ENSC 001 Midterm 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/219
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:49 AM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
1
New cards
What are the three aquatic ecosystems?
1) Freshwater
2) Estuaries
3) Marine
2) Estuaries
3) Marine
2
New cards
Weather
defined by day to day weather
3
New cards
Climate
defined by long term and precipitation
4
New cards
Biome
a large, relatively distinct terrestrial region with similar climate, soil, plants, and animals, regardless of where it occurs in the world.
5
New cards
How many biomes are there?
There are nine major biomes
1)Tundra
2) Boreal Forest
3)Temperate rainforest
4)Temperate deciduous forests
5)Grassland
6)Chaparral
7) Deserts
8)Savanna
9)Tropical rainforest
1)Tundra
2) Boreal Forest
3)Temperate rainforest
4)Temperate deciduous forests
5)Grassland
6)Chaparral
7) Deserts
8)Savanna
9)Tropical rainforest
6
New cards
Biome location is determined by?
It is determined by climate: temperature (which varies with both latitude and elevation) and precipitation.
7
New cards
What happens at biomes at the same latitude?
Even at the same latitude, biomes can change due to precipitation. i.e goes from tropical rain forest to dry tropical desert.
8
New cards
When you go up in latitude what happens to the biomes?
Going up in temperature is the same thing as going up in latitude. You can go from the desert to the peak of mountain.
9
New cards
Tundra (arctic or alpine)
Is a treeless biome in the far north with harsh, cold winters and extremely short summers.
There is a lack of trees due to the lack of precipitation.
There is a lack of trees due to the lack of precipitation.
10
New cards
Precipitation and Temperature in the Tundra?
Precipitation is extremely low: 10-25 cm/yr
Temperature: (5-50 degrees F)
Temperature: (5-50 degrees F)
11
New cards
Tundra soil and productivity?
Nutrient poor soils with little organic material --> permafrost present
There is low primary productivity because there isn't enough energy flow through the food web
Low species richness because vegetation is mostly grass and sedges and the food web is simple
There is low primary productivity because there isn't enough energy flow through the food web
Low species richness because vegetation is mostly grass and sedges and the food web is simple
12
New cards
Boreal Forests
A region of coniferous forests in the northern hemisphere, south of the tundra. (Canada and Alaska)
Covers about 11% of the land
Covers about 11% of the land
13
New cards
Precipitation and Temperature at the Boreal Forests?
Precipitation is 2x more than tundra: 50cm/yr
Temperature (4-60 degrees F) growing season is a little longer than the tundra, about 6 months above freezing temperature.
Temperature (4-60 degrees F) growing season is a little longer than the tundra, about 6 months above freezing temperature.
14
New cards
Boreal forests soil and productivity?
Soil is acidic and mineral poor with patchy permafrost
Vegetation is comprised of drought-resistant conifers
-> white spruce
-> balsam fir
-> eastern larch
Productivity is a little higher compared to tundra...
mostly small animals and migrating birds, a few larger animals such as caribou and moose are present
Vegetation is comprised of drought-resistant conifers
-> white spruce
-> balsam fir
-> eastern larch
Productivity is a little higher compared to tundra...
mostly small animals and migrating birds, a few larger animals such as caribou and moose are present
15
New cards
Temperate rainforest
Coniferous biome with cool weather, dense fog and high precipitation. (Northwest US: Washington and Oregon)
16
New cards
Precipitation and Temperature in the temperate rainforest?
There is about 127cm/yr = lots of precipitation
rain is heaviest during the winter
Temperature: Winters are mild and Summer are cool (42-60 F)
rain is heaviest during the winter
Temperature: Winters are mild and Summer are cool (42-60 F)
17
New cards
Temperate rainforest soil and productivity?
Soils are nutrient poor, but high in organic material because of dropped needles. The soil is nutrient poor because cool temperature slows decomposition.
Dominant Vegetation: Large evergreen trees, old-growth forest
Productivity: Very high species richness, variety of cool climate animal life
Dominant Vegetation: Large evergreen trees, old-growth forest
Productivity: Very high species richness, variety of cool climate animal life
18
New cards
Temperate deciduous forests
Forest biome that occurs in temperate areas with a moderate amount of precipitation. (Entire East Coast)
19
New cards
Precipitation and Temperature in the temperate deciduous forests?
Precipitation: 75-150cm/yr
Temperature: Seasonality, the biggest difference from everything else:
hot summers (extremely humid bc more moisture in the air 89%)
cold winters (37 degrees)
Spans from 37-77 degrees F
Temperature: Seasonality, the biggest difference from everything else:
hot summers (extremely humid bc more moisture in the air 89%)
cold winters (37 degrees)
Spans from 37-77 degrees F
20
New cards
Temperate deciduous forest soil and productivity?
Topsoil is rich in organic material and underlain by clay
vegetation is primarily deciduous
--> oak, maple, beech
animals
--> deer, bear, small animals
biome has been regenerated after farming and timber harvest
vegetation is primarily deciduous
--> oak, maple, beech
animals
--> deer, bear, small animals
biome has been regenerated after farming and timber harvest
21
New cards
Grassland
grasslands with hot summers, cold winters, and too little precipitation to support trees
90% of this biome has been lost to farmland (middle of US), this is because it's flat and you don't need to knock down trees
90% of this biome has been lost to farmland (middle of US), this is because it's flat and you don't need to knock down trees
22
New cards
Precipitation in the Grassland?
25-75 cm/yr tall grass prairies and short grass prairies
temperature (23-55 degrees)
temperature (23-55 degrees)
23
New cards
Grassland soil and productivity?
Soil has thick, organic material rich organic horizon, periodic fires prevent tree and shrub growth.
Animals: Used to be covered with bison (no more), smaller animals are still present (e.g. prairie dogs)
Animals: Used to be covered with bison (no more), smaller animals are still present (e.g. prairie dogs)
24
New cards
Chaparral
Called a Mediterranean Climate seen in Southern California and Greece
25
New cards
Temperature at Chaparral
Mild and moist winters
Hot and dry summers
Frequent fires
(52-74 degrees F)
Hot and dry summers
Frequent fires
(52-74 degrees F)
26
New cards
Chaparral soil and productivity?
Soil is thin and often not fertile
Vegetation: dense growth of evergreen shrubs, lush during the growing season
Animals: Mule deer, chipmunks, many species of birds
Vegetation: dense growth of evergreen shrubs, lush during the growing season
Animals: Mule deer, chipmunks, many species of birds
27
New cards
Deserts
Biome where lack of precipitation limits plant growth
28
New cards
Temperature and Precipitation in the Desert
Temp can vary greatly in 24hr period as well as yearly based on location (43-77F)
Precipitation less than 25cm/yr
Precipitation less than 25cm/yr
29
New cards
Desert soil and productivity?
Soils low in nutrients and high in salts
Productivity is low (primary) , vegetation is sparse (cacti and sagebrush), animals are very small to regulate temperature, not a lot of species diversity
Productivity is low (primary) , vegetation is sparse (cacti and sagebrush), animals are very small to regulate temperature, not a lot of species diversity
30
New cards
Savanna
Tropical grassland with widely scattered trees
located in Africa, around the equator
located in Africa, around the equator
31
New cards
Temperature and Precipitation in Savanna
Temperature varies little throughout the year (55-77 deg F)
Precipitation seasons regulated by precipitation, not temperature (76-150cm/yr)
Not as much rain as other forests, prone to fires
during the summer very little rain
Precipitation seasons regulated by precipitation, not temperature (76-150cm/yr)
Not as much rain as other forests, prone to fires
during the summer very little rain
32
New cards
Soil and Productivity in the Savanna's
Soil low in nutrients due to leaching
Vegetation --> wide expanses of grass, occasional Acacia trees, fire adaptive characteristics
Animals --> herds of hoofed animals, large predators - lions, hyenas
Vegetation --> wide expanses of grass, occasional Acacia trees, fire adaptive characteristics
Animals --> herds of hoofed animals, large predators - lions, hyenas
33
New cards
Tropical rainforest
lush, species-rich biome that occurs where climate is warm and moist throughout the year. Around equator (south america, amazon)
34
New cards
Precipitation tropical rainforest
200-450cm/yr
rains in summer, dry in winter
precipitation is much higher despite same latitude and roughly same temp
rains in summer, dry in winter
precipitation is much higher despite same latitude and roughly same temp
35
New cards
Productivity and soil in the tropical rainforest
Very productive
Most species-rich
Ancient, weathered, nutrient-poor soil --> nutrients tied up in vegetation, not soil
Vegetation --> 3 distinct canopy layers
Animals --> most abundant insect, reptiles and amphibians on earth
Most species-rich
Ancient, weathered, nutrient-poor soil --> nutrients tied up in vegetation, not soil
Vegetation --> 3 distinct canopy layers
Animals --> most abundant insect, reptiles and amphibians on earth
36
New cards
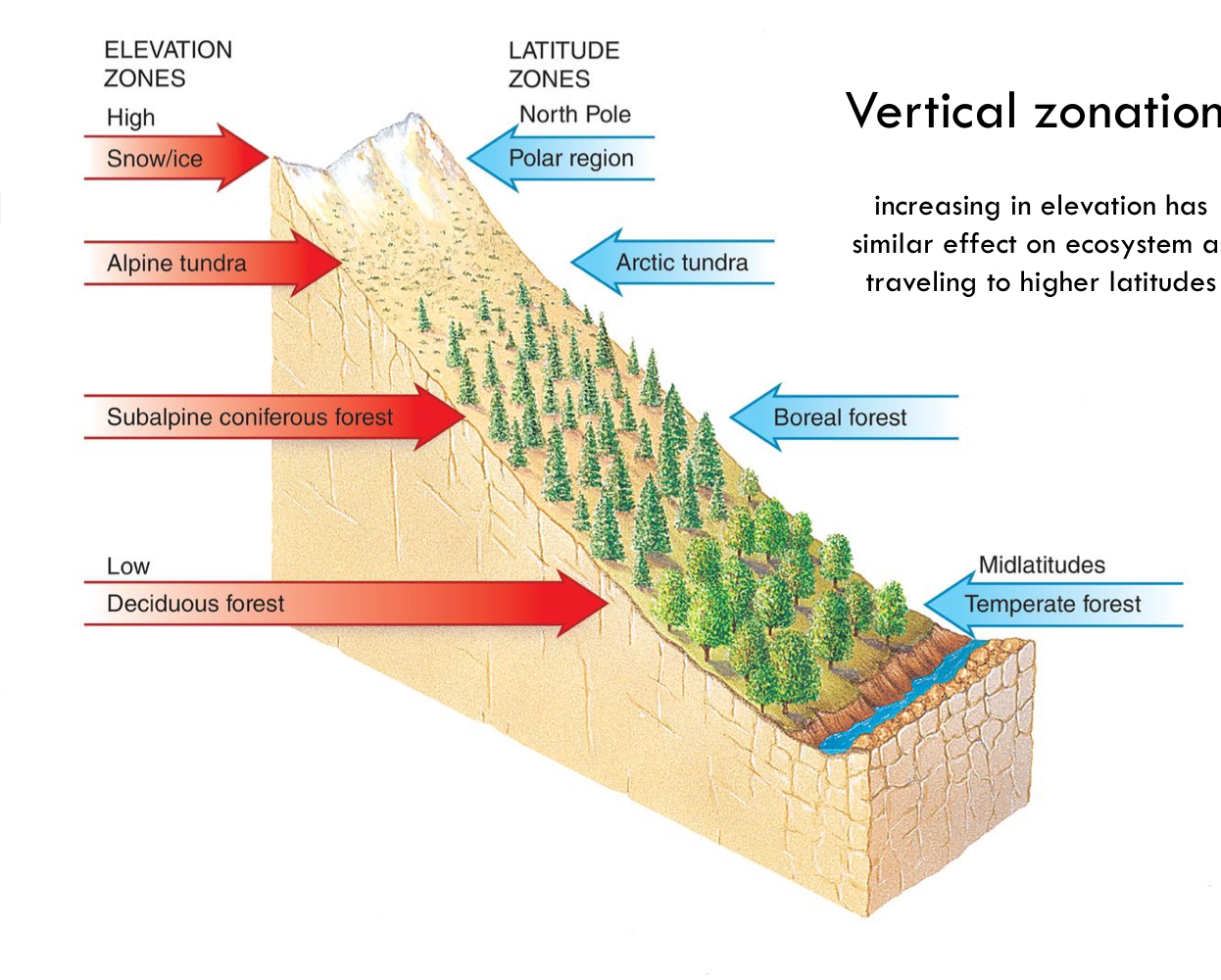
Vertical Zonation
increasing in elevation has similar effect on ecosystem as traveling to higher latitudes
37
New cards
Aquatic Ecosystem
Fundamental division: Freshwater (no salt) , Saltwater
Aquatic ecosystems are affected by: Dissolved oxygen level, light penetration, pH, presence/absence of currents
Aquatic ecosystems are affected by: Dissolved oxygen level, light penetration, pH, presence/absence of currents
38
New cards
3 main ecological categories of organisms
Plankton - free floating (the current moves them)
--> Phytoplankton - photosynthetic
--> Zooplankton - animal-like
Nekton - strong swimming
Benthos- bottom dwelling (crabs and lobsters that hang at the bottom)
--> Phytoplankton - photosynthetic
--> Zooplankton - animal-like
Nekton - strong swimming
Benthos- bottom dwelling (crabs and lobsters that hang at the bottom)
39
New cards
Freshwater ecosystems
Rivers and streams (lotic or flowing waters)
Lakes and ponds (lentic or standing water)
Marshes and swamps (standing water)
--> represents 2% of earth's surface
--> assist in recycling water back to the oceans
Lakes and ponds (lentic or standing water)
Marshes and swamps (standing water)
--> represents 2% of earth's surface
--> assist in recycling water back to the oceans
40
New cards
River continuum concept
Everything begins at the little headwater streams
water moves from headwaters to rivers to coastal ocean
change in physical features and food sources (abiotic differences)
results in change in biological features and ecosystem function
in streams, organisms adapted to fast flowing water (hooks, suction, flattened bodies)
in rivers, adaptation for swimming (streamlined)
water moves from headwaters to rivers to coastal ocean
change in physical features and food sources (abiotic differences)
results in change in biological features and ecosystem function
in streams, organisms adapted to fast flowing water (hooks, suction, flattened bodies)
in rivers, adaptation for swimming (streamlined)
41
New cards
Lakes and ponds
Body of freshwater that does not flow
3 zones
Littoral Zone, Limnetic Zone, Produndal Zone
Experience thermal stratification (depending on depth)
3 zones
Littoral Zone, Limnetic Zone, Produndal Zone
Experience thermal stratification (depending on depth)
42
New cards
Littoral Zone
shallow water area along the shore
43
New cards
Limnetic Zone
open water beyond the littoral zone
44
New cards
Profundal Zone
beneath the limnetic zone of deep lakes
45
New cards
Thermal stratification
temperature changes sharply with depth
thermocline
thermocline
46
New cards
Thermocline
Temperature transition between warmer surface water and colder water at depth (difference in density)
only present in warm months
only present in warm months
47
New cards
Marshes and swamps
land with shallow, fresh water for at least part of the year
characteristic soil and vegetation
were once regularly filled
recently--> ecosystem services have been better recognized
----> flood protection, water filtering, etc.
characteristic soil and vegetation
were once regularly filled
recently--> ecosystem services have been better recognized
----> flood protection, water filtering, etc.
48
New cards
Estuaries
Where freshwater and saltwater mix
eflux of fresh water going out, salt water coming in
Highly variable environment: Temperature, salinity, depth of light penetration
Highly productive: nutrient transported from land, tidal action circulates, high level of light penetrates shallow water, plants provide photosynthetic car
eflux of fresh water going out, salt water coming in
Highly variable environment: Temperature, salinity, depth of light penetration
Highly productive: nutrient transported from land, tidal action circulates, high level of light penetrates shallow water, plants provide photosynthetic car
49
New cards
Salt Marshes
usually in temperate estuaries
shallow wetlands dominated by a few species of salt tolerant grasses --> seen as worthless, filled in, and constructed over
services are extensive --> buffer land from storm energy, large cycling of organic matter for coast, habitat (particularly birds)
shallow wetlands dominated by a few species of salt tolerant grasses --> seen as worthless, filled in, and constructed over
services are extensive --> buffer land from storm energy, large cycling of organic matter for coast, habitat (particularly birds)
50
New cards
Marine ecosystem
pelagic environment --> shallower depths
subdivided into life zones
-intertidal zone
-benthic zone
-pelagic environment (neritic and oceanic provinces)
subdivided into life zones
-intertidal zone
-benthic zone
-pelagic environment (neritic and oceanic provinces)
51
New cards
Intertidal Zone
where salt water meets land
area of shoreline between low and high tide
biologically productive habitat
Stressful habitat --> splash zone, wave action, flooding, drying out
area of shoreline between low and high tide
biologically productive habitat
Stressful habitat --> splash zone, wave action, flooding, drying out
52
New cards
Benthic Zone
bottom of the ocean
ocean floor, extending from tidal zone to deep sea trenches
sediment is mostly mud --> burrowing worms and claims
3 zones: Bathyal, Abyssal, Hadal
ocean floor, extending from tidal zone to deep sea trenches
sediment is mostly mud --> burrowing worms and claims
3 zones: Bathyal, Abyssal, Hadal
53
New cards
Bathyal zones
200m - 4000m deep
54
New cards
Abyssal zones
4000m - 6000m deep
55
New cards
Hadal zones
6000m - bottom of deep sea trenches
56
New cards
Pelagic environment
all of the open ocean water, main divisions based on depth and light penetration
57
New cards
Euphotic zone
surface to 150m
sufficient light for photosynthesis; organisms are all floaters or swimmers
sufficient light for photosynthesis; organisms are all floaters or swimmers
58
New cards
Neritic province
Organisms are floaters or swimmers (zooplankton, whales)
water that overlies the continental shelf (to depth of 200m)
hypothermal vents
water that overlies the continental shelf (to depth of 200m)
hypothermal vents
59
New cards
Oceanic province
Water that overlies depths greater than 200m
Organisms are filter feeders, scavengers and predators
--> no light for photosynthesis, organisms adapted for darkness
--> marine snow (food particles falling from euphotic zone) support some life
Organisms are filter feeders, scavengers and predators
--> no light for photosynthesis, organisms adapted for darkness
--> marine snow (food particles falling from euphotic zone) support some life
60
New cards
Human impacts on the ocean
Nonpoint Source Polution, Invasive Species, Overfishing, Bycatch, Aquaculture, Point Source Pollution, Coastal Development, Habitat Destruction, Climate Change
61
New cards
What are the two indicators for human health?
Infant morality and Life expectancy
62
New cards
Infant mortality
how many children die before age of 1 year per 1,000 births (measured at county, state, region, and country levels)
63
New cards
Life expectancy
how long people are expected to live
64
New cards
Does life expectancy and infant mortality vary between industrialized vs. developing countries?
Yes!
It depends on access to basic necessities ( education, food, clean water, electricity, etc.)
It also depends on access to healthcare and public health services (prevention, medicine, antibiotics, vaccines, etc.)
It depends on access to basic necessities ( education, food, clean water, electricity, etc.)
It also depends on access to healthcare and public health services (prevention, medicine, antibiotics, vaccines, etc.)
65
New cards
Infant mortality rate (per 1000) by country (2013)
Industrialized countries have low infant mortality rates
Developing countries have very high infant mortality rates because they don't have access to health care and needed necessities (Africa)
Developing countries have very high infant mortality rates because they don't have access to health care and needed necessities (Africa)
66
New cards
Infant Mortality Rate (1950-2015)
in the US in 1950 it was about 32 but went down to 10 (pretty low)
whereas india went from 185 to about 50 (still high)
afghanistan ent from 245 in 1960 to about about 75 in 2015 (extremely high still)
whereas india went from 185 to about 50 (still high)
afghanistan ent from 245 in 1960 to about about 75 in 2015 (extremely high still)
67
New cards
Average life expectancy by country (years)
Industrialized countries (especially those with universal health care) have higher life expectancy about 70-80yrs old
Emerging countries have life expectancy from anything from 64 to under 40 yrs old (parts of Africa)
Emerging countries have life expectancy from anything from 64 to under 40 yrs old (parts of Africa)
68
New cards
Life expectancy in the US Counties
Coastal counties have higher life expectancy than those in the inland countries bc the inland counties have a lower income so less healthcare.
Those that live near the Mississippi river experience a life expectancy that is almost 20 years less than the highest part of the country (around 60yrs). Many public health issues and is a very poor low income area.
Those that live near the Mississippi river experience a life expectancy that is almost 20 years less than the highest part of the country (around 60yrs). Many public health issues and is a very poor low income area.
69
New cards
Life expectancy vs. household income within the US
Those that have a lower income die earlier... women die less early than the men that are in the same lower income conditions
Those that have a higher income die later... women and men have a smaller gap difference
Women top percentage income: 88.8 yrs
Women bottom percentage income: 78.5 yrs
Men top percentage income: 87.3 yrs
Men bottom percentage income: 72.3 yrs
Those that have a higher income die later... women and men have a smaller gap difference
Women top percentage income: 88.8 yrs
Women bottom percentage income: 78.5 yrs
Men top percentage income: 87.3 yrs
Men bottom percentage income: 72.3 yrs
70
New cards
What is health like in highly developed countries?
Health is relatively good --> avg life expectancy for men is 75 and 80 for women
the leading causes of death are chronic (associated with living longer)
--> cardiovascular disease (24%) and cancer (23%)
some premature deaths are caused by lifestyle
--> poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking
--> obesity and aging are major risk factors
the leading causes of death are chronic (associated with living longer)
--> cardiovascular disease (24%) and cancer (23%)
some premature deaths are caused by lifestyle
--> poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking
--> obesity and aging are major risk factors
71
New cards
Body mass index (BMI)
BMI = (Weight x 703) / Height^2
Weight in pounds, height in inches
BMI categories
underweight less than 18.5
healthy 18.5-24.9
overweight 25-29.9
obese over 30
(not accurate for muscular people)
Weight in pounds, height in inches
BMI categories
underweight less than 18.5
healthy 18.5-24.9
overweight 25-29.9
obese over 30
(not accurate for muscular people)
72
New cards
Why is obesity in men over 18 more common in industrialized countries?
More common in industrialized countries (North America) because industrialized countries have access to excess food and a more sedimentary lifestyle compared to those from emerging countries
73
New cards
Obesity rates by US counties
Once again coastal counties are not as bad, there is a very noticeable difference in the southeast counties because almost 50% of pop. is obese, they have higher obesity, higher cardiovascular disease, and lower incomes.
74
New cards
Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Rates by US counties
Coastal counties not as much, increased a lot in south east areas and inland areas. (due to lower income)
75
New cards
Cancer rates by country
Industrialized countries have higher rates of cancer because cancer is the disease of the old... the longer you live the greater your odds of getting cancer.
Those in emerging countries simply do not live long enough to develop cancer.
Those in emerging countries simply do not live long enough to develop cancer.
76
New cards
What cancer kills the most?
Lung and Pancreatic because it's extremely hard to screen for so it's usually to late to do anything about it.
Breast and Prostate cancer are easy to develop but can usually be caught early enough to treat.
Breast and Prostate cancer are easy to develop but can usually be caught early enough to treat.
77
New cards
Multistage Carcinogenesis
Technical term that describes how cancer is formed
78
New cards
What are the stages of Multistage Carcinogenesis?
1) Initiation - group of cells that have been exposed
2) Promotion - eventually mutations start to divide
3) Malignant Conversion - becomes more invasive
4) Progression - moves away form original site and goes through the blood stream
5) Cancer (metastasis)
This all happens over a long period of time
2) Promotion - eventually mutations start to divide
3) Malignant Conversion - becomes more invasive
4) Progression - moves away form original site and goes through the blood stream
5) Cancer (metastasis)
This all happens over a long period of time
79
New cards
What is health like in developing countries?
Biggest challenges are malnutrition, unsafe water, poor sanitation
The life expectancy is overall around 65 years but the lowest in the poorest countries are around 45 yrs (bc of AIDS epidemics)
Childhood mortality rate is high --> malnutrition, diarrheal disease, malaria, HIV/AIDS
The life expectancy is overall around 65 years but the lowest in the poorest countries are around 45 yrs (bc of AIDS epidemics)
Childhood mortality rate is high --> malnutrition, diarrheal disease, malaria, HIV/AIDS
80
New cards
Emerging disease
-not previously observed in humans
-usually jumps from an animal host
examples: AIDS, lyme disease, West Nile Virus
-usually jumps from an animal host
examples: AIDS, lyme disease, West Nile Virus
81
New cards
Reemerging disease
-existed in the past and recently increasing in incidence
examples: tuberculosis, yellow fever, malaria
examples: tuberculosis, yellow fever, malaria
82
New cards
Why are there emergence/reemergence of diseases?
Evolutions of diseases so it transitions to human hosts, diseases become more resistant to antibiotics, urbanization and crowding, more elderly who are susceptible to disease, pollution and environmental degradation, growth in international travel and commerce, and poverty and social inequality
83
New cards
What is the rate of typhoid fever in the US?
Was high in the 1920s but decreased to almost 0 by 1960 due to treating water supplies properly.
Chlorination was introduced in 1908 to treat drinking water supplies, and chlorine is still the most common disinfectant used in the US
Chlorination was introduced in 1908 to treat drinking water supplies, and chlorine is still the most common disinfectant used in the US
84
New cards
Typhoid fever
Source: injestion of water contaminated with the bacterium Salmonella enterica tyohi
Some Symptoms: Fevers up to 104 degrees, stomach pains, headache, loss of appetite, rash of flat, rose-colored spots
Annual cases
5700 cases per year in the US (75% come from traveling overseas)
21.5 million cases and 200,000 deaths per year in the Developing world
Some Symptoms: Fevers up to 104 degrees, stomach pains, headache, loss of appetite, rash of flat, rose-colored spots
Annual cases
5700 cases per year in the US (75% come from traveling overseas)
21.5 million cases and 200,000 deaths per year in the Developing world
85
New cards
Environmental Pollution and Disease
Difficult to link pollutants to effects on people due to persistence, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification.
pollution contaminates air, water, soil, food --> humans come into contact --> exposure to pollution causes adverse health effects
pollution contaminates air, water, soil, food --> humans come into contact --> exposure to pollution causes adverse health effects
86
New cards
What are the core disciplines that underpin the field of environmental health?
1) exposure assessment
2) toxicology
3) epidemiology
2) toxicology
3) epidemiology
87
New cards
Persistence
A characteristic of certain chemicals that are extremely stable and may take many years to break down into simpler forms by natural processes.
Natural decomposers (bacteria) have not evolved a way to break it down
Examples: Synthetic Chemicals such as DDT
Natural decomposers (bacteria) have not evolved a way to break it down
Examples: Synthetic Chemicals such as DDT
88
New cards
Bioaccumulation
Buildup of a persistent toxic substance in an organism's body often in fatty tissues
--> synthetic chemicals do not metabolize well and remain in the body for extended periods of time
Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) is a good example of bioaccumulation because the concentration increases in breast milk over time passes.
Ex #2: As fish fishes grow up they continue to have an increase in contaminant levels
--> synthetic chemicals do not metabolize well and remain in the body for extended periods of time
Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) is a good example of bioaccumulation because the concentration increases in breast milk over time passes.
Ex #2: As fish fishes grow up they continue to have an increase in contaminant levels
89
New cards
Biomagnification
The increased concentration of toxic chemicals in the tissues of organisms that are at higher levels in food webs
ex: 0.00005ppm in the water --> 0.04 ppm in primary producer --> 0.16ppm in primary consumer --> 0.28ppm in secondary consumer --> 2.07 ppm in secondary consumer ---> 75.5 ppm in tertiary consumer. This is an increase of 1.5 million times
bc of this DDT nearly killed off the bald eagle
travels through the food web
ex: 0.00005ppm in the water --> 0.04 ppm in primary producer --> 0.16ppm in primary consumer --> 0.28ppm in secondary consumer --> 2.07 ppm in secondary consumer ---> 75.5 ppm in tertiary consumer. This is an increase of 1.5 million times
bc of this DDT nearly killed off the bald eagle
travels through the food web
90
New cards
Endocrine disrupters
A chemical that mimics or interferes with the actions of the endocrine system in humans and wildlife
--> ex: PCBs, dioxins, heavy metals (lead and mercury) , DDT
Animals exposed to these chemicals have altered reproductive development and are often sterile
--> ex: PCBs, dioxins, heavy metals (lead and mercury) , DDT
Animals exposed to these chemicals have altered reproductive development and are often sterile
91
New cards
Do endocrine disruptors contribute to rising cancer rates?
Yes, hormonally related cancers are increasing (breast and testicular)
Phthalates have been implicated as potential endocrine disrupters --> which are common ingredients in cosmetics, fragrances, nail polish, medication, toys, and food packaging
Phthalates have been implicated as potential endocrine disrupters --> which are common ingredients in cosmetics, fragrances, nail polish, medication, toys, and food packaging
92
New cards
Bisphenol A (BPA)
is a potential endocrine disruptor
it is a chemical in hard plastics (baby & drink bottles)
banned in many countries and CA (not in US and Australia)
it is a chemical in hard plastics (baby & drink bottles)
banned in many countries and CA (not in US and Australia)
93
New cards
What is environmental health?
According to the World Health Organization
"Environmental health addresses all the physical, chemical, and biological factors external to a person, and all the related factors impacting behaviors. It encompasses the assessment and control of those environmental factors that can potentially affect health."
"Environmental health addresses all the physical, chemical, and biological factors external to a person, and all the related factors impacting behaviors. It encompasses the assessment and control of those environmental factors that can potentially affect health."
94
New cards
Exposure Assessment
Certain measurements out in the field
i.e transmission of covid within a population
i.e transmission of covid within a population
95
New cards
toxicology
is the study of the effects of toxicants on the human body
96
New cards
epidemiology
the branch of medical science dealing with the transmission and control of disease
97
New cards
risk assessment
what's the scene, what's the toxicity? Is the risk small or is it actually a problem?
is it economically worth it to work on the risk?
is it economically worth it to work on the risk?
98
New cards
risk management
identifying steps and policies that can help manage the risks
99
New cards
What are some indoor aggregate human exposure?
Inhalation of Contaminated Air, House dust, Drinking Water, Food, Plastics, Flame retardants, Dermal exposure through touching dust
100
New cards
What are some outdoor aggregate human exposure?
Air, Soil, Drinking Water, Recreation water, Food, Outdoor air is going to be driven by ozone exposure, particulate matter, and vehicle emissions.