in the anterior pituitary gland?
growth hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, prolactin and melanocyte stimulating hormone
prolactin
milk production
melanocyte stimulating hormone
pigmentation
growth hormone
governs our height, bone length and muscle growth
adrenocorticotropic hormone
functions to stimulate the production and release of cortisol
damage to the hypothalamus may result in what disruptions
· Sleep-wake cycle
· Body temperature
· Control of body fluids (osmolarity)
· Feeding and drinking behaviors
· Gut motility
· Secretion of ADH and oxytocin
· Control of reproductive functions/sexual activity
· CV control center in brainstem
what does a hypothalamic lesion result in?
may result in hypothalamic syndrome which has numerous symptoms including diabetes insipidus, endocrine balance, temperature dysregulation, abnormal sleep, behavioral changes
thalamus function
large egg-shaped component of the diencephalon that acts as a major relay and processing center for all types of sensory and motor information
-consist of two lobes that contain 26 nuclei
what does every major structure for sensory and motor function have connections with?
the thalamus
how much of the diencephalon is composed of the thalamus?
80%
what is the only sensory pathway that does not relay to the thalamus
olfaction
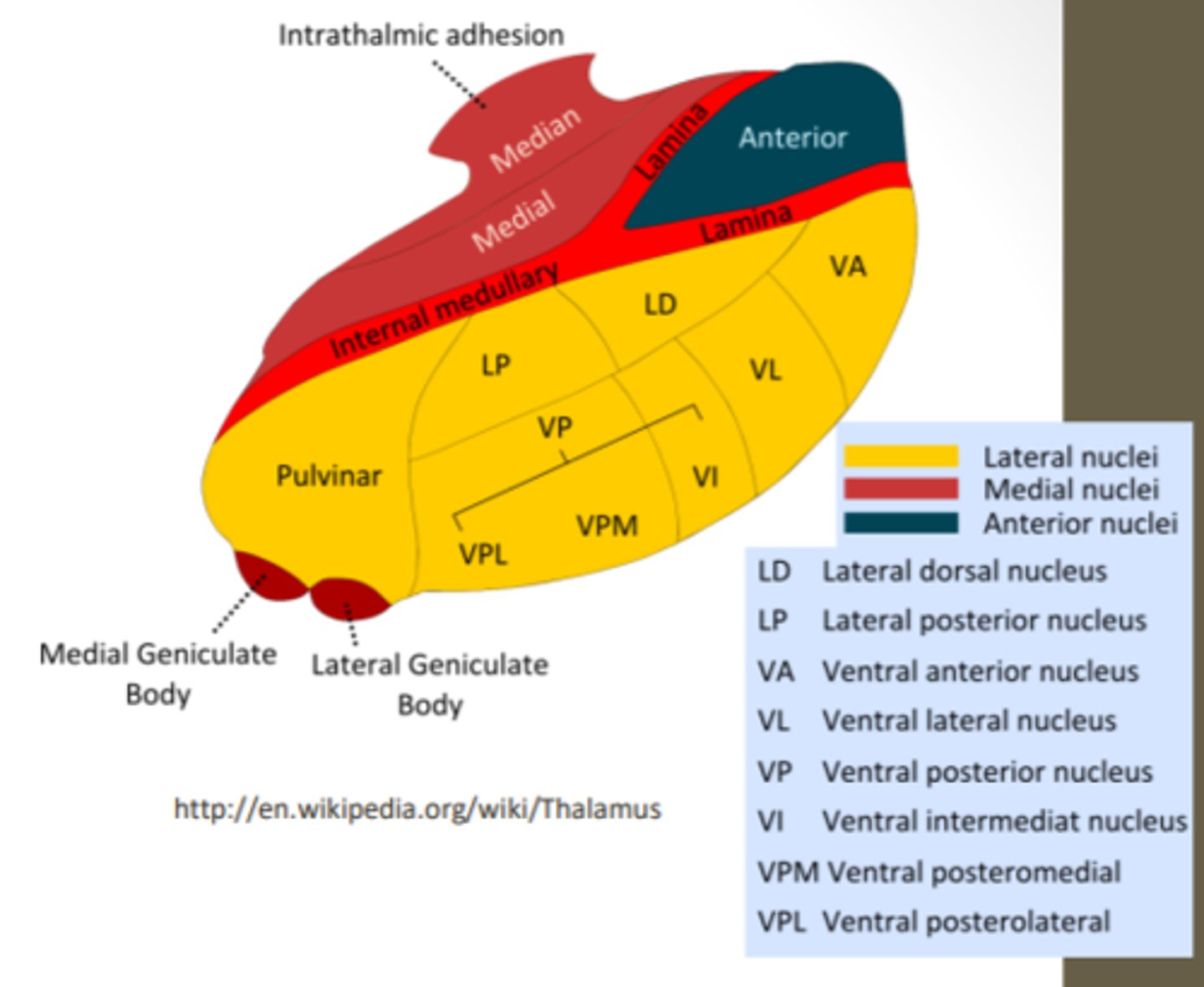
What are the divisions of the thalamus?
What divided the thalamus?
anterior, middle and lateral divisions which are divided by the myelinated internal medullary lamina
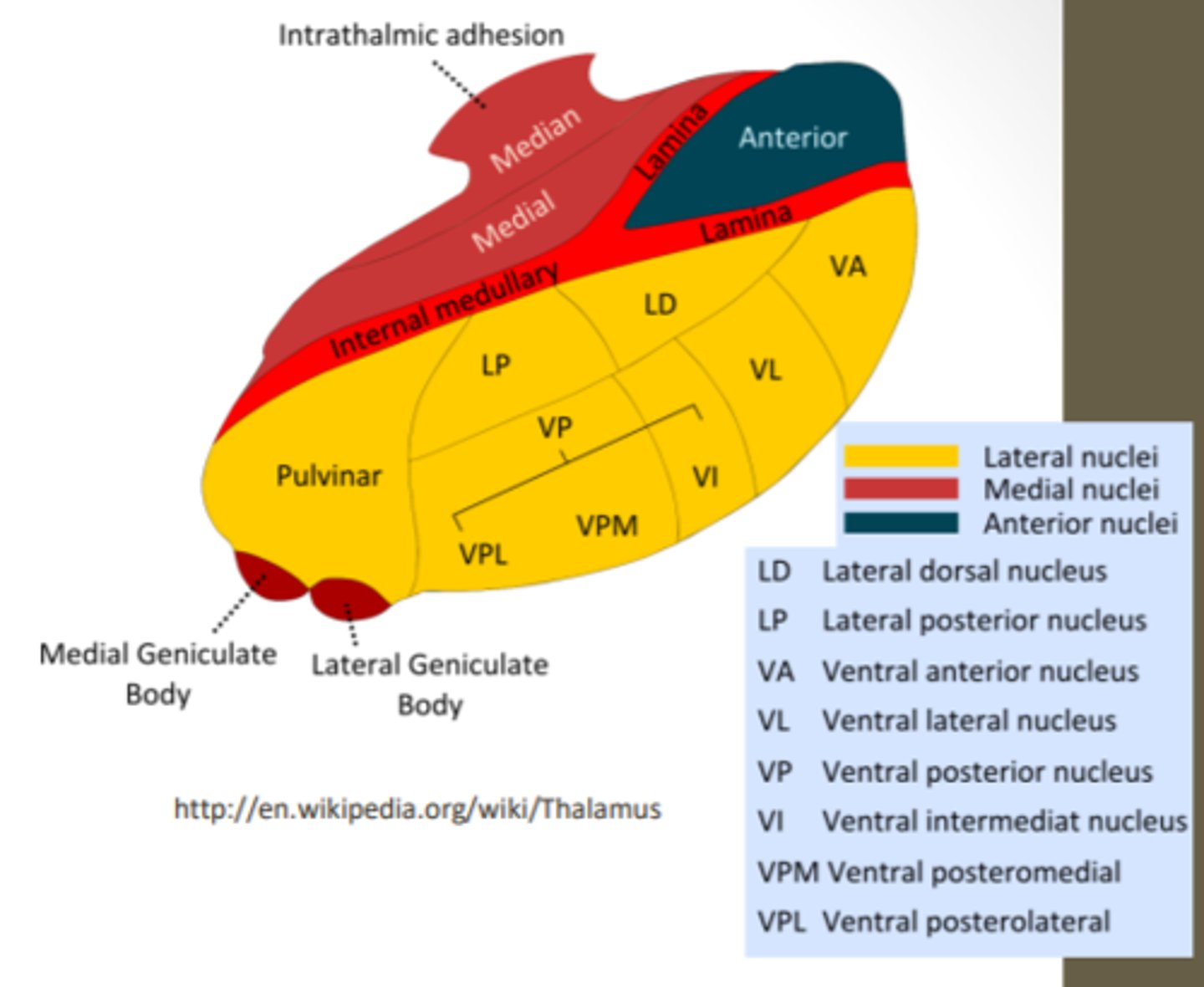
What does the lateral division of the thalamus contain?
composes the bulk of the thalamus and contains the VP, pulvinar, VL, VA, LP and LD nuclei as well as the medial and lateral geniculate bodies
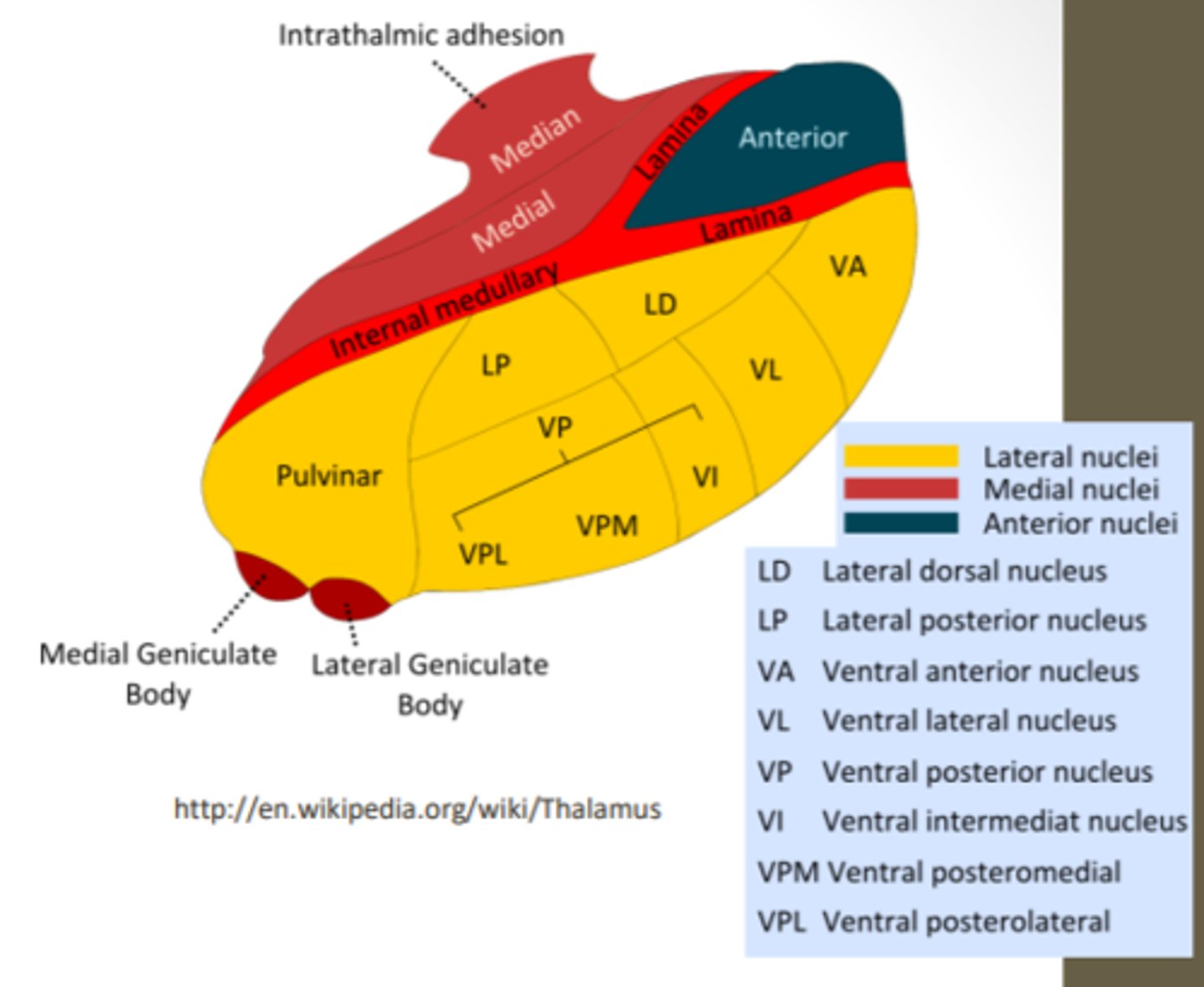
Where is the pulvinar nucleus located? what is the function?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and functions in visual processing and attention
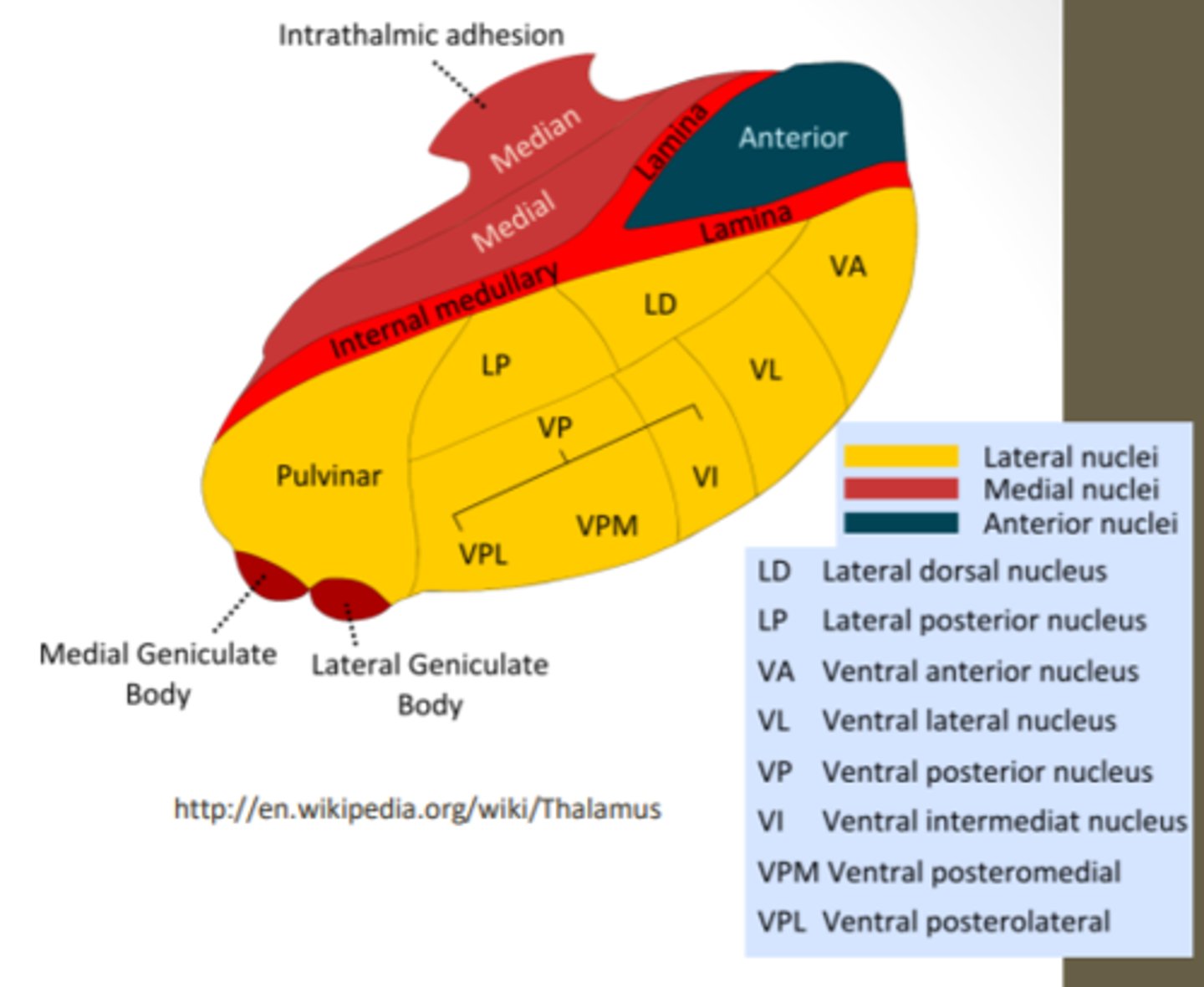
what makes up the ventral posterior nucleus?
consists of the VPL, VPM and VI
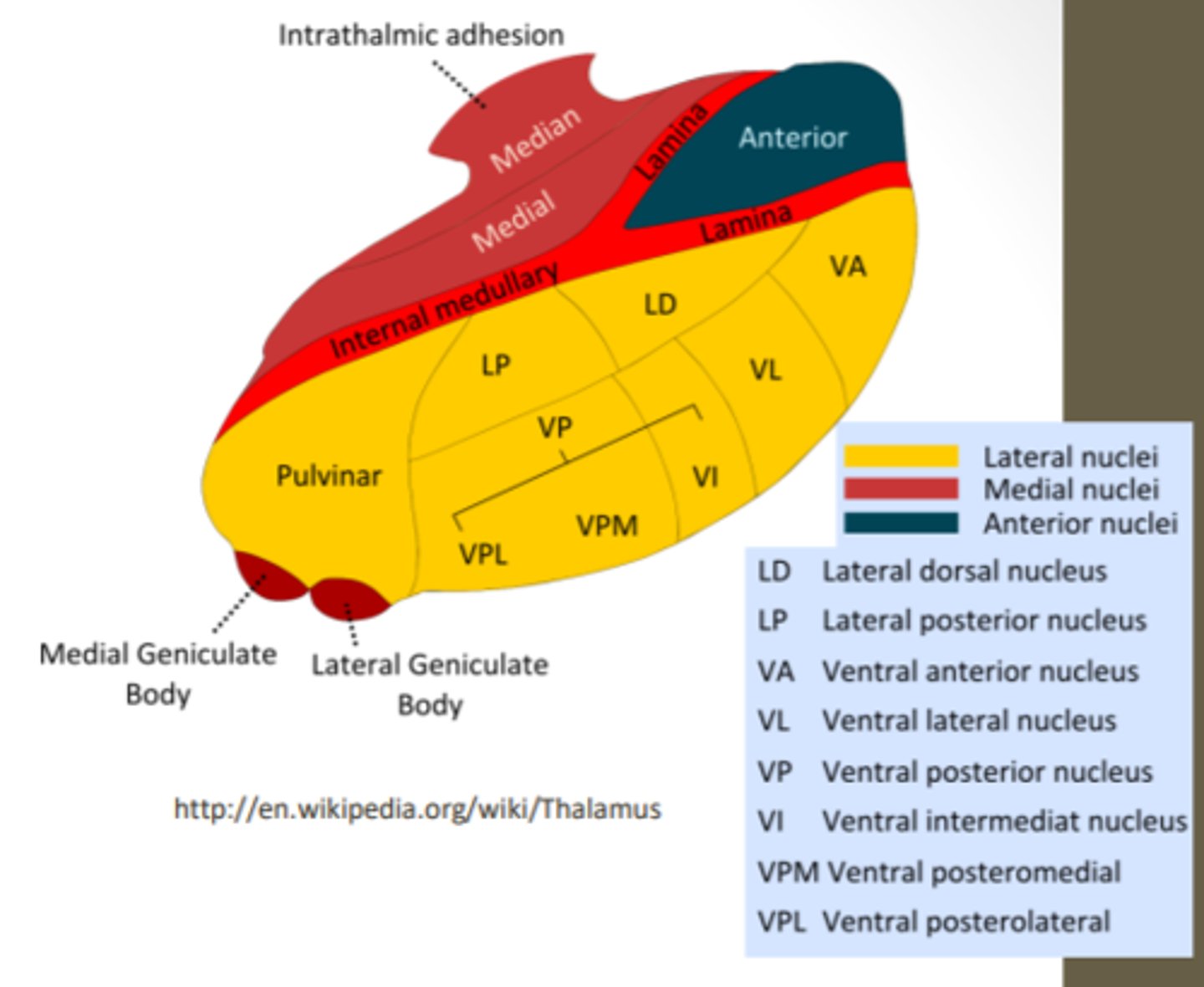
ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) function? What tracts project here?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and functions with somatosensory relay for the body
-DCML and spinothalamic
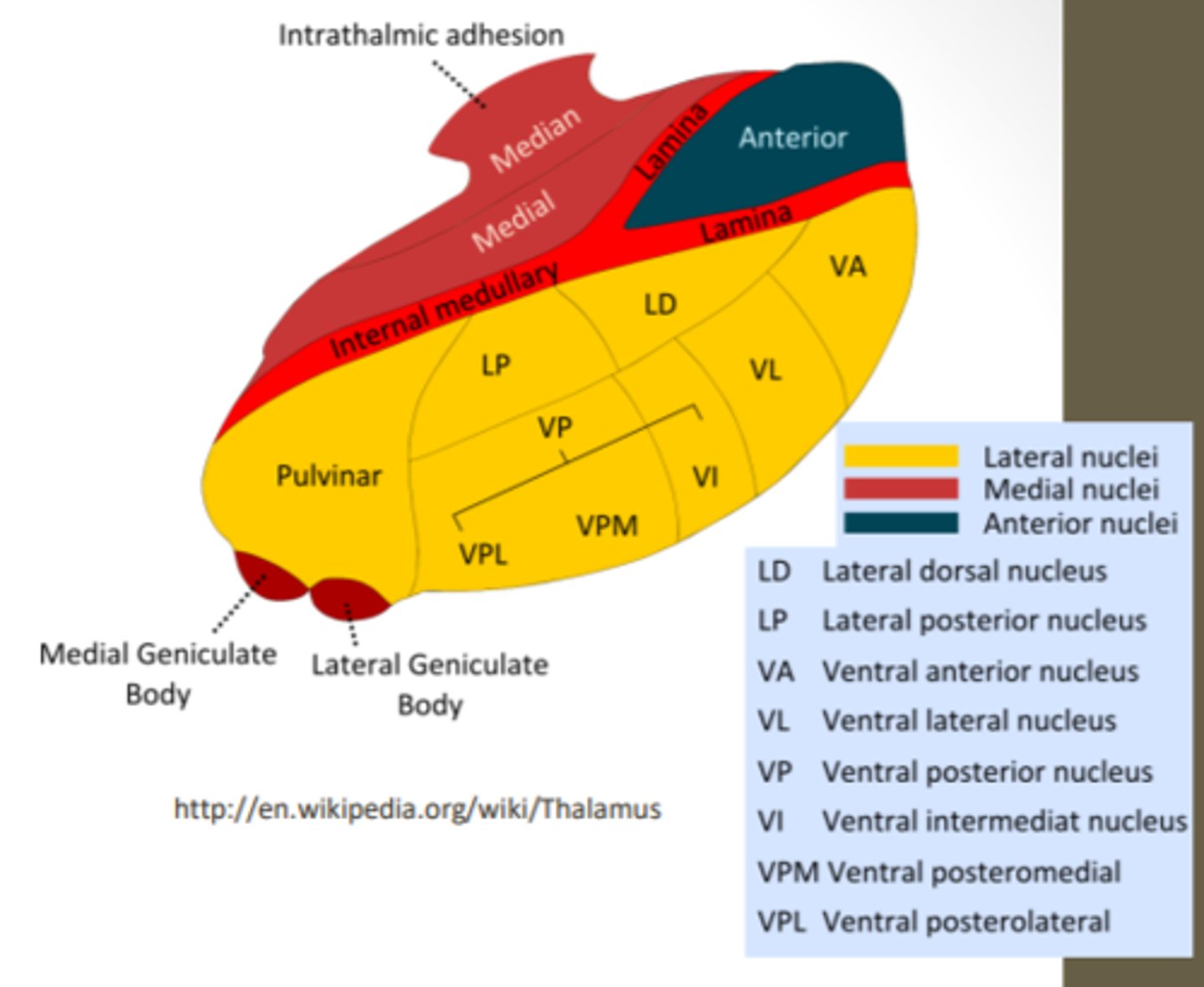
What is the function of the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM)? What pathway projects here?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and functions with somatosensory relay for the head
-trigeminal pathway
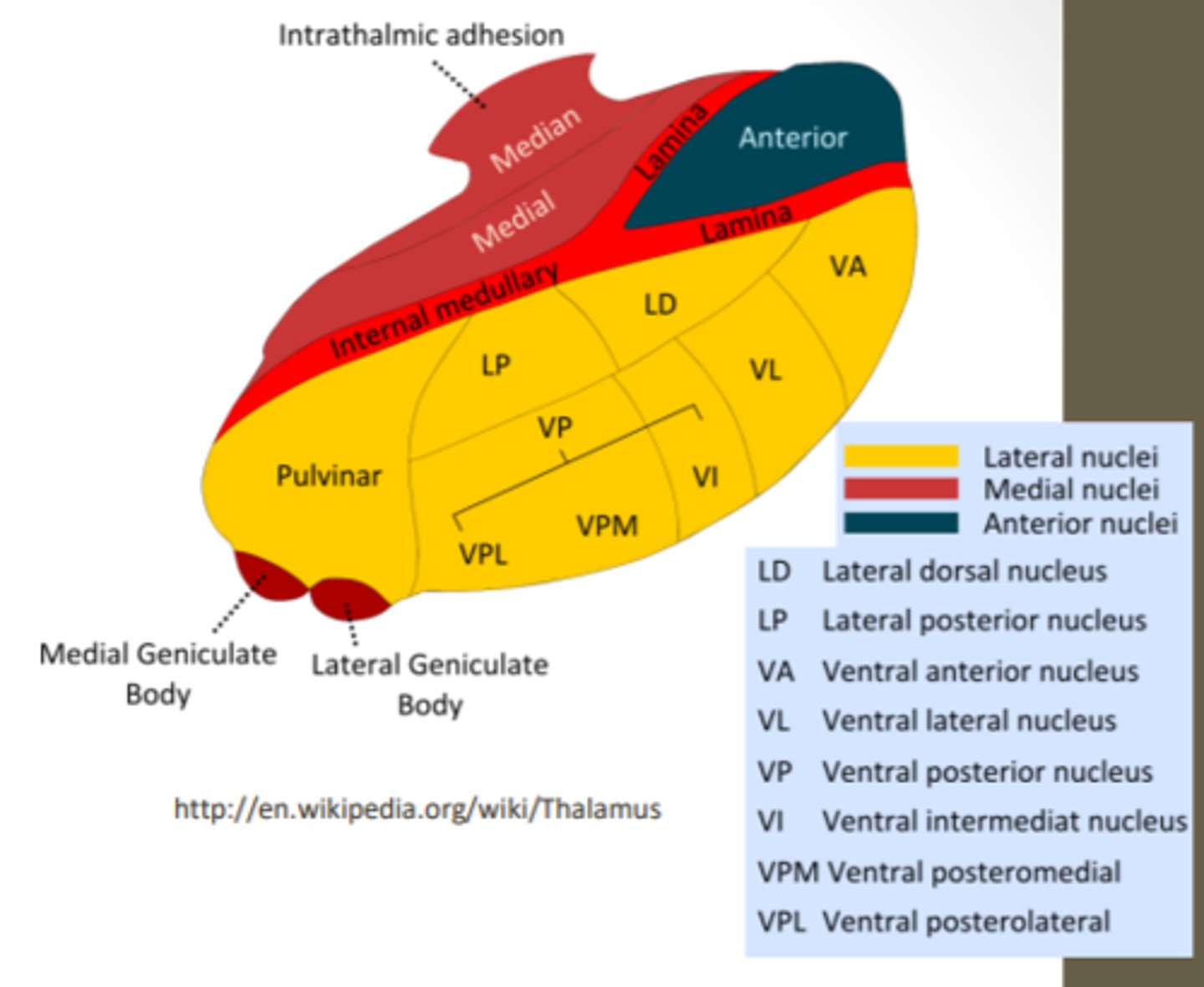
What is the function of the ventral anterior (VA) and ventral lateral nuclei (VL)?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and are involved in motor control circuits that include the cerebellum and basal ganglia
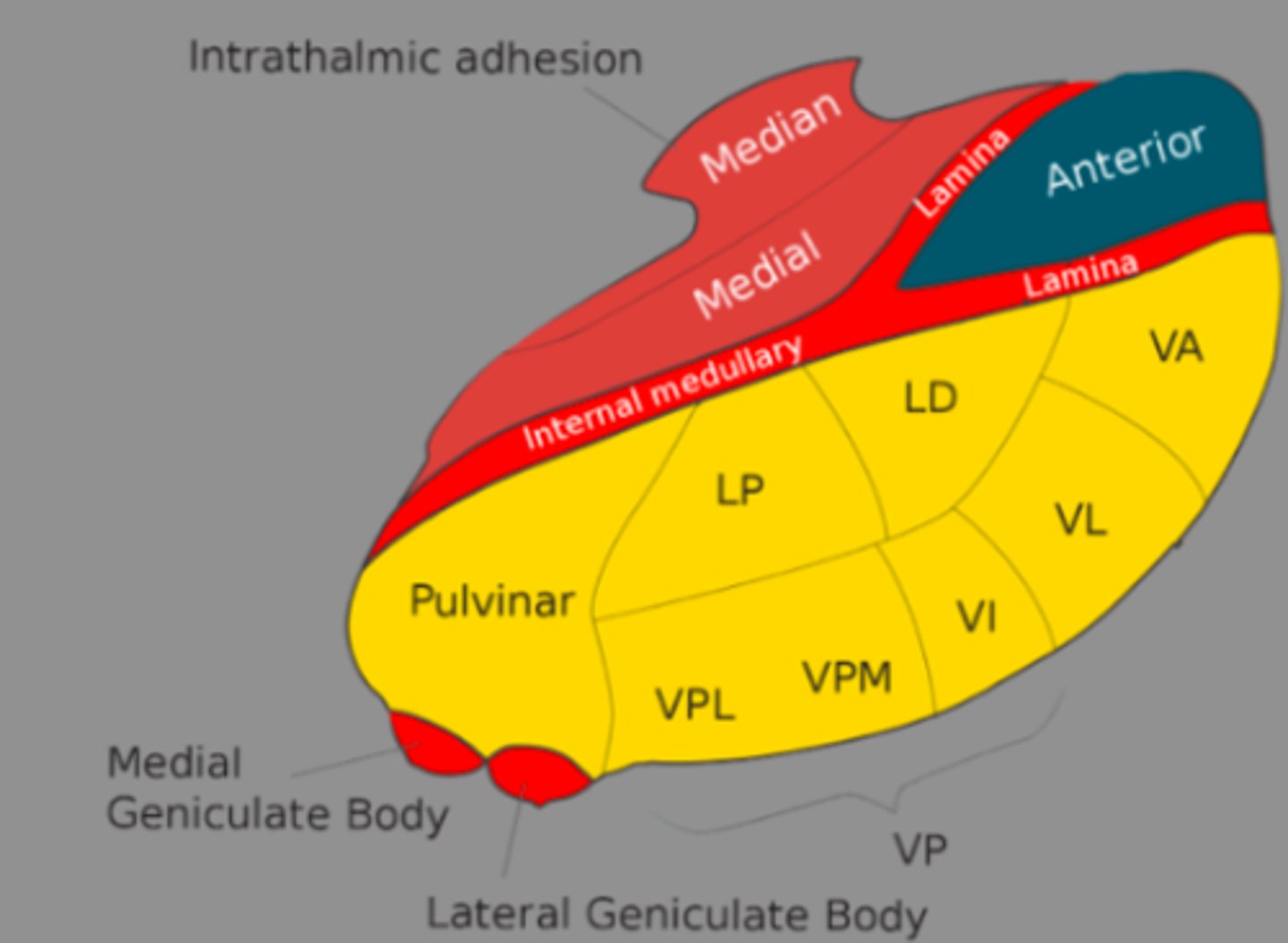
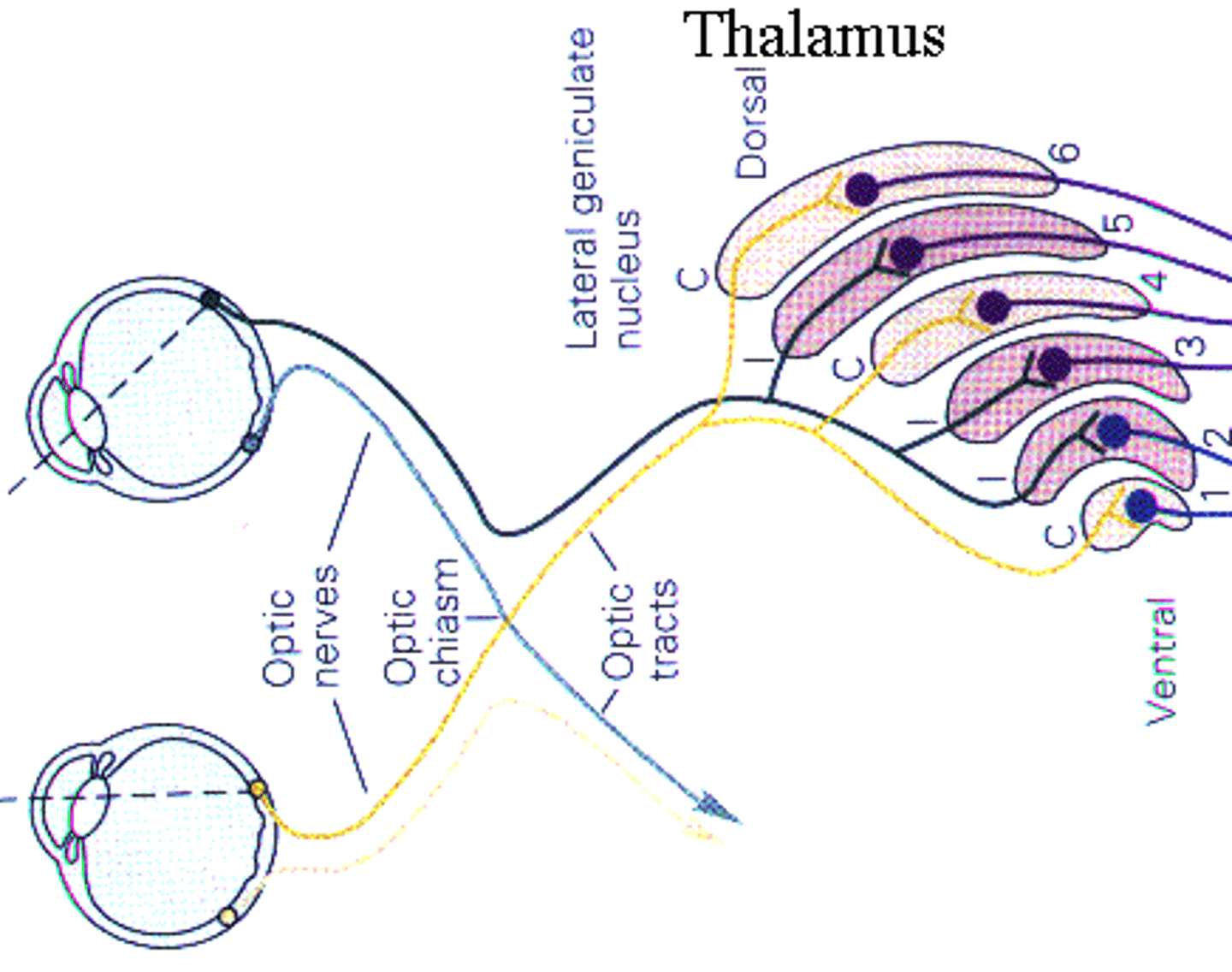
What is the funcrtion of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and is responsible for visual projections
What is the function of the medial geniculate nucleus?
found in the lateral division of the thalamus and is responsible for the auditory system
function of thalamic nuclei
act as a pipeline through which information can flow to the cerebral cortex while deciding which information should reach the cerebral cortex accurately for further processing
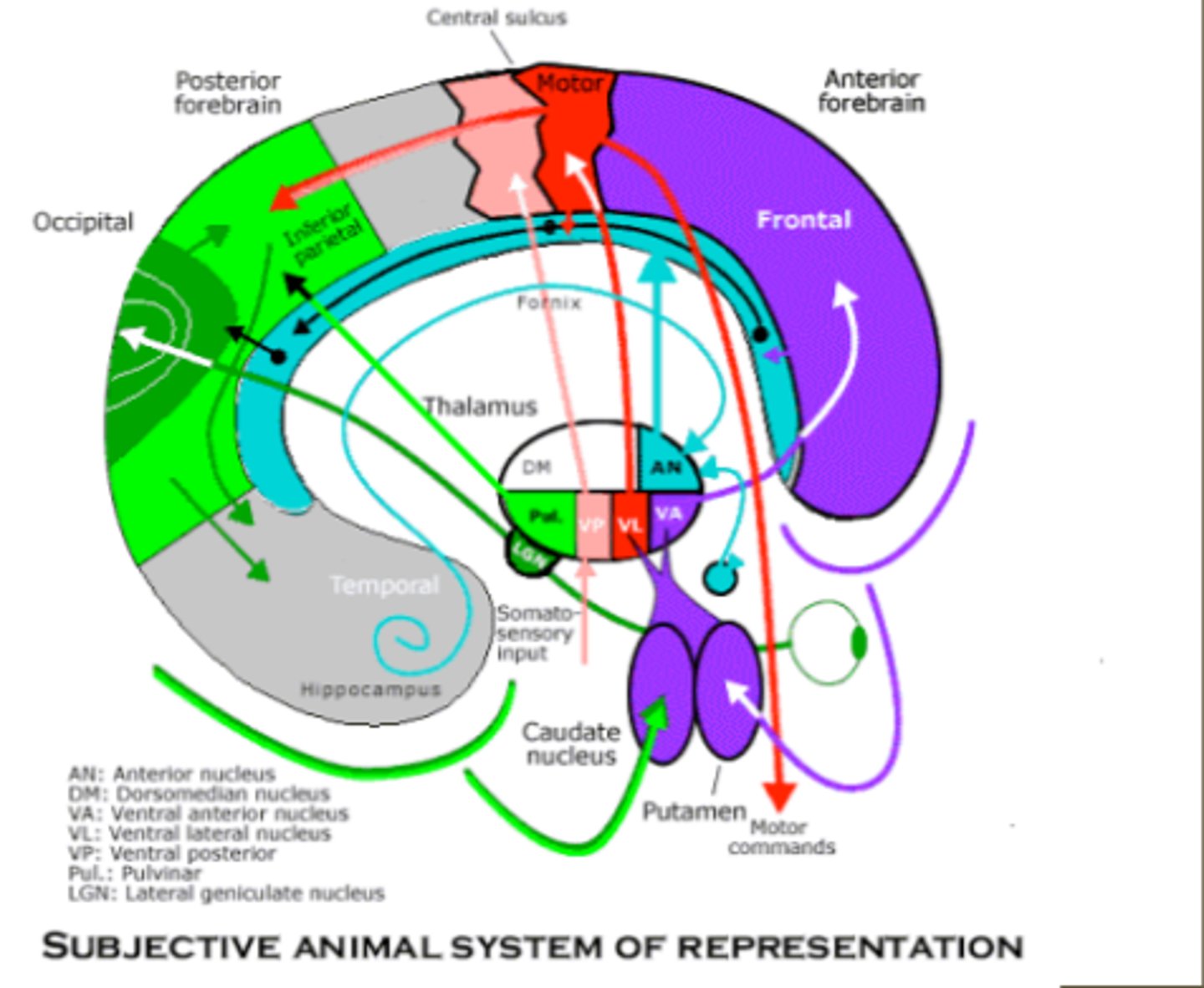
what are the 2 characteristics of the thalamic nuclei? Is the reticular nucleus a thalamic nucleus why or why not?
all nuclei are a mixture of projection neurons (75%) and small inhibitory interneurons. No, the reticular nucleus does NOT have projections into the thalamus, it just surrounds the thalamus to inhibit (modulates) projections going INTO the thalamus.
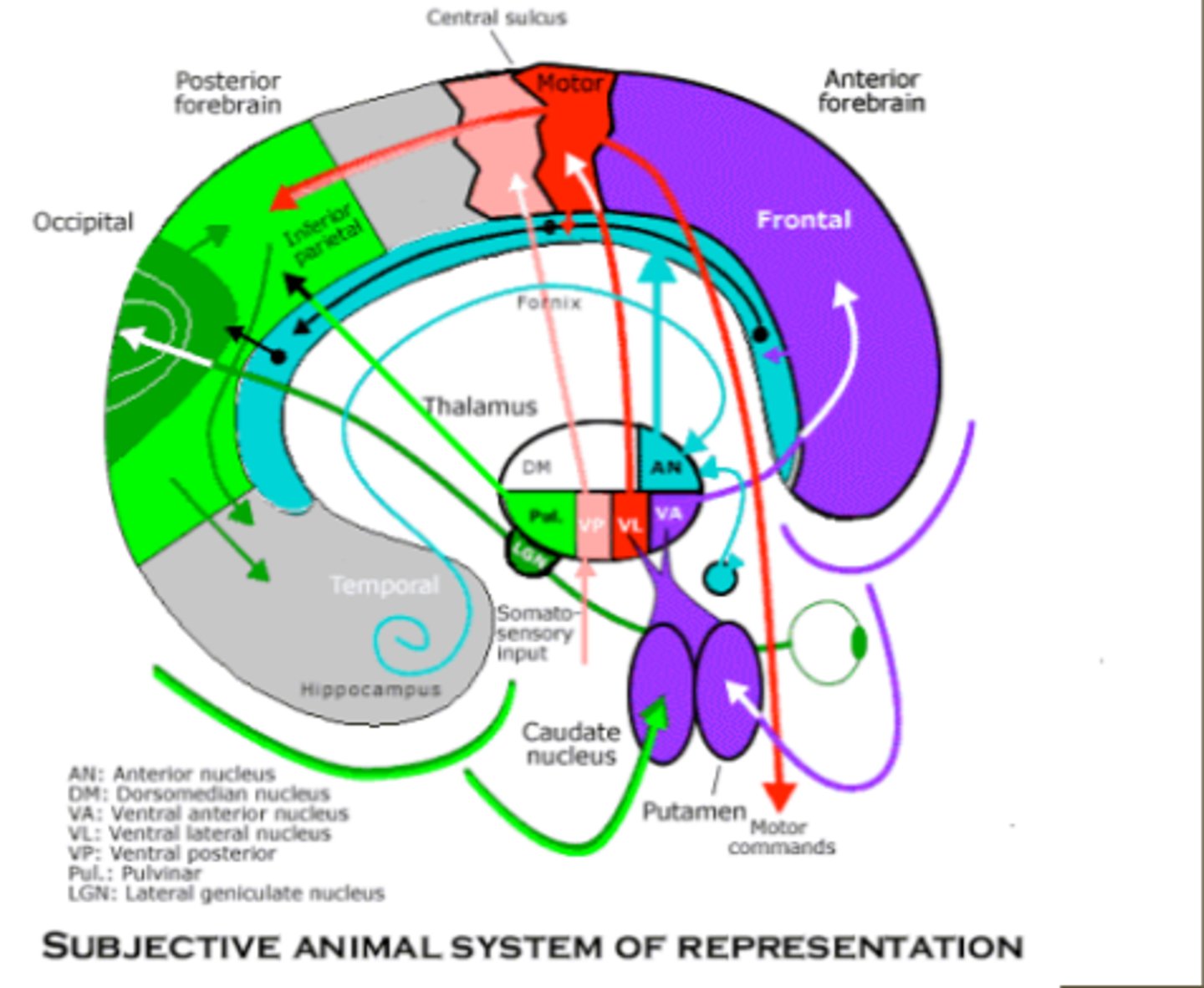
inputs of the thalamus
consists of specific and regulatory inputs
specific inputs to the nuclei of the thalamus
these inputs convey information that a given thalamic nucleus may pass on accurately to the cerebral cortex
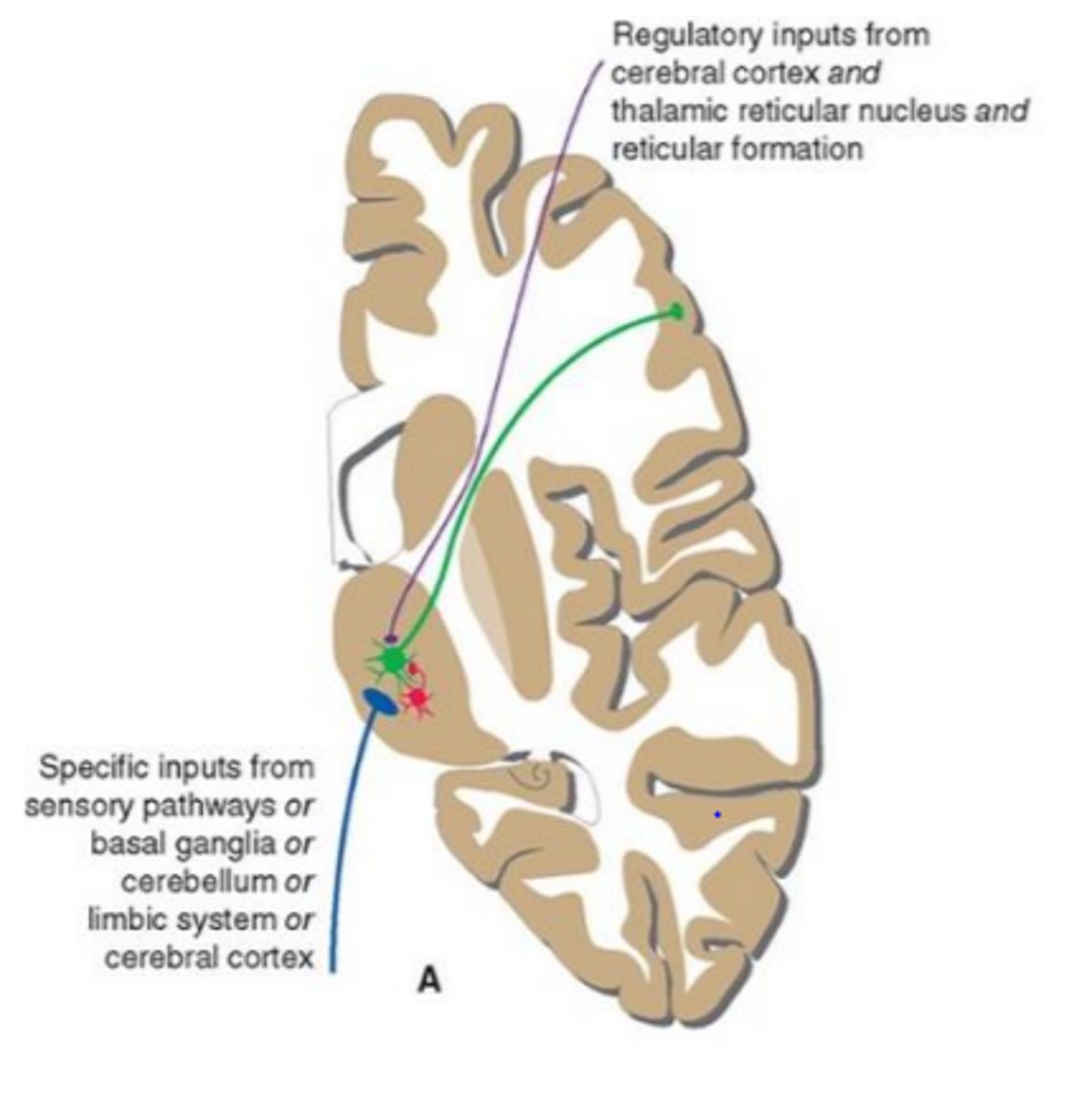
regulatory inputs to the nuclei of the thalamus
regulatory inputs largely descend from the cortex and contribute to decisions about the form in which information leaves a thalamic nucleus
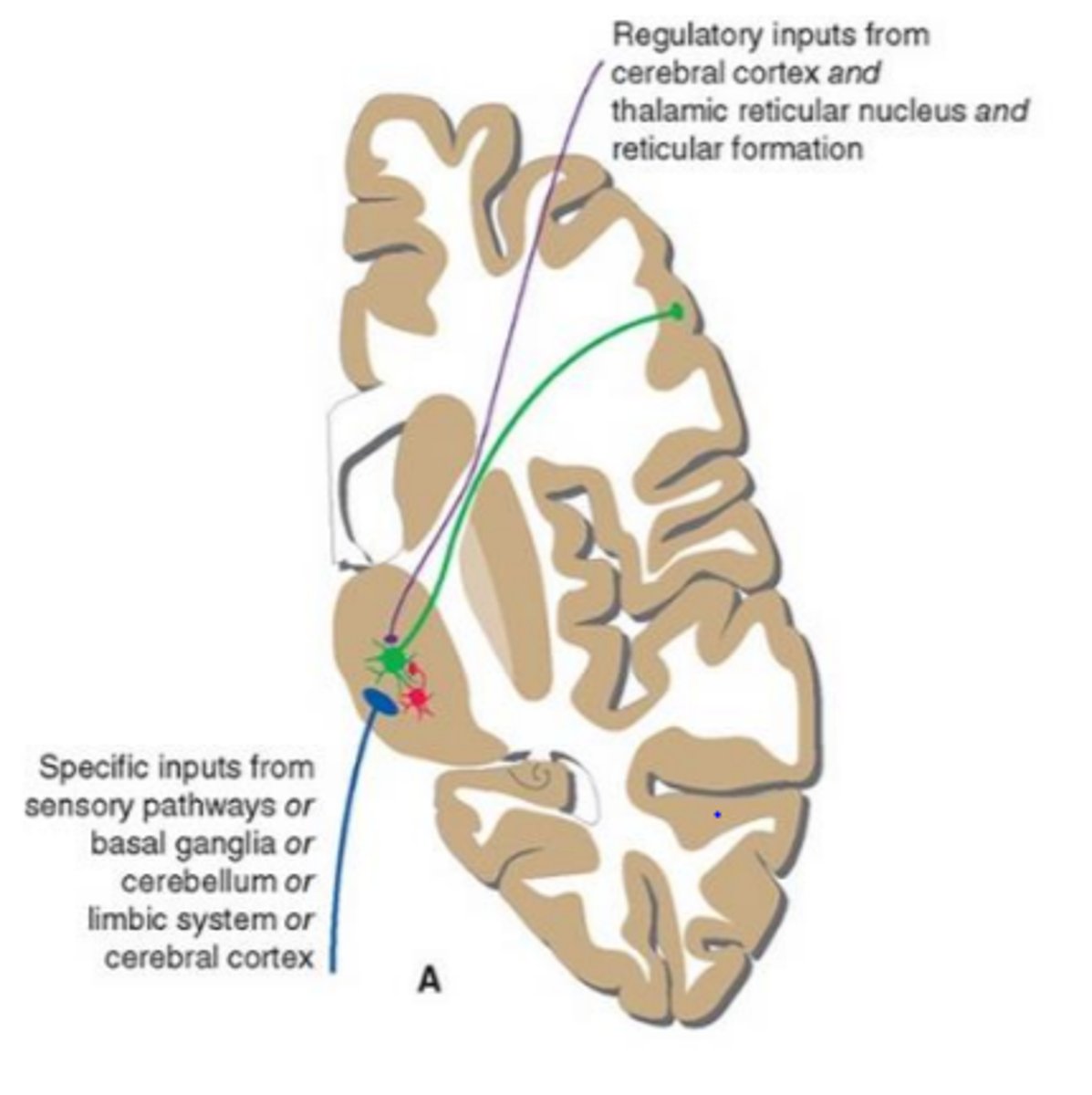
where do thalamic regulatory inputs come from
-the cortical area that a specific thalamic nucleus projects
-the thalamic reticular nucleus
-the brainstem reticular formation
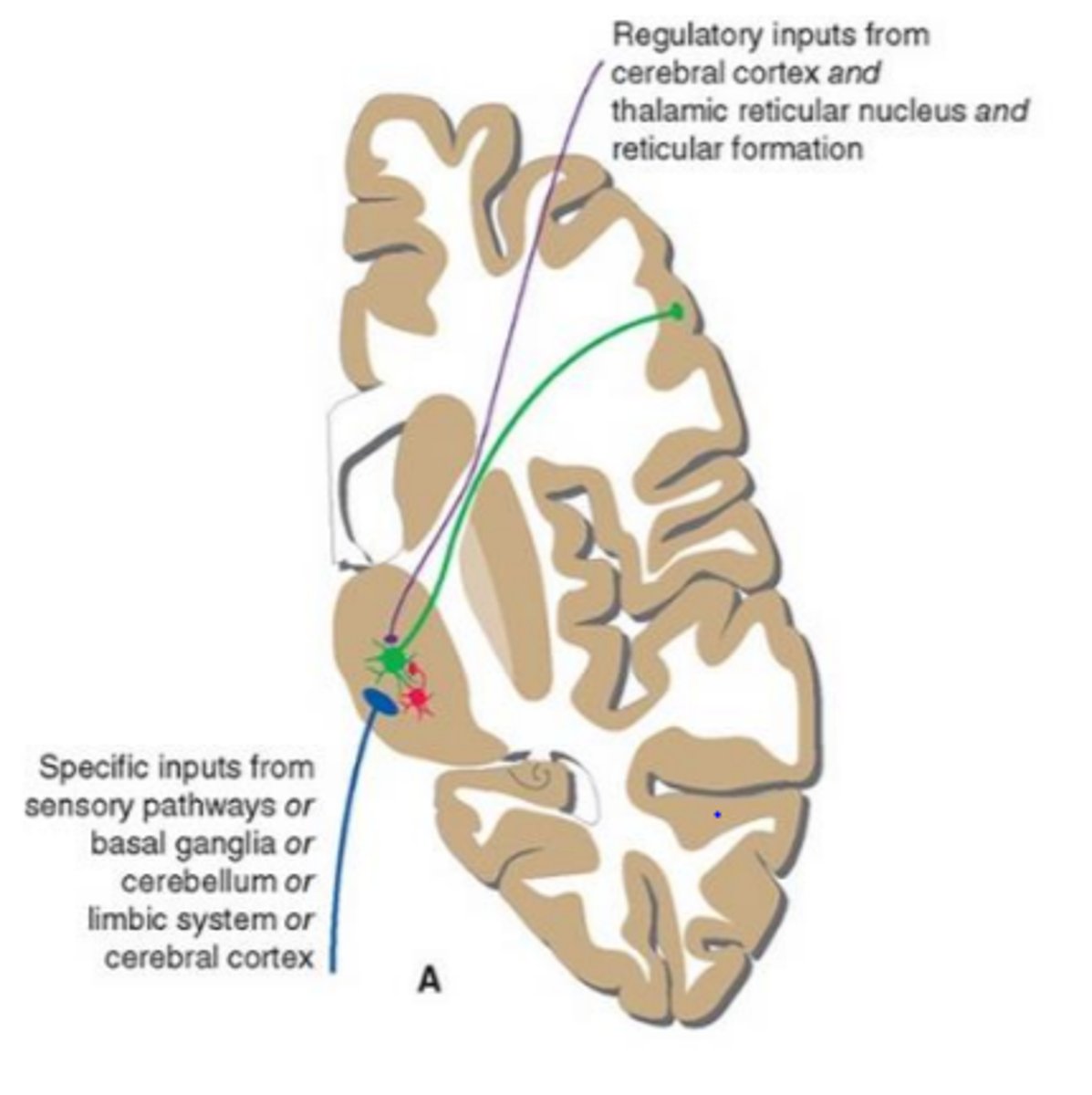
what type of thalamic input is greater
regulatory
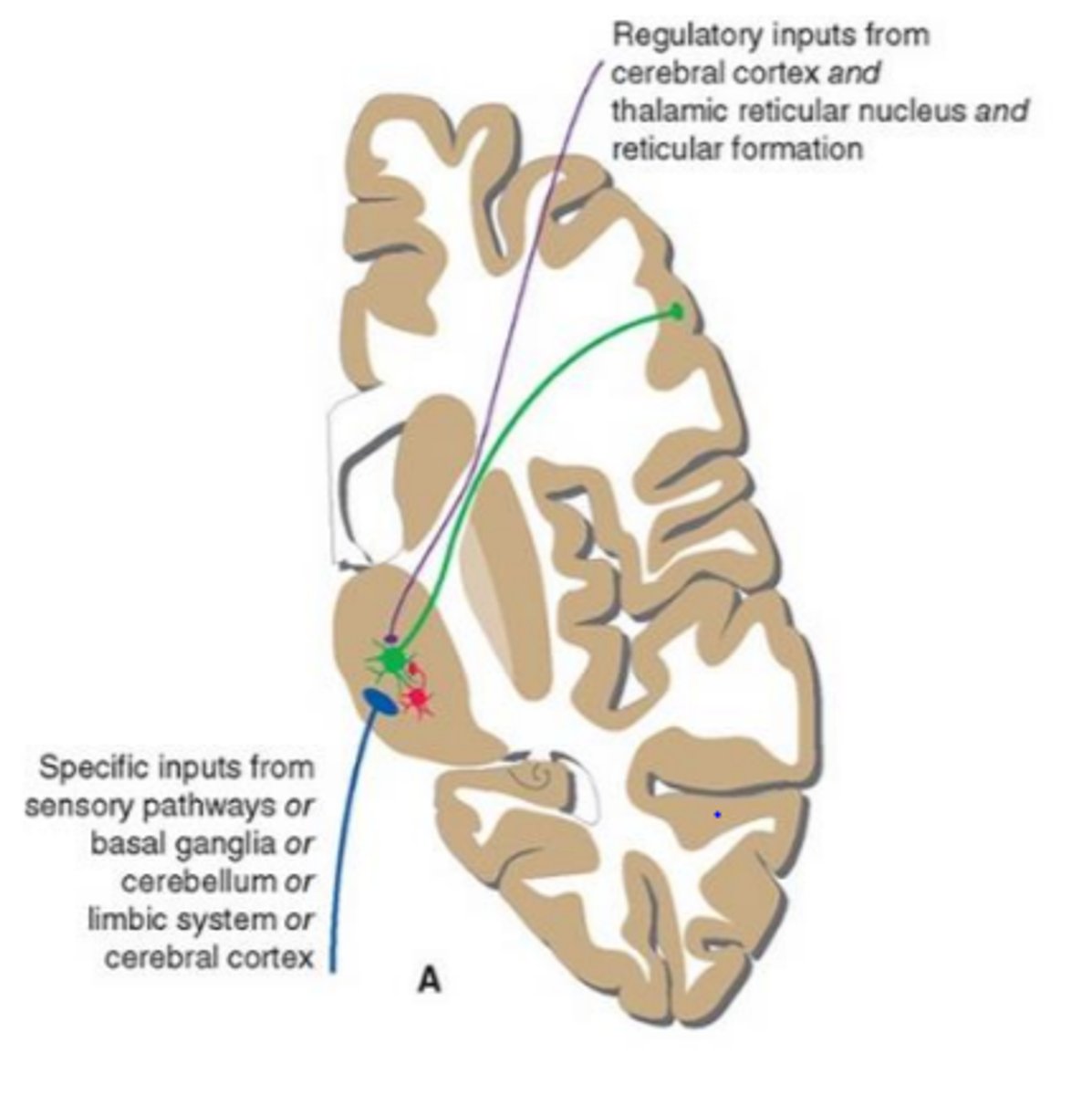
categories of thalamic nuclei
distinctive patterns of inputs/outputs allows us to categorize thalamic nuclei into 3 groups including:
-relay nuclei
-association nuclei
-intralaminar/midline nuclei
relay nuclei of the thalamus
function to receive well-defined bundles of specific input fibers and project to particular functional areas of the cerebral cortex
association nuclei
function to receive their major inputs from the cerebral cortex itself and some from a variety of subcortical structures
-important in the distribution and gating of information between cortical areas
intralaminar and midline nuclei
appear to have a special role in the function of the basal nuclei and limbic system. project
to areas of cerebral cortex and to parts of the basal nuclei and
limbic system
where do inputs to the intralaminar and midline nuclei come from
from a wide array of sites, prominently including parts of the basal nuclei and limbic system
where does the intralaminar and midline nuclei project
to areas of the cerebral cortex and parts of the basal nuclei and limbic system
thalamic outputs
information runs to very specific parts of the cortex depending on the nucleus
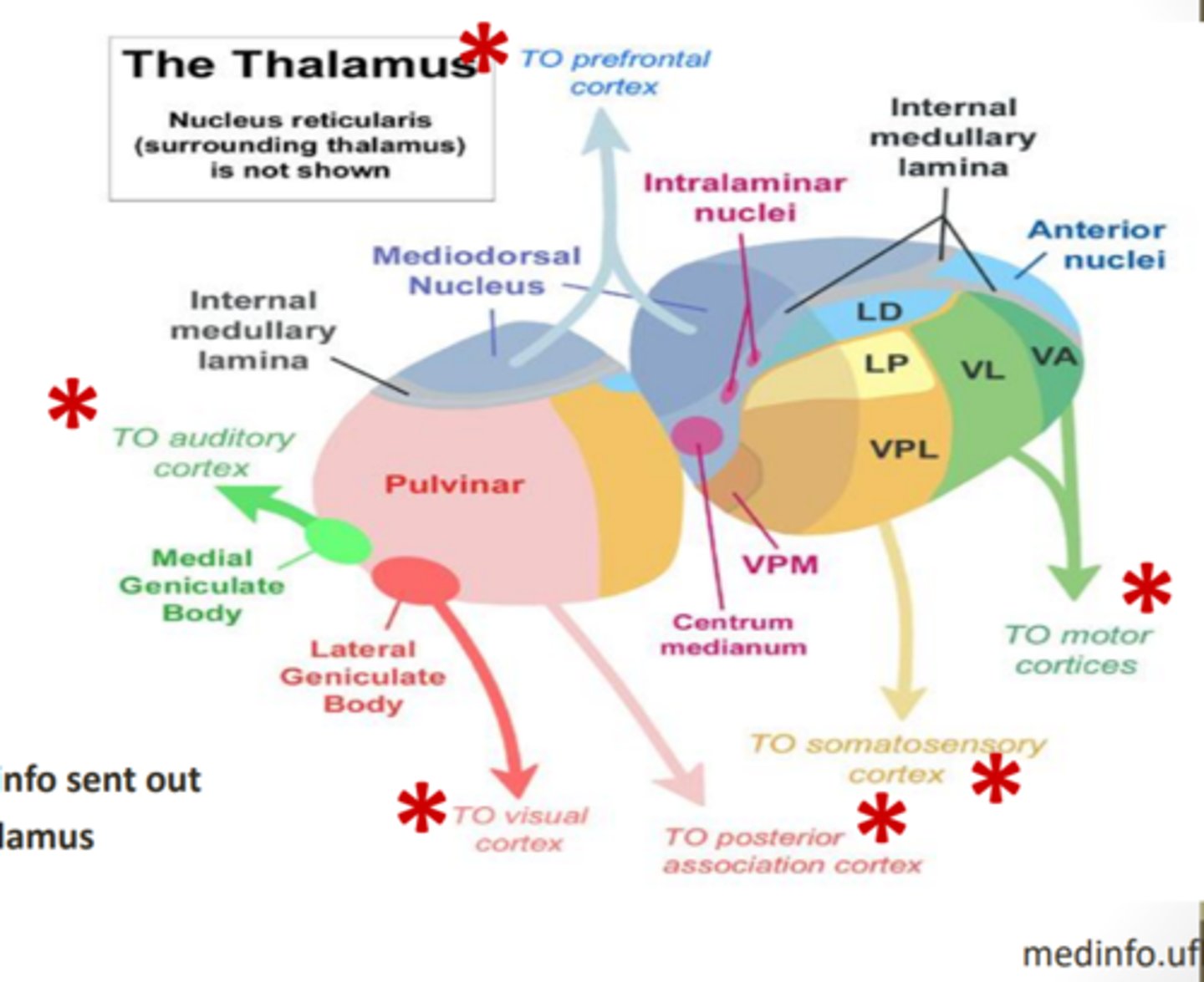
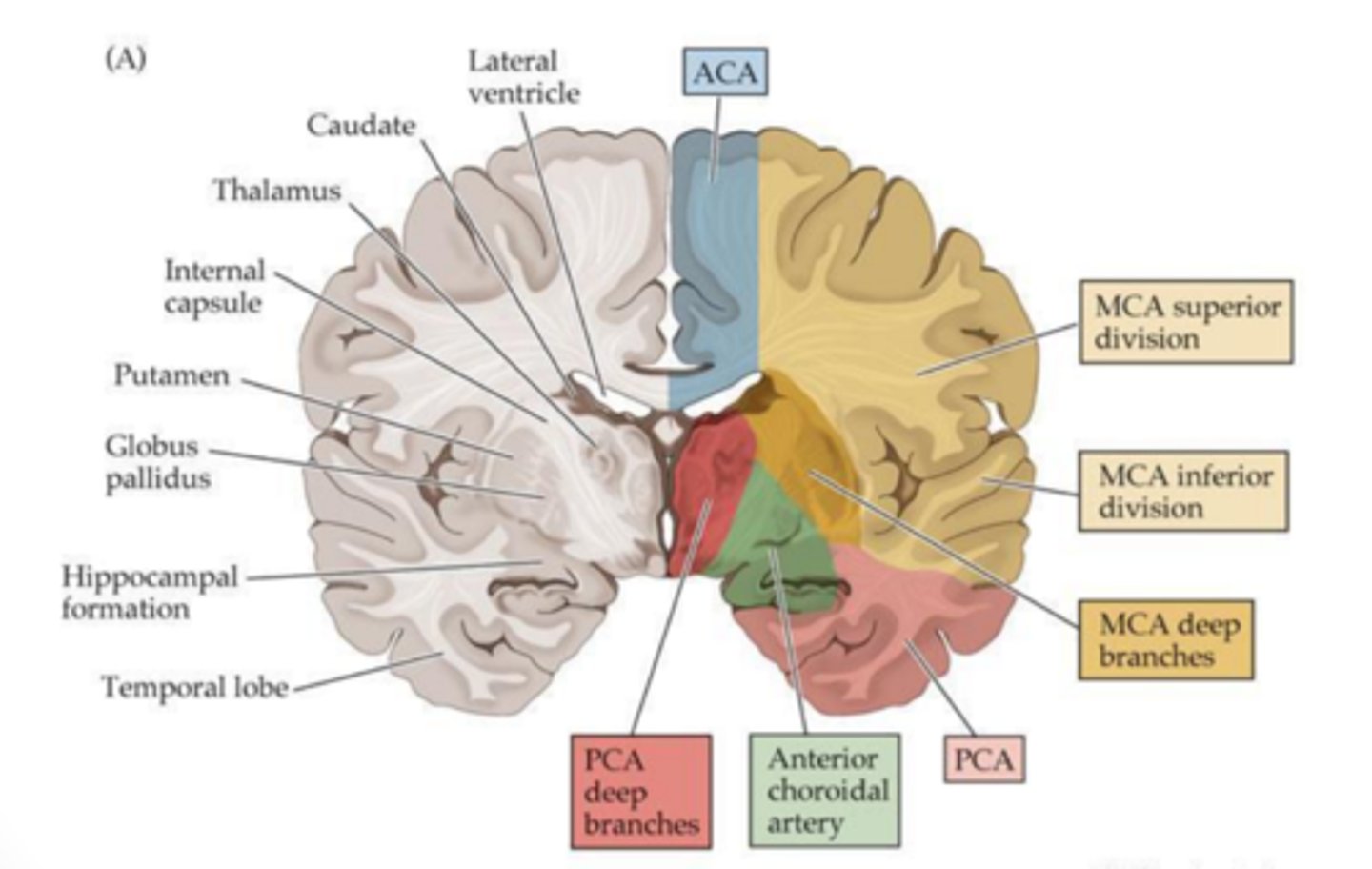
where does the thalamus receive blood supply from?
the PCA
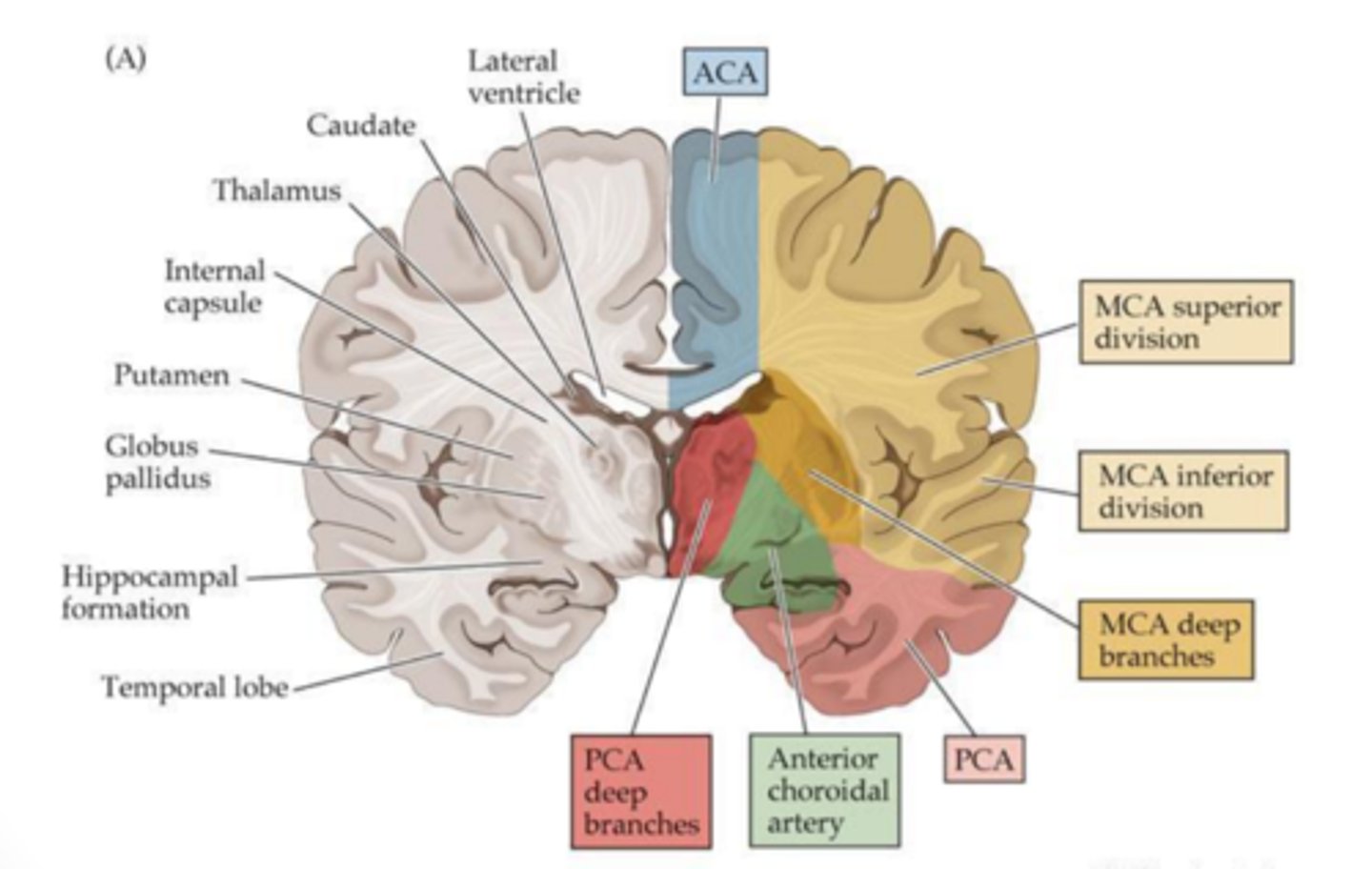
where does the internal capsule receive blood supply?
anterior choroidal and MCA