Anatomy of the eye
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
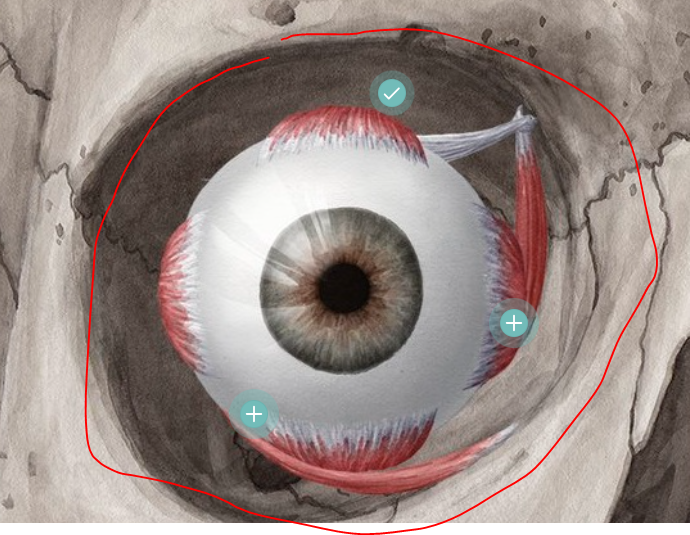
eye socket
hosts the eyeball and associated structures
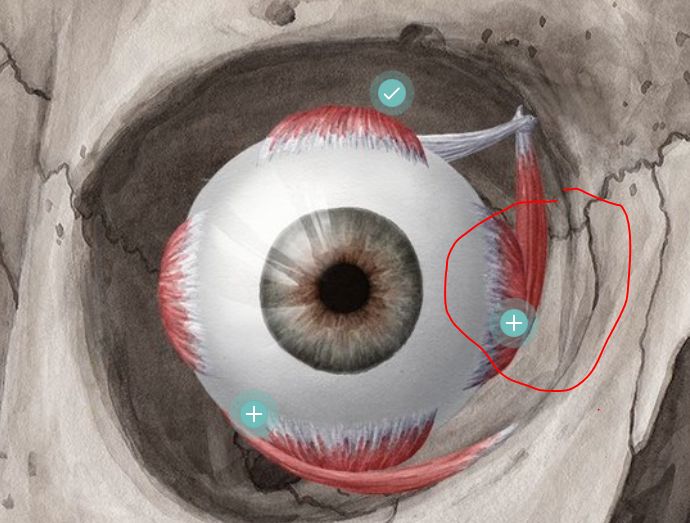
eye muscle
6 major muscles attached to eyeball, work to rotate the eye, move the eye up/down/side-to-side, can move eye in any direction
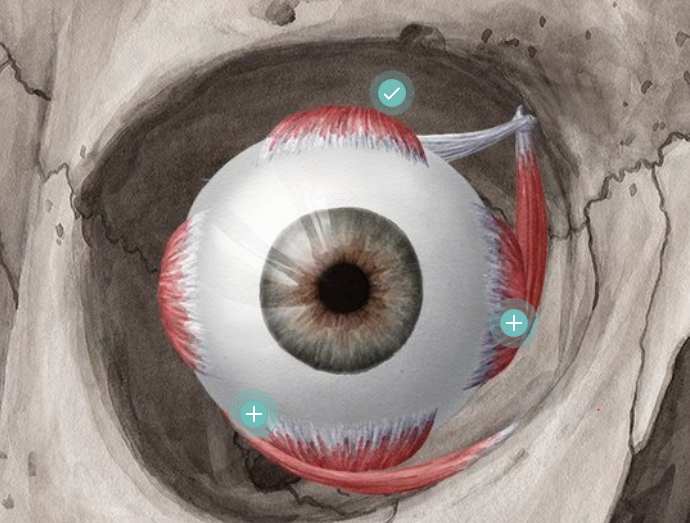
eyeball
largest structure in the eye socket, captures an image
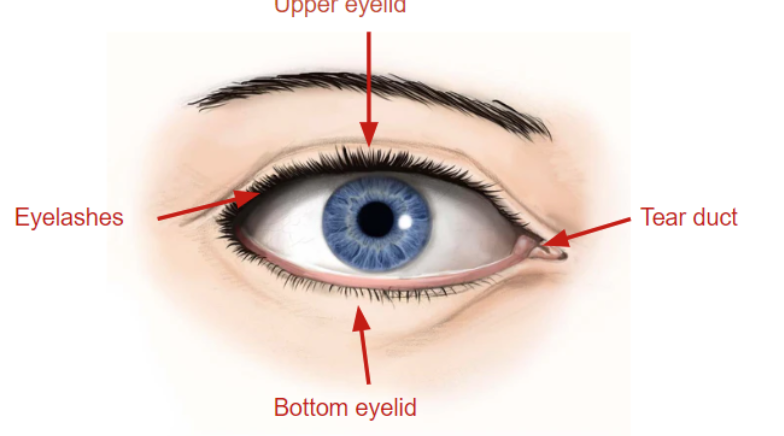
eyelids
soft tissues that protect and cover the eyeball, helps prevent injury/infection/disease
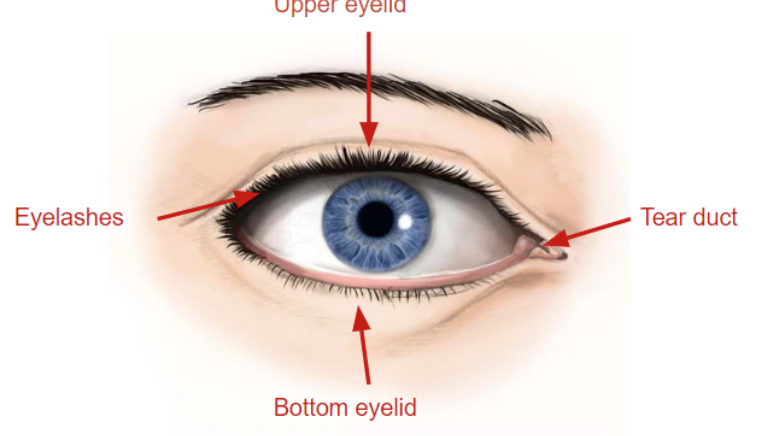
eyelashes
hairs that grow on edges of eyelids, sensitive to touch which signals the eye to close to protect from foreign particles
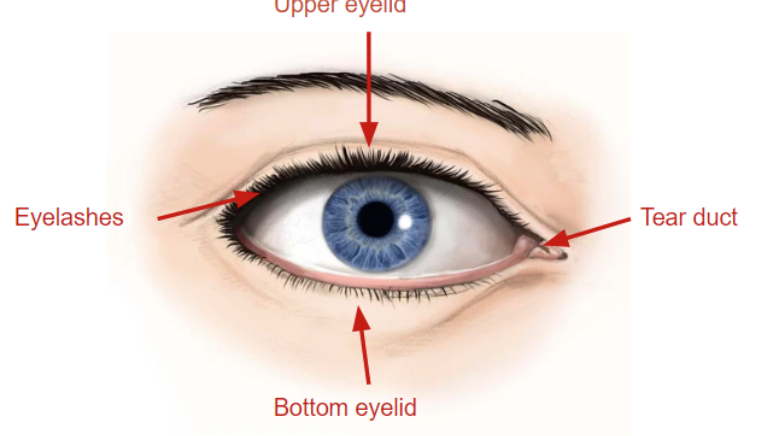
tear duct
in the inner corner of eye, part of tear drainage system that goes from the eye, back of the nose, and down the throat
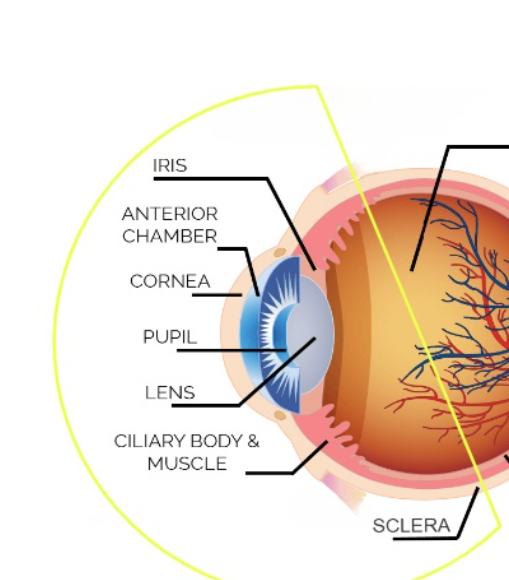
anterior segment of eye
iris, anterior chamber, cornea, pupil, lens, ciliary body & muscle, sclera
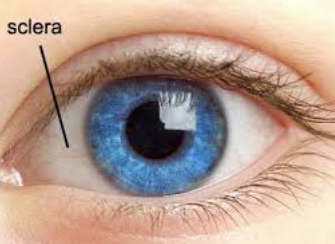
sclera
white part that covers eye surface, strong and allows for extraocular muscle attachment
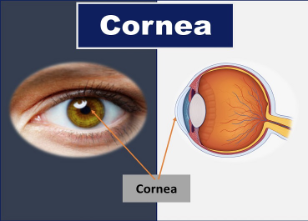
cornea
like a window, transparent (no blood vessels), allows light to transmit and focus to the back of the eye to protect, is the 1st point of refraction (dome shaped), in front of the iris and pupil, 70% of the eye’s focusing power
anterior chamber
behind the cornea is a fluid-filled space, the fluid is an aqueous humor, is constantly being produced and drained to keep eye pressure, nourishes eye
iris
colored part of the eye, has the dilator and the sphincter that help control pupil size
pupil
black hole in the middle of the iris, transmits light to the retina, changes due to muscles of the iris and amount of light present
lens
behind the pupil, helps focus the light and changes shape to help focus on up close objects, tiny fibers are attached to hold the lens which suspends it from the wall, has the ciliary body and muscle which are located behind the iris, 30% of the eye’s focusing power
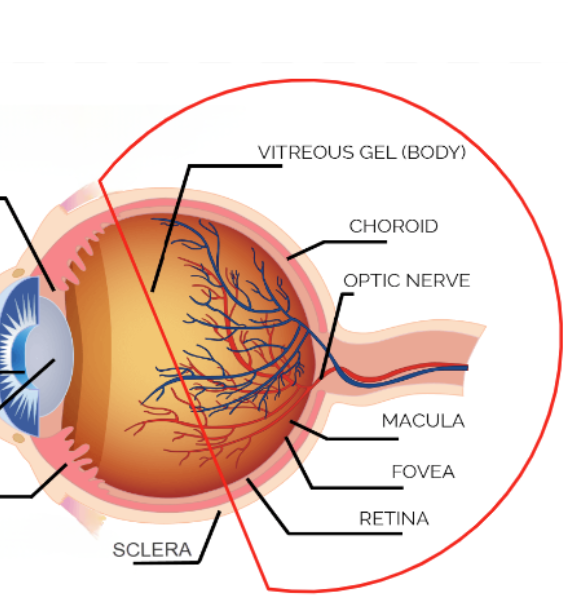
posterior segment
vitreous gel (body), choroid, optic nerve, macula, fovea, retina
vitreous body
in between the lens and the back of the eye, makes up 80% of the eye, has the jellylike substance (vitreous humor), has water/collagen/proteins/salts/sugars, maintains the shape of the eye and protects the inner structures
choroid
thin pigmented layer between retina and sclera, has blood vessels that nourish the back of the eye with oxygen and nutrients, helps protect the blood vessels and absorbs the light
optic nerve
communication cable made of millions of fibers that trasmit visual messages
retina
thin light sensitive membrane that lines the back of the eye, sends the electrical impulses from light and sends them through the optic nerve, it discriminates colors/detects movement/identifies shapes, center of the retina is the macula which is essential for central fine detailed vision
macula
has special light sensitive cells which allows us to see fine details and colors, the center is the fovea and is responsible for the clear central 20/20 vision