control of heartbeat/ electrical activity of the heart
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what is the heart made up of?
cardiac muscle
myogenic
The heart can initiate its own contractions within its muscle, without nerve impulses.
name the features of the heart that controls its heartbeat →location
→role
-sino-atrial node (SAN)
→wall of right atrium
→ a pacemaker
-atrioventricular node (AVN)
→in the right atrium, near the septum
→receives the impulse from the SAN.
-bundle of His
→ in septum
→conducts the impulse from the AVN to the Purkyne tissue.
-Purkyne tissue
→ventricular walls
→conducts the impulse to the ventricle walls
describe how heart beat occurs
-The SAN produces electrical impulses [waves of excitation/ depolarisation]
-the impulse spreads across the atria, causing the atria to contract
-The impulse reaches the atrioventricular node (AVN) and is delayed slightly→This allows the ventricles to fill up with blood before contracting
-The bundle of His receives the impulse and conducts it to the apex (base) of the heart.
-the impulse travels through the Purkyne fibres, which branch through the ventricle walls
-This causes the ventricles to contract from the bottom up
![<p>-The <strong>SAN</strong> produces <u>electrical impulses</u> [waves of excitation/ depolarisation]</p><p>-the impulse spreads across the atria, causing the atria to <u>contract</u></p><p>-The impulse reaches the <strong>atrioventricular node (AVN) </strong>and is <u>delayed slightly</u>→This allows the ventricles to fill up with blood before contracting</p><p>-The <strong>bundle of His</strong> receives the impulse and conducts it to the apex (base) of the heart.</p><p>-the impulse travels through the <strong>Purkyne fibres</strong>, which <u>branch through the ventricle walls</u><br>-This causes the ventricles to contract from the <u>bottom up</u></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3cb7e394-c447-4202-b977-cd430d6b046f.png)
role of non-conducting tissue
prevents the electrical impulse from passing directly from the atria to the ventricles.
What changes in the body may change heart activity? (3)
-exercise
-stress
-sleep
name of machine used to check function of heart.
→What does it record?
→how do they work?
Electrocardiograph
→records the electrical activity of the heart
→electrodes are placed on the chest to record change in polarisation in the heart muscle
what happens when heart muscle contracts and relaxes
-it depolarises (loses electrical charge) when it contracts
-it repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes
name of trace produced by electrocardiograph
→parts of it
electrocardiogram (ECG)
→ -P wave→ contraction (depolarisation) of the atria
-QRS complex→ contraction (depolarisation) of the ventricles [Q→ electrical impulses going down the Bundle of His]
-T wave→ relaxation (repolarisation) of the ventricles
![<p><strong>electrocardiogram (ECG)</strong></p><p>→ -<strong>P wave</strong>→ contraction (depolarisation) of the atria</p><p> -<strong>QRS complex</strong>→ contraction (depolarisation) of the ventricles [Q→ <span>electrical impulses going down the Bundle of His]</span></p><p> -<strong>T wave</strong>→ relaxation (repolarisation) of the ventricles</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f0568eb8-e6f2-4860-95a2-6e2ad3418f6f.png)
heart rate formula
heart rate=60/ time taken for one heartbeat
normal heart rate
60-100 bpm
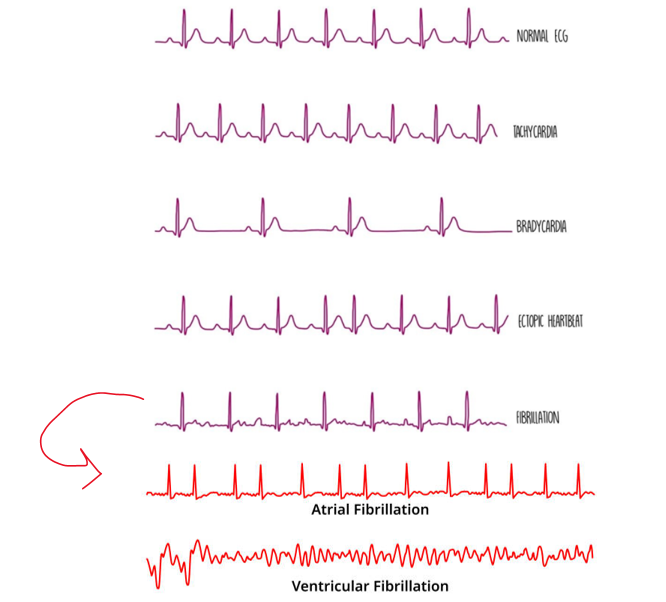
types of abnormal activity
Tachycardia - fast heartbeat (over 100 bpm)
Bradycardia - slow heartbeat (under 60 bpm)
ectopic heartbeat - an extra heartbeat that occurs out of the normal rhythm.
fibrillation - irregular heartbeat
→2 types: atrial and ventricular fibrillation
how might some abnormal activity be treated?
pacemaker for bradycardia
reduce stress for ectopic heartbeat