Biological diversity chapter 16
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Did Darwin come up with evolution?
no he came up with the mechanism to explain evolution
evolution acts on ________ but we measure based on ______
individuals (phenotypes), population (looking at alleles)
true or false all animals produce more offspring than can survive? if true what does this lead to?
true, this leads to lots of competition for resources.
true or false all traits are based on environment
false some traits are based on genetics, some are based on environment
does evolution have an end goal?
evolution does not have an end goal.
what is inference?
differential reproductive success
what is differential reproductive success?
a composite measure of how well you survive and reproduce (in terms of the local environment)
what are some examples of why we learn evolutionary biology?
antibiotics causing super bugs and HIV needing a cocktail of drugs to be effective against it
What is natural selection?
when an animal selects a mate based on inheritable things that will lead to being more likely to survive
what is artificial selection
when humans force animals with certain phenotypes to reproduce (ex. dogs)
What is your fitness level if you dont reproduce?
zero or near zero
true or false evolution is slow
false evolution can occur quickly (for some flies it can evolve over hours, days, weeks.
if evolution is slow what occurs over a long time?
speciation
what is a hypothesis?
a conjecture which may or may not be true
what is a theory?
an idea which is tested over and over which has not been refuted just refined
true or false evolution is a theory about the origin of life?
false, evolution by natural selection is focused on how life ad survival changed after origin
is evolution linear?
no
is fitness different based on who you mate with?
yes
Is evolution the same as natural selection?
no
true or false evolution is random
false it is not random. only some variants survive
does natural selection try to adapt?
no natural selection does not give what they need it just acts on the phenotype/genotype most likely to survive
does natural selection give organisms what they need?
no natural selection is constantly changing and if there is no phenotype that fits the environment that organism will go extinct
what is kin selection?
where you would do anything to let your kind survive
what is direct fitness?
when you have your own kids
what is indirect fitness?
when you help your family have kids
What is altruism?
behavior of an animal that benefits another at its own expense (ex. prairie dog)
is evolution a theory?
yes
How do evolutionary biologists study evolution?
by studying species with a quick turn around time
true or false evolutionary biology is unifying across all life sciences?
true
true or false evolutionary biology cannot be integrated into psychology?
false evolutionary biology can be used to explain alot of different topics
what explains diversity/ is an important driver of evolution?
natural selection
what can evolution help explain?
diversity of life and how populations evolve over generations in response to environmental pressures
What is considered human mediated evolution?
artificial selection
true or false humans don’t have the same selection pressure as other animals
true
Can humans adapt and evolve during their lifetime?
no that is why you look cross generation
is fitness a set measure?
no fitness is a relative (dynamic process) that changes based on phenotypes and the surrounding environment
endomentional space measures _____
fitness
What is a population?
a group of interbreeding individuals of a species that live together in a specific place
true or false heritability is not a continuum
false heritability is a continuum
is it considered selection if there is no genetic component?
no
what does evolution come from?
variability and the heritability of that variation
did darwin study darwin finches or mocking birds first?
mocking birds
What is adaption?
an inherited characteristic making it better for survival and reproduction.
does adaption continue if the environment stays the same?
yes if the environment is stable the adaption will make it even more suited or that field
What is fitness?
a composite measure of survival and reproductive success (a relative measure for that specific generation)
does fitness require variable components?
yes
Mutation
random heritable changes in the DNA sequences.
what can cause mutations
errors in DNA replication
physical agents
chemical agents
biological agents
do prey adapt to the environment?
yes
can there be more than one peak (optimum) fitness?
yes you can have two peak (optimum) fitness
What is the rate of change in a population determined by?
generation times, shorter generations change quicker
What are the two ways you can study natural selection and fitness?
passive and active study
What are some examples of model studies for evolution?
darwin finches
flies
yeast
stickelback
guppies
mice
zebrafish
bowerbirds
What is natural theology?
aristotle’s classification system mixed with biblical creation
What were the three main points stated by natural theology?
organisms had been specially created by god
species could never change or become extinct
new species could never arrise
Who developed the branch of biology that classifies organisms (taxonomy)
Carolus Linnaeus
how did Carolus Linnaeus develop taxonomy?
started naming things based on phenotypes, used common phenotypes as genus and determined common ancestry
are aquired characteristics inherited?
no they are not inherited
what is epigenetics?
the study of noninherited factors that affect genes
Why is darwin’s voyage important?
because he observed biodiverse animals with different phenotypes surviving in different areas
what three major areas of studies provided insight for darwin?
Geology and fossil records
studying geology (new at darwins time)
earth was older than originally thought
looks at fossils
geographic and distribution of species
travel was rare so they usually only saw one phenotype for an animal
comparitive morphology of species
people paid to shoot animals for museums for people to see different animals
What information did earths geology and the fossil records give?
change in the earths lay out (marine fossils found on mountain)
species CAN go extinct
and fossils showed things could evolve
what is biogeography ?
studies of the world distribution of plants and animals
What are vestigial structures?
useless parts observed today- must have functioned in ancestral organisms
What is homology
the study of likeness (inherited by a common ancestor)
what is homoplasy?
similarities but not inherited by a common ancestor just due to similar environment (ex. sharks and orcas)
What is coevolution
where organisms evolve with the environment
What was darwins conclusion?
all organisms are related by a common ancestor but have changed or evolved over time
How many years did darwin wait to publish his findings and why?
12-14 years and he waited because he was worried about backlash
Who had an idea similar to darwins?
Wallace
Why did darwin finally publish his findings?
because Wallace sent him a letter with the same idea so darwin rushed to publish it
What was Malthus influence on Darwin and Wallace?
stated that gains in agricultural technology cant keep up to allow proper food supply if populations grow exponentially, this influenced Darwin and Wallace idea of competition
What is carrying capacity?
the number of resources able to support a specific number of individuals
true or false humans can artificially increase the carrying capacity until a certain threshold
true
What is evolution?
the change in allele frequency over time
How many factors affect evolution and what are they?
4:
natural selection
drift
migration
mutation
What is the primary mechanism of evolution
natural selection
true or false mutations play a bigger role in evolution than was once believed
False, mutations play a smaller part in evolution than was one believed
What were darwin’s original 4 postules
individuals within populations are variable
the variables among individuals are at least in part passed from parents to offspring
in every generation, some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others
survival and reproduction of individuals is not random
What are the semantics of natural selection?
darwinian fitness and adaption
What is darwinian fitness?
the ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in its environment
is darwinian fitness a relative measure?
yes
What is adaption?
trait or characteristic of an organism that increases its fitness relative to individuals without the trait
Did darwin study darwin finches?
no, they were just named after darwin
How long have they been studying the fitness of darwin finches on the island?
since 1973
What is sexual dimorphism?
a size difference due to sex
What is sexual chromatism
a different colour due to sex
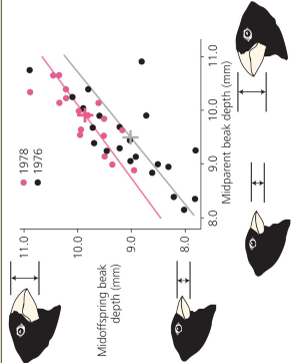
What would be the trendline of a variable trait if it was not due to inheritance? why?
flat because there would be no relationship between the parents and the kids
what is the gene responsible for coding for beak size?
BMP4
is the survival and reproduction random for darwin finches?
no it is nonrandom
Is natural selection forward looking?
no it is not looking forward, natural selection is adapted to previous environments and may or may not help depending on if that environment has changed
is natural selection nonrandom
yes it is not a random process despite mutation being the source of variation
what is an example of evolution due to mutation?
bullet in the car analogy
is fitness circular?
no its not, the fitness is reliant on variations that survive and reproduce, the theory defines favorable as the ability to survive and reproduce. only requirement is the variant needs to be heritable and not random
does natural selection act on populations?
no, natural selection acts on individuals and is not for the good of a species just for the ability to survive and repopulate
does natural selection need to perfection?
no it does not.
What were the original roadblocks for evolution
how was variability generated in populations
how were “variations” passed onto the offspring
age of the earth (Lord Kelvin’s calculations)
what two propositions does modern synthesis rely on
gradual evolution results from small genetic changes that are acted upon by natural selection
the origin of a species and higher taxa (macroevolution) can be explained in terms of natural selection acting on individuals (microevolution)
how is darwins first postule (individuals within populations are variable) now read?
(now that genetics are understood) it is read as a result of mutation creating new alleles and segregation and independent assortment shuffling alleles into new combinations, individuals within populations are variable for traits
How is darwins second postule (the variations among individuals are atleast in part passed from parents to offspring) now read
individuals pass their alleles onto their offspring intact (discrete units; one from mom one from dad)