Biology - 5 Communicable Diseases - 5.9 Human Defence Responses & 5.10 More About Plant Diseases & 5.11 Plant Defence Responses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Skin defences [4]
- barrier to microorganisms
- if cut, platelets cause clotting and create a scab; a barrier
- produces antimicrobial secretions to destroy pathogens
- covered in 'healthy' microorganisms that form another barrier
Respiratory and digestive defences [3]
- nose is full of hairs and mucus that trap pathogens and particulates
- trachea and bronchi secrete mucus to trap pathogens, then cilia waft it up to the throat where it is swallowed
- stomach produces acid that destroys pathogens in this mucus as well as in food and drink
Phagocyte
white blood cell that destroys pathogens by engulfing and digesting them
Lymphocyte
white blood cell that produces antibodies or antitoxins
Antibody
a protein that acts against a specific antigen and destroys it
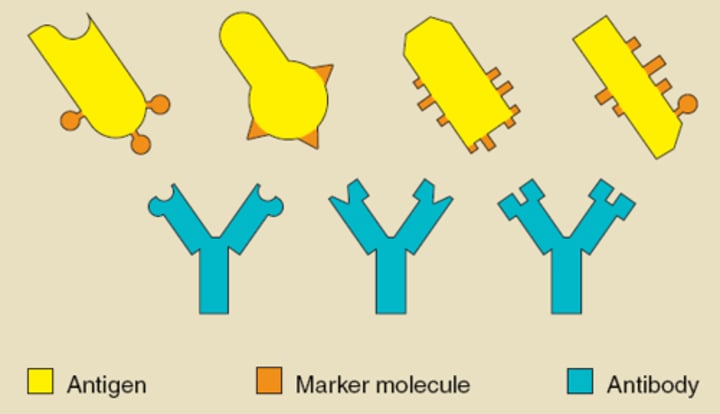
Antigen
substance that triggers an immune response
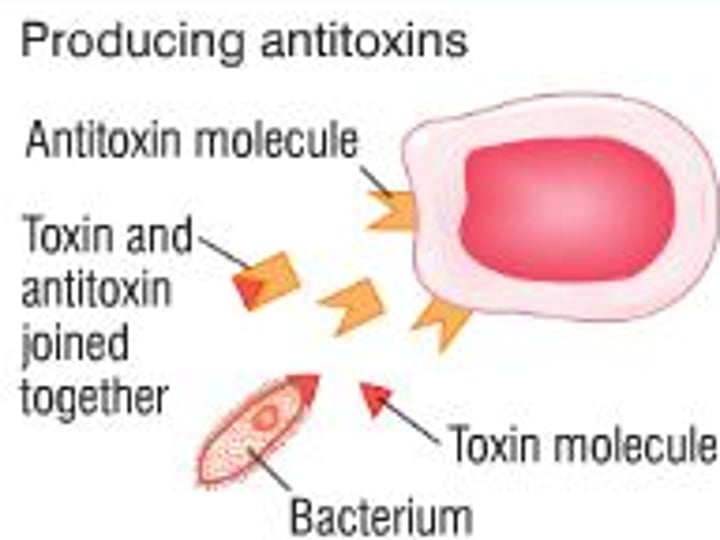
Antitoxin
agent that works to destroy (cancel out) toxins
Aphid
any of various small plant-sucking insects
What do aphids do to plants? [3]
- use their mouth to pierce and drink from the sugar-rich phloem sap
- take away products of photosynthesis
- act as vectors of disease
How can aphids be destroyed?
- chemical pesticides
- biological pest control (ladybirds) in enclosed spaces
Nematode worms and insect larvae...
feed on or in the plant roots and damage them, limiting the plant's water supply
Nitrate deficiency in plants [2]
- needed for production and synthesis of proteins
- growth will be stunted
Magnesium deficiency in plants [3]
- needed to produce chlorophyll
- yellowing leaves (chlorosis)
- stunted growth
Chlorosis
yellowing of leaves
Physical barriers (plants) [4]
- cellulose walls
- waxy cuticle is waterproof and acts as barrier
- bark on trees/layer of dead cells on stems
- leaf fall in Autumn
Chemical barriers [3]
- for example, mint and witch hazel
- plants produce antibacterial chemicals
- can be extracted for use
Defences against herbivores
- poisons
- thorns
- hairy stems and/or leaves
- drooping or curling when touched
- mimicry
Poison examples [3]
- foxglove
- deadly nightshade
- yew
Thorn examples [3]
- brambles
- cacti
- gorse
Hairy stems/leaves examples [3]
- lamb's ears
- pelargoniums
- nettles
Drooping or curling when touched example
mimosa pudica
How can mimicry be used?
imitating butterfly eggs to deter butterflies/caterpillars