Oceans and coasts
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Factors that impact coastlines
Tectonic setting
Materials present at the shore
Energy of water and wind striking the coast
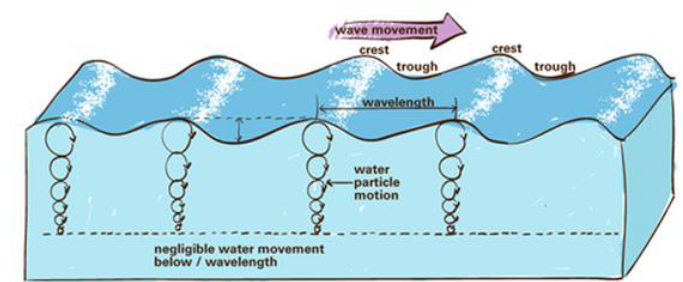
Waves
Small undulations on the water surface that are generated by wind
Propagate through water away from source
Modifies shorelines when they break
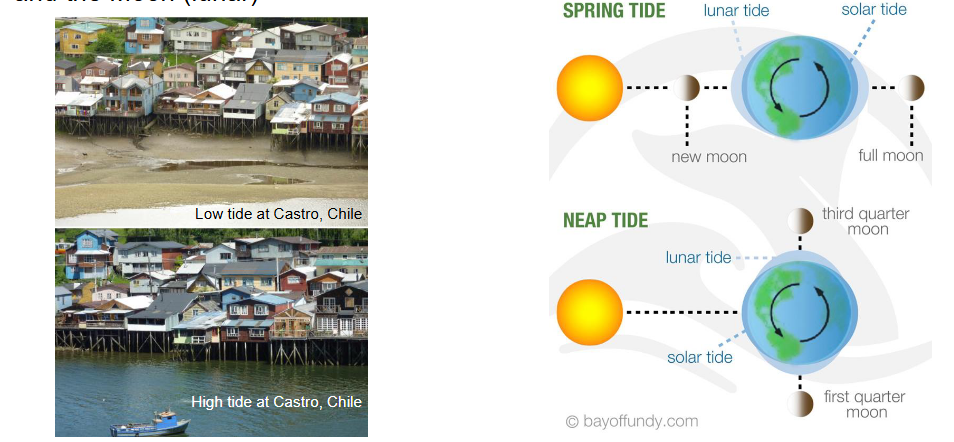
Tides
Small variations in local sea level due to gravitational effects of both the Sun and the Moon
Creates currents
Bay of Fundy has the highest tides in the world
Storm surge
Localized increase in water level of an ocean or large lake
Caused by the high winds and extreme low pressure associated with major storms
Factors that affect the magnitude of the surge are
Speed at which the storm approaches the coast
Geometry of the particular coastline
Tsunamis
Caused by earthquakes, landslides, or volcanic eruptions
Can travel across entire ocean basins with minimal energy loss
Beaches
Gently sloping depositional surfaces washed over by waves and covered by sediment
Change seasonally with more fine grained sand in the summer and rocky during the winter, This is because of wave energy and the resulting movement of sand and other sediments (winter = less waves but stronger, summer = more waves but weaker)
Emergent vs Submergent coastline
Emergent
When water is getting lower relative to the local coast
Submergent
When water is getting higher relative to the local coast
Currents
Distinct bodies of water moving in a definite direction
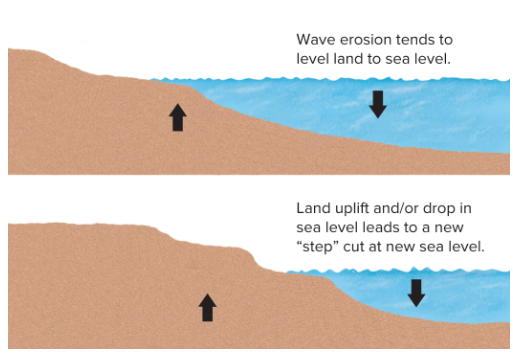
Wave-cut platforms
Form when land is elevated or sea level falls
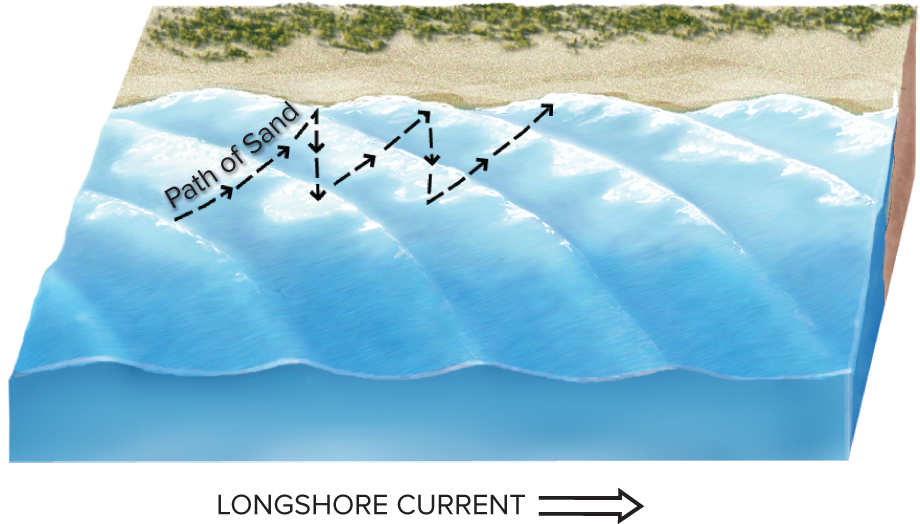
Littoral drift
Gradual sand movement down the beach in the same general direction as the motion of the longshore current
Longshore current
Net movement of water parallel to a coastline, arising when waves and currents approach the shore at an angle
Storm tide
The overall water level during a storm, Sum of storm surge + normal tides