Community Ecology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Species richness
The number of species in a community
Species evenness
the relative abundance of the different species in a community
Species diversity
Species richness and evenness
Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index
Index to quantify species diversity
If similar in richness then the more even is more diverse
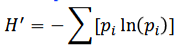
Why measure species diversity
It offers insight into a community’s health and stability
A higher H indicates productivity and stability
A lower H can signal a community is under stress
Ecosystem Analyses
Energy and nutrient flow through communities
How communities resist environmental stresses
The overall function and resilience of communities
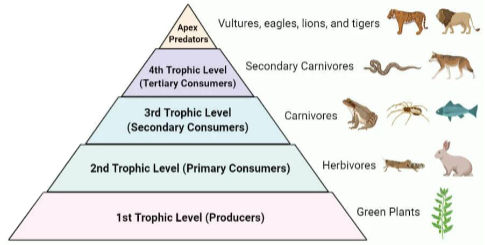
Trophic Level
Trophic levels are linked by the feeding relationships within the community
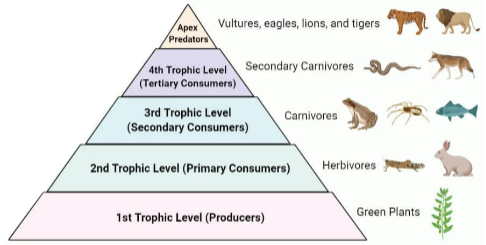
Grazing food web
Primary Producers (Plants)
Primary Consumers (Herbivores)
Secondary Consumers (Carnivores)
Tertiary Consumers (Secondary carnivores)
Apex Predators (Vultures, eagles, lions, tigers)
Detrital food web
Detritivores and decomposers
Direct Interactions effects
When the actions of one species directly impacts another species
Cheetahs kill gazelles
Bee pollinates flowers
Indirect Interactions effects
When the actions of one species on another is mediated by a third species
Birds indirectly benefiting a plant by reducing the number of caterpillars
Trophic cascade (effects go down the trophic levels)
Trophic cascade
Introducing or removing a top keystone predator
It effects trick down throughout trophic levels
Bob Paine
Trophic cascade in intertidal communities
Sea stars were a top predator and created diversity within the intertidal community by regulating the population of dominant mussels.
Keystone predator
A predator that has a large but indirect effect on its native habitats
Sea stars (Bob Paine)
Ecological succession
The change in species composition of a community over time
Observing succession directly
Document changes in community composition over time
The island of Krakatau in Indonesia
Researchers have documented the colonization of new ecosystems after volcano erupted.
Difficult because succession happens over decades
Observing succession Indirectly
Examine communities that began succession at different times
The size of the lakes in Michigan have shrunk
Ecologists assumed that plants farthest from the lake were the oldest and reflected more advance stages of succession
Difficult to know whether the initial conditions were the same in different communities
Primary Succession
Begins from scratch
Takes a long time (hundreds to thousands of years)
first lichens develop on bare rock
Secondary succession
Occur in areas of devastation where above ground vegetation is eliminated
from fires, logging, tornadoes…
Takes less time (decades to hundreds of years)
Pioneer species
Less competitive stage so…
Small
Reproduce early
Little parental investments
High reproductive rate
long seed viability
low shade tolerance
Climax species
More competitive stage so…
Large
reproduce late
Exhibit more parental investment
low reproductive rate
short seed viability
high shade tolerance
Island Biogeography
Understanding what determines species richness and diversity in communities
Islands are consider natural laboratories
Examining the impact of the island size and distance from the mainland on species richness
Island Biogeorgraphy Takeaways
Size matters
Large: Greater species abunadnace
Small: Greater species extinction
Distance to mainland matters
Closer: Higher diversity
Farther: Lower richness
Rates of immigration vs extinction
Equilibrium theory of species diversity
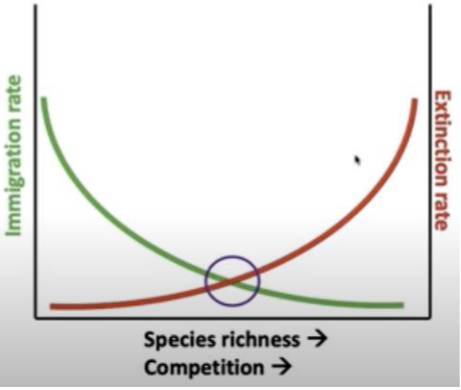
Large, close islands
High species richness
High Immigration
Low extinction
High competition
Small, distant islands
Low species richness
Low immigration
High extinction