skeletal system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:20 AM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
1
New cards
ax-
axis
2
New cards
-blast
bud, a growing organism in early stages
3
New cards
canal-
channel
4
New cards
carp-
wrist
5
New cards
-clast
break
6
New cards
intra-
inside
7
New cards
inter-
among, between
8
New cards
odont-
tooth
9
New cards
poie-
make, produce
10
New cards
arth-
joint
11
New cards
burs-
bag, purse
12
New cards
ov-
egglike
13
New cards
sutur-s
sewing
14
New cards
classifications of bones
long(ex: femur), short(ex: wrist), irregular(ex: vertebrae), flat(ex: ribs), sesamoid(ex: patella)
15
New cards
epiphysis
expanded ends of longbone. Covered w/ articular cartilage.
16
New cards
diaphysis
the shaft of the bone
17
New cards
periosteum
tough, vascular(blood vessels) covering connective fibrous tissue. -muscles attach here.
18
New cards
compact bone
tightly packed tissue-no gaps. gives bone strength.
19
New cards
spongy bone
spaces like a sponge. many branching bony plates called trabeculae.
20
New cards
medullary canal
tube running down the center of diaphysis. lined w/ endosteum.
21
New cards
endosteum
thin membrane containing bone forming cells
22
New cards
red marrow
found in spongy bone, makes blood cell(hematopoietic tissue).
23
New cards
yellow marrow
found in medullary canal=stores fat
24
New cards
major function of bones
support and protect softer tissue, body structure+muscle attachment, blood cell formation, storage of inorganic salts.
25
New cards
blood cell formation=
hematopoiesis
26
New cards
what are ex. of inorganic salts stored in bones
calcium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, carbonate ions).
27
New cards
osteoblasts
blasts build bone=bone forming cells.
28
New cards
osteoclasts
remodel, destroy the calcifiied matrix.
29
New cards
osteocytes
bone cells in bony chambers called lacunae(were osteoblastes)
30
New cards
central canal(microscopic structures of long bone)=
blood vessels+nerves
31
New cards
canaliculi(microscopic structures of long bone)
bring 02+nutrients
32
New cards
layers(microscopic structures of long bone)
lamellae
33
New cards
surrounds central canal(microscopic structures of long bone)
osteon
34
New cards
primary ossification center
in the center of the diaphysis where bony tissue begins to replace hyaline cartilage.
35
New cards
secondary ossification center
appears later in development inside the epiphyses-spongy bone forms in all directions
36
New cards
band of cartilage left between the 2 ossification centers
epiphyseal disk/plate or metaphysis
37
New cards
vitamin d is necessary for:
proper absorption of calcium in the small intestine(w/o enough calcium, bone is soft, ricekts form). -> found in milk & eggs.
38
New cards
Vit. A and C are required for:
normal bone development and growth.
39
New cards
Vitamin A=
osteoblast and osteoclast activity(carrots)
40
New cards
Vitamin C=
collagen synthesis-osteoblasts need this to make bone matrix(oranges).
41
New cards
growth hormone
pituitary gland
42
New cards
in adults, too much growth hormone causes...
acromegaly(causes body tissues and bones to grow faster)/pituitary gigantism
43
New cards
growth hormone stimulates:
division of cartilage cells w/in metaphysis.
44
New cards
too little growth hormone
pituitary dwarfism
45
New cards
thyroxin
stimulates the replacement of cartilage in metaphysis w/ bony tissue.
46
New cards
parathyroid hormone
stimulate osteoclast activity to help break down bone
47
New cards
sex hormones
promote formation of bone & also stimulate ossification of metaphysis(stop bone lengthening).
48
New cards
physical stress
stimulates bone growth. muscles pull on bones+causes bone tissue to thicken+strengthen. Conversely, lack of exercise causes bones to be thinner+weaker(atrophy).
49
New cards
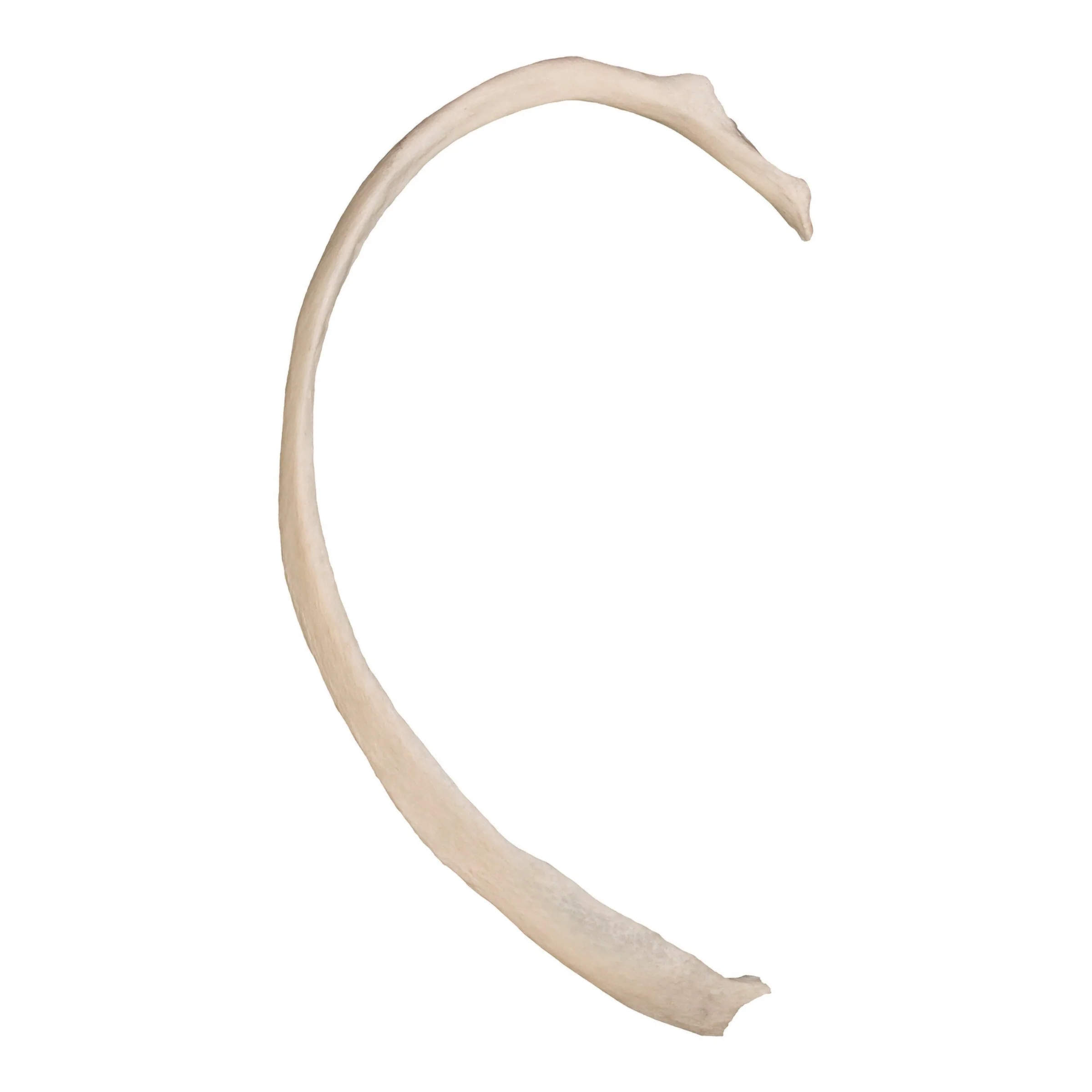

rib, c-shpaed, rounded, skinny
50
New cards
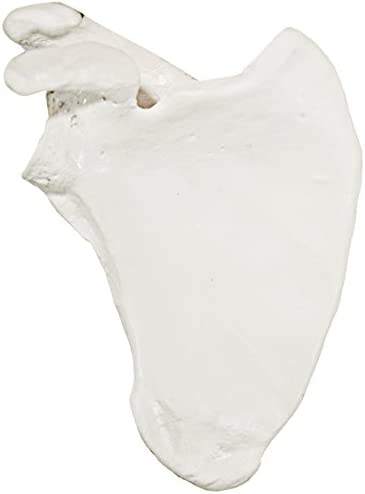
scapula, looks like heart, flat
51
New cards
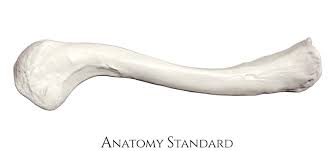
clavicle, squigly, skinny
52
New cards
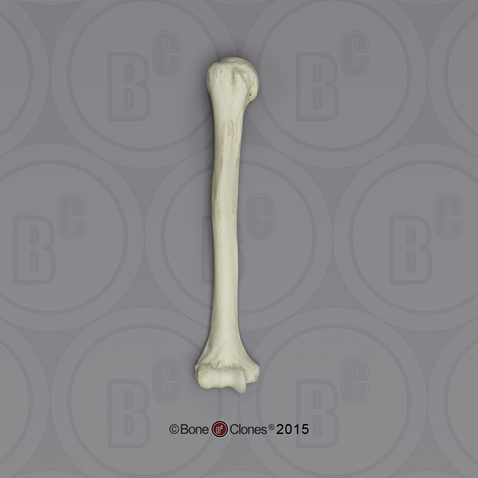
humerus, smaller than femur, big, thick
53
New cards
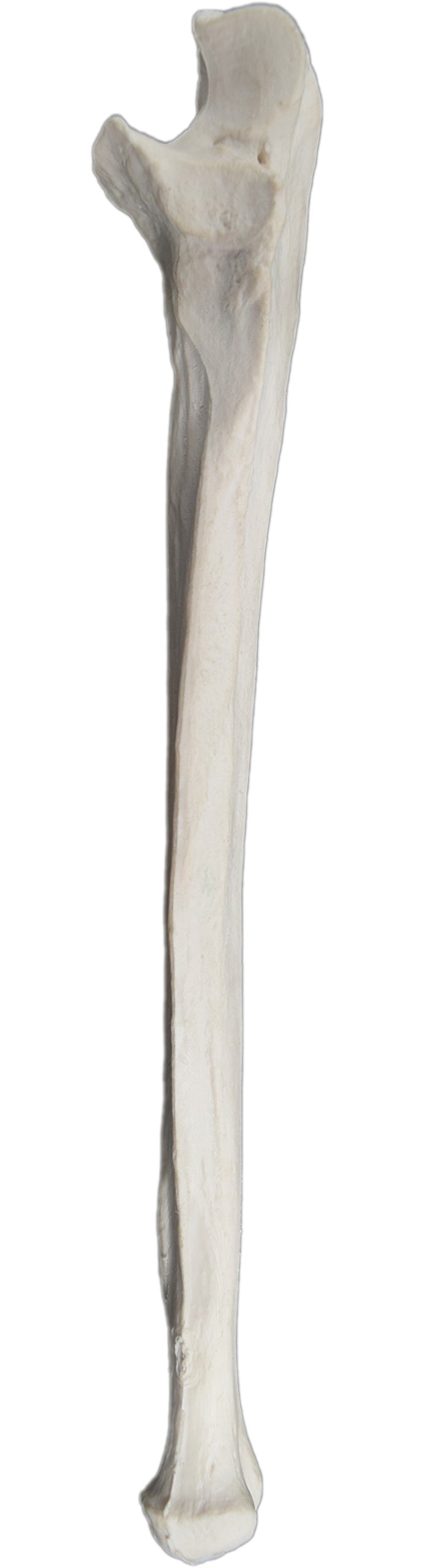

ulna, space for connection to elbow, has a u
54
New cards
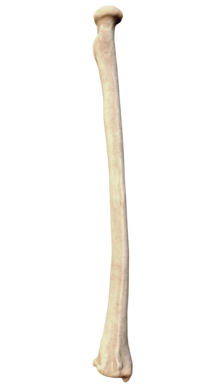
radius, looks like nail, wraps toward fingers
55
New cards
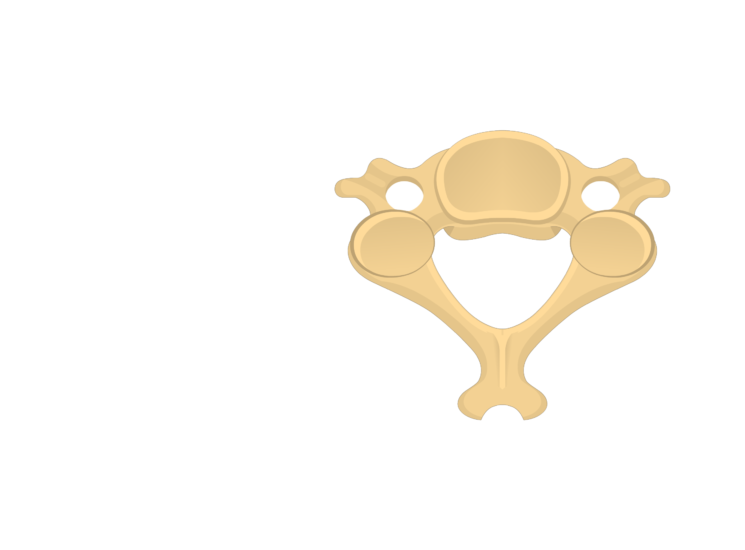
cervical vertebrae, small, skinny, big hole, looks more movable
56
New cards
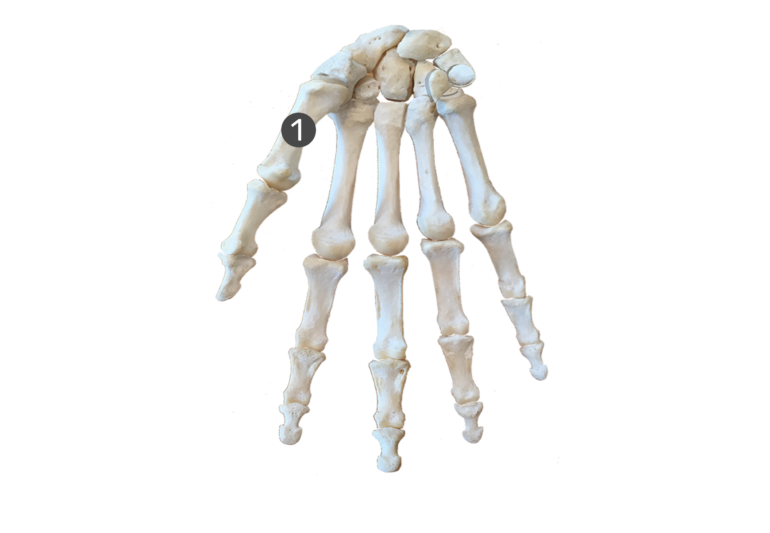
metacarpal-looks like a hand
57
New cards
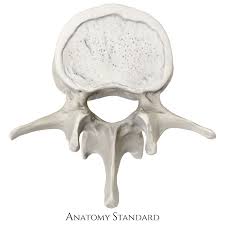
lumbar vertebrae-flatter than thoracic, smaller hole
58
New cards
green stick fracture
bends on one side-children
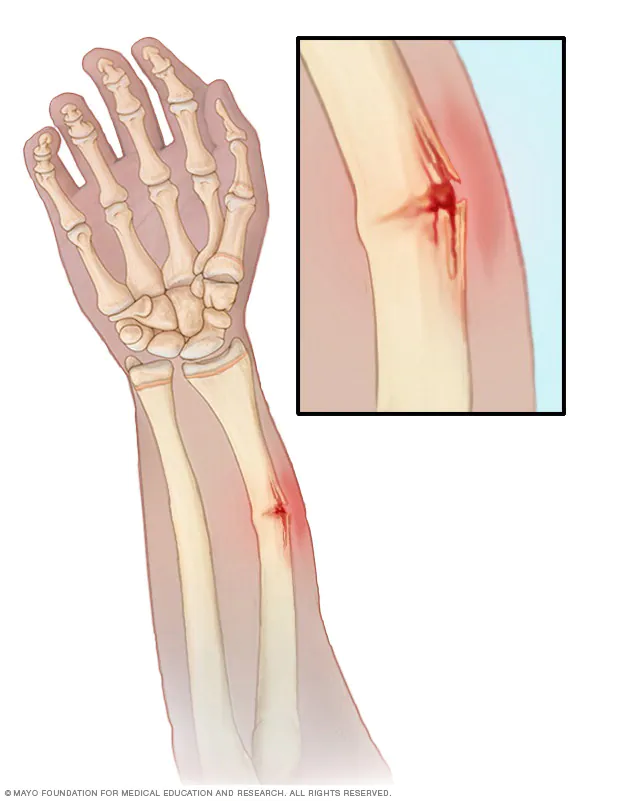
59
New cards
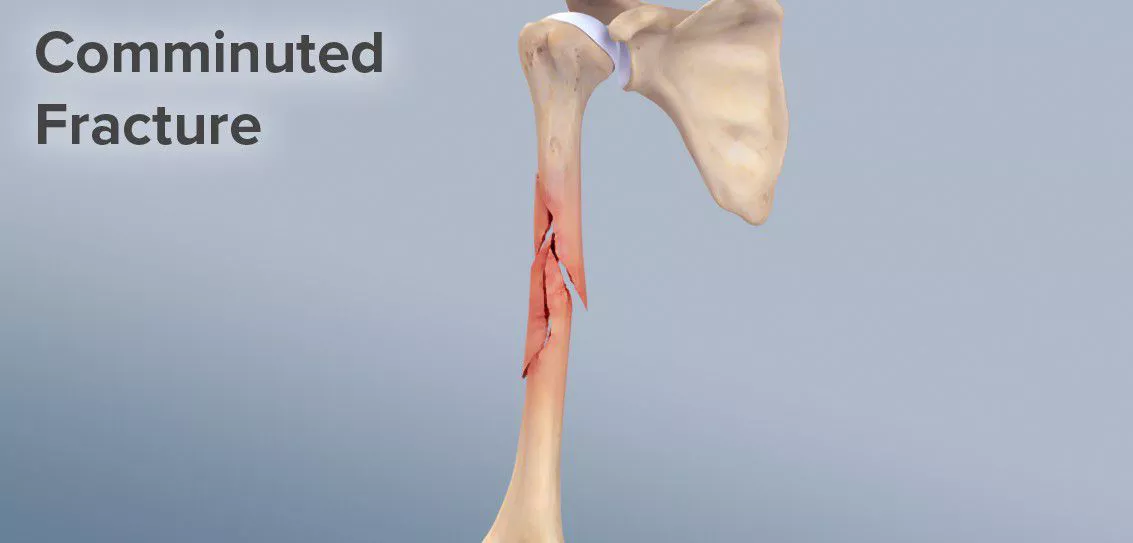
comminuted fracture
shattered
60
New cards
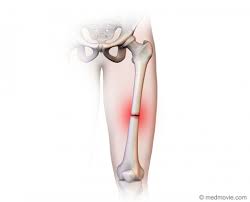
transverse fracture
across the bone
61
New cards
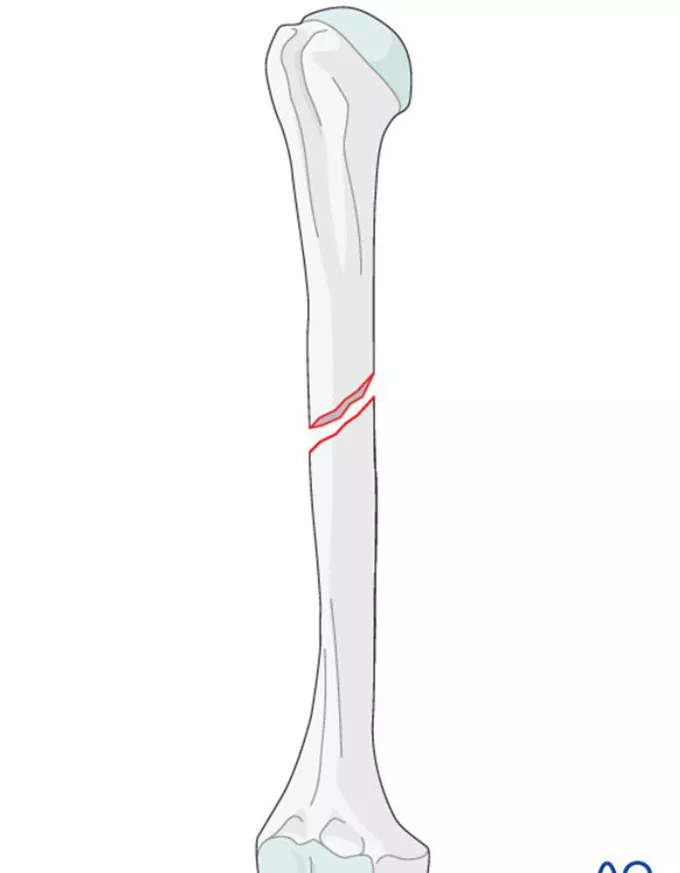
oblique fracture
diagonal break
62
New cards
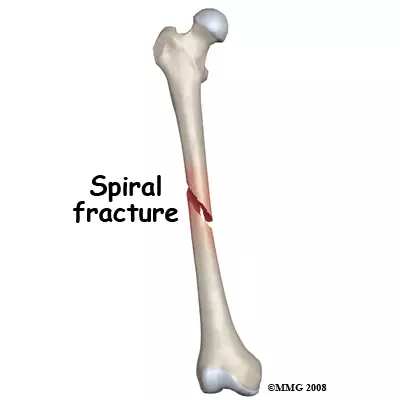
spiral fracture
twisted
63
New cards
colles fracture
radial break
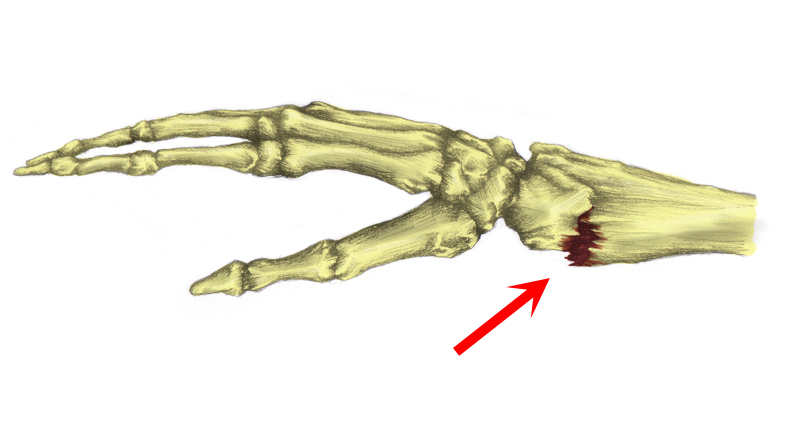
64
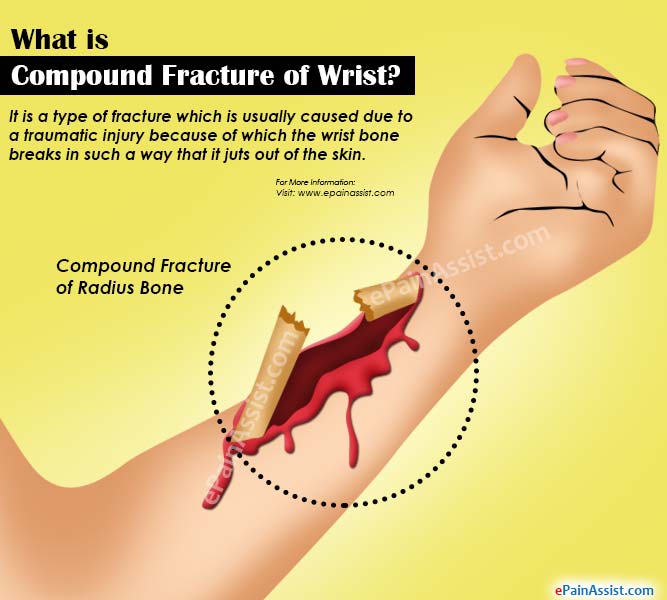
New cards
compound fracture
bone breaks through the skin
65
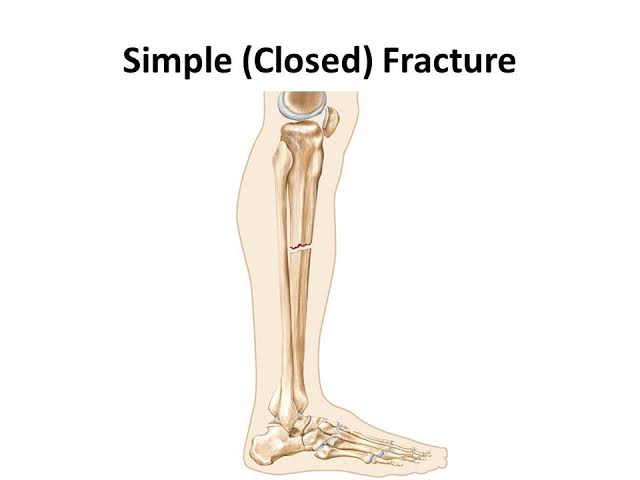
New cards
simple fracture
bone breaks
66
New cards
joint
an articulation, where two bones come together.
67
New cards
joint classification
based on the type of tissue that binds them
68
New cards
3 types of movement
amphiarthrotic, synarthrotic, and diarthrotic
69
New cards
amphiarthrotic
slightly moveable
70
New cards
synarthrotic
immovable
71
New cards
diarthrotic
freely movable
72
New cards
fibrous joints
held together with dense fibrous connective tissue(CT).
73
New cards
Syndesmosis
bones bound by a sheet or bundle of dense CT. Amphiarthrotic. Between the distal tibia and fibula.
74
New cards
Suture
Only in the flat bones of the skull. Dense CT. = sutural ligament. Synarthrotic. Were fontanets soft spots in infants.
75
New cards
Gomphosis
Joint where a cone shaped bony process fits in a bony socket. Teeth.
76
New cards
Cartilaginous joints
hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage
77
New cards
Synchondrosis
bones untied by bands of hyaline cartilage, many are temp. & disappear as growth occurs, synarthrotic.
78
New cards
Ex. of synchondrosis
between manubrium of sternum all of the metaphyses(growth plates).
79
New cards
Symphysis
Articular surfaces are covered by a thin layer of hyaline cartliage & is attached to a pad of fibrocartilage. Amphiarthrotic.
80
New cards
Ex. of symphysis
symphysis pubis(2 coxal bones articulate) & between vertebrae.
81
New cards
Synovial joints
Diarthrotic, most bodies of joints, contain articular cartilage, joint capsule, & synovial membrane
82
New cards
Parts of Synovial Joints
articular cartilage, subchondral plate, joint capsule, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, menisci, bursae
83
New cards
Joint capsule
tubular. 1. dense white fibrous CT- fibers attach to periosteum. 2. Ligaments-relatively inelastic, binds bone to bone.
84
New cards
articular cartilage
resistant to wear, prevents friction
85
New cards
subchondral plate
thickened layer of bone, shock absorption and protect joint from body weight and exercise.
86
New cards
synovial membrane
shiny loose CT, lines the synovial cavity
87
New cards
menisci
discs of fibrocartilage between articular surfaces
88
New cards
synovial fluid
clear viscous(thicker) fluid which moistens and lubricates the joint. Supplies the articular cartilage with nutrients.
89
New cards
bursae
fluid filled sacs. commonly found between skin and underlying bony prominences. cushion + aid tendons in movement.
90
New cards
ball and socket
egg shaped ball in a cup sized socket. widest ROM possible.
91
New cards
condyloid joints
(ellipsoidal)oval part in an ellipsoidal cavity. Variety of movement except rotation.
92
New cards
Gliding joints
(Plane). Flat or slightly curved surfaces. Slight back and forth motions.
93
New cards
Hinge joints
convex surface in a concave surface. movement in one plane, like a door.
94
New cards
Ex. of ball and socket joint
Humerus to scapula, femur to coxal.
95
New cards
Ex. of condyloid joint
metacarpals+phalanges
96
New cards
Ex. of gliding joints
carpals, tarsals.
97
New cards
Ex. of hinge joints
ulna to humerus, tibia to femur, all phalanges
98
New cards
Pivot joints
cylindrical surface rotating in a ring of bone or ligament. Rotation around a central axis.
99
New cards
Ex. of pivot joints
C1 to C2, radius to humerus
100
New cards
Saddle joints
have both convex and concoct surfaces. variety of movement in 2 planes.