Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes; Organelles
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Archea
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan
Bacteria
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls containing peptidoglycan
Eukarya
Domain of all organisms whose cells have nuclei, including protists, plants, fungi, and animals
3 domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Eukaryote
A complex cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotic cells
contain their own organs AKA "organelles" and can live as single-celled organisms and they make up all multicellular organisms
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Ribosomes
makes proteins; assemble amino acids into proteins
4 kingdoms of eukarya
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
Kingdom Protista
Simplest eukaryotic organisms; single-celled and some looked like a green leaf
Kingdom Fungi
Consists of unicellular and multicellular organisms that cannot make their own food (heterotrophs) (mushrooms, molds, mildew)
Kingdom Plantae
Complex, multi-cellular organisms that use photosynthesis to make food. (mosses, flowering plants)
Kingdom Animalia
contain organisms that are multicellular eukaryotes including vertebrates and invertebrates. (sponges, hydra, insects, fish, mammals)
Cell Size is Limited
too little =cant contain all the organelles necessary to carry on there life processes
too big = too big for things to diffuse around in effectively and efficiently
The surface area-to-volume ratio of a cell
As a cell grows in size, its surface area to volume ratio decreases. It performs chemical reactions faster, but it has a harder time getting nutrients in and waste out.
The volume of a cell
determines the amount of chemical activity it can carry out per unit time.
The surface are of a cell
determines the amount of substances the cell can take in from the environment and the amount of waste it can release.
Organelle functions #1
transporting waste to cell membrane and out of the cell
Organelle functions #2
transforming energy in food (glucose) into energy cell functions
Organelle functions #3
maintaining the cell's structure
Organelle functions #4
making large biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids)
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
Mitachondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
Cell Wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth because it lacks ribosomes on its surface. An endomembrane system where lipids are created, processing of drugs and poison are absorbed, storing calcium ions
Protein transport
When the molecule is ready to be transported out of the Endoplasmic Reticulum it gets packaged into a transport vesicle. This vesicle is made of proteins from the ER then it travels to Golgi Apparatus.
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell (digestive enzymes)
Proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues; carries out vital functions across cells
Chromosomes Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes: have one chromosome which is double-stranded and circular. Eukaryotes: the number of chromosomes is dependent on different species; tightly coiled of DNA and associated proteins make up chromatin
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
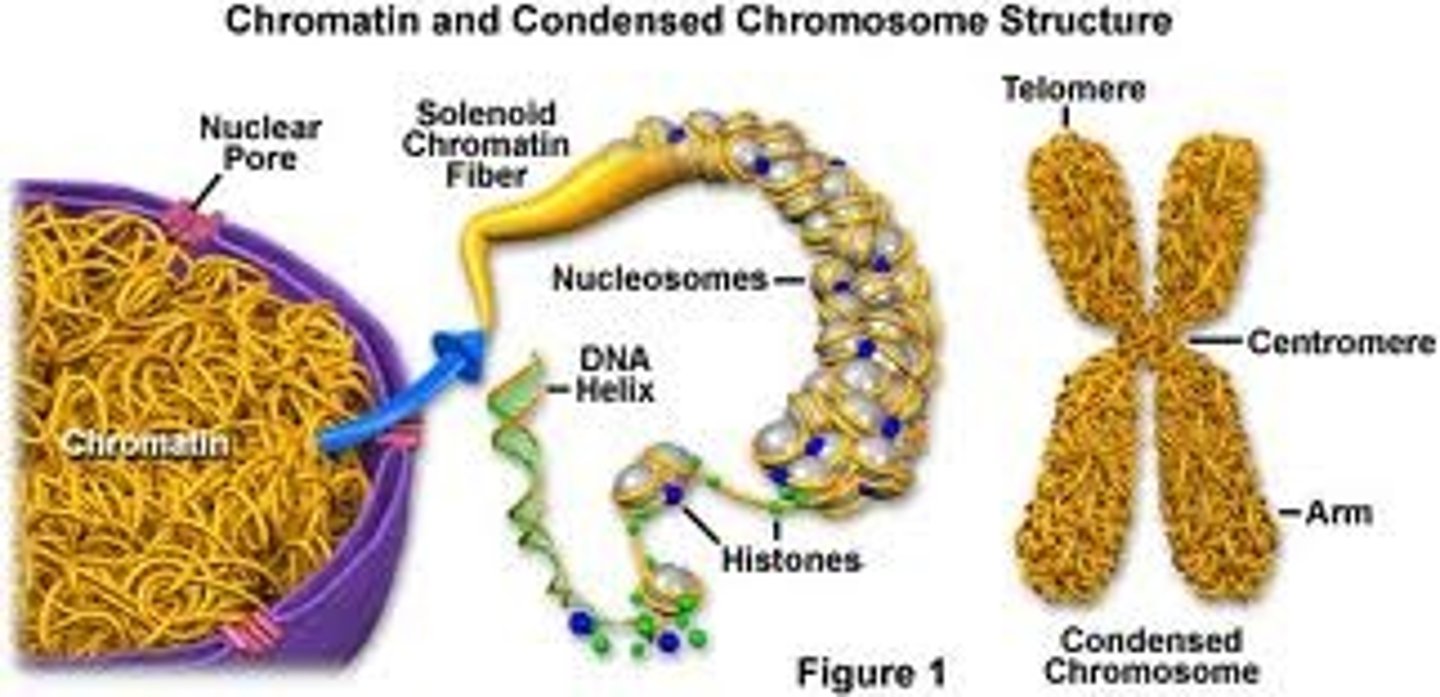
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
sister chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
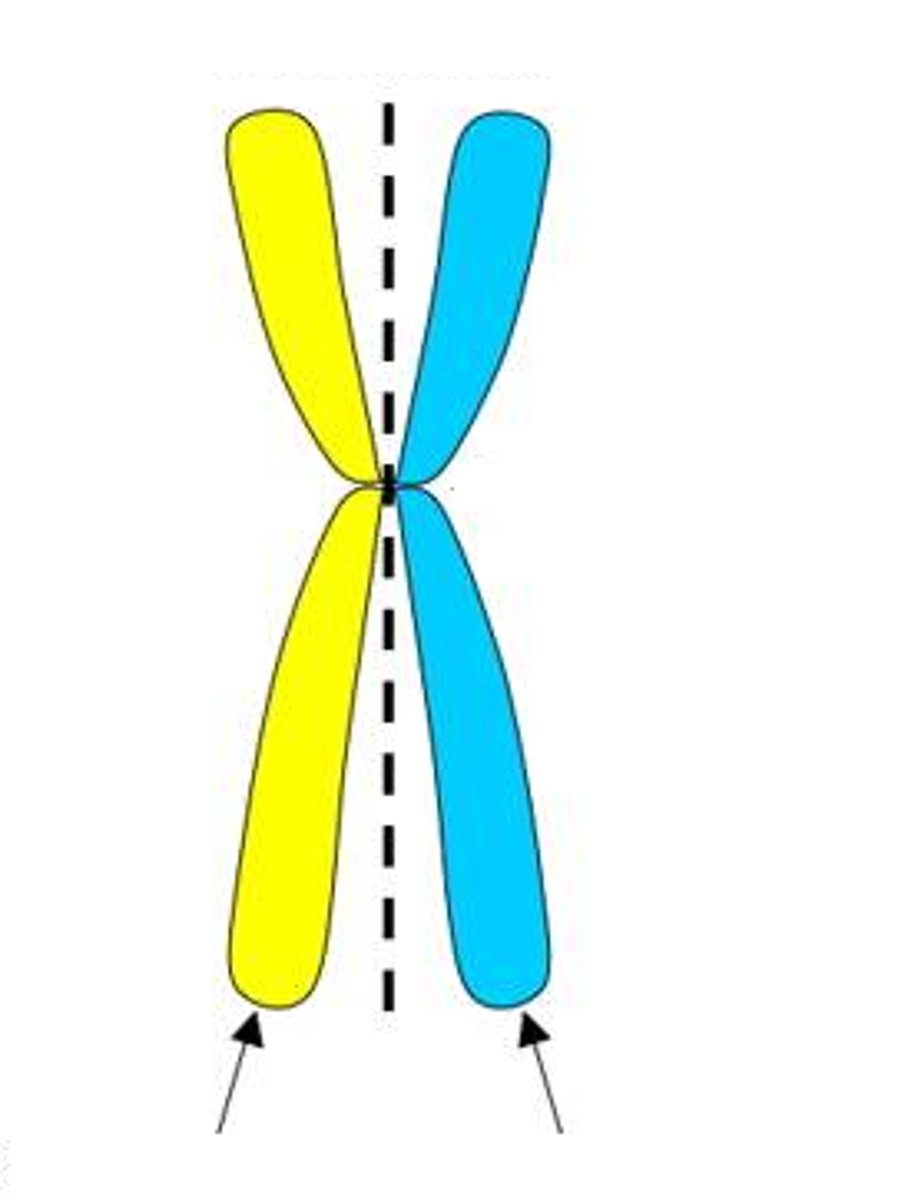
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
endomembrane system
This system is involved in the production and transportation of cell's protein and other products or waste. Separates cells into different compartments or organelles
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
plasma membrane
a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and other molecules interspersed throughout; it is a barrier between the cell interior and the exterior environment
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Insulin
protein hormone made by cells of pancreas that enables tp take cells to take glucose in from blood
Endocytosis
opposite of exocytosis; process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Pintocytosis
cellular drinking; taking in liquids but the cell wants substances within the liquid, not the actual liquid.
endosymbiotic theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
contractile vacuole
founded in certain single-celled protist; they act as pumps to get rid of excess water from the cell
food vaculoes
ingest food particles and then the particles fuse with a lysosomes which contains enzymes for digestion